The In Situ Structure of T-Series T1 Reveals a Conserved Lambda-Like Tail Tip
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Production and Purification of Siphophages T1
2.2. Data Acquisition and Image Processing
2.3. Symmetry-Mismatch and Local Reconstruction of the Head–Connector Complex
2.4. Local Reconstructions of the Tail Tube and Tail Tip
2.5. Atomic Modeling Building and Refinement
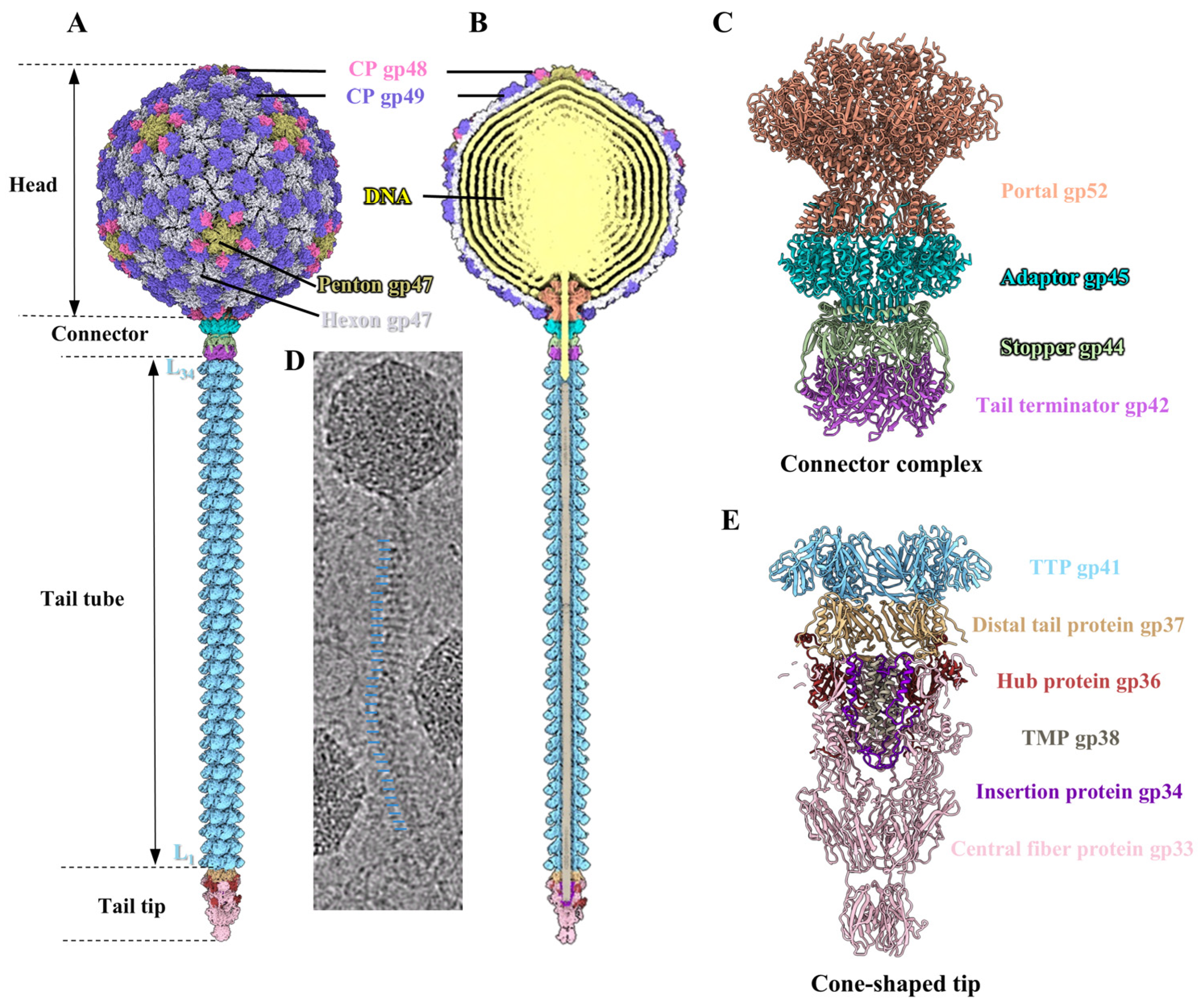
2.6. Overall Structure of Phage T1
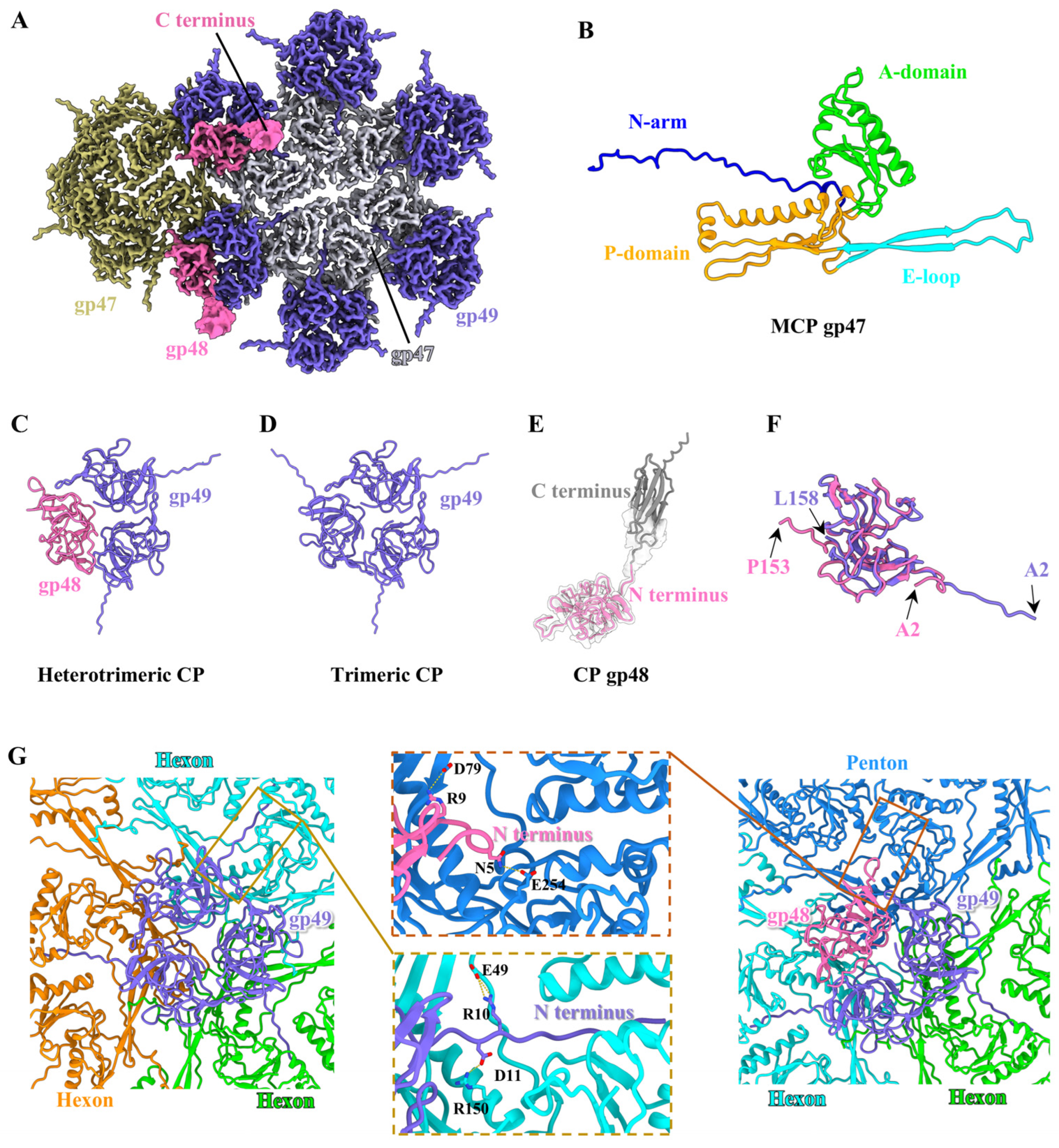
2.7. Structure of the Head
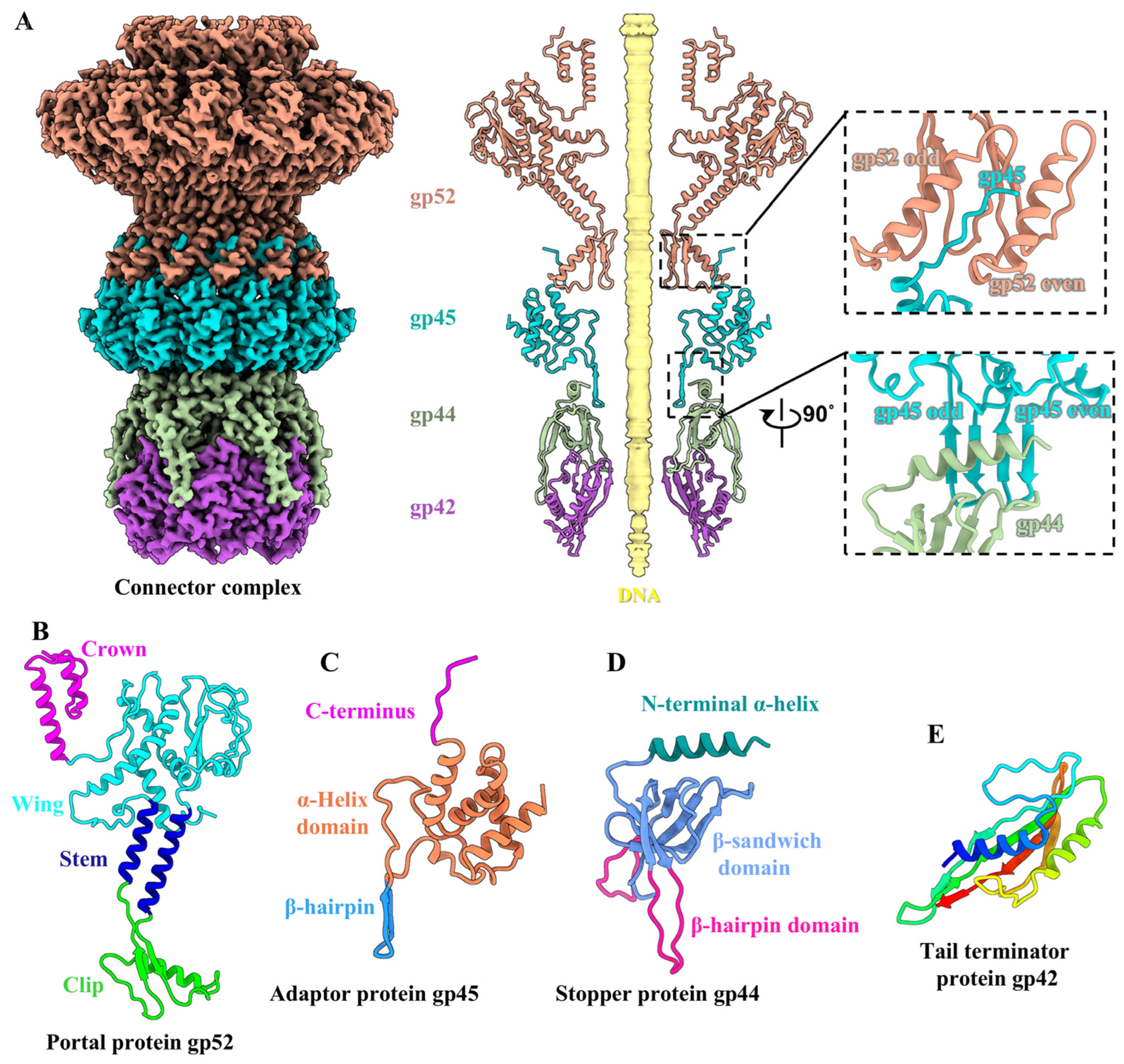
2.8. Structure of the Connector Complex
2.9. Structure of the Tail Tube
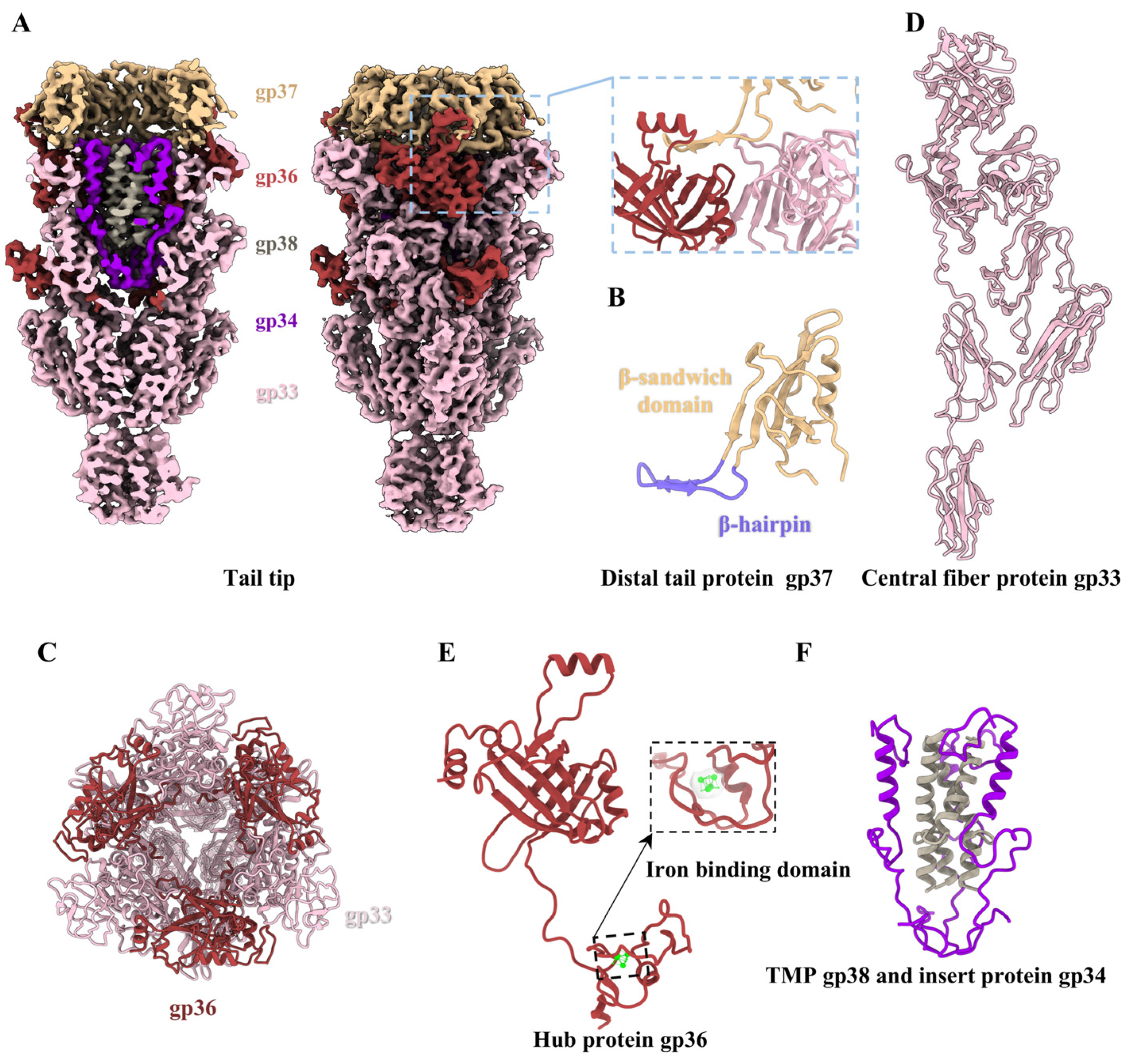
2.10. Structure of the Tail Tip
3. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davidson, A.R.; Cardarelli, L.; Pell, L.G.; Radford, D.R.; Maxwell, K.L. Long noncontractile tail machines of bacteriophages. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 726, 115–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Linares, R.; Arnaud, C.A.; Degroux, S.; Schoehn, G.; Breyton, C. Structure, function and assembly of the long, flexible tail of siphophages. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2020, 45, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobrega, F.L.; Vlot, M.; de Jonge, P.A.; Dreesens, L.L.; Beaumont, H.J.E.; Lavigne, R.; Dutilh, B.E.; Brouns, S.J.J. Targeting mechanisms of tailed bacteriophages. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bebeacua, C.; Lai, L.; Vegge, C.S.; Brøndsted, L.; van Heel, M.; Veesler, D.; Cambillau, C. Visualizing a Complete Siphoviridae Member by Single-Particle Electron Microscopy: The Structure of Lactococcal Phage TP901-1. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulet, A.; Spinelli, S.; Mahony, J.; Cambillau, C. Conserved and Diverse Traits of Adhesion Devices from Siphoviridae Recognizing Proteinaceous or Saccharidic Receptors. Viruses 2020, 12, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinelli, S.; Veesler, D.; Bebeacua, C.; Cambillau, C. Structures and host-adhesion mechanisms of lactococcal siphophages. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Tan, L.; Tan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Song, J.; Cheng, L.; Liu, H. Structure of the siphophage neck–Tail complex suggests that conserved tail tip proteins facilitate receptor binding and tail assembly. PLoS Biol. 2023, 21, e3002441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, R.; Moiseenko, A.V.; Chen, T.H.; Kulikov, E.E.; Golomidova, A.K.; Orekhov, P.S.; Street, M.A.; Sokolova, O.S.; Letarov, A.V.; Wolf, M. Nearly complete structure of bacteriophage DT57C reveals architecture of head-to-tail interface and lateral tail fibers. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Sun, H.; Wei, S.; Cai, L.; Liu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Xin, J.; Chen, Z.; Que, Y.; Kong, Z.; et al. Structure and proposed DNA delivery mechanism of a marine roseophage. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.M.; Dunstan, R.A.; Grinter, R.; Belousoff, M.J.; Wang, J.; Pickard, D.; Venugopal, H.; Dougan, G.; Lithgow, T.; Coulibaly, F. The architecture and stabilisation of flagellotropic tailed bacteriophages. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizziah, J.L.; Manning, K.A.; Dearborn, A.D.; Dokland, T. Structure of the host cell recognition and penetration machinery of a Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veesler, D.; Spinelli, S.; Mahony, J.; Lichiere, J.; Blangy, S.; Bricogne, G.; Legrand, P.; Ortiz-Lombardia, M.; Campanacci, V.; van Sinderen, D.; et al. Structure of the phage TP901-1 1.8 MDa baseplate suggests an alternative host adhesion mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8954–8958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentová, L.; Füzik, T.; Nováček, J.; Hlavenková, Z.; Pospíšil, J.; Plevka, P. Structure and replication of Pseudomonas aeruginosa phage JBD30. EMBO J. 2024, 43, 4384–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Duan, J.; Gu, Z.; Ge, X.; Zeng, J.; Wang, J. Architecture of the bacteriophage lambda tail. Structure 2024, 32, 35–46.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Tang, H.; Xiao, H.; Chen, W.; Song, J.; Zheng, J.; Liu, H. Structures of Mature and Urea-Treated Empty Bacteriophage T5: Insights into Siphophage Infection and DNA Ejection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonani, R.R.; Esteves, N.C.; Scharf, B.E.; Egelman, E.H. Cryo-EM structure of flagellotropic bacteriophage Chi. Structure 2024, 32, 856–865.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Wang, J. Structural mechanism of bacteriophage lambda tail’s interaction with the bacterial receptor. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linares, R.; Arnaud, C.A.; Effantin, G.; Darnault, C.; Epalle, N.H.; Boeri Erba, E.; Schoehn, G.; Breyton, C. Structural basis of bacteriophage T5 infection trigger and E. coli cell wall perforation. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade9674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Berg, B.; Silale, A.; Baslé, A.; Brandner, A.F.; Mader, S.L.; Khalid, S. Structural basis for host recognition and superinfection exclusion by bacteriophage T5. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2211672119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laganenka, L.; Sander, T.; Lagonenko, A.; Chen, Y.; Link, H.; Sourjik, V. Quorum Sensing and Metabolic State of the Host Control Lysogeny-Lysis Switch of Bacteriophage T1. mBio 2019, 10, e01884-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M.D.; Martin, N.L.; Kropinski, A.M. The genome and proteome of coliphage T1. Virology 2004, 318, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexler, H. Bacteriophage T1. In The Bacteriophages the Viruses; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1988; pp. 235–258. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay, N.; Ritchie, D.A. Phage head assembly in bacteriophage T1. Virology 1984, 132, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killmann, H.; Videnov, G.; Jung, G.; Schwarz, H.; Braun, V. Identification of receptor binding sites by competitive peptide mapping: Phages T1, T5, and phi 80 and colicin M bind to the gating loop of FhuA. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.R.; Figurski, D.H.; Schreil, W.H. The synthesis of coliphage T1 DNA: Degradation of the host chromosome. Virology 1981, 108, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexler, H. Specialized transduction of the biotin region of Escherichia coli by phage T1. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1977, 152, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clokie, M.R.; Millard, A.D.; Letarov, A.V.; Heaphy, S. Phages in nature. Bacteriophage 2011, 1, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, W.; Ojima, S.; Tamura, A.; Azam, A.H.; Kondo, K.; Yuancheng, Z.; Cui, L.; Shintani, M.; Suzuki, M.; Takahashi, Y.; et al. Harnessing a T1 Phage-Derived Spanin for Developing Phage-Based Antimicrobial Development. BioDesign Res. 2024, 6, 0028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kongari, R.; Snowden, J.; Berry, J.D.; Young, R. Localization and Regulation of the T1 Unimolecular Spanin. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00380-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K. Gctf: Real-time CTF determination and correction. J. Struct. Biol. 2016, 193, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimanius, D.; Forsberg, B.O.; Scheres, S.H.; Lindahl, E. Accelerated cryo-EM structure determination with parallelisation using GPUs in RELION-2. Elife 2016, 5, e18722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivioja, T.; Ravantti, J.; Verkhovsky, A.; Ukkonen, E.; Bamford, D. Local average intensity-based method for identifying spherical particles in electron micrographs. J. Struct. Biol. 2000, 131, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, S.D.; Butcher, S.J.; Cheng, R.H.; Baker, T.S. Three-dimensional reconstruction of icosahedral particles—the uncommon line. J. Struct. Biol. 1996, 116, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuman-Commike, P.A.; Chiu, W. Improved common line-based icosahedral particle image orientation estimation algorithms. Ultramicroscopy 1997, 68, 231–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhou, N.; Chen, W.; Zhu, B.; Wang, X.; Xu, B.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Cheng, L. Near-Atomic Resolution Structure Determination of a Cypovirus Capsid and Polymerase Complex Using Cryo-EM at 200kV. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, H.; Cheng, L. Symmetry-mismatch reconstruction of genomes and associated proteins within icosahedral viruses using cryo-EM. Biophys. Rep. 2016, 2, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xiao, H.; Wang, X.; Song, S.; Han, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, F.; Wang, L.; Song, J.; Liu, H.; et al. Structural changes of a bacteriophage upon DNA packaging and maturation. Protein Cell 2020, 11, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Xiao, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Tan, Z.; Han, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, F.; Liu, Z.; Song, J.; et al. Structural changes in bacteriophage T7 upon receptor-induced genome ejection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2102003118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Cheng, L. Cryo-EM shows the polymerase structures and a nonspooled genome within a dsRNA virus. Science 2015, 349, 1347–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheres, S.H. RELION: Implementation of a Bayesian approach to cryo-EM structure determination. J. Struct. Biol. 2012, 180, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludtke, S.J.; Baldwin, P.R.; Chiu, W. EMAN: Semiautomated software for high-resolution single-particle reconstructions. J. Struct. Biol. 1999, 128, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, P.D.; Afonine, P.V.; Bunkóczi, G.; Chen, V.B.; Davis, I.W.; Echols, N.; Headd, J.J.; Hung, L.W.; Kapral, G.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; et al. PHENIX: A comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucukelbir, A.; Sigworth, F.J.; Tagare, H.D. Quantifying the local resolution of cryo-EM density maps. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; McMullan, G.; Faruqi, A.R.; Murshudov, G.N.; Short, J.M.; Scheres, S.H.; Henderson, R. High-resolution noise substitution to measure overfitting and validate resolution in 3D structure determination by single particle electron cryomicroscopy. Ultramicroscopy 2013, 135, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikoff, W.R.; Liljas, L.; Duda, R.L.; Tsuruta, H.; Hendrix, R.W.; Johnson, J.E. Topologically linked protein rings in the bacteriophage HK97 capsid. Science 2000, 289, 2129–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, H.; Fan, F.; Zheng, J.; Xiao, H.; Tan, Z.; Song, J.; Kan, B.; Liu, H. Three-dimensional structures of Vibrio cholerae typing podophage VP1 in two states. Structure 2024, 32, 2364–2374.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Chen, W.; Xiao, H.; Yang, F.; Li, X.; Song, J.; Cheng, L.; Liu, H. A Capsid Structure of Ralstonia solanacearum podoviridae GP4 with a Triangulation Number T = 9. Viruses 2022, 14, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hardies, S.C.; Fokine, A.; Klose, T.; Jiang, W.; Cho, B.C.; Rossmann, M.G. Structure of the Marine Siphovirus TW1: Evolution of Capsid-Stabilizing Proteins and Tail Spikes. Structure 2018, 26, 238–248.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zeng, J.; Wang, J. Structural basis of bacteriophage lambda capsid maturation. Structure 2022, 30, 637–645.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Wang, J.; Zhu, D.; Wang, N.; Gao, Q.; Chen, W.; Tang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; et al. Cryo-EM structure of a herpesvirus capsid at 3.1 Å. Science 2018, 360, eaao7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedeo, C.L.; Teschke, C.M.; Alexandrescu, A.T. Keeping It Together: Structures, Functions, and Applications of Viral Decoration Proteins. Viruses 2020, 12, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayfield, O.W.; Shkoporov, A.N.; Yutin, N.; Khokhlova, E.V.; Smith, J.L.R.; Hawkins, D.; Koonin, E.V.; Hill, C.; Antson, A.A. Structural atlas of a human gut crassvirus. Nature 2023, 617, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedeo, C.L.; Cingolani, G.; Teschke, C.M. Portal Protein: The Orchestrator of Capsid Assembly for the dsDNA Tailed Bacteriophages and Herpesviruses. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2019, 6, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Chen, W.; Xiao, H.; Yang, F.; Song, J.; Cheng, L.; Liu, H. Asymmetric Structure of Podophage GP4 Reveals a Novel Architecture of Three Types of Tail Fibers. J. Mol. Biol. 2023, 435, 168258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlov, I.; Roche, S.; Brasilès, S.; Lukoyanova, N.; Vaney, M.C.; Tavares, P.; Orlova, E.V. CryoEM structure and assembly mechanism of a bacterial virus genome gatekeeper. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Hou, C.D.; Lokareddy, R.K.; Yang, R.; Forti, F.; Briani, F.; Cingolani, G. High-resolution cryo-EM structure of the Pseudomonas bacteriophage E217. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Jiang, Y.L.; Zhang, J.T.; Zhu, J.; Du, K.; Yu, R.C.; Wei, Z.L.; Kong, W.W.; Cui, N.; Li, W.F.; et al. Fine structure and assembly pattern of a minimal myophage Pam3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2213727120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, P.; Scholl, D.; Prokhorov, N.S.; Avaylon, J.; Shneider, M.M.; Browning, C.; Buth, S.A.; Plattner, M.; Chakraborty, U.; Ding, K.; et al. Action of a minimal contractile bactericidal nanomachine. Nature 2020, 580, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Li, N.; Wang, X.; Cheng, J.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Cai, B.; Wang, Y.P.; Jin, Q.; et al. Cryo-EM Structure and Assembly of an Extracellular Contractile Injection System. Cell 2019, 177, 370–383.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J.; Xiao, H.; Liu, H. In Situ Structures of the Ultra-Long Extended and Contracted Tail of Myoviridae Phage P1. Viruses 2023, 15, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinke, M.; Schröder, G.F.; Lange, A. Major tail proteins of bacteriophages of the order Caudovirales. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonani, R.R.; Palmer, L.K.; Esteves, N.C.; Horton, A.A.; Sebastian, A.L.; Kelly, R.J.; Wang, F.; Kreutzberger, M.A.B.; Russell, W.K.; Leiman, P.G.; et al. An extensive disulfide bond network prevents tail contraction in Agrobacterium tumefaciens phage Milano. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaud, C.A.; Effantin, G.; Vivès, C.; Engilberge, S.; Bacia, M.; Boulanger, P.; Girard, E.; Schoehn, G.; Breyton, C. Bacteriophage T5 tail tube structure suggests a trigger mechanism for Siphoviridae DNA ejection. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, P.L.; Duda, R.L.; Nassur, J.; Conway, J.F.; Huet, A. Mobile Loops and Electrostatic Interactions Maintain the Flexible Tail Tube of Bacteriophage Lambda. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, M.; Prokhorov, N.S.; Loessner, M.J.; Leiman, P.G. Reprogramming bacteriophage host range: Design principles and strategies for engineering receptor binding proteins. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 68, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, W.; Pell, L.G.; Bona, D.; Tsai, A.; Dai, X.X.; Edwards, A.M.; Hendrix, R.W.; Maxwell, K.L.; Davidson, A.R. Tail tip proteins related to bacteriophage λ gpL coordinate an iron-sulfur cluster. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 2450–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsura, I. Determination of bacteriophage lambda tail length by a protein ruler. Nature 1987, 327, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Hendrix, R.W.; Duda, R.L. Chaperone–protein interactions that mediate assembly of the bacteriophage lambda tail to the correct length. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 1004–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhou, J.; Peng, Z.; Peng, Y.; Song, J.; Zheng, J.; Liu, H. The In Situ Structure of T-Series T1 Reveals a Conserved Lambda-Like Tail Tip. Viruses 2025, 17, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030351
Chen Y, Xiao H, Zhou J, Peng Z, Peng Y, Song J, Zheng J, Liu H. The In Situ Structure of T-Series T1 Reveals a Conserved Lambda-Like Tail Tip. Viruses. 2025; 17(3):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030351
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yuan, Hao Xiao, Junquan Zhou, Zeng Peng, Yuning Peng, Jingdong Song, Jing Zheng, and Hongrong Liu. 2025. "The In Situ Structure of T-Series T1 Reveals a Conserved Lambda-Like Tail Tip" Viruses 17, no. 3: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030351
APA StyleChen, Y., Xiao, H., Zhou, J., Peng, Z., Peng, Y., Song, J., Zheng, J., & Liu, H. (2025). The In Situ Structure of T-Series T1 Reveals a Conserved Lambda-Like Tail Tip. Viruses, 17(3), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030351





