Isolation, Identification, and Pathogenicity of an Avian Reovirus Epidemic Strain in Xinjiang, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cells and Experimental Animals
2.3. LMH Cell Recovery
2.4. Virus Isolation and Propagation
2.5. Virus Identification by RT-PCR
2.6. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) Identification of the Virus
2.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) of ARV
2.8. Viral Replication Kinetics In Vitro
2.9. Pathogenicity Assessment in SPF Chicken Embryos and Chicks
3. Results
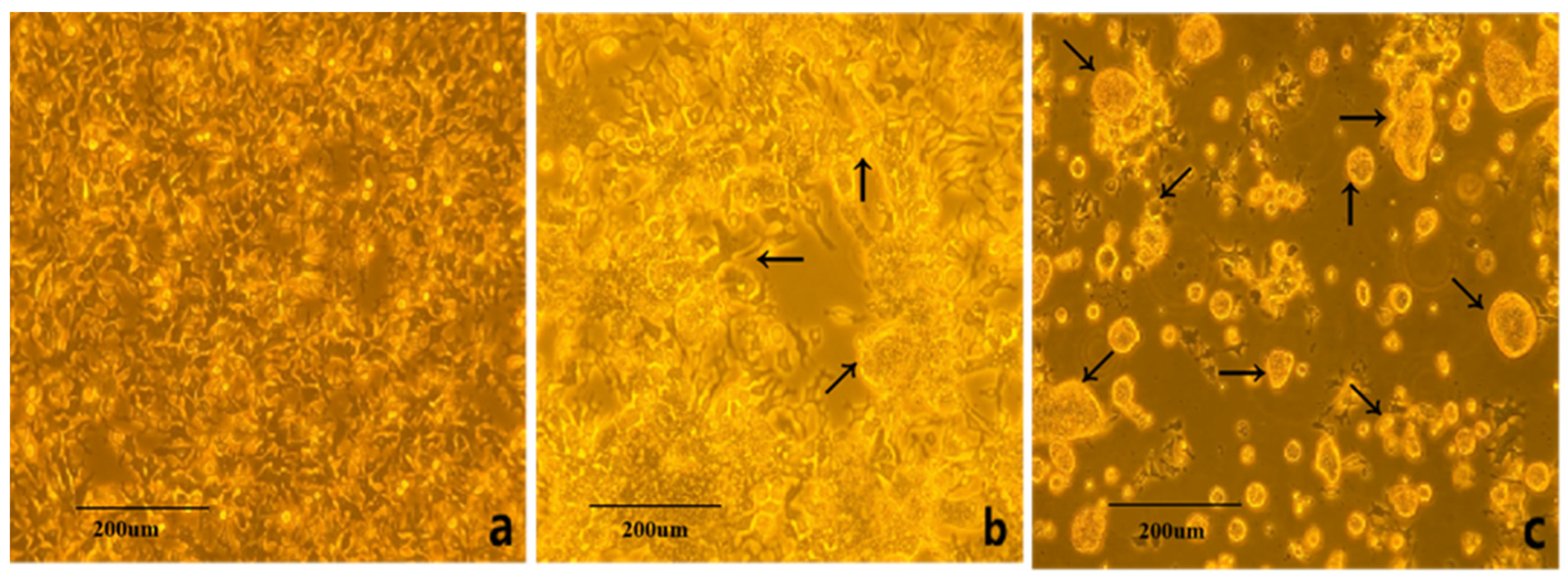
3.1. Virus Isolation and Cultivation
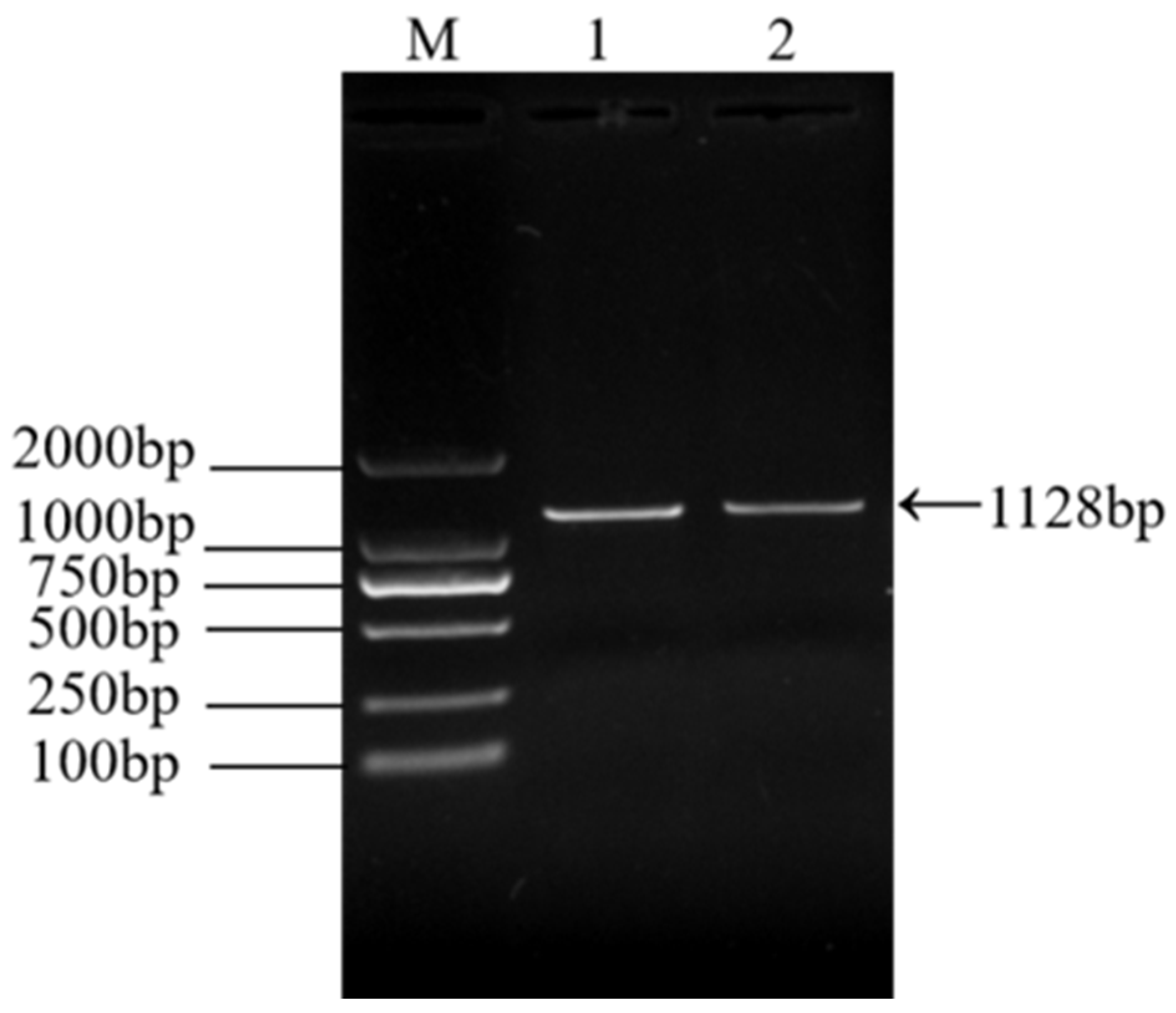
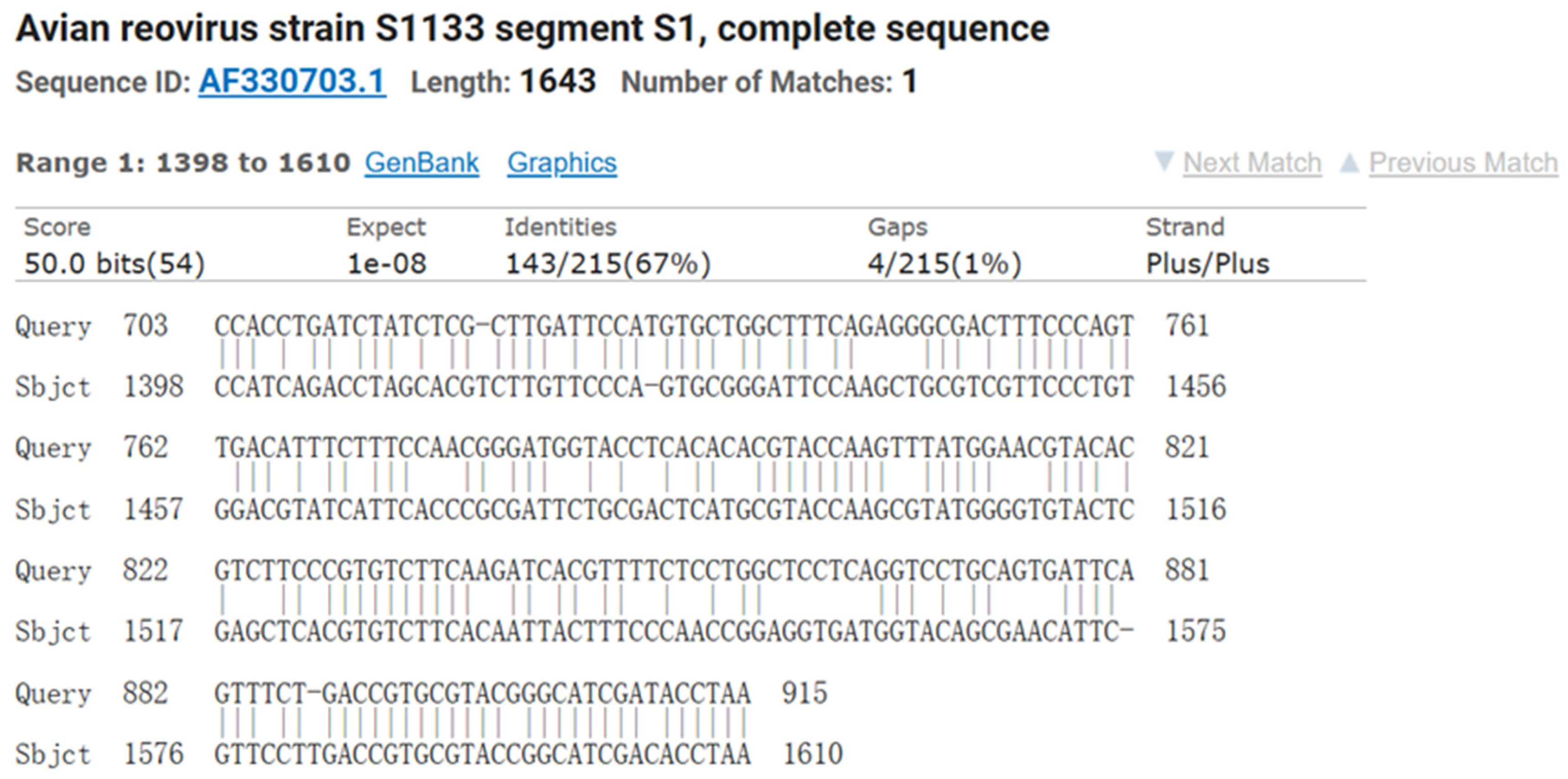
3.2. RT-PCR Identification of ARV Virus
3.3. Fluorescent Quantitative PCR Identification of ARV Virus
3.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (EM) Observation
3.5. In Vitro Replication Kinetics of the Virus
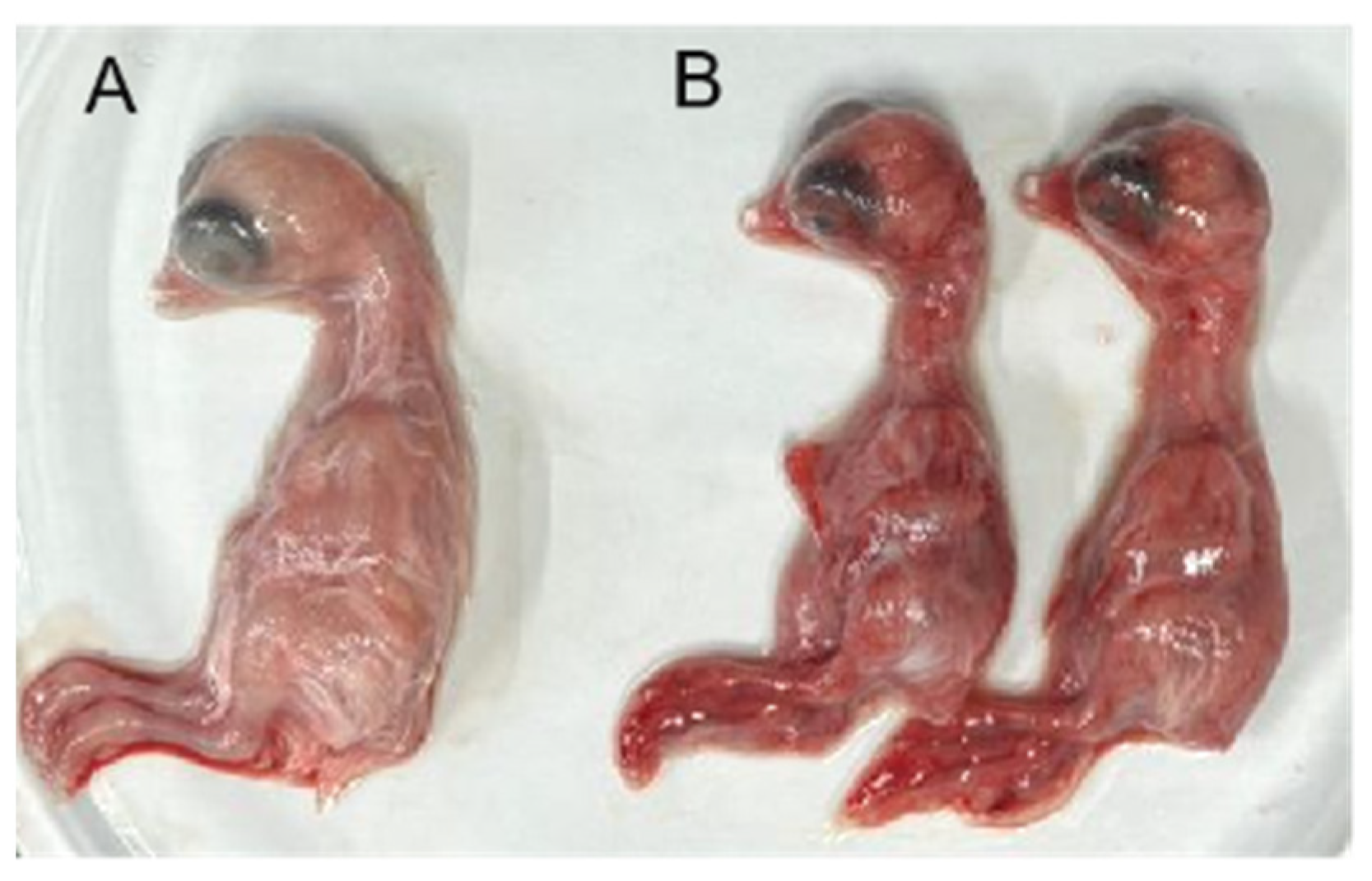
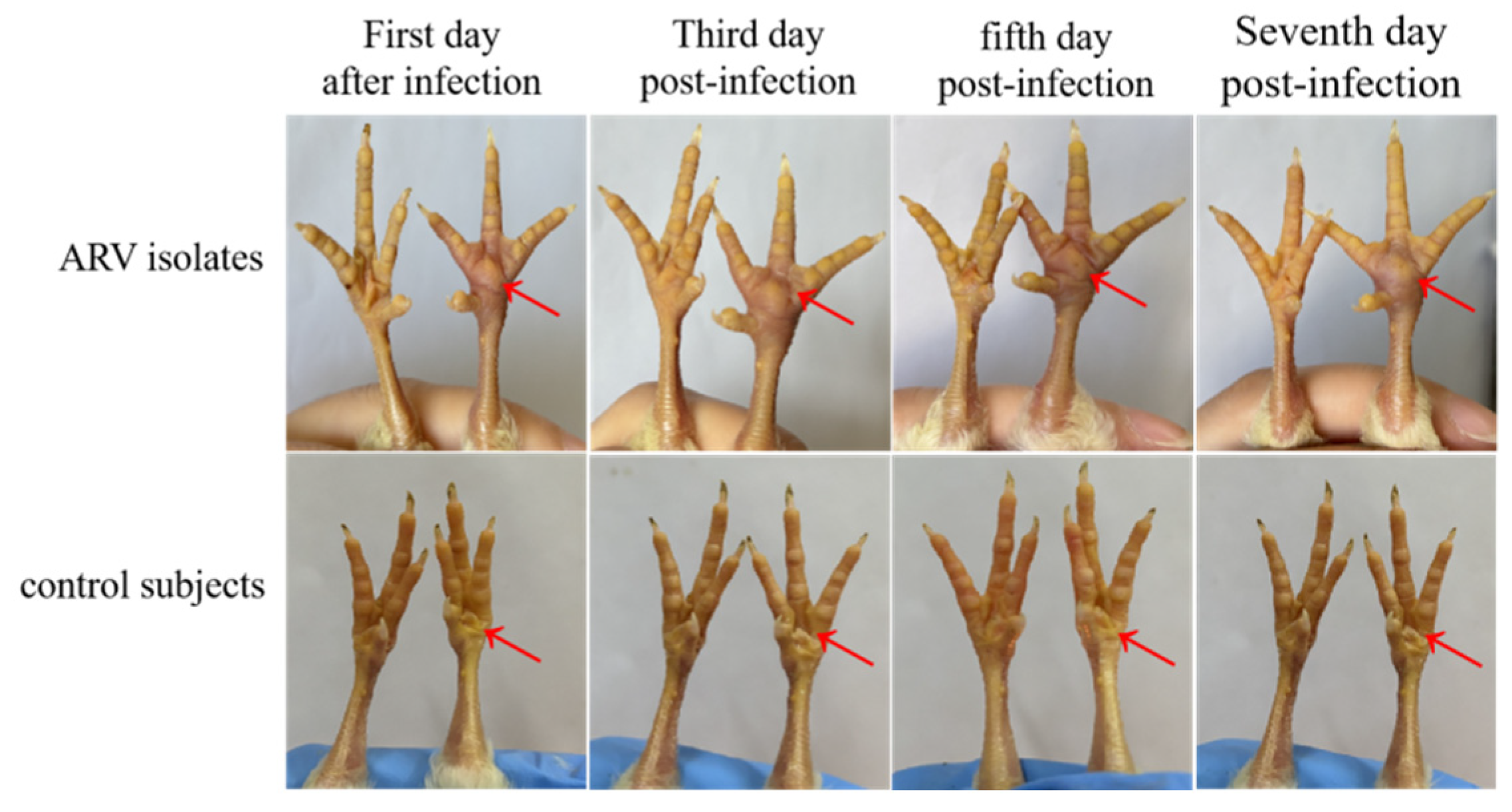
3.6. Pathogenicity of the ARV Isolate in Chicken Embryos and SPF Chickens
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moreira, F.A.B.C.L. Contribution to the Study of Emerging Infectious Diseases in Broiler Breeders. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de Tras-os-Montes e Alto Douro, Vila Real, Portugal, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sellers, H.S. Current limitations in control of viral arthritis and tenosynovitis caused by avian reoviruses in commercial poultry. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 206, 152–156. [Google Scholar]
- Nour, I.; Mohanty, S.K. Avian Reovirus: From Molecular Biology to Pathogenesis and Control. Viruses 2024, 16, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitcovski, J.; Goyal, S.M. Avian reovirus infections. In Diseases of Poultry, 14th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 382–400. [Google Scholar]
- Benavente, J.; Martínez-Costas, J. Avian reovirus: Structure and biology. Virus Res. 2007, 123, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhama, K.; Saminathan, M.; Karthik, K.; Tiwari, R.; Shabbir, M.Z.; Kumar, N.; Malik, Y.S.; Singh, R.K. Avian rotavirus enteritis–an updated review. Vet. Q. 2015, 35, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.-J.; Lin, P.-Y.; Lee, J.-W.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Shih, W.-L. Retardation of cell growth by avian reovirus p17 through the activation of p53 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 336, 709–715. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Xie, L.; Xie, Z.; Wan, L.; Huang, J.; Deng, X.; Xie, Z.Q.; Luo, S.; Zeng, T.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Dynamic changes in the expression of interferon-stimulated genes in joints of SPF chickens infected with avian reovirus. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 618124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoerr, F.J. Clinical aspects of immunosuppression in poultry. Avian Dis. 2010, 54, 2–15. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.C. Reovirus infections. In Diseases of Poultry, 13th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 351–373. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, D.; Dhama, K.; Agarwal, R.; Sonal; Singh, P.; Ravikumar, G.; Malik, Y.S.; Mishra, B. Avian Reoviruses. In Recent Advances in Animal Virology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Bodelón, G.; Labrada, L.; Martınez-Costas, J.; Benavente, J. The avian reovirus genome segment S1 is a functionally tricistronic gene that expresses one structural and two nonstructural proteins in infected cells. Virology 2001, 290, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egaña-Labrin, S.; Hauck, R.; Figueroa, A.; Stoute, S.; Shivaprasad, H.L.; Crispo, M.; Corsiglia, C.; Zhou, H.; Kern, C.; Crossley, B.; et al. Genotypic characterization of emerging avian reovirus genetic variants in California. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9351. [Google Scholar]
- Haggett, P.; Gunawardena, K. Determination of population thresholds for settlement functions by the Reed-Muench method. In The Professional Geographer; Hamilton: New York, NY, USA, 1964; Volume 16, pp. 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kovács, E.; Varga-Kugler, R.; Mató, T.; Homonnay, Z.; Tatár-Kis, T.; Farkas, S.; Kiss, I.; Bányai, K.; Palya, V. Identification of the main genetic clusters of avian reoviruses from a global strain collection. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 9, 1094761. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.-R.; Kim, S.-W.; Shang, K.; Park, J.-Y.; Zhang, J.-F.; Jang, H.-K.; Wei, B.; Cha, S.-Y.; Kang, M. Avian reoviruses from wild birds exhibit pathogenicity to specific pathogen free chickens by footpad route. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 844903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markis, M. Evaluation of pathogenicity and antigenicity of avian reoviruses and disease control through vaccination. Avian Dis. 2022, 66, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zou, Z.; Song, S.; Liu, H.; Gong, X.; Li, B.; Liu, P.; Wang, Q.; Liu, F.; Luan, D.; et al. Epidemiological Analysis of Avian Reovirus in China and Research on the Immune Protection of Different Genotype Strains from 2019 to 2020. Vaccines 2023, 11, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Luo, D.; Gao, J.; Li, K.; Liu, C.; Qi, X.; Cui, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; et al. A novel variant of avian reovirus is pathogenic to vaccinated chickens. Viruses 2023, 15, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, S.L.; Marton, S.; Dandár, E.; Kugler, R.; Gál, B.; Jakab, F.; Bálint, Á.; Kecskeméti, S.; Bányai, K. Lineage diversification, homo-and heterologous reassortment and recombination shape the evolution of chicken orthoreoviruses. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanaty, A.; Mosaad, Z.; Elfeil, W.M.; Badr, M.; Palya, V.; Shahein, M.A.; Rady, M.; Hess, M. Isolation and Genotypic Characterization of New Emerging Avian Reovirus Genetic Variants in Egypt. Poultry 2023, 2, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yan, M.; Tang, Y.; Diao, Y. Sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of partial S1 genes of avian orthoreovirus isolates in Shandong province during 2015–2017. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 2416–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Guo, L.; Jiang, X.; Wang, H.; Yao, Z.; Zhu, S.; Diao, Y.; Tang, Y. Discovery of a novel recombinant avian orthoreovirus in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 260, 109094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Sun, R.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; et al. First isolation and genomic characterization of avian reovirus from black swans (Cygnus atratus) in China. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egaña-Labrin, S.; Jerry, C.; Roh, H.J.; Da Silva, A.P.; Corsiglia, C.; Crossley, B.; Rejmanek, D.; Gallardo, R.A. Avian reoviruses of the same genotype induce different pathology in chickens. Avian Dis. 2021, 65, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayalew, L.E.; Ahmed, K.A.; Popowich, S.; Lockerbie, B.-C.; Gupta, A.; Tikoo, S.K.; Ojkic, D.; Gomis, S. Virulence of emerging arthrotropic avian reoviruses correlates with their ability to activate and traffic interferon-γ producing cytotoxic CD8+ T cells into gastrocnemius tendon. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 869164. [Google Scholar]
- Dawe, W. Characterization of Immune Responses to Avian Reovirus Variants and Evaluation of an Attenuation Method. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Georgia, Athens, GA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Egana-Labrin, S.C. Molecular, Pathogenic, and Antigenic Characterization of Emerging Avian Reovirus Variant Strains. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Davis, CA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Zuo, Z.; Dang, X.; Gao, H.; Meng, Q.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S. Isolation, Identification, and Pathogenicity of an Avian Reovirus Epidemic Strain in Xinjiang, China. Viruses 2025, 17, 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040499
Ma X, Li W, Liu Z, Zuo Z, Dang X, Gao H, Meng Q, Yang L, Wang Y, Zhang S. Isolation, Identification, and Pathogenicity of an Avian Reovirus Epidemic Strain in Xinjiang, China. Viruses. 2025; 17(4):499. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040499
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xin, Weiqi Li, Zhaoquan Liu, Zhipeng Zuo, Xinyu Dang, Hengyun Gao, Qingling Meng, Lin Yang, Yongjie Wang, and Shilei Zhang. 2025. "Isolation, Identification, and Pathogenicity of an Avian Reovirus Epidemic Strain in Xinjiang, China" Viruses 17, no. 4: 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040499
APA StyleMa, X., Li, W., Liu, Z., Zuo, Z., Dang, X., Gao, H., Meng, Q., Yang, L., Wang, Y., & Zhang, S. (2025). Isolation, Identification, and Pathogenicity of an Avian Reovirus Epidemic Strain in Xinjiang, China. Viruses, 17(4), 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040499





