Phage Endolysins as an Alternative Biocontrol Strategy for Pathogenic and Spoilage Microorganisms in the Food Industry
Abstract
1. Introduction
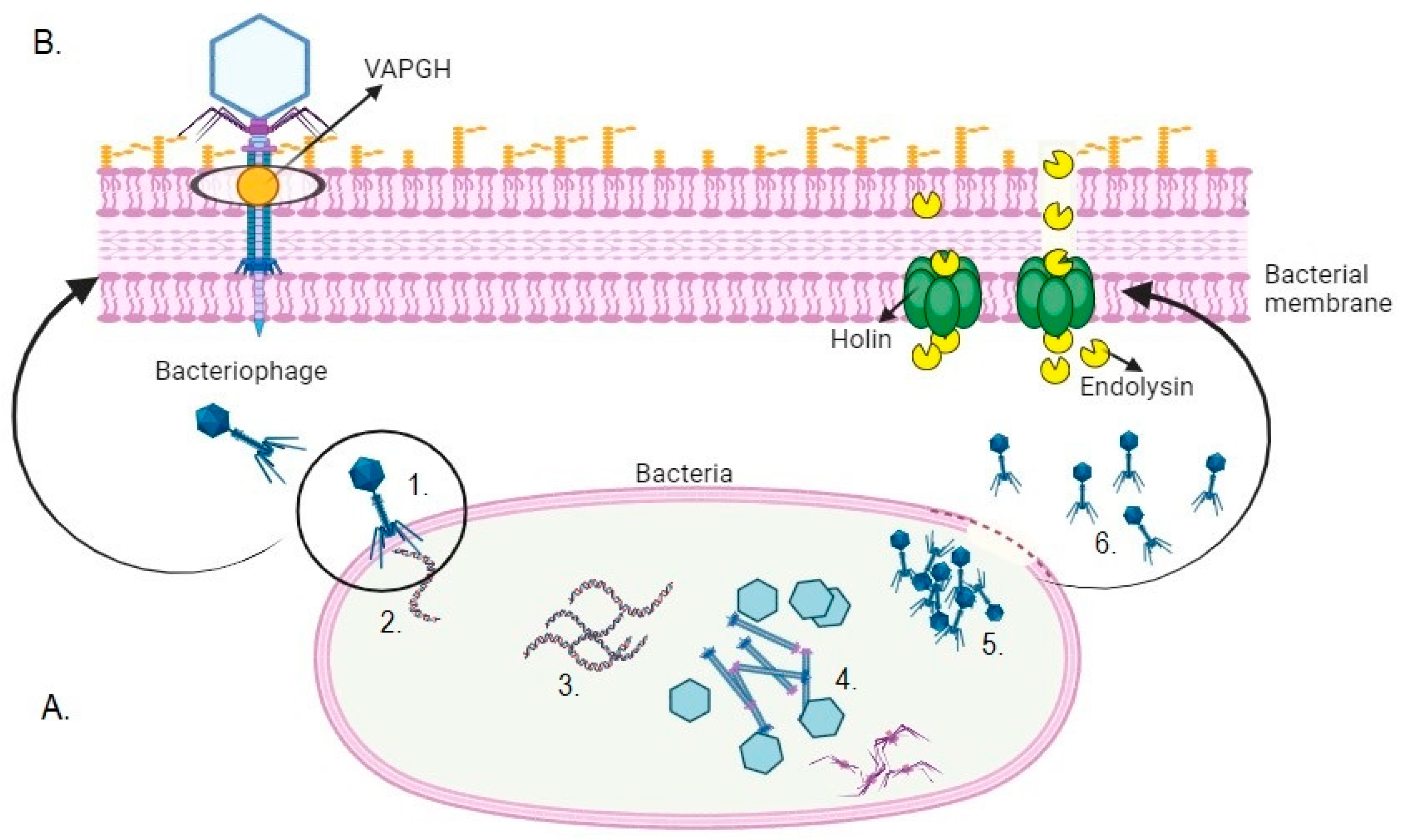
2. Bacteriophages and Their Enzymes During the Infection Process
3. Phage Enzymes
4. Strategies for Mining and Identifying Phage Endolysins
5. Application of Phage Enzymes in Foods for the Control of Gram-Positive Bacteria
5.1. Enzymes for the Control of Staphylococcus aureus
5.2. Enzymes for the Control of Listeria monocytogenes
5.3. Enzymes for the Control of Clostridium perfringens
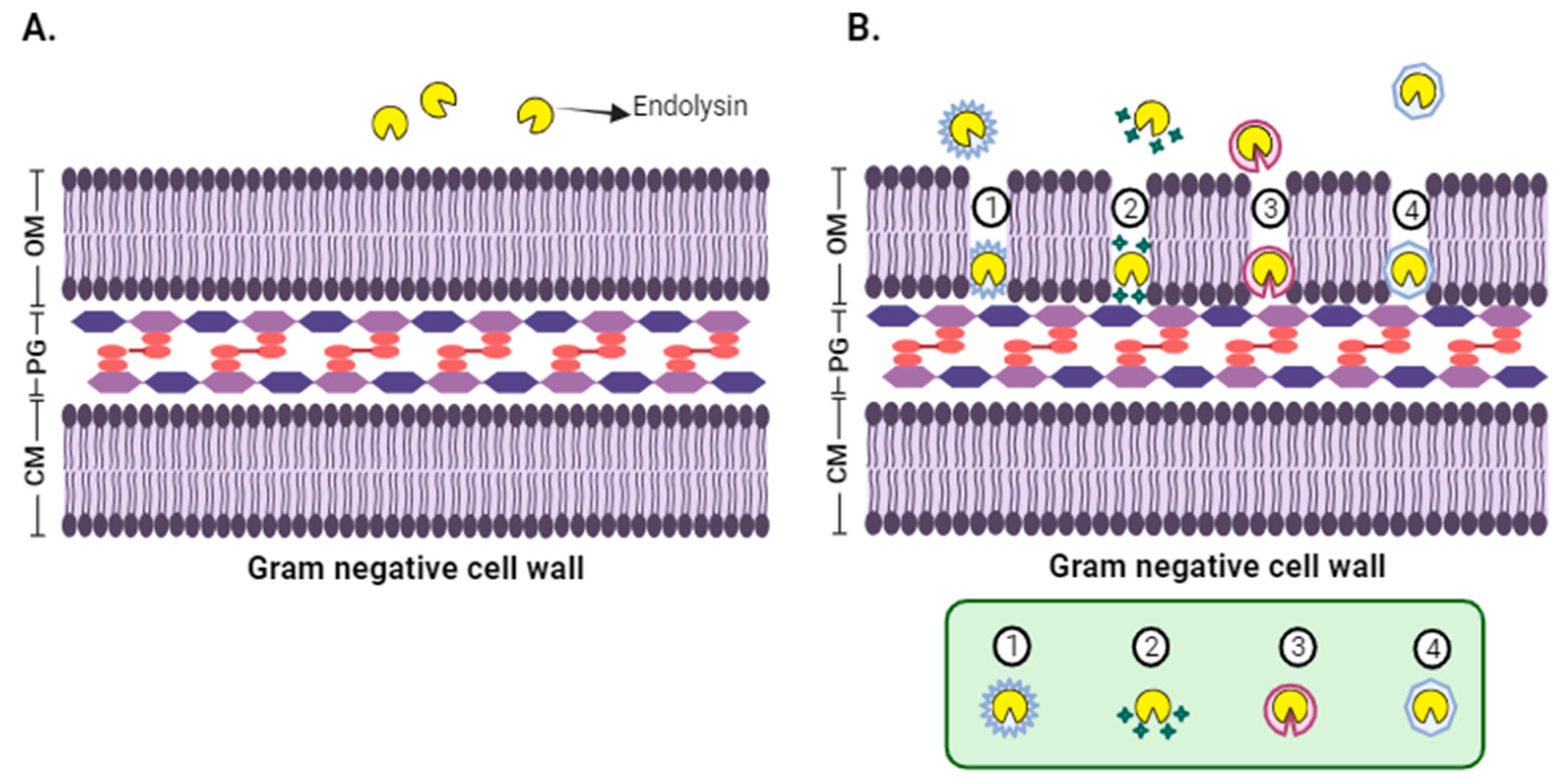
6. Application of Phage Enzymes in Foods for the Control of Gram-Negative Bacteria
7. Other Studies of Applications of Phage Enzymes in the Biocontrol of Microorganisms
8. Strengths and Limitations of Using Enzymes
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torres, Y.F.; Borda, M.G.; Ramírez, G. Patógenos asociados a enfermedades transmitidas por alimentos en restaurantes escolares de Colombia. Rev. Chil. Nutr. 2017, 44, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Food Safety. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/food-safety (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Farrukh, M.; Munawar, A.; Nawaz, Z.; Hussain, N.; Bin Hafeez, A.; Szweda, P. Antibiotic resistance and preventive strategies in foodborne pathogenic bacteria: A comprehensive review. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okaiyeto, S.A.; Sutar, P.P.; Chen, C.; Ni, J.-B.; Wang, J.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Zhang, J.-S.; Xu, M.-Q.; Fang, X.-M.; Zhang, C.; et al. Antibiotic resistant bacteria in food systems: Current status, resistance mechanisms, and mitigation strategies. Agric. Commun. 2024, 2, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisboa, H.M.; Pasquali, M.B.; dos Anjos, A.I.; Sarinho, A.M.; de Melo, E.D.; Andrade, R.; Batista, L.; Lima, J.; Diniz, Y.; Barros, A. Innovative and Sustainable Food Preservation Techniques: Enhancing Food Quality, Safety, and Environmental Sustainability. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, Y.; Wang, C.; Zayda, M.; Maung, A.T.; Mohammadi, T.N.; Duc, H.M.; Yu, P.; Ma, M.; Gong, D.; et al. Biocontrol of Salmonella Typhimurium in milk, lettuce, raw pork meat and ready-to-eat steamed-chicken breast by using a novel bacteriophage with broad host range. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 402, 110295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Ha, E.; Kong, M.; Ryu, S. A novel chimeric endolysin with enhanced lytic and binding activity against Clostridium perfringens. LWT 2023, 181, 114776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, K.W.; Mao, L.; Mustapha, A. CAM-21, a novel lytic phage with high specificity towards Escherichia coli O157:H7 in food products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 386, 110026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyarcan, E.K.; Evran, E.; Guven, K.; Ekiz, E.; Soykut, E.A.; Boyaci, I.H. Evaluating the efficacy of a phage cocktail against Pseudomonas fluorescens group strains in raw milk: Microbiological, physical, and chemical analyses. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjay; Kumar, A.; Abhishek; Malik, H.; Dubal, Z.B.; Jaiswal, R.K.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, B.; Agarwal, R.K. Isolation and characterization of Salmonella phages and phage cocktail mediated biocontrol of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in chicken meat. LWT 2022, 155, 112957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, A.; Shehzadi, U.; Islam, F.; Afzaal, M.; Ali, R.; Ali, Y.A.; Chauhan, A.; Biswas, S.; Khurshid, S.; Usman, I.; et al. Bacteriophages and food safety: An updated overview. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 3621–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.J.; Kim, T.-Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Jeon, M.-H.; Noh, D.-I.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, C.-H.; Lim, E.-S.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, E.-W.; et al. Identification and characterization of the novel bacteriophage BPVP-3325 for the biocontrol of Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection in seafood. Aquaculture 2022, 561, 738669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Gao, L.; Yuan, L.; Chen, C.; Yang, Z. Control of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Seafood Using the Combination of Lytic Phages and Citric Acid. Foods 2025, 14, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zia, S.; Alkheraije, K.A. Recent trends in the use of bacteriophages as replacement of antimicrobials against food-animal pathogens. Front. Veter- Sci. 2023, 10, 1162465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guliy, O.I.; Evstigneeva, S.S. Bacteria- and Phage-Derived Proteins in Phage Infection. Front. Biosci. 2025, 30, 24478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, K.-S.; Shu, M.; Tang, M.-X.; Yang, W.-Y.; Wang, S.-C.; Zhong, C.; Wu, G.-P. Molecular cloning, expression and characterization of a bacteriophage JN01 endolysin and its antibacterial activity against E. coli O157:H7. LWT 2022, 165, 113705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliakbarlu, J.; Manafi, L.; Mortazavi, N.; Lin, L.; Kaboudari, A. The antibacterial activity of endolysins against food-borne pathogenic bacteria in vitro and foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 65, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dai, J.; Wu, S.; Rong, D.; Huang, J.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, J.; Ye, Q.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; et al. The food application of a novel Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage vB_SA_STAP152 and its endolysin LysP152 with high enzymatic activity under cold temperature. Food Microbiol. 2025, 128, 104710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Kong, M.S.; Koo, O.K. Endolysin-based biocontrol strategies against Listeria monocytogenes in food: A comprehensive review. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2025, 34, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Zhang, M.; Lv, Q.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Cai, Y. Application and potential therapeutic effect of endolysin Lys1472 against Clostridium perfringens in chicken meat. LWT 2025, 216, 117332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, H.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, M. Control of Bacillus cereus in rice cake and food contact surfaces with novel Becedseptimavirus genus phage BCC348 and its partial SPOR domain-containing endolysin LysBCC348. LWT 2024, 213, 117034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, Z.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Lu, S.; Rao, X. Therapeutic potential of bacteriophage endolysins for infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 30, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gontijo, M.T.P.; Jorge, G.P.; Brocchi, M. Current Status of Endolysin-Based Treatments against Gram-Negative Bacteria. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, K.; Shu, M.; Zhong, C.; Zhao, Y.; Bao, S.; Pan, H.; Wang, S.; Wu, G. Characterization of a broad-spectrum endolysin rLysJNwz and its utility against Salmonella in foods. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 3229–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; He, J.; Nyaruaba, R.; Wei, H.; Li, Y. Endolysins as Effective Agents for Decontaminating S. typhimurium, E. coli, and L. monocytogenes on Mung Bean Seeds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, P.; Ming, Z.; Liu, X.; Shao, Y.; Pan, H.; Ding, Y.; Wang, X. Expression and characterization of a novel endolysin LysPFX32 as potential biological antimicrobial agent against Pseudomonas fluorescens for pork preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 294, 139448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampara, A.; Sørensen, M.C.H.; Gencay, Y.E.; Grimon, D.; Kristiansen, S.H.; Jørgensen, L.S.; Kristensen, J.R.; Briers, Y.; Elsser-Gravesen, A.; Brøndsted, L. Developing Innolysins Against Campylobacter jejuni Using a Novel Prophage Receptor-Binding Protein. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 619028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, F.; Gangakhedkar, R.; Nair, G.; El-Didamony, G.; Askora, A.; Jain, V.; El-Shibiny, A. Pseudomonas Phage ZCPS1 Endolysin as a Potential Therapeutic Agent. Viruses 2023, 15, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Ryu, S.; Kong, M. Phage-derived proteins: Advancing food safety through biocontrol and detection of foodborne pathogens. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2025, 24, e70124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, T.; Meng, F.; Lu, F.; Bie, X.; Zhao, H.; Sun, J.; Lu, Z.; Lu, Y. An endolysin Salmcide-p1 from bacteriophage fmb-p1 against gram-negative bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 1597–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.; Lan, J.; Liang, L.; Xia, K.; Li, L.; Yang, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, T. The antibacterial activity of a novel highly thermostable endolysin, LysKP213, against Gram-negative pathogens is enhanced when combined with outer membrane permeabilizing agents. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1454618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, S. Diversities and interactions of phages and bacteria in deep-sea sediments as revealed by metagenomics. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1337146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leprince, A.; Mahillon, J. Phage Adsorption to Gram-Positive Bacteria. Viruses 2023, 15, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teytsa, H.M.N.; Tsanou, B.; Bowong, S.; Lubuma, J.M.-S. Bifurcation analysis of a phage-bacteria interaction model with prophage induction. Math. Med. Biol. A J. IMA 2021, 38, 28–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Luo, G.; Hou, F.; Zhou, C.; Liu, X.; Lei, Z.; Niu, D.; Ran, T.; Tan, Z. A review of bacteriophage and their application in domestic animals in a post-antibiotic era. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 949, 174931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, A. The future of bacteriophage biology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2003, 4, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksyuk, A.A.; Rossmann, M.G. Bacteriophage Assembly. Viruses 2011, 3, 172–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serwer, P. A Perspective on Studies of Phage DNA Packaging Dynamics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedon, S.T. Bacteriophages as Drivers of Evolution: An Evolutionary Ecological Perspective; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–377. [Google Scholar]
- Harshitha, N.; Rajasekhar, A.; Saurabh, S.; Sonalkar, R.; Tejashwini, M.; Das Mitra, S. Bacteriophages: Potential Biocontrol Agents and Treatment Options for Bacterial Pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Newsl. 2022, 44, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, D.; Fernández, L.; Rodríguez, A.; García, P. Are Phage Lytic Proteins the Secret Weapon to Kill Staphylococcus aureus? mBio 2018, 9, e01923-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briers, Y.; Walmagh, M.; Van Puyenbroeck, V.; Cornelissen, A.; Cenens, W.; Aertsen, A.; Oliveira, H.; Azeredo, J.; Verween, G.; Pirnay, J.-P.; et al. Engineered Endolysin-Based “Artilysins” To Combat Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Pathogens. mBio 2014, 5, e01379-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Liao, X.; Zhang, S.; Ding, T.; Ahn, J. Application of phage-derived enzymes for enhancing food safety. Food Res. Int. 2025, 209, 116318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtimka, S.; Pillay, P.; Kwezi, L.; Pooe, O.J.; Tsekoa, T.L. An Exploratory Review of the Potential of Lytic Proteins and Bacteriophages for the Treatment of Tuberculosis. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashani, H.H.; Schmelcher, M.; Sabzalipoor, H.; Hosseini, E.S.; Moniri, R. Recombinant Endolysins as Potential Therapeutics against Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Current Status of Research and Novel Delivery Strategies. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 31, e00071-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.; São-José, C. More than a hole: The holin lethal function may be required to fully sensitize bacteria to the lytic action of canonical endolysins. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 102, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, T.; Park, T.; Young, R. Mutational analysis of the S21 pinholin. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.C.B.; Chen, X.; Ho, M.K.Y.; Xia, J.; Leung, S.S.Y. Bacteriophage-derived endolysins to target gram-negative bacteria. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 589, 119833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.H.; Ahammad, T.; Sahu, I.D.; Rotich, N.C.; Daufel, A.; Lorigan, G.A. Determining the helical tilt angle and dynamic properties of the transmembrane domains of pinholin S2168 using mechanical alignment EPR spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Biomembr. 2023, 1865, 184154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.M.; Rasheed, F.; Yang, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, R. Endolysins: A new antimicrobial agent against antimicrobial resistance. Strategies and opportunities in overcoming the challenges of endolysins against Gram-negative bacteria. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1385261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.M.; Chen, J.-H.; Zhang, R.; Liu, B. A comprehensive review of the applications of bacteriophage-derived endolysins for foodborne bacterial pathogens and food safety: Recent advances, challenges, and future perspective. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1259210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, F.; Zhan, W.; Li, Z.; Zou, L.; Zhao, Q. Challenges for the application of bacteriophages as effective antibacterial agents in the food industry. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agún, S.; Fernández, L.; Rodríguez, A.; García, P. Deletion of the amidase domain of endolysin LysRODI enhances antistaphylococcal activity in milk and during fresh cheese production. Food Microbiol. 2022, 107, 104067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, E.; Pennone, V.; Reilly, K.; Grant, I.R.; Campbell, K.; Altermann, E.; McAuliffe, O. Inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes by Phage Lytic Enzymes Displayed on Tailored Bionanoparticles. Foods 2022, 11, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, B.; Kong, M.; Lee, Y.; Ryu, S. Development of a Novel Chimeric Endolysin, Lys109 With Enhanced Lytic Activity Against Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 615887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, D.; Briers, Y. Lysins breaking down the walls of Gram-negative bacteria, no longer a no-go. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 68, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Wu, J.; Guo, F.; Dong, B.; Xu, L. CWLy-pred: A novel cell wall lytic enzyme identifier based on an improved MRMD feature selection method. Genomics 2020, 112, 4715–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazir, A.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. Phage Endolysins: Advances in the World of Food Safety. Cells 2023, 12, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Ruiz, I.; Coutinho, F.H.; Rodriguez-Valera, F. Thousands of Novel Endolysins Discovered in Uncultured Phage Genomes. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ouyang, X.; Kong, J. The potential of the endolysin Lysdb from Lactobacillus delbrueckii phage for combating Staphylococcus aureus during cheese manufacture from raw milk. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 3545–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, H.; Kong, M.; Ryu, S. Characterization of LysPBC4, a novel Bacillus cereus-specific endolysin of bacteriophage PBC4. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2016, 363, fnw092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kong, M.; Ryu, S. Bacteriophage PBC1 and Its Endolysin as an Antimicrobial Agent against Bacillus cereus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 2274–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, D.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Martínez, B.; Rodríguez, A.; García, P. Effective Removal of Staphylococcal Biofilms by the Endolysin LysH5. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, B.; Yun, J.; Lim, J.-A.; Shin, H.; Heu, S.; Ryu, S. Characterization of LysB4, an endolysin from the Bacillus cereus-infecting bacteriophage B4. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Bao, H.; Billington, C.; Hudson, J.A.; Wang, R. Isolation and lytic activity of the Listeria bacteriophage endolysin LysZ5 against Listeria monocytogenes in soya milk. Food Microbiol. 2012, 31, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2014, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oechslin, F.; Menzi, C.; Moreillon, P.; Resch, G. The multidomain architecture of a bacteriophage endolysin enables intramolecular synergism and regulation of bacterial lysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Struck, D.K.; Deaton, J.; Wang, I.-N.; Young, R. A signal-arrest-release sequence mediates export and control of the phage P1 endolysin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6415–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisson, H.M.; Jackson, S.A.; Fagerlund, R.D.; Warring, S.L.; Fineran, P.C. Gram-negative endolysins: Overcoming the outer membrane obstacle. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2024, 78, 102433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.-Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; McAnulla, C.; McWilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. InterProScan 5: Genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teufel, F.; Armenteros, J.J.A.; Johansen, A.R.; Gíslason, M.H.; Pihl, S.I.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 6.0 predicts all five types of signal peptides using protein language models. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallgren, J.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Pedersen, M.D.; Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Marcatili, P.; Nielsen, H.; Krogh, A.; Winther, O. DeepTMHMM predicts alpha and beta transmembrane proteins using deep neural networks. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-X.; Tang, H.; Li, W.-C.; Wu, H.; Chen, W.; Ding, H.; Lin, H. Identification of Bacterial Cell Wall Lyases via Pseudo Amino Acid Composition. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1654623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Yu, S.; Li, J.; Lao, Z.; Yang, X.; Lin, Z. DeepMineLys: Deep mining of phage lysins from human microbiome. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dego, O.K.; Vidlund, J. Staphylococcal mastitis in dairy cows. Front. Veter. Sci. 2024, 11, 1356259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaiuolo, M.; Lefebvre, D.; Mutel, I.; Vingadassalon, N.; Merda, D.; Hennekinne, J.-A.; Nia, Y. First report of enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus argenteus as a foodborne pathogen. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 394, 110182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Yoon, H.; Kang, D.-H.; Chang, P.-S.; Ryu, S. Endolysin LysSA97 is synergistic with carvacrol in controlling Staphylococcus aureus in foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 244, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deddefo, A.; Mamo, G.; Asfaw, M.; Amenu, K. Factors affecting the microbiological quality and contamination of farm bulk milk by Staphylococcus aureus in dairy farms in Asella, Ethiopia. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golban, M.; Charostad, J.; Kazemian, H.; Heidari, H. Phage-Derived Endolysins Against Resistant Staphylococcus spp.: A Review of Features, Antibacterial Activities, and Recent Applications. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2024, 14, 13–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.-W.; Lee, Y.-D.; Park, J.-H. Characteristics for phage-encoded cell wall hydrolase of LysSAP27 to reduce staphylococcal food poisoning. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Kim, M.; Ryu, S. Characterization of a novel endolysin LysSA11 and its utility as a potent biocontrol agent against Staphylococcus aureus on food and utensils. Food Microbiol. 2017, 68, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, O.; Agún, S.; Fernández, L.; Khalil, S.A.; Rodríguez, A.; García, P. Impact of the calcium concentration on the efficacy of phage phiIPLA-RODI, LysRODIΔAmi and nisin for the elimination of Staphylococcus aureus during lab-scale cheese production. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 399, 110227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigore-Gurgu, L.; Bucur, F.I.; Mihalache, O.A.; Nicolau, A.I. Comprehensive Review on the Biocontrol of Listeria monocytogenes in Food Products. Foods 2024, 13, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Nassau, T.J.; Lenz, C.A.; Scherzinger, A.S.; Vogel, R.F. Combination of endolysins and high pressure to inactivate Listeria monocytogenes. Food Microbiol. 2017, 68, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misiou, O.; van Nassau, T.J.; Lenz, C.A.; Vogel, R.F. The preservation of Listeria -critical foods by a combination of endolysin and high hydrostatic pressure. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 266, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Sánchez, L.A.; Van Tassell, M.L.; Miller, M.J. Antimicrobial behavior of phage endolysin PlyP100 and its synergy with nisin to control Listeria monocytogenes in Queso Fresco. Food Microbiol. 2018, 72, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenda, T.; Jarosz, A.; Sapała, M.; Grenda, A.; Patyra, E.; Kwiatek, K. Clostridium perfringens—Opportunistic Foodborne Pathogen, Its Diversity and Epidemiological Significance. Pathogens 2023, 12, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassi, L. Clostridial toxins: Potent poisons, potent medicines. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2005, 11, 391–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.-H.; Kwon, J.-G.; O’Sullivan, D.J.; Ryu, S.; Lee, J.-H. Development of an endolysin enzyme and its cell wall–binding domain protein and their applications for biocontrol and rapid detection of Clostridium perfringens in food. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiya, H.; Okada, M.; Tamai, E.; Shimamoto, T.; Shimamoto, T.; Nariya, H. A Putative Amidase Endolysin Encoded by Clostridium perfringens St13 Exhibits Specific Lytic Activity and Synergizes with the Muramidase Endolysin Psm. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Hu, M.; Luo, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. Characterization of the Clostridium perfringens phage endolysin cpp-lys and its application on lettuce. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 405, 110343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Liu, B.; Wu, L.; Bao, H.; García, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H. A Broad-Spectrum Phage Endolysin (LysCP28) Able to Remove Biofilms and Inactivate Clostridium perfringens Strains. Foods 2023, 12, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, T.N.; Lin, Y.; Maung, A.T.; Shen, C.; Zhao, J.; El-Telbany, M.; Zayda, M.; Masuda, Y.; Honjoh, K.-I.; Miyamoto, T. Characterization and antibacterial activity of highly thermo- and pH-stable endolysin LysCPQ7 and its application as a biocontrol agent against Clostridium perfringens in milk and cheese. Food Control 2023, 156, 110157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larpin, Y.; Oechslin, F.; Moreillon, P.; Resch, G.; Entenza, J.M.; Mancini, S. In vitro characterization of PlyE146, a novel phage lysin that targets Gram-negative bacteria. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, T.; Zhang, C. Engineering strategies and challenges of endolysin as an antibacterial agent against Gram-negative bacteria. Microb. Biotechnol. 2024, 17, e14465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.-H.; Duc, H.M.; Masuda, Y.; Honjoh, K.-I.; Miyamoto, T. Application of endolysin LysSTG2 as a potential biocontrol agent against planktonic and biofilm cells of Pseudomonas on various food and food contact surfaces. Food Control 2022, 131, 108460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briers, Y.; Walmagh, M.; Grymonprez, B.; Biebl, M.; Pirnay, J.-P.; Defraine, V.; Michiels, J.; Cenens, W.; Aertsen, A.; Miller, S.; et al. Art-175 Is a Highly Efficient Antibacterial against Multidrug-Resistant Strains and Persisters of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3774–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Yang, E.; Chang, P.-S.; Ryu, S. Preparation and characterization of endolysin-containing liposomes and evaluation of their antimicrobial activities against gram-negative bacteria. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2019, 128, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xu, D.; Wang, L.; Qu, M.; Li, F.; Tan, Z.; Yao, L. Characterization of a broad-spectrum endolysin LysSP1 encoded by a Salmonella bacteriophage. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 5461–5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.-C.; Ahn, J. Assessment of bacteriophage-encoded endolysin as a potent antimicrobial agent against antibiotic-resistant Salmonella Typhimurium. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 168, 105576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Wang, J.; Ahn, J. Synergistic antimicrobial activity of essential oils in combination with phage endolysin against Salmonella Typhimurium in cooked ground beef. Food Control 2023, 157, 110187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. An Endolysin LysSE24 by Bacteriophage LPSE1 Confers Specific Bactericidal Activity against Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Strains. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliga, P.; Goolappa, P.T.; Shekar, M.; Kallappa, G.S. Cloning, Characterization, and Antibacterial Properties of Endolysin LysE Against Planktonic Cells and Biofilms of Aeromonas hydrophila. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2023, 15, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; Yang, H.; Yan, N.; Hou, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, M. Bacteriostatic effects of phage F23s1 and its endolysin on Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J. Basic Microbiol. 2022, 62, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo-López, F.N.; Zermeño-Cervantes, L.A.; Barraza, A.; Loera-Muro, A.; Cardona-Félix, C.S. Biochemical characterization of LysVpKK5 endolysin from a marine vibriophage. Protein Expr. Purif. 2021, 188, 105971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Lin, B. Research Progress on Strategies for Improving the Enzyme Properties of Bacteriophage Endolysins. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Guo, Q.; Li, Z.; Guo, X.; Liu, X. Bacteriophage Endolysin: A Powerful Weapon to Control Bacterial Biofilms. Protein J. 2023, 42, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.-H.; Duc, H.M.; Masuda, Y.; Honjoh, K.-I.; Miyamoto, T. Endolysin LysSTG2: Characterization and application to control Salmonella Typhimurium biofilm alone and in combination with slightly acidic hypochlorous water. Food Microbiol. 2021, 98, 103791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, H.; Lin, H.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Lv, X.; Ju, L. Characterizations of the endolysin Lys84 and its domains from phage qdsa002 with high activities against Staphylococcus aureus and its biofilms. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2021, 148, 109809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Geng, P.; Sun, J.; Yuan, Z.; Hu, X. Characterization of two newly isolated bacteriophages PW2 and PW4 and derived endolysins with lysis activity against Bacillus cereus group strains. Virus Res. 2021, 302, 198489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonova, N.P.; Vasina, D.V.; Rubalsky, E.O.; Fursov, M.V.; Savinova, A.S.; Grigoriev, I.V.; Usachev, E.V.; Shevlyagina, N.V.; Zhukhovitsky, V.G.; Balabanyan, V.U.; et al. Modulation of Endolysin LysECD7 Bactericidal Activity by Different Peptide Tag Fusion. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Phage | Endolysin | Bacterium | Food | Conditions of Application | Results | Appointment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| phiLdb | Lysdb | S. aureus | Pasteurized milk in cheese making | Cell conc.: 104 CFU/mL Salt: 2.5% Conditions: 10 °C for 6 weeks | Cell count: Control: 2 × 109 CFU/mL (raw milk) and 3.9 × 107 CFU/g (cheese). Sample with Lysdb in cheese: 2.7 × 103 CFU/g | [60] |
| PBC4 | LysPBC4 | Bacillus cereus | Turbidity reduction assay (in vitro) | Endolysin conc.: 0.4 μM. Cell conc.: OD600: 1.0 Conditions: 37 °C, Tris-HCl 20 mM, pH 8.0 | Reduced OD600: 1.0 to 0.1 with LysPBC4, after 30 min. | [61] |
| PBC1 | LysPBC1 LysPBC1_EAD | B. cereus, Bacillus subtilis | Turbidity reduction assay (in vitro) | Endolysin conc.: 0.4 μM. Cell conc.: OD600: 1.2 (B. cereus) and 1.0 (B. subtilis) Conditions: 37 °C, Tris-HCl 20 mM, pH 8.0 | In B. cereus, OD600 decreased 1.2 to 0.2 with LysPBC1 and to 0.7 with LYSPBC1_EAD in 30 min. In B. subtilis, OD600 decreased from 0.9 to 0.6 with LysPBC1 and to 0.4 with LysPBC1_EAD in 30 min. | [62] |
| vB_SauS-phiIPLA88 | LysH5 | S. aureus and S. epidermidis | In vitro assay against biofilms with 24 h of formation | Endolysin conc.: 0.15 µM, Cell conc.: 106 CFU/mL Additional substances: lysostaphin: 0.2 µM or Sodium phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 7): 200 µL Conditions: TSB, 6 h at 37 °C | Reduction of sessile cells from 1 to 3 log10 CFU/well | [63] |
| B4 | LysB4 | B. cereus, B. subtilis, L. monocytogenes. E. coli, P. aeruginosa, Cronobacter sakazakii, Salmonella and Shigella | Turbidity reduction assay (in vitro) | Endolysin conc.: 0.05 µg/µL Cell conc.: OD600: 0.8–1.0 Additional substances: 0.1 M EDTA for Gram-negative bacteria. | 70% lytic activity in Gram-negative, 100% in B. cereus and B. subtilis. Optimal pH: 8–10 Optimal temperature: 50 °C NaCl: 0–200 mM | [64] |
| FWLLm3 | LysZ5 | L. monocytogenes | Soy milk | Endolysin conc.: 40 U/mL Cell conc.: 104 CFU/mL Conditions: 4 °C for 3 h | Reduction: 5 log10 CFU/mL, after 3 h incubation at 4 °C | [65] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soto Lopez, M.E.; Mendoza-Corvis, F.; Salgado-Behaine, J.J.; Hernandez-Arteaga, A.M.; González-Peña, V.; Burgos-Rivero, A.M.; Cortessi, D.; Vidigal, P.M.P.; Pérez-Sierra, O. Phage Endolysins as an Alternative Biocontrol Strategy for Pathogenic and Spoilage Microorganisms in the Food Industry. Viruses 2025, 17, 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040564
Soto Lopez ME, Mendoza-Corvis F, Salgado-Behaine JJ, Hernandez-Arteaga AM, González-Peña V, Burgos-Rivero AM, Cortessi D, Vidigal PMP, Pérez-Sierra O. Phage Endolysins as an Alternative Biocontrol Strategy for Pathogenic and Spoilage Microorganisms in the Food Industry. Viruses. 2025; 17(4):564. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040564
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoto Lopez, Maryoris E., Fernando Mendoza-Corvis, Jose Jorge Salgado-Behaine, Ana M. Hernandez-Arteaga, Víctor González-Peña, Andrés M. Burgos-Rivero, Derrick Cortessi, Pedro M. P. Vidigal, and Omar Pérez-Sierra. 2025. "Phage Endolysins as an Alternative Biocontrol Strategy for Pathogenic and Spoilage Microorganisms in the Food Industry" Viruses 17, no. 4: 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040564
APA StyleSoto Lopez, M. E., Mendoza-Corvis, F., Salgado-Behaine, J. J., Hernandez-Arteaga, A. M., González-Peña, V., Burgos-Rivero, A. M., Cortessi, D., Vidigal, P. M. P., & Pérez-Sierra, O. (2025). Phage Endolysins as an Alternative Biocontrol Strategy for Pathogenic and Spoilage Microorganisms in the Food Industry. Viruses, 17(4), 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17040564








