Establishment and Evaluation of Fatigue Mice Model in the Convalescence Phase of Influenza A
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Virus Strain
2.3. Drugs and Reagents
2.4. Experimental Methods
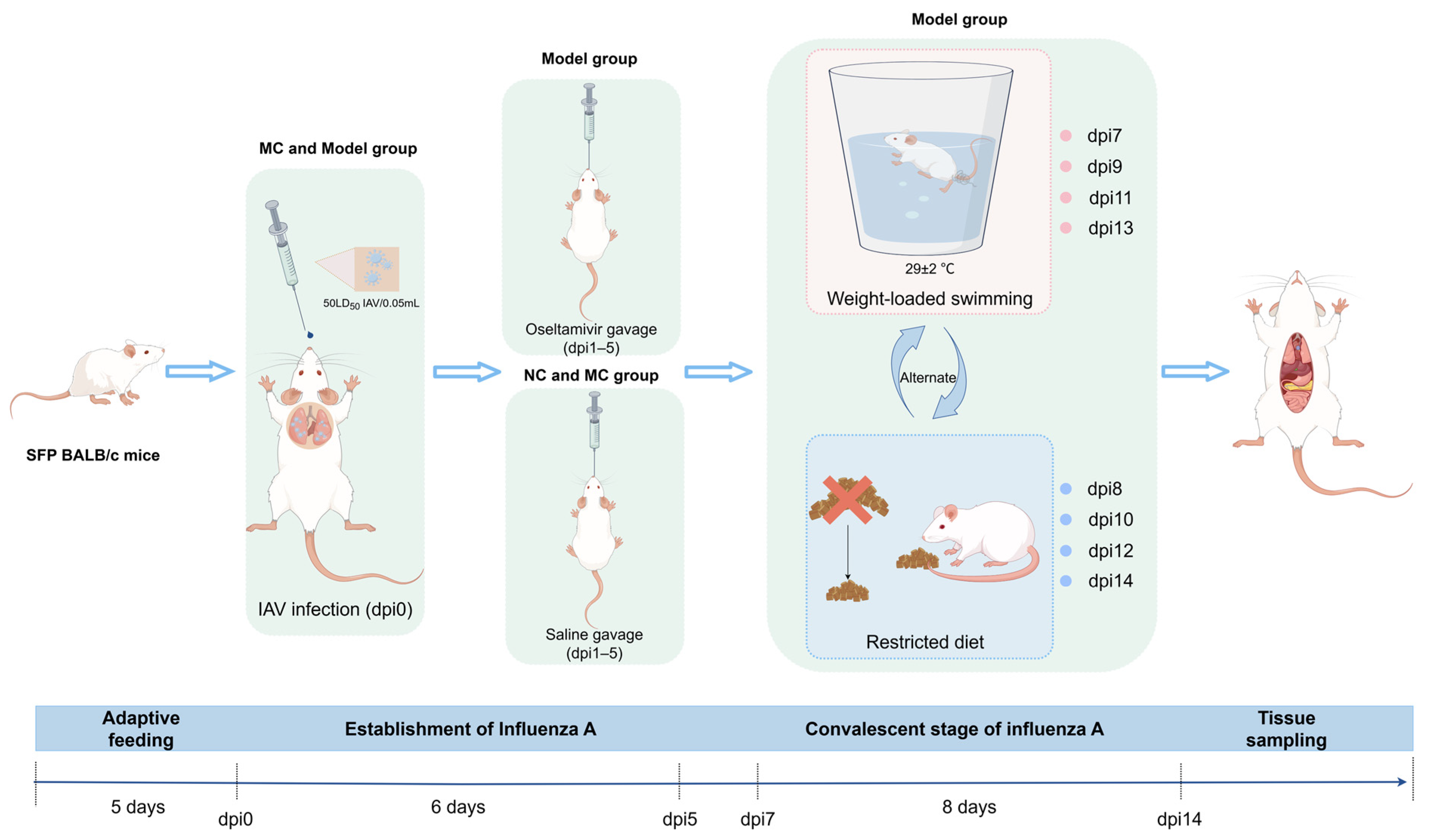
2.4.1. Experimental Grouping and Model Establishment
2.4.2. Body Weight Monitoring
2.4.3. Syndrome Observation
2.4.4. Organ Index
2.4.5. Final Exhaustive Swimming Duration
2.4.6. Histopathological Observation
2.4.7. Virus Expression Level Determination
2.4.8. Tissue Pro-Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Expression Levels
2.4.9. Oxidative Stress Indicators Detection
2.4.10. Electron Microscopy Observation of Mitochondria in Cells
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Syndrome Observation in TCM
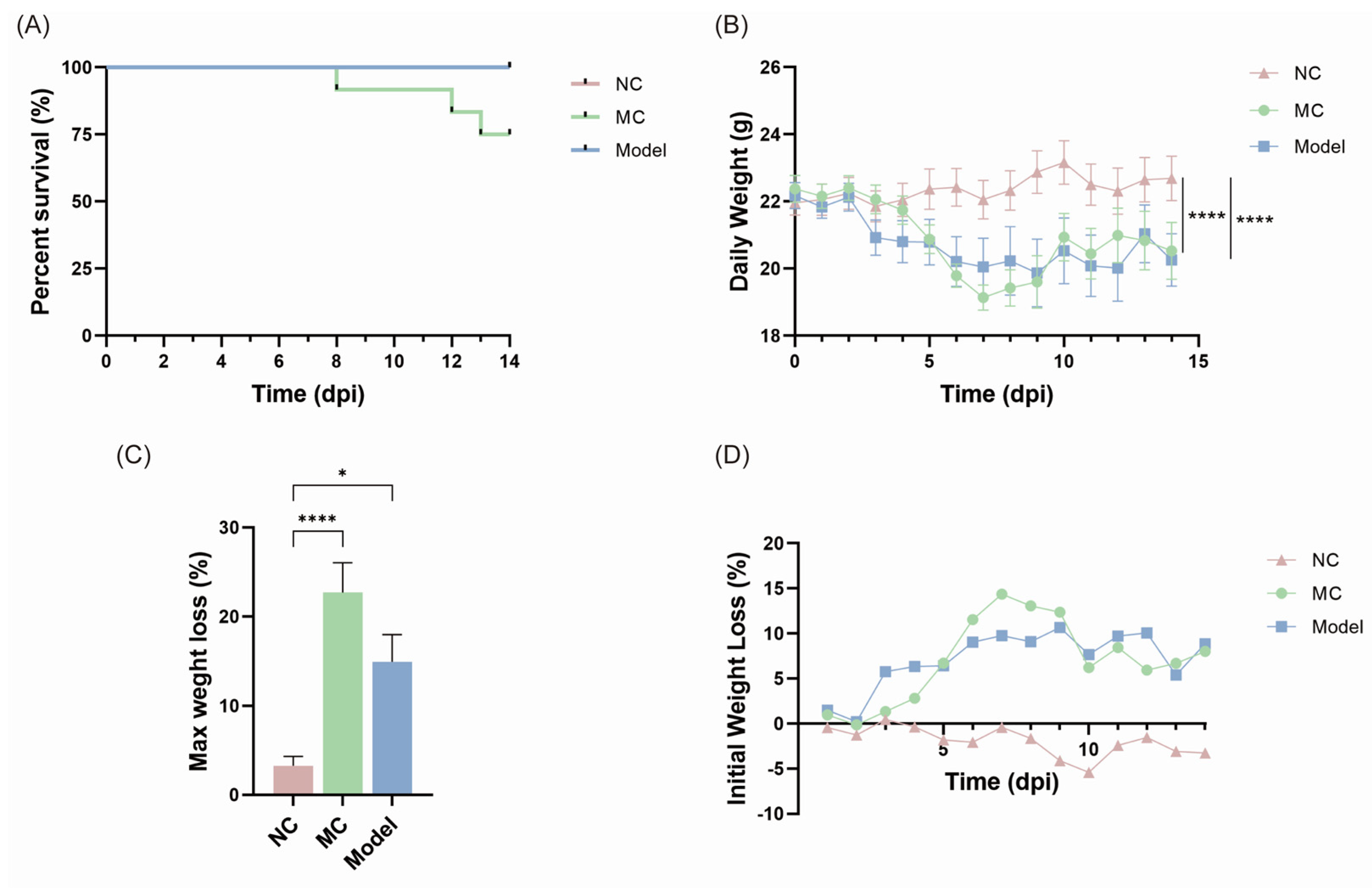
3.2. Body Weight Changes and Survival Rates
3.3. Pneumonia Convalescence Phase of Mice
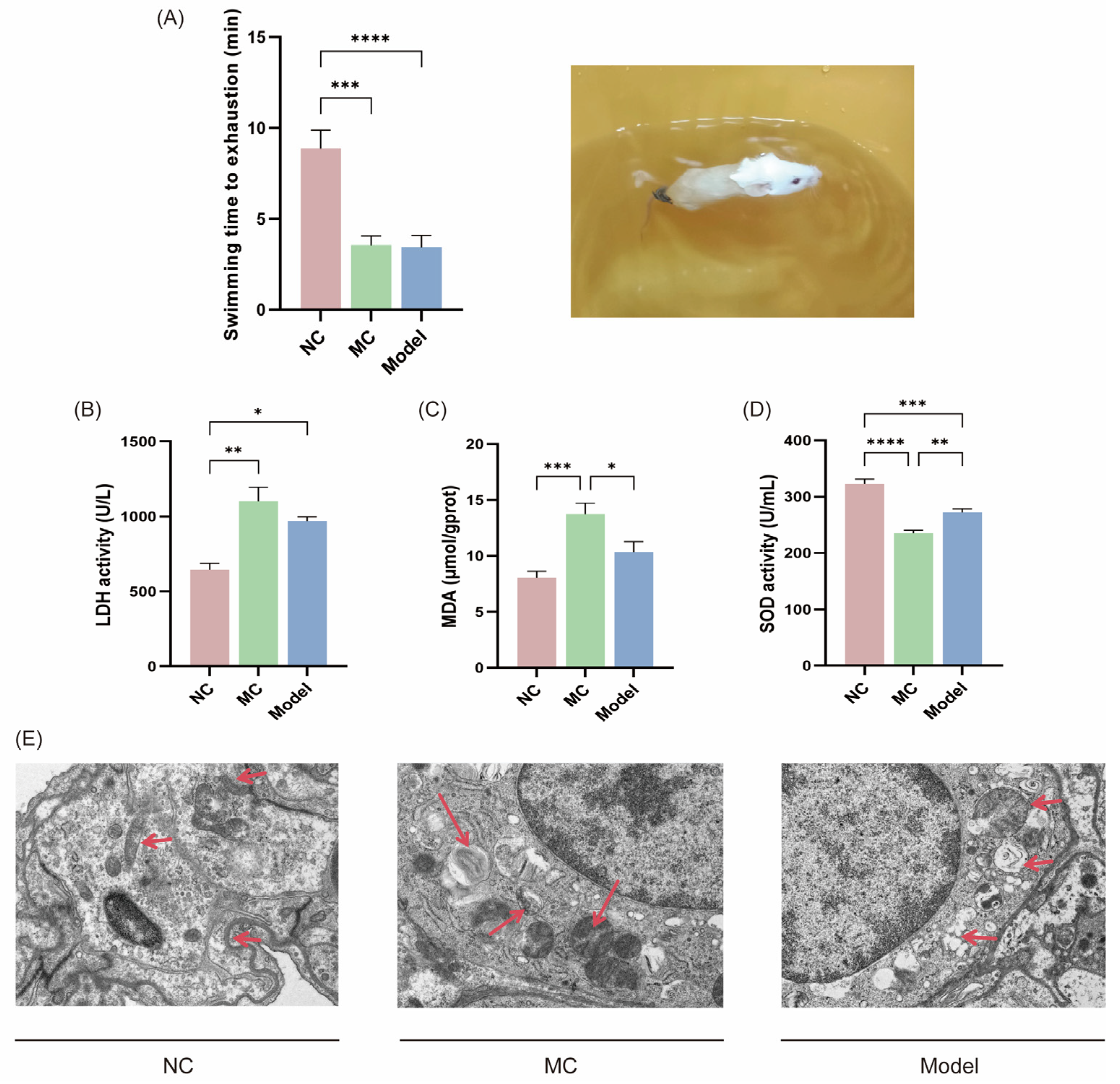
3.4. Fatigue-Related Behavioral Experiments and Laboratory Indicators
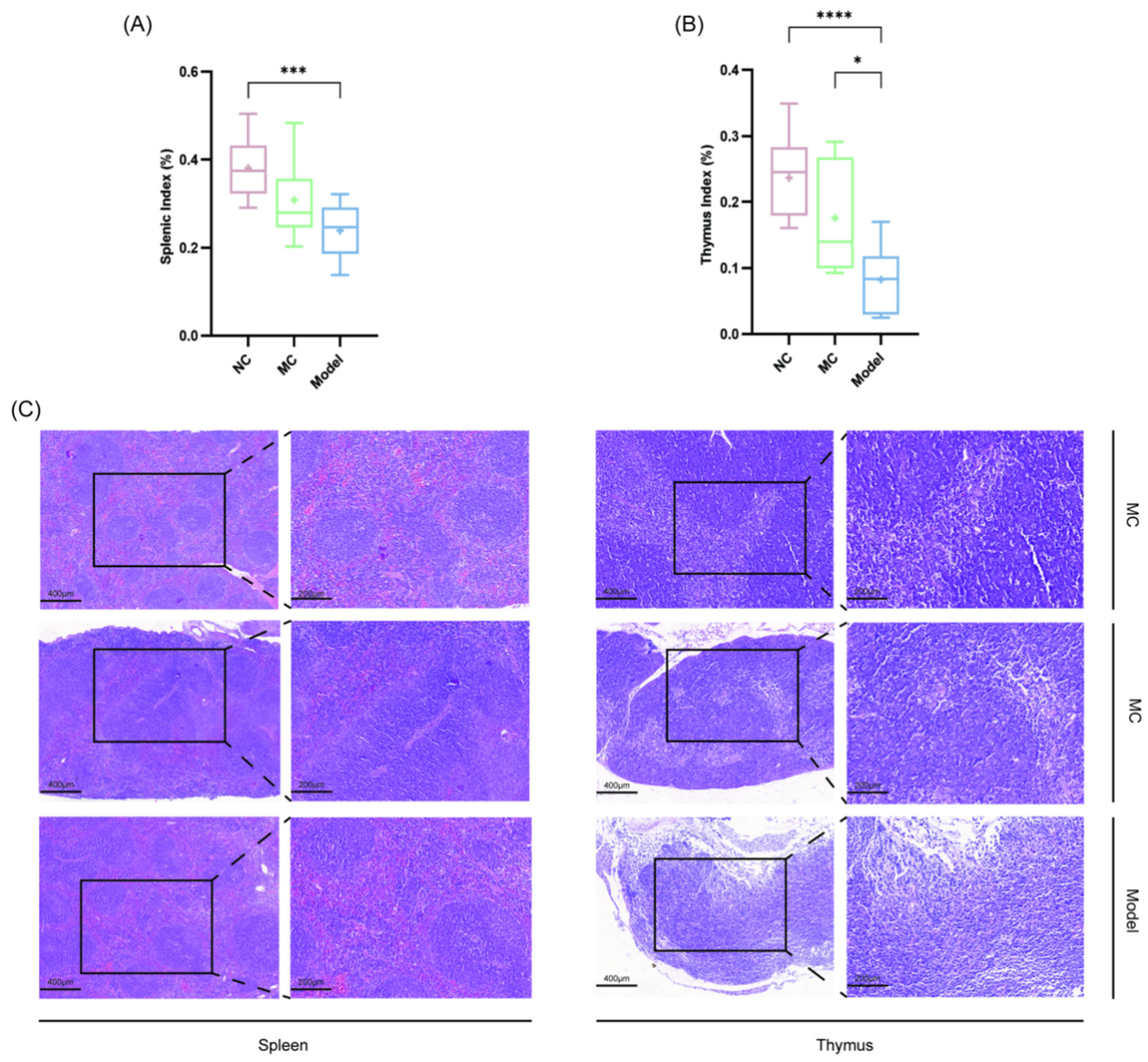
3.5. Immune Organ Indices and Histopathological Assessment
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IAV | Influenza A virus |
| PASC | SARS-CoV-2 infection |
| TCM | Traditional Chinese medicine |
| dpi | days post-inoculation |
| PVFS | post-viral fatigue syndrome |
| SHS | suboptimal health status |
| NP | Nucleoprotein |
| MDA | malondialdehyde |
| LDH | lactate dehydrogenase |
| SOD | total superoxide dismutase |
References
- Gao, Y.; Guyatt, G.; Uyeki, T.M.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Y.; Xu, J.; Zheng, Q.; Li, Z.; et al. Antivirals for treatment of severe influenza: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet 2024, 404, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Riel, D.; den Bakker, M.A.; Leijten, L.M.; Chutinimitkul, S.; Munster, V.J.; de Wit, E.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Fouchier, R.A.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Kuiken, T. Seasonal and pandemic human influenza viruses attach better to human upper respiratory tract epithelium than avian influenza viruses. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 1614–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, J.W.; Tan, K.S.; Ler, S.G.; Gunaratne, J.; Choi, H.; Seet, J.E.; Chow, V.T. Insights into Early Recovery from Influenza Pneumonia by Spatial and Temporal Quantification of Putative Lung Regenerating Cells and by Lung Proteomics. Cells 2019, 8, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Tang, H. Aberrant coagulation causes a hyper-inflammatory response in severe influenza pneumonia. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Meng, X.; Li, G.; Fan, Y.; Ma, L. Multislice spiral CT findings of H1N1 influenza and pneumonia dynamic changes. J. Pract. Med. Imaging 2016, 17, 325–327. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ippolito, E.; Belcaro, G.; Luzzi, R.; Hosoi, M.; Dugall, M.; Rohdewald, P.; Feragalli, B.; Cotellese, R.; Peterzan, P. Robuvit®: Improvement of fatigue in medical convalescence. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2018, 58, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Platt, M.P.; Gilley, R.P.; Brown, D.; Dube, P.H.; Yu, Y.; Gonzalez-Juarbe, N. Influenza Causes MLKL-Driven Cardiac Proteome Remodeling During Convalescence. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 570–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehandru, S.; Merad, M. Pathological sequelae of long-haul COVID. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Xu, X.; Wei, X.; Feng, W.; Huang, H.; Liu, H.; Xu, R.; Lin, J.; Han, L.; Zhang, D. Natural medicines for the treatment of fatigue: Bioactive components, pharmacology, and mechanisms. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 148, 104409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Bai, B.; Nie, G.; Ke, X. Investigationon Laws of Dialectical Staging and Etiology and Pathogenesis of 472 Cases Neotype H1N1 Influenza A. Shenzhen J. Integr. Tradit. Chin. West. Med. 2011, 21, 72–76. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of influenza (2020 version). Chin. J. Viral Dis. 2020, 401–411. (In Chinese)
- Mantle, D.; Hargreaves, I.P.; Domingo, J.C.; Castro-Marrero, J. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation in Post-Viral Fatigue Syndrome: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Russell, A.; Yan, Y. Traditional Chinese medicine and new concepts of predictive, preventive and personalized medicine in diagnosis and treatment of suboptimal health. EPMA J. 2014, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yan, Y.; Guo, Z.; Hou, H.; Garcia, M.; Tan, X.; Anto, E.O.; Mahara, G.; Zheng, Y.; Li, B.; et al. All around suboptimal health—A joint position paper of the Suboptimal Health Study Consortium and European Association for Predictive, Preventive and Personalised Medicine. EPMA J. 2021, 12, 403–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yan, Y. Suboptimal health: A new health dimension for translational medicine. Clin. Transl. Med. 2012, 1, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Fu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, S.; Song, F.; Liu, Z. Based on urine metabolomics to study the mechanism of Qi-deficiency affecting type 2 diabetes rats using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2021, 1179, 122850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, F.; Cai, Y.; Xie, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Zheng, F.; Yue, H. Intervention effects of ginseng on spleen-qi deficiency in rats revealed by GC-MS-based metabonomic approach. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 217, 114834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.L.; Yan, M.Q.; Su, J.; Yu, J.J.; Ye, S.Y.; Fu, M.; Hu, X.L.; Niu, Z.W.; Wu, W.Y.; Chen, S.M.; et al. Effects of Dendrobium officinale ultrafine powder on sub-health mice induced by unhealthy lifestyle based on neuroendocrine immune system. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 12436–12450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Cai, Y.; Shao, X.; Ma, B. Improving the activity of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on sub-health mice. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 2033–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Hao, W.; Ma, B.; Chen, Z. Improvement effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on sub-health mice. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2015, 18, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar]
- Sabikunnahar, B.; Lahue, K.G.; Asarian, L.; Fang, Q.; McGill, M.M.; Haynes, L.; Teuscher, C.; Krementsov, D.N. Sex differences in susceptibility to influenza A virus infection depend on host genotype. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0273050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mytle, N.; Leyrer, S.; Inglefield, J.R.; Harris, A.M.; Hickey, T.E.; Minang, J.; Lu, H.; Ma, Z.; Andersen, H.; Grubaugh, N.D.; et al. Influenza Antigens NP and M2 Confer Cross Protection to BALB/c Mice against Lethal Challenge with H1N1, Pandemic H1N1 or H5N1 Influenza A Viruses. Viruses 2021, 13, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Ma, X.; Fan, B.; Liu, Z.; Wang, K.; Feng, Z.; Sun, G.; Li, L. Role of Toll-like receptor 4 in pulmonary inflammation induced by influenza A virus. Chin. J. Pathophysiol. 2023, 39, 1357–1365. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pavlova, E.L.; Simeonova, L.S.; Gegova, G.A. Combined efficacy of oseltamivir, isoprinosine and ellagic acid in influenza A(H3N2)-infected mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 98, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Toyomasu, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Linden, D.R.; Szurszewski, J.H.; Nelson, H.; Farrugia, G.; Kashyap, P.C.; Chia, N.; Ordog, T. Altered gut microbiota in female mice with persistent low body weights following removal of post-weaning chronic dietary restriction. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, W.J.; Park, M.N.; Lee, J.; Shin, J.H.; Shin, D.M. Renal transcriptome profiles in mice reveal the need for sufficient water intake irrespective of the drinking water type. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.H.; Tsai, W.J.; Loke, S.H.; Wu, T.S.; Chiou, W.F. Astragalus membranaceus flavonoids (AMF) ameliorate chronic fatigue syndrome induced by food intake restriction plus forced swimming. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 122, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, M.P.; Lerner, A.M.; Ho, K.L. Diminution in the Size of the Thymus in Mice During Forced Swimming. J. Infect. Dis. 1981, 143, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.; Huang, C.T.; Chen, T.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Chiu, C.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Chang, C.S.; He, Y.C. IL-10 inhibits neuraminidase-activated TGF-β and facilitates Th1 phenotype during early phase of infection. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lauder, S.N.; Jones, E.; Smart, K.; Bloom, A.; Williams, A.S.; Hindley, J.P.; Ondondo, B.; Taylor, P.R.; Clement, M.; Fielding, C.; et al. Interleukin-6 limits influenza-induced inflammation and protects against fatal lung pathology. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 2613–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zuo, X.; Zhang, S.; Ouyang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Wang, F.; Wang, G. The Mechanism behind Influenza Virus Cytokine Storm. Viruses 2021, 13, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreychyn, M.; Melnyk, L.; Zavidniiuk, N.; Nychyk, N.; Iosyk, I. Interleukins in the pathogenesis of influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections. Epidemiol. Infect. 2024, 152, e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atramont, A.; Martin, G.L.; Singer, M.; Tajahmady, A.; Agamaliyev, E.; Harhay, M.O.; Leone, M.; Legrand, M. One-Year Survival and Hospital-Free Days in Critically Illness After Viral Pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 209, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laporte, L.R.; Chavez, A.V.; Ranzani, O.T.; Caldas, J.; Passos, R.D.; Ramos, J.G. Long-term outcomes for epidemic viral pneumonia survivors after discharge from the intensive care unit: A systematic review. Einstein 2024, 22, eRW0352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geto, Z.; Molla, M.D.; Challa, F.; Belay, Y.; Getahun, T. Mitochondrial Dynamic Dysfunction as a Main Triggering Factor for Inflammation Associated Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases. J. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 13, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komaroff, A.L.; Lipkin, W.I. ME/CFS and Long COVID share similar symptoms and biological abnormalities: Road map to the literature. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1187163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannister, B.A. Post-infectious disease syndrome. Postgrad. Med. J. 1988, 64, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name | Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| GAPDH (Forward primer) GAPDH (Reverse primer) | AGCTCGCTGTGAGCTGCTGAC TGTACACATGTATTCACGTCTG |
| IAV NP (Forward primer) IAV NP (Reverse primer) | CCTGTGTGTATGGACCTGCC CTCTTGGGACCACCTTCGTC |
| IL-10 (Forward primer) IL-10 (Reverse primer) | AGAGAAGCATGGCCCAGAAATCAAG AGAGAAGCATGGCCCAGAAATCAAG |
| IL-6 (Forward primer) IL-6 (Reverse primer) | TTCTTGGGACTGATGCTGGTGAC CTGTTGGGAGTGGTATCCTCTGTG |
| TNF-α (Forward primer) TNF-α (Reverse primer) | TAGCCCACGTCGTAGCAAAC ACAAGGTACAACCCATCGGC |
| TGF-β (Forward primer) TGF-β (Reverse primer) | AAGGAGACGGAATACAGGGC GGAAGGGCCGGTTCATGT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, X.; Zhang, C.; Shi, J.; Ji, X.; Wang, K.; Li, L.; He, Q. Establishment and Evaluation of Fatigue Mice Model in the Convalescence Phase of Influenza A. Viruses 2025, 17, 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050593
Zeng X, Zhang C, Shi J, Ji X, Wang K, Li L, He Q. Establishment and Evaluation of Fatigue Mice Model in the Convalescence Phase of Influenza A. Viruses. 2025; 17(5):593. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050593
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Xiaoke, Cheng Zhang, Jianing Shi, Xuan Ji, Keying Wang, Ling Li, and Qinghu He. 2025. "Establishment and Evaluation of Fatigue Mice Model in the Convalescence Phase of Influenza A" Viruses 17, no. 5: 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050593
APA StyleZeng, X., Zhang, C., Shi, J., Ji, X., Wang, K., Li, L., & He, Q. (2025). Establishment and Evaluation of Fatigue Mice Model in the Convalescence Phase of Influenza A. Viruses, 17(5), 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17050593






