Orthopoxvirus Genome Evolution: The Role of Gene Loss
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Poxvirus Phylogeny
2.2. Poxvirus Genome Annotation
The Poxvirus Genome Annotation System
2.3. Orthopoxvirus Gene Prediction
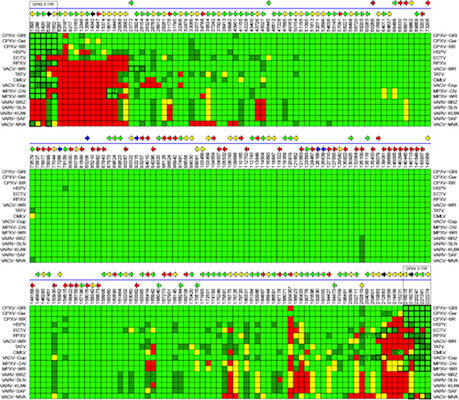
2.4. Comparative Analysis of Orthopoxvirus Gene Content
| Species | Strain Name | Abbreviation | Genome Length | Length of ITR | Haploid Gene Count | Genes in ITR | Genome GC% | Accession # | PubMed ID (Reference) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Camelpox virus | Camelpox virus strain M-96 from Kazakhstan | CMLV | 205,719 | 7736 | 188 | 3 | 33.2 | AF438165 (NC_003391) | 12033760 [73] |
| Cowpox virus | Cowpox virus strain Brighton Red | CPXV-BR | 224,499 | 9710 | 209 | 5 | 33.4 | AF482758 (NC_003663) | 6961398 [74] |
| Cowpox virus | Cowpox virus strain Germany 91-3 | CPXV-Ger | 228,250 | 7374 | 211 | 5 | 33.5 | DQ437593 | 16873609 [23] |
| Cowpox virus | Cowpox virus strain GRI-90 | CPXV-Gri | 223,666 | 8303 | 212 | 5 | 33.7 | X94355 | 9568042 [75] |
| Ectromelia virus | Ectromelia virus strain Moscow | ECTV | 209,771 | 9413 | 193 | 5 | 33.2 | AF012825 (NC_004105) | 14675635 [76] |
| Monkeypox virus | Monkeypox virus strain MPXV-WRAIR7-61; Walter Reed 267 | MPXV-WR | 199,195 | 8749 | 182 | 6 | 33.1 | AY603973 | 16023693 [28] |
| Monkeypox virus | Monkeypox virus strain Zaire-96-I-16 | MPXV-ZAI | 196,858 | 6378 | 183 | 4 | 33.1 | AF380138 (NC_003310) | 11734207 [77] |
| Taterapox virus | Taterapox virus strain Dahomey 1968 | TATV | 198,050 | 4779 | 189 | 3 | 33.3 | DQ437594 (NC_008291) | 16873609 [23] |
| Vaccinia virus | Horsepox virus strain MNR-76 | HSPV | 212,633 | 7527 | 203 | 5 | 33.1 | DQ792504 | 16940536 [78] |
| Vaccinia virus | Rabbitpox virus | RPXV | 197,731 | 10022 | 192 | 6 | 33.5 | AY484669 | 16227218 [79] |
| Vaccinia virus | Vaccinia virus strain Ankara | VACV-MVA | 177,923 | 9644 | 174 | 2 | 33.1 | U94848 | 9601507 [80] |
| Vaccinia virus | Vaccinia virus strain Copenhagen | VACV-Cop | 191,738 | 11967 | 187 | 6 | 33.4 | M35027 | 2219722 [58] |
| Vaccinia virus | Vaccinia virus strain WR (Western Reserve) | VACV-WR | 194,711 | 10186 | 190 | 6 | 33.3 | AY243312 (NC_006998) | |
| Variola virus | Variola virus strain Brazil 1966 (v66-39 Sao Paulo) | VARV-BRZ | 188,062 | 518 | 180 | 0 | 32.7 | DQ441419 | 16873609 [23] |
| Variola virus | Variola virus strain Kuwait 1967 (K1629) | VARV-KUW | 185,853 | 522 | 179 | 0 | 32.7 | DQ441433 | 16873609 [23] |
| Variola virus | Variola virus strain Sierra Leone 1969 (V68-258) | VARV-SLN | 187,014 | 196 | 179 | 0 | 32.7 | DQ441437 | 16873609 [23] |
| Variola virus | Variola virus strain South Africa 1965 (103 T'vaal, Nelspruit) | VARV-SAF | 185,881 | 526 | 179 | 0 | 32.7 | DQ441436 | 16873609 [23] |
2.5. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Genome Sequences
3.2. Multiple Sequence Alignments and Phylogenetic Tree Construction
3.3. Poxvirus Genome Annotation System (PGAS)
3.3.1. Sequence Comparison
3.3.2. Genomic Comparative Analysis
3.3.3. Promoter Prediction
3.3.4. Characterization of Coding Potential Using Glimmer
3.3.5. Semi-Automatic Gene Prediction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Odom, M.R.; Hendrickson, R.C.; Lefkowitz, E.J. Poxvirus protein evolution: Family wide assessment of possible horizontal gene transfer events. Virus Res. 2009, 144, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauquet, C.M.; Mayo, M.A.; Maniloff, J.; Desselberger, U.; Ball, L.A. Virus Taxonomy: VIIIth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; Academic Press (Elsevier): London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mercer, A.A.; Schmidt, A.; Weber, O.F. Poxviruses; Birkhäuser Verlag: Basel, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, J.W.; McFadden, G. Origin and evolution of poxviruses. In Origin and Evolution of Viruses, 2nd ed.; Domingo, E., Parrish, C.R., Holland, J.J., Eds.; Academic Press (Elsevier): London, UK, 2008; pp. 431–446. [Google Scholar]
- DeFilippis, V.R.; Villarreal, L.P. Virus evolution. In Fields Virology, 4th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2001; pp. 353–370. [Google Scholar]
- Beukema, E.L.; Brown, M.P.; Hayball, J.D. The potential role of fowlpox virus in rational vaccine design. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2006, 5, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulman, E.R.; Afonso, C.L.; Lu, Z.; Zsak, L.; Kutish, G.F.; Rock, D.L. Genome of lumpy skin disease virus. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 7122–7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, C.L.; Tulman, E.R.; Lu, Z.; Zsak, L.; Osorio, F.A.; Balinsky, C.; Kutish, G.F.; Rock, D.L. The genome of swinepox virus. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werden, S.J.; McFadden, G. The role of cell signaling in poxvirus tropism: The case of the M-T5 host range protein of myxoma virus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1784, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.; McIntyre, P.; McInnes, A.E.C.; Lewis-Jones, S. Human sealpox resulting from a seal bite: Confirmation that sealpox virus is zoonotic. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 152, 791–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macneil, A.; Lederman, E.; Reynolds, M.G.; Ragade, N.J.; Talken, R.; Friedman, D.; Hall, W.; Shwe, T.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Smith, S.; Davidson, W.; Hughes, C.; Damon, I.K. Diagnosis of Bovine-Associated Parapoxvirus Infections in Humans: Molecular and Epidemiological Evidence. Zoonoses Public Health 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.D.; Werchniak, A.E.; Li, Y.; Brennick, J.B.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Kline, R.; Damon, I.; Klaus, S.N. Tanapox infection in a college student. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarian, S.H.; Barrett, J.W.; Stanford, M.M.; Johnston, J.B.; Essani, K.; McFadden, G. Tropism of Tanapox virus infection in primary human cells. Virology 2007, 368, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, C.L.; Delhon, G.; Tulman, E.R.; Lu, Z.; Zsak, A.; Becerra, V.M.; Zsak, L.; Kutish, G.F.; Rock, D.L. Genome of deerpox virus. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, D.; Diven, D.G. Molluscum contagiosum. Dermatol. Online J. 2003, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangari, D.S.; Miller, M.A.; Stevenson, G.W.; Thacker, H.L.; Sharma, A.; Mittal, S.K. Cutaneous and systemic poxviral disease in red (Tamiasciurus hudsonicus) and gray (Sciurus carolinensis) squirrels. Vet. Pathol. 2009, 46, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, C.L.; Tulman, E.R.; Delhon, G.; Lu, Z.; Viljoen, G.J.; Wallace, D.B.; Kutish, G.F.; Rock, D.L. Genome of crocodilepox virus. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 4978–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerson, G.L.; Li, Y.; Frace, M.A.; Olsen-Rasmussen, M.A.; Khristova, M.L.; Govil, D.; Sammons, S.A.; Regnery, R.L.; Karem, K.L.; Damon, I.K.; Carroll, D.S. The phylogenetics and ecology of the orthopoxviruses endemic to North America. PLoS One 2009, 4, e7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werden, S.J.; Rahman, M.M.; McFadden, G. Poxvirus host range genes. Adv. Virus Res. 2008, 71, 135–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Essbauer, S.; Pfeffer, M.; Meyer, H. Zoonotic poxviruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giulio, D.B.; Eckburg, P.B. Human monkeypox: An emerging zoonosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2004, 4, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Drillien, R.; Spehner, D.; Buller, R.M. Restricted replication of ectromelia virus in cell culture correlates with mutations in virus-encoded host range gene. Virology 1992, 187, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, J.J.; Sammons, S.A.; Frace, A.M.; Osborne, J.D.; Olsen-Rasmussen, M.; Zhang, M.; Govil, D.; Damon, I.K.; Kline, R.; Laker, M.; Li, Y.; Smith, G.L.; Meyer, H.; Leduc, J.W.; Wohlhueter, R.M. Genome sequence diversity and clues to the evolution of variola (smallpox) virus. Science 2006, 313, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubser, C.; Smith, G.L. The sequence of camelpox virus shows it is most closely related to variola virus, the cause of smallpox. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 855–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damon, I.K. Poxviruses. In Fields Virology, 5th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 353–370. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.K.; Hosamani, M.; Balamurugan, V.; Bhanuprakash, V.; Rasool, T.J.; Yadav, M.P. Buffalopox: An emerging and re-emerging zoonosis. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2007, 8, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.A.; Kotwal, G.J. Immune response to poxvirus infections in various animals. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2002, 28, 149–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Li, G.; Liszewski, M.K.; Atkinson, J.P.; Jahrling, P.B.; Feng, Z.; Schriewer, J.; Buck, C.; Wang, C.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Esposito, J.J.; Harms, T.; Damon, I.K.; Roper, R.L.; Upton, C.; Buller, R.M. Virulence differences between monkeypox virus isolates from West Africa and the Congo basin. Virology 2005, 340, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardison, R.C. Comparative genomics. PLoS Biol. 2003, 1, E58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisen, J.A.; Wu, M. Phylogenetic analysis and gene functional predictions: phylogenomics in action. Theor. Popul. Biol. 2002, 61, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicheritz-Ponten, T.; Andersson, S.G. A phylogenomic approach to microbial evolution. Nucl. Acid. Res. 2001, 29, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhon, G.; Tulman, E.R.; Afonso, C.L.; Lu, Z.; de la Concha-Bermejillo, A.; Lehmkuhl, H.D.; Piccone, M.E.; Kutish, G.F.; Rock, D.L. Genomes of the parapoxviruses ORF virus and bovine papular stomatitis virus. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarian, S.H.; Barrett, J.W.; Frace, A.M.; Olsen-Rasmussen, M.; Khristova, M.; Shaban, M.; Neering, S.; Li, Y.; Damon, I.K.; Esposito, J.J.; Essani, K.; McFadden, G. Comparative genetic analysis of genomic DNA sequences of two human isolates of Tanapox virus. Virus Res. 2007, 129, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulman, E.; Afonso, C.; Lu, Z.; Zsak, L.; Kutish, G.; Rock, D. The genome of canarypox virus. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winters, E.; Baroudy, B.M.; Moss, B. Molecular cloning of the terminal hairpin of vaccinia virus DNA as an imperfect palindrome in an Escherichia coli plasmid. Gene 1985, 37, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchlinsky, M.; Garon, C.F.; Moss, B. Molecular cloning and sequence of the concatemer junction from vaccinia virus replicative DNA. Viral nuclease cleavage sites in cruciform structures. J. Mol. Biol. 1988, 199, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massung, R.F.; Knight, J.C.; Esposito, J.J. Topography of variola smallpox virus inverted terminal repeats. Virology 1995, 211, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.L.; Chan, Y.S.; Howard, S.T. Nucleotide sequence of 42 kbp of vaccinia virus strain WR from near the right inverted terminal repeat. J. Gen. Virol. 1991, 72, 1349–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefkowitz, E.J.; Wang, C.; Upton, C. Poxviruses: Past, present and future. Virus Res. 2006, 117, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, C.L.; Tulman, E.R.; Lu, Z.; Zsak, L.; Kutish, G.F.; Rock, D.L. The genome of fowlpox virus. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 3815–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condit, R.C.; Moussatche, N.; Traktman, P. In a nutshell: Structure and assembly of the vaccinia virion. Adv. Virus Res. 2006, 66, 31–124. [Google Scholar]
- Stanford, M.M.; McFadden, G.; Karupiah, G.; Chaudhri, G. Immunopathogenesis of poxvirus infections: forecasting the impending storm. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2007, 85, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.B.; McFadden, G. Technical knockout: understanding poxvirus pathogenesis by selectively deleting viral immunomodulatory genes. Cell Microbiol. 2004, 6, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubser, C.; Hué, S.; Kellam, P.; Smith, G.L. Poxvirus genomes: A phylogenetic analysis. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.L.; Friedman, R. Poxvirus genome evolution by gene gain and loss. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2005, 35, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.L.; Irausquin, S.; Friedman, R. The evolutionary biology of poxviruses. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2009, 10, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLysaght, A.; Baldi, P.F.; Gaut, B.S. Extensive gene gain associated with adaptive evolution of poxviruses. PNAS 2003, 100, 15655–15660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, K.; Deng, R.; Wang, J.; Feng, J.; Huang, M.; Wang, X. Genome-based phylogeny of poxvirus. Intervirology 2006, 49, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upton, C.; Hogg, D.; Perrin, D.; Boone, M.; Harris, N.L. Viral genome organizer: A system for analyzing complete viral genomes. Virus Res. 2000, 70, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, R.; Rozanov, M.; Lomsadze, A.; Tatusova, T.; Borodovsky, M. Improving gene annotation of complete viral genomes. Nucl. Acid. Res. 2003, 31, 7041–7055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, C.L.; Tulman, E.R.; Lu, Z.; Oma, E.; Kutish, G.F.; Rock, D.L. The Genome of Melanoplus sanguinipes Entomopoxvirus. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 533–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawden, A.L.; Glassberg, K.J.; Diggans, J.; Shaw, R.; Farmerie, W.; Moyer, R.W. Complete genomic sequence of the amsacta moorei entomopoxvirus: Analysis and comparison with other poxviruses. Virology 2000, 274, 120–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upton, C.; Slack, S.; Hunter, A.L.; Ehlers, A.; Roper, R.L. Poxvirus orthologous clusters: Toward defining the minimum essential poxvirus genome. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 7590–7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vliet, K.; Mohamed, M.R.; Zhang, L.; Villa, N.Y.; Werden, S.J.; Liu, J.; McFadden, G. Poxvirus proteomics and virus-host protein interactions. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2009, 73, 730–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condit, R.C.; Moussatche, N.; Traktman, P. In a nutshell: Structure and assembly of the vaccinia virion. Adv. Virus Res. 2006, 66, 31–124. [Google Scholar]
- Mahalingam, S.; Damon, I.K.; Lidbury, B.A. 25 years since the eradication of smallpox: Why poxvirus research is still relevant. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 636–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFadden, G. Poxvirus Tropism. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goebel, S.J.; Johnson, G.P.; Perkus, M.E.; Davis, S.W.; Winslow, J.P.; Paoletti, E. The complete DNA sequence of vaccinia virus. Virology 1990, 179, 247–266, 517–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, G.P.; Goebel, S.J.; Paoletti, E. An update on the vaccinia virus genome. Virology 1993, 196, 381–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picardi, E.; Pesole, G. Computational methods for ab initio and comparative gene finding. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 609, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baxevanis, A.D. An overview of gene identification: Approaches, strategies, and considerations. Curr. Protoc. Bioinformatics 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Mistry, J.; Tate, J.; Coggill, P.; Heger, A.; Pollington, J.E.; Gavin, O.L.; Gunasekaran, P.; Ceric, G.; Forslund, K.; Holm, L.; Sonnhammer, E.L.; Eddy, S.R.; Bateman, A. The Pfam protein families database. Nucl. Acid.Res. 2010, 38, D211–D222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcher, A.L.; Harmon, D.; Kasif, S.; White, O.; Salzberg, S.L. Improved microbial gene identification with GLIMMER. Nucl. Acid. Res. 1999, 27, 4636–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, A.G.; Baldi, P.; Brunak, S.; Chauvin, Y. Characterization of prokaryotic and eukaryotic promoters using hidden Markov models. Proc. Int. Conf. Intell. Syst. Mol. Biol. 1996, 4, 182–191. [Google Scholar]
- Salzberg, S.L.; Delcher, A.L.; Kasif, S.; White, O. Microbial gene identification using interpolated Markov models. Nucl. Acid. Res. 1998, 26, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Needleman, S.B.; Wunsch, C.D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 1970, 48, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozak, M. Interpreting cDNA sequences: Some insights from studies on translation. Mamm. Genome 1996, 7, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shchelkunov, S.N.; Totmenin, A.V. Two types of deletions in orthopoxvirus genomes. Virus Genes 1995, 9, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, A.R.; Weisberg, A.S.; Moss, B. Congregation of orthopoxvirus virions in cytoplasmic A-type inclusions is mediated by interactions of a bridging protein (A26p) with a matrix protein (ATIp) and a virion membrane-associated protein (A27p). J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7592–7602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senkevich, T.G.; White, C.L.; Weisberg, A.; Granek, J.A.; Wolffe, E.J.; Koonin, E.V.; Moss, B. Expression of the vaccinia virus A2.5L redox protein is required for virion morphogenesis. Virology 2002, 300, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkevich, T.G.; White, C.L.; Koonin, E.V.; Moss, B. Complete pathway for protein disulfide bond formation encoded by poxviruses. PNAS 2002, 99, 6667–6672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, C.L.; Tulman, E.R.; Lu, Z.; Zsak, L.; Sandybaev, N.T.; Kerembekova, U.Z.; Zaitsev, V.L.; Kutish, G.F.; Rock, D.L. The genome of camelpox virus. Virology 2002, 295, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickup, D.J.; Bastia, D.; Stone, H.O.; Joklik, W.K. Sequence of terminal regions of cowpox virus DNA: Arrangement of repeated and unique sequence elements. PNAS 1982, 79, 7112–7116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchelkunov, S.N.; Safronov, P.F.; Totmenin, A.V.; Petrov, N.A.; Ryazankina, O.I.; Gutorov, V.V.; Kotwal, G.J. The genomic sequence analysis of the left and right species-specific terminal region of a cowpox virus strain reveals unique sequences and a cluster of intact ORFs for immunomodulatory and host range proteins. Virology 1998, 243, 432–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Danila, M.I.; Feng, Z.; Buller, R.M.; Wang, C.; Han, X.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Upton, C. The genomic sequence of ectromelia virus, the causative agent of mousepox. Virology 2003, 317, 165–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shchelkunov, S.N.; Totmenin, A.V.; Babkin, I.V.; Safronov, P.F.; Ryazankina, O.I.; Petrov, N.A.; Gutorov, V.V.; Uvarova, E.A.; Mikheev, M.V.; Sisler, J.R.; Esposito, J.J.; Jahrling, P.B.; Moss, B.; Sandakhchiev, L.S. Human monkeypox and smallpox viruses: Genomic comparison. FEBS Lett. 2001, 509, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulman, E.R.; Delhon, G.; Afonso, C.L.; Lu, Z.; Zsak, L.; Sandybaev, N.T.; Kerembekova, U.Z.; Zaitsev, V.L.; Kutish, G.F.; Rock, D.L. Genome of horsepox virus. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 9244–9258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Chen, N.; Roper, R.L.; Feng, Z.; Hunter, A.; Danila, M.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Buller, R.M.; Upton, C. Complete coding sequences of the rabbitpox virus genome. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 2969–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoine, G.; Scheiflinger, F.; Dorner, F.; Falkner, F.G. The complete genomic sequence of the modified vaccinia Ankara strain: Comparison with other orthopoxviruses. Virology 1998, 244, 365–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assarsson, E.; Greenbaum, J.A.; Sundström, M.; Schaffer, L.; Hammond, J.A.; Pasquetto, V.; Oseroff, C.; Hendrickson, R.C.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Tscharke, D.C.; Sidney, J.; Grey, H.M.; Head, S.R.; Peters, B.; Sette, A. Kinetic analysis of a complete poxvirus transcriptome reveals an immediate-early class of genes. PNAS 2008, 105, 2140–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yutin, N.; Wolf, Y.I.; Raoult, D.; Koonin, E.V. Eukaryotic large nucleo-cytoplasmic DNA viruses: Clusters of orthologous genes and reconstruction of viral genome evolution. Virol. J. 2009, 6, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.A.; Jun, S.R.; Sims, G.E.; Kim, S.H. Whole-proteome phylogeny of large dsDNA virus families by an alignment-free method. PNAS 2009, 106, 12826–12831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, C.H. The tree of life viewed through the contents of genomes. Meth. Mol. B. 2009, 532, 141–161. [Google Scholar]
- Davison, A.J.; Benko, M.; Harrach, B. Genetic content and evolution of adenoviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 2895–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, L.A. High-frequency homologous recombination in vaccinia virus DNA. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 1788–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherardi, M.M.; Esteban, M. Recombinant poxviruses as mucosal vaccine vectors. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 2925–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.S.; Shi, S.; Zauderer, M. Construction of cDNA libraries in vaccinia virus. Meth. Mol. B. 2004, 269, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Shackelton, L.A.; Holmes, E.C. The evolution of large DNA viruses: Combining genomic information of viruses and their hosts. Trends Microbiol. 2004, 12, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, N.A. Microbial minimalism: Genome reduction in bacterial pathogens. Cell 2002, 108, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Dudley, J.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucl. Acid. Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, N.; Pachter, L. MAVID: Constrained ancestral alignment of multiple sequences. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudno, M.; Do, C.B.; Cooper, G.M.; Kim, M.F.; Davydov, E.; Green, E.D.; Sidow, A.; Batzoglou, S. LAGAN and Multi-LAGAN: Efficient tools for large-scale multiple alignment of genomic DNA. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. MODELTEST: Testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 817–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altekar, G.; Dwarkadas, S.; Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. Parallel Metropolis-coupled Markov chain Monte Carlo for Bayesian phylogenetic inference. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusfield, D. Algorithms on Strings, Trees, and Sequences: Computer Science and Computational Biology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, C. Homology in classical and molecular biology. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1988, 5, 603–625. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stein, L. Genome annotation: From sequence to biology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, M.G.; Hartzell, G.; Harris, N.L.; Ohler, U.; Abril, J.F.; Lewis, S.E. Genome annotation assessment in Drosophila melanogaster. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 483–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, W.R. Rapid and sensitive sequence comparison with FASTP and FASTA. Meth. Enzymology 1990, 183, 63–98. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, B.; Goldstein, R.A. Detecting distant homologs using phylogenetic tree-based HMMs. Proteins 2003, 52, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churbanov, A.; Winters-Hilt, S. Implementing EM and Viterbi algorithms for Hidden Markov Model in linear memory. BMC Bioinformatics 2008, 9, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lefkowitz, E.J. SS-Wrapper: A package of wrapper applications for similarity searches on Linux clusters. BMC Bioinformatics 2004, 5, 171. [Google Scholar]
- Ureta-Vidal, A.; Ettwiller, L.; Birney, E. Comparative genomics: Genome-wide analysis in metazoan eukaryotes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2003, 4, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkevich, T.G.; Koonin, E.V.; Bugert, J.J.; Darai, G.; Moss, B. The genome of molluscum contagiosum virus: Analysis and comparison with other poxviruses. Virology 1997, 233, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, C.R.; Amano, H.; Ueda, Y.; Qin, J.; Miyamura, T.; Suzuki, T.; Li, X.; Barrett, J.W.; McFadden, G. Complete genomic sequence and comparative analysis of the tumorigenic poxvirus Yaba monkey tumor virus. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 13335–13347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, A.G.; Baldi, P.; Chauvin, Y.; Brunak, S. The biology of eukaryotic promoter prediction—A review. Comput. Chem. 1999, 23, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fickett, J.W.; Tung, C.S. Assessment of protein coding measures. Nucl. Acid. Res. 1992, 20, 6441–6450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Genome | Gene Status | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intact | Truncated | Fragmented | Missing | |
| CPXV-GRI | 209 | 3 | 0 | 2 |
| CPXV-Ger | 208 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| CPXV-BR | 206 | 3 | 1 | 4 |
| HSPV | 181 | 22 | 4 | 7 |
| ECTV | 172 | 21 | 7 | 14 |
| RPXV | 179 | 13 | 4 | 18 |
| VACV-WR | 178 | 12 | 3 | 21 |
| TATV | 163 | 26 | 7 | 18 |
| CMLV | 174 | 14 | 8 | 18 |
| VACV-Cop | 172 | 15 | 4 | 23 |
| MPXV-ZAI | 176 | 7 | 14 | 17 |
| MPXV-WR | 175 | 7 | 14 | 18 |
| VARV-BRZ | 162 | 18 | 12 | 22 |
| VARV-SLN | 162 | 17 | 11 | 24 |
| VARV-KUW | 162 | 17 | 11 | 24 |
| VARV-SAF | 162 | 17 | 11 | 24 |
| VACV-MVA | 157 | 17 | 7 | 33 |
© 2010 by the authors. licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hendrickson, R.C.; Wang, C.; Hatcher, E.L.; Lefkowitz, E.J. Orthopoxvirus Genome Evolution: The Role of Gene Loss. Viruses 2010, 2, 1933-1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2091933
Hendrickson RC, Wang C, Hatcher EL, Lefkowitz EJ. Orthopoxvirus Genome Evolution: The Role of Gene Loss. Viruses. 2010; 2(9):1933-1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2091933
Chicago/Turabian StyleHendrickson, Robert Curtis, Chunlin Wang, Eneida L. Hatcher, and Elliot J. Lefkowitz. 2010. "Orthopoxvirus Genome Evolution: The Role of Gene Loss" Viruses 2, no. 9: 1933-1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2091933
APA StyleHendrickson, R. C., Wang, C., Hatcher, E. L., & Lefkowitz, E. J. (2010). Orthopoxvirus Genome Evolution: The Role of Gene Loss. Viruses, 2(9), 1933-1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2091933