The Structure of Human Prions: From Biology to Structural Models—Considerations and Pitfalls
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Human Prion Protein Gene (PRNP)
3. Evolutionary Origins of PRNP
4. Polymorphisms and Mutations in the PRNP Gene ORF
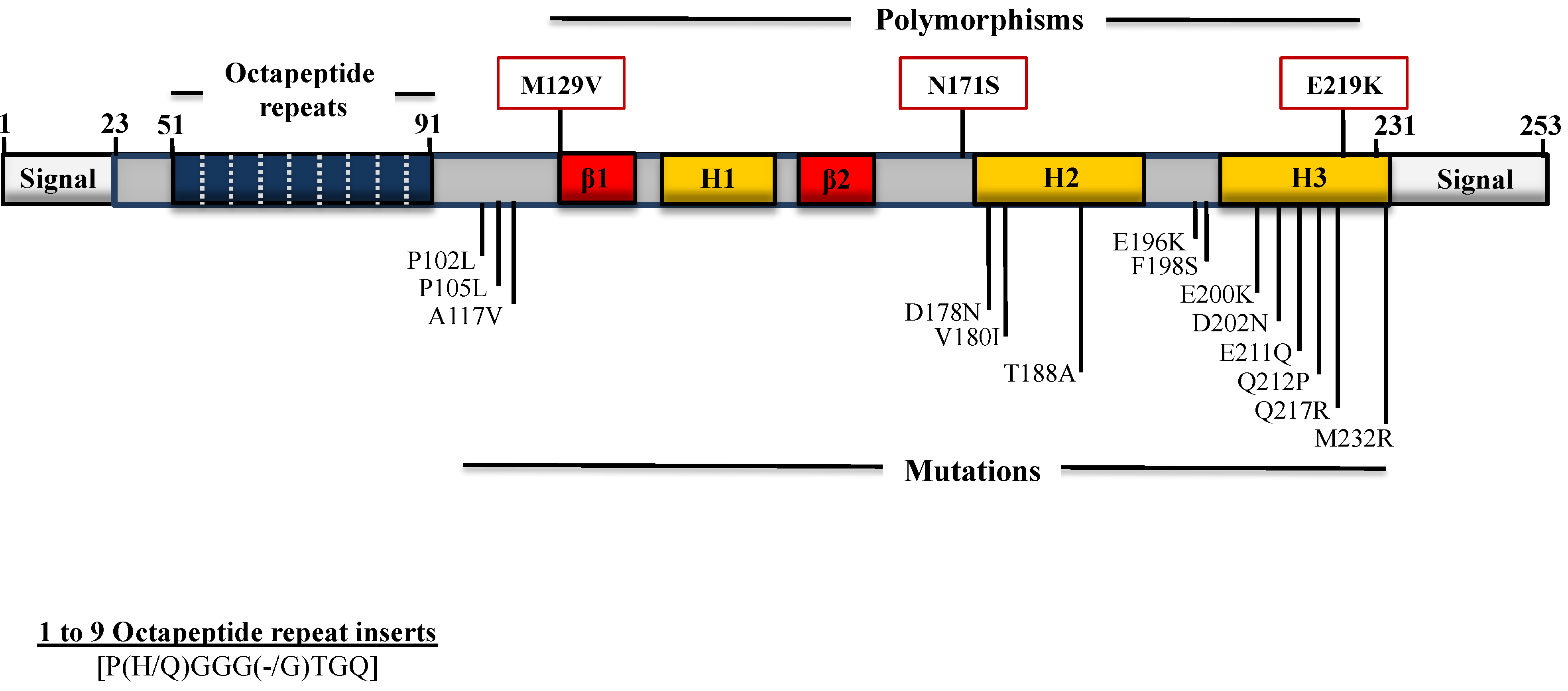
4.1. Mutations Associated with GSS
4.2. Mutations Associated with CJD
- Sporadic CJD (sCJD): the most common type of CJD, accounting for at least 85% of cases. The disease manifests even though the person has no known risk factors for the disease (e.g., no mutation in the PRNP gene);
- Familial CJD (fCJD): accounting for about 5% to 10% of cases of CJD. The individual has a family history of the disease and/or tests positive for a PRNP mutation;
- Iatrogenic CJD (iCJD): accounting for less than 1% of CJD cases. This form of CJD is transmitted by exposure to brain or tissue from an infected person, usually through a medical procedure, such as a blood transfusion or dura mater transplant.
4.3. Mutations Associated with FFI
5. Biochemistry and Structure of Prion Proteins
5.1. Structure of PrPC

5.2. Structure of PrPSc

5.3. Molecular Models for the Structures of PrPSc and PrP 27–30
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Prusiner, S.B. Shattuck lecture-neurodegenerative diseases and prions. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissmann, C. The state of the prion. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zomosa-Signoret, V.; Arnaud, J.D.; Fontes, P.; Alvarez-Martinez, M.T.; Liautard, J.P. Physiological role of the cellular prion protein. Vet. Res. 2008, 39, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajdusek, D.C.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Alpers, M.P. Experimental transmission of a kuru-like syndrome to chimpanzees. Nature 1966, 209, 794–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Asher, D.M.; Alpers, M.P.; Beck, E.; Daniel, P.M.; Matthews, W.B. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (spongiform encephalopathy): Transmission to chimpanzee. Science 1968, 161, 388–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masters, C.L.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease virus isolations from the Gerstmann-Straussler syndrome. With an analysis of the various forms of amyloid plaque deposition in the virus induced spongiform encephalopathies. Brain 1981, 104, 559–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medori, R.; Montagna, P.; Tritschler, H.J.; LeBlanc, A.; Cordelli, P.; Tinuper, P.; Lugaresi, E.; Gambetti, P. Fatal familial insomnia: A second kindred with mutation of prion protein gene at codon 178. Neurology 1992, 42, 669–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medori, R.; Tritschler, H.J.; LeBlanc, A.; Villare, F.; Manetto, V.; Chen, H.Y.; Xue, R.; Leal, S.; Montagna, P.; Cortelli, P.; et al. Fatal familial insomnia, a prion disease with a mutation at codon 178 of the prion protein gene. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 326, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, E.S.; Young, S. Chronic wasting disease of captive mule deer: A spongiform encephalopathy. J. Wildl. Dis. 1980, 16, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, E.S.; Young, S. Spongiform encephalopathy in a Rocky Mountain elk. J. Wildl. Dis. 1982, 18, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, R.; Liberski, P.P. Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE): The end of the beginning or the beginning of the end? Folia Neuropathol. 2004, 42 (Suppl. A), 55–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bradley, R.; Collee, J.G.; Liberski, P.P. Variant CJD (vCJD) and bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE): 10 and 20 years on: Part 1. Folia Neuropathol. 2006, 44, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Collee, J.G.; Bradley, R.; Liberski, P.P. Variant CJD (vCJD) and bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE): 10 and 20 years on: Part 2. Folia Neuropathol. 2006, 44, 102–110. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, G.A.H.; Scott, A.C.; Johnson, C.T.; Gunning, R.F.; Hancock, R.D.; Jeffrey, M.; Dawson, M.; Bradley, R. A novel progressive spongiform encephalopathy in cattle. Vet. Rec. 1987, 121, 419–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, A.A.; Wells, G.A.H.; Scott, A.C.; Kirkwood, J.K.; Barnett, J.E.F. Transmissible spongiform encephalopathy in greater kudu (Tragelaphus strepsiceros). Vet. Rec. 1993, 132, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletwood, A.J.; Furley, C.W. Spongiform encephalopathy in an eland. Vet. Rec. 1990, 126, 215–222. [Google Scholar]
- Willoughby, K.; Kelly, D.F.; Lyeon, D.G.; Wells, G.A.H. Spongiform encephalopathy in a captive puma (Felis concolor). Vet. Res. 1992, 131, 431–434. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, J.L.N.; Lund, L.J.; Done, S.H. The natural occurrence of scrapie in moufflon. Vet. Rec. 1991, 130, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.R.; Ruth, D.; Anderson, R.D.; Smith, W. Studies in scrapie. J. Comp. Pathol. 1950, 60, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, D.; Hartsough, G.R. A scrapie-like disease of mink. In Report of a Scrapie Seminar; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1964; Volume 27, pp. 225–227. [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt, J.M.; Pearson, G.R.; Smerdon, T.N.; Gruffydd-Jones, T.J.; Wells, G.A.; Wilesmith, J.W. Naturally occurring scrapie-like spongiform encephalopathy in five domestic cats. Vet. Rec. 1991, 129, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberski, P.P. Historical overview of prion diseases: A view from afar. Folia Neuropathol. 2012, 50, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.J.; Lebo, R.V.; Clawson, G.A.; Smuckler, E.A. Human prion protein cDNA: Molecular cloning, chromosomal mapping, and biological implications. Science 1986, 233, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretzschmar, H.A.; Stowring, L.E.; Westaway, D.; Stubblebine, W.H.; Prusiner, S.B.; Dearmond, S.J. Molecular cloning of a human prion protein cDNA. DNA 1986, 5, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusiner, S.B. Molecular biology of prion diseases. Science 1991, 14, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, F.; Poulter, M.; Shah, T.; Collinge, J.; Lofthouse, R.; Baker, H.; Ridley, R.; McVey, J.; Crow, T.J. An in-frame insertion in the prion protein gene in familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Mol. Brain Res. 1990, 7, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, T.; Sasaki, S.; Toyama, A.; Takeuchi, H. Copper reduction by the octapeptide repeat region of prion protein: pH dependence and implications in cellular copper uptake. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 8712–8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boellaard, J.W.; Brown, P.; Tateishi, J. Gerstmann–Straussler–Scheinker disease the dilemma of molecular and clinical correlations. Clin. Neuropathol. 1999, 18, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harder, A.; Jendroska, K.; Kreuz, F.; Wirth, T.; Schafranka, C.; Karnatz, N.; Théallier-Janko, A.; Dreier, J.; Lohan, K.; Emmerich, D.; et al. Novel twelve-generation kindred of fatal familial insomnia from Germany representing the entire spectrum of disease expression. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1999, 87, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monari, L.; Chen, S.G.; Brown, P.; Parchi, P.; Petersen, R.B.; Mikol, J.; Gray, F.; Cortelli, P.; Montagna, P.; Ghetti, B. Fatal familial insomnia and familial Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease: Different prion proteins determined by a DNA polymorphism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 2839–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehsani, S.; Tao, R.; Pocanschi, C.L.; Ren, H.; Harrison, P.M.; Schmitt-Ulms, G. Evidence for retrogene origins of the prion gene family. PLoS One 2011, 6, e26800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehsani, S.; Huo, H.; Salehzadeh, A.; Pocanschi, C.L.; Watts, J.C.; Wille, H.; Westaway, D.; Rogaeva, E.; St George-Hyslop, P.H.; Schmitt-Ulms, G. Family reunion—The ZIP/prion gene family. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 93, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt-Ulms, G.; Ehsani, S.; Watts, J.C.; Westaway, D.; Wille, H. Evolutionary descent of prion genes from the ZIP family of metal ion transporters. PLoS One 2009, 4, e7208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt-Ulms, G.; Legname, G.; Baldwin, M.A.; Ball, H.L.; Bradon, N.; Bosque, P.J.; Crossin, K.L.; Edelman, G.M.; DeArmond, S.J.; Cohen, F.E.; et al. Binding of neural cell adhesion molecules (N-CAMs) to the cellular prion protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 314, 1209–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieger, R.; Edenhofer, F.; Lasmezas, C.I.; Weiss, S. The human 37-kDa laminin receptor precursor interacts with the prion protein in eukaryotic cells. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, J.F.; Kurian, D.; Agarwal, S.; Toovey, L.; Hunt, L.; Kirby, L.; Pinheiro, T.J.T.; Banner, S.J.; Gill, A.C. Na+/K+-ATPase is present in scrapie-associated fibrils, modulates PrP misfolding in vitro and links PrP function and dysfunction. PLoS One 2011, 6, e26813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, B.C.; Krapfenbauer, K.; Cairns, N.; Belay, G.; Bajo, M.; Lubec, G. Overexpressed protein disulphide isomerase in brains of patients with sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 334, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collinge, J. Prion diseases of human and animals: Their causes and molecular basis. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 519–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, M.; Dryden, A.J.; Hughes, J.T.; Collinge, J. Homozygous prion protein genotype predisposes to sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Nature 1991, 352, 340–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.; Mastrianni, J.A. The prion disease. J. Geriatr. Psychiatr. Neurol. 2010, 23, 277–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doh-ura, K.; Kitamoto, T.; Sakaki, Y.; Tateishi, J. CJD discrepancy. Nature 1991, 353, 801–802. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kitamoto, T.; Tateishi, J. Human prion diseases with variant prion protein. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B 1994, 343, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Minematsu, K.; Moriyasu, H.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yutani, C.; Kitamoto, T.; Furukawa, H. A Japanese family with a variant of Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1997, 62, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hizume, M.; Kobayashi, A.; Teruya, K.; Ohashi, H.; Ironside, J.W.; Mohri, S.; Kitamoto, T. Human prion protein (PrP) 219 K is converted to PrPSc but shows heterozygous inhibition in variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 3603–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Michele, G.; Pocchiari, M.; Petraroli, R.; Manfredi, M.; Caneve, G.; Coppola, G.; Casali, C.; Saccà, F.; Piccardo, P.; Salvatore, E.; et al. Variable phenotype in a P102L Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker Italian family. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2003, 30, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, K.; Baker, H.F.; Crow, T.J.; Poulter, M.; Owen, F.; Terwilliger, J.D.; Westaway, D.; Ott, J.; Prusiner, S.B. Linkage of a prion protein missense variant to Gerstmann-Straussler syndrome. Nature 1989, 338, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamoto, T.; Ohta, M.; Doh-ura, K.; Hitoshi, S.; Terao, Y.; Tateishi, J. Novel missense variants of prion protein in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease or Gerstmann-Straussler syndrome. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 191, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doh-ura, K.; Tateishi, J.; Sasaki, H.; Kitamoto, T.; Sakaki, Y. Pro-Leu change at position 102 of prion protein is the most common but not the sole mutation related to Gerstmann-Straussler syndrome. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989, 163, 974–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, K.; Dloughy, S.R.; Farlow, M.R.; Cass, C.; da Costa, M.; Conneally, P.M.; Hodes, M.E.; Ghetti, B.; Prusiner, S.B. Mutant prion proteins in Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker disease with neurofibrillary tangles. Nat. Genet. 1992, 1, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccardo, P.; Dlouhy, S.R.; Lievens, P.M.; Young, K.; Bird, T.D.; Nochlin, D.; Dickson, D.W.; Vinters, H.V.; Zimmerman, T.R.; Mackenzie, I.R.; et al. Phenotypic variability of Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease is associated with prion protein heterogeneity. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1998, 57, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldfarb, L.G.; Brown, P.; McCombie, W.R.; Goldgaber, D.; Swergold, G.D.; Wills, P.R.; Cervenakova, L.; Baron, H.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Gajdusek, D.C. Transmissible familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease associated with five, seven, and eight extra octapeptide coding repeats in the PRNP gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 10926–10930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gool, W.A.; Hensels, G.W.; Hoogerwaard, E.M.; Wiezer, J.H.; Wesseling, P.; Bolhuis, P.A. Hypokinesia and presenile dementia in a Dutch family with a novel insertion in the prion protein gene. Brain 1995, 118, 1565–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laplanche, J.L.; Hachimi, K.H.; Durieux, I.; Thuillet, P.; Defebvre, L.; Delasnerie-Lauprêtre, N.; Peoc’h, K.; Foncin, J.F.; Destée, A. Prominent psychiatric features and early onset in an inherited prion disease with a new insertional mutation in the prion protein gene. Brain 1999, 122, 2375–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldfarb, L.G.; Haltia, M.; Brown, P.; Nieto, A.; Kovanen, J.; McCombie, W.R.; Trapp, S.; Gajdusek, D.C. New mutation in scrapie amyloid precursor gene (at codon 178) in Finnish Creutzfedt-Jakob kindred. Lancet 1991, 337, 425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.; Boyd, A.; Fletcher, A.; Byron, K.; Harper, C.; McLean, C.A.; Masters, C.L. Novel prion protein gene mutation in an octogenarian with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch. Neurol. 2000, 57, 1058–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peoc’h, K.; Manivet, P.; Beaudry, P.; Attane, F.; Besson, G.; Hannequin, D.; Delasnerie-Lauprêtre, N.; Laplanche, J.L. Identification of three novel mutations (E196K, V203I, E211Q) in the prion protein gene (PRNP) in inherited prion diseases with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease phenotype. Hum. Mutat. 2000, 15, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldgaber, D.; Goldfarb, L.G.; Brown, P.; Asher, D.M.; Brown, W.T.; Lin, S.; Teener, J.W.; Feinstone, S.M.; Rubenstein, R.; Kascsak, R.J.; et al. Mutations in familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker’s syndrome. Exp. Neurol. 1989, 106, 204–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrianni, J.A.; Lannicola, C.; Myers, R.M.; DeArmond, S.; Prusiner, S.B. Mutation of the prion protein gene at codon 208 in familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 1996, 47, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pocchiari, M.; Salvatore, M.; Cutruzzolá, F.; Genuardi, M.; Allocatelli, C.T.; Masullo, C.; Macchi, G.; Alemá, G.; Galgani, S.; Xi, Y.G.; et al. A new point mutation of the prion protein gene in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann. Neurol. 1993, 34, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laplanche, J.L.; Delasnerie-Lauprêtre, N.; Brandel, J.P.; Dussaucy, M.; Chatelain, J.; Launay, J.M. Two novel insertions in the prion protein gene in patients with late-onset dementia. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1995, 4, 1109–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldfarb, L.G.; Brown, P.; Little, B.W.; Cervenáková, L.; Kenney, K.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Gajdusek, D.C. A new (two-repeat) octapeptide coding insert mutation in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 1993, 43, 2392–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, F.; Lofthouse, R.; Crow, T.J.; Baker, H.F.; Poulter, M.; Collinge, J.; Risby, D.; Ridley, R.M.; Hsiao, K.; Prusiner, S.B. Insertion in prion protein gene in familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet 1989, 1, 51–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medori, R.; Tritschler, H.J. Prion protein gene analysis in three kindreds with Fatal Familial Insomnia (FFI): Codon 178 mutation and codon 129 polymorphism. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1993, 53, 822–827. [Google Scholar]
- Schenkein, J.; Montagna, P. Self management of fatal familial insomnia. Part 1: What is FFI? Medscape Gen. Med. 2006, 8, 65. [Google Scholar]
- Oesch, B.; Westaway, D.; Wälchi, M.; McKinley, M.; Kent, S.B.H.; Aebersold, R.; Barry, R.A.; Tempst, P.; Teplow, D.B.; Hood, L.E.; et al. A cellular gene encodes scrapie PrP 27-30 protein. Cell 1985, 40, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, R.K.; McKinley, M.P.; Bowman, K.A.; Braunfeld, M.B.; Barry, R.A.; Prusiner, S.B. Separation and properties of cellular and scrapie prion proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 2310–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, K.M.; Baldwin, M.; Nguyen, J.; Gasset, M.; Serban, A.; Groth, D.; Mehlhorn, I.; Huang, Z.; Fletterick, R.J.; Cohen, F.E.; et al. Conversion of α-helices into β-sheets features in the formation of the scrapie prion proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 10962–10966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caughey, B.W.; Dong, A.; Bhat, K.S.; Ernst, D.; Hayes, S.F.; Caughey, W.S. Secondary structure analysis of the scrapie-associated protein PrP 27-30 in water by infrared spectroscopy. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 7672–7680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riesner, D. Biochemistry and structure of PrP C and PrP Sc. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 66, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vey, M.; Pilkuhn, S.; Wille, H.; Nixon, R.; DeArmond, S.J.; Smart, E.J.; Anderson, R.G.; Taraboulos, A.; Prusiner, S.B. Subcellular colocalization of the cellular and scrapie prion proteins in caveolae-like membranous domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14945–14949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, P.J.; Mironov, A., Jr.; Peretz, D.; van Donselaar, E.; Leclerc, E.; Erpel, S.; DeArmond, S.J.; Burton, D.R.; Williamson, R.A.; Vey, M.; et al. Trafficking of prion proteins through a caveolae-mediated endosomal pathway. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 162, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riek, R.; Hornemann, S.; Wider, G.; Billeter, M.; Glockshuber, R.; Wüthrich, K. NMR structure of the mouse prion protein domain PrP(121-231). Nature 1996, 382, 180–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riek, R.; Hornemann, S.; Wider, G.; Glockshuber, R.; Wüthrich, K. NMR characterization of the full-length recombinant murine prion protein, mPrP(23-231). FEBS Lett. 1997, 413, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hornemann, S.; Schorn, C.; Wüthrich, K. NMR structure of the bovine prion protein isolated from healthy calf brains. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Gabriel, J.M.; Baldwin, M.A.; Fletterick, R.J.; Prusiner, S.B.; Cohen, F.E. Proposed three-dimensional structure for the cellular prion protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 7139–7143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahn, R.; Liu, A.; Lührs, T.; Riek, R.; von Schroetter, C.; Lopez Garcia, F.; Billeter, M.; Calzolai, L.; Wider, G.; Wüthrich, K. NMR solution structure of the human prion protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, T.L.; Liu, H.; Ulyanov, N.B.; Farr-Jones, S.; Zhang, H.; Donne, D.G.; Kaneko, K.; Groth, D.; Mehlhorn, I.; Prusiner, S.B.; Cohen, F.E. Solution structure of a 142-residue recombinant prion protein corresponding to the infectious fragment of the scrapie isoform. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 10086–10091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surewicz, W.K.; Apostol, M.I. Prion protein and its conformational conversion: A structural perspective. Top. Curr. Chem. 2011, 305, 135–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maiti, N.B.; Surewicz, W.K. The role of disulfide bridge in the folding and stability of the recombinant human prion protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 2427–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappai, R.; Collins, S.J. Structural biology of prions. In Prions: A Challenge for Science, Medicine, and the Public Health System; Rabenau, H.F., Cinatl, J., Doerr, H.W., Eds.; Contributions Microbiology Basel: Karger, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 11, pp. 14–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hornshaw, M.P.; McDermott, J.R.; Candy, J.M. Copper binding to the N-terminal tandem repeat regions of mammalian and avian prion protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 207, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stӧckel, J.; Safar, J.; Wallace, A.C.; Cohen, F.E.; Prusiner, S.B. Prion protein selectively binds copper(II) ions. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 7185–7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauly, P.C.; Harris, D.A. Copper stimulates endocytosis of the prion protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 33107–33110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spevacek, A.R.; Evans, E.G.B.; Miller, J.L.; Meyer, H.C.; Pelton, J.G. Millhauser Zinc drives a tertiary fold in the prion protein with familial disease mutation sites at the interface. Structure 2013, 21, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, N.T.; Griffiths, H.H.; Hooper, N.M. Neuronal zinc regulation and the prion protein. Prion 2013, 7, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartz, J.C.; Bessen, R.A.; Mckenzie, D.; Marsh, R.F.; Aiken, J.M. Adaptation and selection of prion protein strain conformations following interspecies transmission of transmissible mink encephalopathy. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 5542–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norstrom, E.M.; Mastrianni, J.A. The AGAAAAGA palindrome in PrP is required to generate a productive PrPSc-PrPC complex that leads to prion propagation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 27236–27243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holscher, C.; Delius, H.; Burkle, A. Overexpression of nonconvertible PrPc delta114-121 in scrapie-infected mouse neuroblastoma cells leads to trans-dominant inhibition of wild-type PrP(Sc) accumulation. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chabry, J.; Caughey, B.; Chesebro, B. Specific inhibition of in vitro formation of protease-resistant prion protein by synthetic peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 13203–13207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millhauser, G.L. The rich chemistry of the copper and zinc sites in cellular prion protein. In Prions and Diseases; Zou, W.Q., Gambetti, P., Eds.; Physiology and Pathophysiology; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Jiang, D.; McDonald, A.; Hao, Y.; Millhauser, G.L.; Zhou, F. Copper redox cycling in the prion protein depends critically on binding mode. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 12229–12237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Espinoza, R.; Soto, C. High-resolution structure of infectious prion protein: The final frontier. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasset, M.; Baldwin, M.A.; Fletterick, R.J.; Prusiner, S.B. Perturbation of the secondary structure of the scrapie prion protein under conditions that alter infectivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, J.T.; Inouye, H.; Baldwin, M.A.; Fletterick, R.J.; Cohen, F.E.; Prusiner, S.B.; Kirschner, D.A. X-ray diffraction of scrapie prion rods and PrP peptides. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 252, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wille, H.; Bian, W.; McDonald, M.; Kendall, A.; Colby, D.W.; Bloch, L.; Ollesch, J.; Borovinskiy, A.L.; Cohen, F.E.; Prusiner, S.B.; et al. Natural and synthetic prion structure from X-ray fiber diffraction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16990–16995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prusiner, S.B. Prions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1998, 95, 13363–13383. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Safar, J.; Wille, H.; Itri, V.; Groth, D.; Serban, H.; Torchia, M.; Cohen, F.E.; Prusiner, S.B. Eight prion strains have PrPSc molecules with different conformations. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Requena, J.R.; Wille, H. The structure of the infectious prion protein. Prion 2014, 8, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Prusiner, S.B.; Cohen, F.E. Scrapie prions a three-dimensional model of an infectious fragment. Fold. Des. 1996, 1, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnovas, V.; Baron, G.S.; Offerdahl, D.K.; Raymond, G.J.; Caughey, B.; Surewicz, W.K. Structural organization of brain-derived mammalian prions examined by hydrogen-deuterium exchange. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baron, G.S.; Hughson, A.G.; Raymond, G.J.; Offerdahl, D.K.; Barton, K.A.; Raymond, L.D.; Dorward, D.W.; Caughey, B. Effect of glycans and the glycophosphatidylinositol anchor on strain dependent conformations of scrapie prion protein: Improved purifications and infrared spectra. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 4479–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Fernández, E.; Alonso, J.; Pastrana, M.A.; Ramos, A.; Stitz, L.; Vidal, E.; Dynin, I.; Petsch, B.; Silva, C.J.; Requena, J.R. Structural organization of mammalian prions as probed by limited proteolysis. PLoS One 2012, 7, e50111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downing, D.T.; Lazo, N.D. Molecular modelling indicates that the pathological conformations of prion proteins might be beta-helical. Biochem. J. 1999, 343, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Govaerts, C.; Wille, H.; Prusiner, S.B.; Cohen, F.E. Evidence for assembly of prions with left-handed β-helices into trimers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8342–8347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wille, H.; Michelitsch, M.D.; Guenebaut, V.; Supattapone, S.; Serban, A.; Cohen, F.E.; Agard, D.A.; Prusiner, S.B. Structural studies of the scrapie prion protein by electron crystallography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3563–3568. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Langedijk, J.P.; Fuentes, G.; Boshuizen, R.; Bonvin, A.M. Two-rung model of a left-handed beta-helix for prions explains species barrier and strain variation in transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 360, 907–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marco, M.L.; Daggett, V. From conversion to aggregation: Protofibril formation of the prion protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2293–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tattum, M.H.; Cohen-Krausz, S.; Thumanu, K.; Wharton, C.W.; Khalili-Shirazi, A.; Jackson, G.S.; Orlova, E.V.; Collinge, J.; Clarke, A.R.; Thumanu, K.; et al. Elongated oligomers assemble into mammalian PrP amyloid fibrils. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 357, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirai, T.; Saito, M.; Kobayashi, A.; Asano, M.; Hizume, M.; Ikeda, S.; Teruya, K.; Morita, M.; Kitamoto, T. Evaluating Prion Models Based on Comprehensive Mutation Data of Mouse PrP. Structure 2014, 22, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunes, K.C.; Clark, S.C.; Cox, D.L.; Singh, R.R. Left handed beta helix models for mammalian prion fibrils. Prion 2008, 2, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobb, N.J.; Sönnichsen, F.D.; McHaourab, H.; Surewicz, W.K. Molecular architecture of human prion protein amyloid: A parallel, in-register beta-structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18946–18951. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kraus, A.; Groveman, B.R.; Caughey, B. Prions and the potential transmissibility of protein misfolding diseases. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 67, 543–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groveman, B.R.; Dolan, M.A.; Taubner, L.M.; Kraus, A.; Wickner, R.B.; Caughey, B. Parallel in-register intermolecular beta sheet architectures for prion seeded PrP amyloids. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 24129–24142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, G.G.; Puopolo, M.; Ladogana, A.; Pocchiari, M.; Budka, H.; van Duijn, C.; Collins, S.J.; Boyd, A.; Giulivi, A.; Coulthart, M.; et al. Genetic prion disease: The EUROCJD experience. Hum. Genet. 2005, 118, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, G.G.; Trabattoni, G.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Ironside, J.W.; Knight, R.S.; Budka, H. Mutations of the prion protein gene phenotypic spectrum. J. Neurol. 2002, 249, 1567–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladogana, A.; Puopolo, M.; Poleggi, A.; Almonti, S.; Mellina, V.; Equestre, M.; Pocchiari, M. High incidence of genetic human transmissible spongiform encephalopathies in Italy. Neurology 2005, 64, 1592–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Acevedo-Morantes, C.Y.; Wille, H. The Structure of Human Prions: From Biology to Structural Models—Considerations and Pitfalls. Viruses 2014, 6, 3875-3892. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6103875
Acevedo-Morantes CY, Wille H. The Structure of Human Prions: From Biology to Structural Models—Considerations and Pitfalls. Viruses. 2014; 6(10):3875-3892. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6103875
Chicago/Turabian StyleAcevedo-Morantes, Claudia Y., and Holger Wille. 2014. "The Structure of Human Prions: From Biology to Structural Models—Considerations and Pitfalls" Viruses 6, no. 10: 3875-3892. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6103875
APA StyleAcevedo-Morantes, C. Y., & Wille, H. (2014). The Structure of Human Prions: From Biology to Structural Models—Considerations and Pitfalls. Viruses, 6(10), 3875-3892. https://doi.org/10.3390/v6103875





