Relevance of Viroporin Ion Channel Activity on Viral Replication and Pathogenesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Ion Channels Formed by Viroporins


3. Ion Channel Activity and Virus-Host Interaction
3.1. Virus Production
3.1.1. Viral Entry

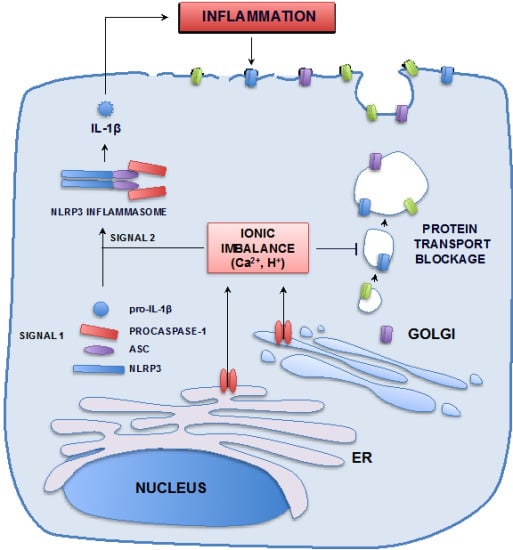
3.1.2. Remodeling of Cell Organelles
3.1.3. Protection of the Viral Progeny
3.1.4. Release of Newly Formed Virions
3.2. Pathogenesis

4. Summary and Future Prospects
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubyak, G.R. Ion homeostasis, channels, and transporters: An update on cellular mechanisms. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2004, 28, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieva, J.L.; Madan, V.; Carrasco, L. Viroporins: Structure and biological functions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, A.S.; Visch, H.J.; de Mattia, F.; van Dommelen, M.M.; Swarts, H.G.; Luyten, T.; Callewaert, G.; Melchers, W.J.; Willems, P.H.; van Kuppeveld, F.J. The coxsackievirus 2B protein increases efflux of ions from the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi, thereby inhibiting protein trafficking through the Golgi. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 14144–14150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewart, G.D.; Sutherland, T.; Gage, P.W.; Cox, G.B. The Vpu protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 forms cation-selective ion channels. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 7108–7115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henkel, M.; Mitzner, D.; Henklein, P.; Meyer-Almes, F.J.; Moroni, A.; Difrancesco, M.L.; Henkes, L.M.; Kreim, M.; Kast, S.M.; Schubert, U.; et al. The proapoptotic influenza A virus protein PB1-F2 forms a nonselective ion channel. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlovic, D.; Neville, D.C.; Argaud, O.; Blumberg, B.; Dwek, R.A.; Fischer, W.B.; Zitzmann, N. The hepatitis C virus p7 protein forms an ion channel that is inhibited by long-alkyl-chain iminosugar derivatives. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6104–6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, L.H.; Holsinger, L.J.; Lamb, R.A. Influenza virus M2 protein has ion channel activity. Cell 1992, 69, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, L.; McKinlay, C.; Gage, P. SARS coronavirus E protein forms cation-selective ion channels. Virology 2004, 330, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surya, W.; Li, Y.; Verdia-Baguena, C.; Aguilella, V.M.; Torres, J. MERS coronavirus envelope protein has a single transmembrane domain that forms pentameric ion channels. Virus Res. 2015, 201, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdia-Baguena, C.; Nieto-Torres, J.L.; Alcaraz, A.; Dediego, M.L.; Torres, J.; Aguilella, V.M.; Enjuanes, L. Coronavirus E protein forms ion channels with functionally and structurally-involved membrane lipids. Virology 2012, 432, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdia-Baguena, C.; Nieto-Torres, J.L.; Alcaraz, A.; Dediego, M.L.; Enjuanes, L.; Aguilella, V.M. Analysis of SARS-CoV E protein ion channel activity by tuning the protein and lipid charge. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1828, 2026–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, A.L.; Griffin, S.; Rowlands, D.; Harris, M.; Yi, M.; Lemon, S.M.; Weinman, S.A. Intracellular proton conductance of the hepatitis C virus p7 protein and its contribution to infectious virus production. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmann, E.; Pietschmann, T. Hepatitis C virus p7-a viroporin crucial for virus assembly and an emerging target for antiviral therapy. Viruses 2010, 2, 2078–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madan, V.; Castello, A.; Carrasco, L. Viroporins from RNA viruses induce caspase-dependent apoptosis. Cell. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmick, R.; Halder, U.C.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Chanda, S.; Nandi, S.; Bagchi, P.; Nayak, M.K.; Chakrabarti, O.; Kobayashi, N.; Chawla-Sarkar, M. Rotaviral enterotoxin nonstructural protein 4 targets mitochondria for activation of apoptosis during infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 35004–35020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichinohe, T.; Pang, I.K.; Iwasaki, A. Influenza virus activates inflammasomes via its intracellular M2 ion channel. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, M.; Yanagi, Y.; Ichinohe, T. Encephalomyocarditis virus viroporin 2B activates NLRP3 inflammasome. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantafilou, K.; Kar, S.; Vakakis, E.; Kotecha, S.; Triantafilou, M. Human respiratory syncytial virus viroporin SH: A viral recognition pathway used by the host to signal inflammasome activation. Thorax 2013, 68, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantafilou, K.; Kar, S.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.; Triantafilou, M. Rhinovirus-induced calcium flux triggers NLRP3 and NLRC5 activation in bronchial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAuley, J.L.; Tate, M.D.; MacKenzie-Kludas, C.J.; Pinar, A.; Zeng, W.; Stutz, A.; Latz, E.; Brown, L.E.; Mansell, A. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by IAV virulence protein PB1-F2 contributes to severe pathophysiology and disease. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Hou, Q.; Zhong, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Li, W.; Wen, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Zhong, F. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus activates inflammasomes of porcine alveolar macrophages via its small envelope protein E. Virology 2013, 442, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto-Torres, J.L.; Dediego, M.L.; Verdia-Baguena, C.; Jimenez-Guardeño, J.M.; Regla-Nava, J.A.; Fernandez-Delgado, R.; Castaño-Rodriguez, C.; Alcaraz, A.; Torres, J.; Aguilella, V.M.; et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus envelope protein ion channel activity promotes virus fitness and pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantafilou, K.; Triantafilou, M. Ion flux in the lung: Virus-induced inflammasome activation. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Lu, W.; Chen, J.; Xie, S.; Shi, H.; Hsu, H.; Yu, W.; Xu, K.; Bian, C.; Fischer, W.B.; et al. PEDV ORF3 encodes an ion channel protein and regulates virus production. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, K.; Lv, W.; Yu, W.; Xie, S.; Xu, K.; Schwarz, W.; Xiong, S.; Sun, B. The ORF4a protein of human coronavirus 229E functions as a viroporin that regulates viral production. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Zheng, B.J.; Xu, K.; Schwarz, W.; Du, L.; Wong, C.K.; Chen, J.; Duan, S.; Deubel, V.; Sun, B. Severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus 3a protein forms an ion channel and modulates virus release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12540–12545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, R.; Carnevale, V.; Fiorin, G.; Levine, B.G.; Polishchuk, A.L.; Balannik, V.; Samish, I.; Lamb, R.A.; Pinto, L.H.; DeGrado, W.F.; et al. Structure and mechanism of proton transport through the transmembrane tetrameric M2 protein bundle of the influenza A virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15075–15080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agirre, A.; Barco, A.; Carrasco, L.; Nieva, J.L. Viroporin-mediated membrane permeabilization. Pore formation by nonstructural poliovirus 2B protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 40434–40441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plugge, B.; Gazzarrini, S.; Nelson, M.; Cerana, R.; Van Etten, J.L.; Derst, C.; DiFrancesco, D.; Moroni, A.; Thiel, G. A potassium channel protein encoded by Chlorella virus PBCV-1. Science 2000, 287, 1641–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, J.W.; Yang, M.; Gu, L.Q. In vitro synthesis, tetramerization and single channel characterization of virus-encoded potassium channel Kcv. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthasarathy, K.; Ng, L.; Lin, X.; Liu, D.X.; Pervushin, K.; Gong, X.; Torres, J. Structural flexibility of the pentameric SARS coronavirus envelope protein ion channel. Biophys. J. 2008, 95, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pervushin, K.; Tan, E.; Parthasarathy, K.; Lin, X.; Jiang, F.L.; Yu, D.; Vararattanavech, A.; Soong, T.W.; Liu, D.X.; Torres, J. Structure and inhibition of the SARS coronavirus envelope protein ion channel. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Mrse, A.A.; Nevzorov, A.A.; Mesleh, M.F.; Oblatt-Montal, M.; Montal, M.; Opella, S.J. Three-dimensional structure of the channel-forming trans-membrane domain of virus protein “u” (Vpu) from HIV-1. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 333, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, S.W.; Ng, L.; Lin, X.; Gong, X.; Torres, J. Structure and ion channel activity of the human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) small hydrophobic protein transmembrane domain. Protein Sci. 2008, 17, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luik, P.; Chew, C.; Aittoniemi, J.; Chang, J.; Wentworth, P., Jr.; Dwek, R.A.; Biggin, P.C.; Venien-Bryan, C.; Zitzmann, N. The 3-dimensional structure of a hepatitis C virus p7 ion channel by electron microscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12712–12716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetherill, L.F.; Holmes, K.K.; Verow, M.; Muller, M.; Howell, G.; Harris, M.; Fishwick, C.; Stonehouse, N.; Foster, R.; Blair, G.E.; et al. High-risk human papillomavirus E5 oncoprotein displays channel-forming activity sensitive to small-molecule inhibitors. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5341–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosteson, M.T.; Pinto, L.H.; Holsinger, L.J.; Lamb, R.A. Reconstitution of the influenza virus M2 ion channel in lipid bilayers. J. Membr. Biol. 1994, 142, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marassi, F.M.; Ma, C.; Gratkowski, H.; Straus, S.K.; Strebel, K.; Oblatt-Montal, M.; Montal, M.; Opella, S.J. Correlation of the structural and functional domains in the membrane protein vpu from HIV-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 1999, 96, 14336–14341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Lamb, R.A.; Pinto, L.H. Direct measurement of the influenza a virus M2 protein ion channel activity in mammalian cells. Virology 1994, 205, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayvergiya, V.; Wilson, R.; Chorak, A.; Gao, P.F.; Cross, T.A.; Busath, D.D. Proton conductance of influenza virus M2 protein in planar lipid bilayers. Biophys. J. 2004, 87, 1697–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.I.; Schroeder, C. Definitive assignment of proton selectivity and attoampere unitary current to the M2 ion channel protein of influenza A virus. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 3647–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premkumar, A.; Wilson, L.; Ewart, G.D.; Gage, P.W. Cation-selective ion channels formed by p7 of hepatitis C virus are blocked by hexamethylene amiloride. FEBS Lett. 2004, 557, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; To, J.; Verdia-Baguena, C.; Dossena, S.; Surya, W.; Huang, M.; Paulmichl, M.; Liu, D.X.; Aguilella, V.M.; Torres, J. Inhibition of the human respiratory syncytial virus small hydrophobic protein and structural variations in a bicelle environment. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11899–11914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malev, V.V.; Schagina, L.V.; Gurnev, P.A.; Takemoto, J.Y.; Nestorovich, E.M.; Bezrukov, S.M. Syringomycin e channel: A lipidic pore stabilized by lipopeptide? Biophys. J. 2002, 82, 1985–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobko, A.A.; Kotova, E.A.; Antonenko, Y.N.; Zakharov, S.D.; Cramer, W.A. Effect of lipids with different spontaneous curvature on the channel activity of colicin E1: Evidence in favor of a toroidal pore. FEBS Lett. 2004, 576, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Lamb, R.A.; Pinto, L.H. Activation of the M2 ion channel of influenza virus: A role for the transmembrane domain histidine residue. Biophys. J. 1995, 69, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, D.J.; Schlegel, R. The E5 oncoprotein of bovine papillomavirus binds to a 16 kDa cellular protein. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andresson, T.; Sparkowski, J.; Goldstein, D.J.; Schlegel, R. Vacuolar H(+)-ATPase mutants transform cells and define a binding site for the papillomavirus E5 oncoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 6830–6837. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nieto-Torres, J.L.; DeDiego, M.L.; Alvarez, E.; Jimenez-Guardeño, J.M.; Regla-Nava, J.A.; Llorente, M.; Kremer, L.; Shuo, S.; Enjuanes, L. Subcellular location and topology of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus envelope protein. Virology 2011, 415, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, S.; Li, Y.; Yan, J.; Gao, G.F. Na(+)/K (+)-ATPase beta1 subunit interacts with M2 proteins of influenza A and B viruses and affects the virus replication. Sci. China Life Sci. 2010, 53, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geering, K. Function of FXYD proteins, regulators of Na, K-ATPase. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2005, 37, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaves, J.P.; Trieber, C.A.; Ceholski, D.K.; Stokes, D.L.; Young, H.S. Phosphorylation and mutation of phospholamban alter physical interactions with the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 405, 707–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minor, N.T.; Sha, Q.; Nichols, C.G.; Mercer, R.W. The gamma subunit of the Na, K-ATPase induces cation channel activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6521–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, K.; Seharaseyon, J.; Dong, P.; Bour, S.; Marban, E. Mutual functional destruction of HIV-1 Vpu and host Task-1 channel. Mol. Cell 2004, 14, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazrak, A.; Iles, K.E.; Liu, G.; Noah, D.L.; Noah, J.W.; Matalon, S. Influenza virus M2 protein inhibits epithelial sodium channels by increasing reactive oxygen species. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 3829–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.L.; Song, W.; Gao, Z.; Su, X.F.; Nie, H.G.; Jiang, Y.; Peng, J.B.; He, Y.X.; Liao, Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; et al. SARS-CoV proteins decrease levels and activity of human ENaC via activation of distinct PKC isoforms. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2009, 296, L372–L383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmann, E.; Penin, F.; Kallis, S.; Patel, A.H.; Bartenschlager, R.; Pietschmann, T. Hepatitis C virus p7 protein is crucial for assembly and release of infectious virions. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, T.K.; Guan, Y.; Ng, S.S.; Chen, H.; Wong, C.H.; Peiris, J.S.; Poon, L.L. Generation of recombinant influenza A virus without M2 ion-channel protein by introduction of a point mutation at the 5′ end of the viral intron. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strebel, K.; Klimkait, T.; Martin, M.A. A novel gene of HIV-1, Vpu, and its 16-kilodalton product. Science 1988, 241, 1221–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortego, J.; Escors, D.; Laude, H.; Enjuanes, L. Generation of a replication-competent, propagation-deficient virus vector based on the transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus genome. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 11518–11529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almazan, F.; DeDiego, M.L.; Sola, I.; Zuñiga, S.; Nieto-Torres, J.L.; Marquez-Jurado, S.; Andres, G.; Enjuanes, L. Engineering a replication-competent, propagation-defective Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus as a vaccine candidate. mBio 2013, 4, e00650-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeDiego, M.L.; Alvarez, E.; Almazan, F.; Rejas, M.T.; Lamirande, E.; Roberts, A.; Shieh, W.J.; Zaki, S.R.; Subbarao, K.; Enjuanes, L. A severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus that lacks the E gene is attenuated in vitro and in vivo. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 1701–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, L.; Masters, P.S. The small envelope protein E is not essential for murine coronavirus replication. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 4597–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akerstrom, S.; Mirazimi, A.; Tan, Y.J. Inhibition of SARS-CoV replication cycle by small interference rnas silencing specific SARS proteins, 7a/7b, 3a/3b and S. Antivir. Res. 2007, 73, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukreyev, A.; Whitehead, S.S.; Murphy, B.R.; Collins, P.L. Recombinant respiratory syncytial virus from which the entire SH gene has been deleted grows efficiently in cell culture and exhibits site-specific attenuation in the respiratory tract of the mouse. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 8973–8982. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, S.S.; Bukreyev, A.; Teng, M.N.; Firestone, C.Y.; St Claire, M.; Elkins, W.R.; Collins, P.L.; Murphy, B.R. Recombinant respiratory syncytial virus bearing a deletion of either the NS2 or SH gene is attenuated in chimpanzees. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 3438–3442. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Corse, E.; Machamer, C.E. The cytoplasmic tails of infectious bronchitis virus E and M proteins mediate their interaction. Virology 2003, 312, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Guardeño, J.M.; Nieto-Torres, J.L.; DeDiego, M.L.; Regla-Nava, J.A.; Fernandez-Delgado, R.; Castaño-Rodriguez, C.; Enjuanes, L. The PDZ-binding motif of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus envelope protein is a determinant of viral pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.J.; Leser, G.P.; Jackson, D.; Lamb, R.A. The influenza virus M2 protein cytoplasmic tail interacts with the M1 protein and influences virus assembly at the site of virus budding. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 10059–10070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossman, J.S.; Jing, X.; Leser, G.P.; Lamb, R.A. Influenza virus M2 protein mediates ESCRT-independent membrane scission. Cell 2010, 142, 902–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neil, S.J.; Zang, T.; Bieniasz, P.D. Tetherin inhibits retrovirus release and is antagonized by HIV-1 Vpu. Nature 2008, 451, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Damme, N.; Goff, D.; Katsura, C.; Jorgenson, R.L.; Mitchell, R.; Johnson, M.C.; Stephens, E.B.; Guatelli, J. The interferon-induced protein BST-2 restricts HIV-1 release and is downregulated from the cell surface by the viral Vpu protein. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolduan, S.; Votteler, J.; Lodermeyer, V.; Greiner, T.; Koppensteiner, H.; Schindler, M.; Thiel, G.; Schubert, U. Ion channel activity of HIV-1 Vpu is dispensable for counteraction of CD317. Virology 2011, 416, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, M.; Pekosz, A.; Shuck, K.; Pinto, L.H.; Lamb, R.A. Influenza A virus M2 ion channel activity is essential for efficient replication in tissue culture. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Watanabe, S.; Ito, H.; Kida, H.; Kawaoka, Y. Influenza A virus can undergo multiple cycles of replication without M2 ion channel activity. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 5656–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, U.; Ferrer-Montiel, A.V.; Oblatt-Montal, M.; Henklein, P.; Strebel, K.; Montal, M. Identification of an ion channel activity of the Vpu transmembrane domain and its involvement in the regulation of virus release from HIV-1-infected cells. FEBS Lett. 1996, 398, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grambas, S.; Bennett, M.S.; Hay, A.J. Influence of amantadine resistance mutations on the pH regulatory function of the M2 protein of influenza A viruses. Virology 1992, 191, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, L.; Gage, P.; Ewart, G. Hexamethylene amiloride blocks E protein ion channels and inhibits coronavirus replication. Virology 2006, 353, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zebedee, S.L.; Lamb, R.A. Influenza A virus M2 protein: Monoclonal antibody restriction of virus growth and detection of M2 in virions. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 2762–2772. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maeda, J.; Repass, J.F.; Maeda, A.; Makino, S. Membrane topology of coronavirus E protein. Virology 2001, 281, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raamsman, M.J.B.; Locker, J.K.; de Hooge, A.; de Vries, A.A.F.; Griffiths, G.; Vennema, H.; Rottier, P.J.M. Characterization of the coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus strain A59 small membrane protein E. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 2333–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wharton, S.A.; Belshe, R.B.; Skehel, J.J.; Hay, A.J. Role of virion M2 protein in influenza virus uncoating: Specific reduction in the rate of membrane fusion between virus and liposomes by amantadine. J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullough, P.A.; Hughson, F.M.; Skehel, J.J.; Wiley, D.C. Structure of influenza haemagglutinin at the pH of membrane fusion. Nature 1994, 371, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stauffer, S.; Feng, Y.; Nebioglu, F.; Heilig, R.; Picotti, P.; Helenius, A. Stepwise priming by acidic pH and a high K+ concentration is required for efficient uncoating of influenza A virus cores after penetration. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 13029–13046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, N.; Tanaka, S.; Teko, Y.; Mitsui, K.; Kanazawa, H. Four Na+/H+ exchanger isoforms are distributed to Golgi and post-Golgi compartments and are involved in organelle pH regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 1561–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaguchi, T.; Leser, G.P.; Lamb, R.A. The ion channel activity of the influenza virus M2 protein affects transport through the Golgi apparatus. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 133, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruch, T.R.; Machamer, C.E. A single polar residue and distinct membrane topologies impact the function of the infectious bronchitis coronavirus E protein. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, A.S.; de Mattia, F.; van Dommelen, M.M.; Lanke, K.; Melchers, W.J.; Willems, P.H.; van Kuppeveld, F.J. Functional analysis of picornavirus 2B proteins: Effects on calcium homeostasis and intracellular protein trafficking. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3782–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freundt, E.C.; Yu, L.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Welsh, S.; Cheng, A.; Yount, B.; Liu, W.; Frieman, M.B.; Buchholz, U.J.; Screaton, G.R.; et al. The open reading frame 3a protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus promotes membrane rearrangement and cell death. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 1097–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, S.E.; Hyser, J.M.; Utama, B.; Estes, M.K. Autophagy hijacked through viroporin-activated calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase kinase-beta signaling is required for rotavirus replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E3405–E3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.G.; Orci, L. A view of acidic intracellular compartments. J. Cell Biol. 1988, 106, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, K.; Lamb, R.A. Influenza virus M2 protein ion channel activity stabilizes the native form of fowl plague virus hemagglutinin during intracellular transport. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, S.; Watanabe, T.; Kawaoka, Y. Influenza A virus lacking M2 protein as a live attenuated vaccine. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 5947–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladue, D.P.; Holinka, L.G.; Largo, E.; Fernandez Sainz, I.; Carrillo, C.; O’Donnell, V.; Baker-Branstetter, R.; Lu, Z.; Ambroggio, X.; Risatti, G.R.; et al. Classical swine fever virus p7 protein is a viroporin involved in virulence in swine. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6778–6791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeDiego, M.L.; Nieto-Torres, J.L.; Jimenez-Guardeño, J.M.; Regla-Nava, J.A.; Alvarez, E.; Oliveros, J.C.; Zhao, J.; Fett, C.; Perlman, S.; Enjuanes, L. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus envelope protein regulates cell stress response and apoptosis. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeDiego, M.L.; Nieto-Torres, J.L.; Regla-Nava, J.A.; Jimenez-Guardeño, J.M.; Fernandez-Delgado, R.; Fett, C.; Castaño-Rodriguez, C.; Perlman, S.; Enjuanes, L. Inhibition of NF-kappaB mediated inflammation in severe acute respiratory syndome coronavirus-infected mice increases survival. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regla-Nava, J.A.; Nieto-Torres, J.L.; Jimenez-Guardeño, J.M.; Fernandez-Delgado, R.; Fett, C.; Castaño-Rodriguez, C.; Perlman, S.; Enjuanes, L.; DeDiego, M.L. SARS coronaviruses with mutations in E protein are attenuated and promising vaccine candidates. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3870–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obitsu, S.; Ahmed, N.; Nishitsuji, H.; Hasegawa, A.; Nakahama, K.; Morita, I.; Nishigaki, K.; Hayashi, T.; Masuda, T.; Kannagi, M. Potential enhancement of osteoclastogenesis by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 3a/X1 protein. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanzawa, N.; Nishigaki, K.; Hayashi, T.; Ishii, Y.; Furukawa, S.; Niiro, A.; Yasui, F.; Kohara, M.; Morita, K.; Matsushima, K.; et al. Augmentation of chemokine production by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 3a/X1 and 7a/X4 proteins through NF-kappaB activation. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 6807–6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, K.; Huang, C.; Makino, S. SARS coronavirus accessory proteins. Virus Res. 2008, 133, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.L.; Chen, Y.; Chan, C.M.; Chan, C.S.; Chan, P.K.; Chui, Y.L.; Fung, K.P.; Waye, M.M.; Tsui, S.K.; Chan, H.Y. In vivo functional characterization of the SARS-coronavirus 3a protein in drosophila. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 337, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornell, C.T.; Kiosses, W.B.; Harkins, S.; Whitton, J.L. Coxsackievirus B3 proteins directionally complement each other to downregulate surface major histocompatibility complex class I. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 6785–6797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthay, M.A.; Zemans, R.L. The acute respiratory distress syndrome: Pathogenesis and treatment. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2011, 6, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugin, J.; Ricou, B.; Steinberg, K.P.; Suter, P.M.; Martin, T.R. Proinflammatory activity in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids from patients with ards, a prominent role for interleukin-1. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 153, 1850–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grommes, J.; Soehnlein, O. Contribution of neutrophils to acute lung injury. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, G.; Kutuzov, M.A.; Ridge, K.M. The inflammasome in lung diseases. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2012, 303, L627–L633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strowig, T.; Henao-Mejia, J.; Elinav, E.; Flavell, R. Inflammasomes in health and disease. Nature 2012, 481, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, T.; Ockinger, J.; Yu, J.; Byles, V.; McColl, A.; Hofer, A.M.; Horng, T. Critical role for calcium mobilization in activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11282–11287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Planillo, R.; Kuffa, P.; Martinez-Colon, G.; Smith, B.L.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Nunez, G. K(+) efflux is the common trigger of NLRP3 inflammasome activation by bacterial toxins and particulate matter. Immunity 2013, 38, 1142–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, E.I.; Sutterwala, F.S. Initiation and perpetuation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and assembly. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 265, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Ray, R.; Ray, R.B. Hepatitis C virus induces interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta)/IL-18 in circulatory and resident liver macrophages. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 12284–12290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, S.D.; Beales, L.P.; Clarke, D.S.; Worsfold, O.; Evans, S.D.; Jaeger, J.; Harris, M.P.; Rowlands, D.J. The p7 protein of hepatitis C virus forms an ion channel that is blocked by the antiviral drug, amantadine. FEBS Lett. 2003, 535, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxford, J.S. Antivirals for the treatment and prevention of epidemic and pandemic influenza. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2007, 1, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewart, G.D.; Mills, K.; Cox, G.B.; Gage, P.W. Amiloride derivatives block ion channel activity and enhancement of virus-like particle budding caused by HIV-1 protein Vpu. Eur. Biophys. J. 2002, 31, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cady, S.D.; Schmidt-Rohr, K.; Wang, J.; Soto, C.S.; Degrado, W.F.; Hong, M. Structure of the amantadine binding site of influenza M2 proton channels in lipid bilayers. Nature 2010, 463, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govorkova, E.A.; Webster, R.G. Combination chemotherapy for influenza. Viruses 2010, 2, 1510–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, S.; Stgelais, C.; Owsianka, A.M.; Patel, A.H.; Rowlands, D.; Harris, M. Genotype-dependent sensitivity of hepatitis C virus to inhibitors of the p7 ion channel. Hepatology 2008, 48, 1779–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luscombe, C.A.; Huang, Z.; Murray, M.G.; Miller, M.; Wilkinson, J.; Ewart, G.D. A novel hepatitis C virus p7 ion channel inhibitor, BIT225, inhibits bovine viral diarrhea virus in vitro and shows synergism with recombinant interferon-alpha-2b and nucleoside analogues. Antivir. Res. 2010, 86, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, R.C.; Robertson, A.A.; Chae, J.J.; Higgins, S.C.; Munoz-Planillo, R.; Inserra, M.C.; Vetter, I.; Dungan, L.S.; Monks, B.G.; Stutz, A.; et al. A small-molecule inhibitor of the NLRP3 inflammasome for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nieto-Torres, J.L.; Verdiá-Báguena, C.; Castaño-Rodriguez, C.; Aguilella, V.M.; Enjuanes, L. Relevance of Viroporin Ion Channel Activity on Viral Replication and Pathogenesis. Viruses 2015, 7, 3552-3573. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7072786
Nieto-Torres JL, Verdiá-Báguena C, Castaño-Rodriguez C, Aguilella VM, Enjuanes L. Relevance of Viroporin Ion Channel Activity on Viral Replication and Pathogenesis. Viruses. 2015; 7(7):3552-3573. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7072786
Chicago/Turabian StyleNieto-Torres, Jose L., Carmina Verdiá-Báguena, Carlos Castaño-Rodriguez, Vicente M. Aguilella, and Luis Enjuanes. 2015. "Relevance of Viroporin Ion Channel Activity on Viral Replication and Pathogenesis" Viruses 7, no. 7: 3552-3573. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7072786
APA StyleNieto-Torres, J. L., Verdiá-Báguena, C., Castaño-Rodriguez, C., Aguilella, V. M., & Enjuanes, L. (2015). Relevance of Viroporin Ion Channel Activity on Viral Replication and Pathogenesis. Viruses, 7(7), 3552-3573. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7072786