Genetic Diversity and Selective Pressure in Hepatitis C Virus Genotypes 1–6: Significance for Direct-Acting Antiviral Treatment and Drug Resistance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
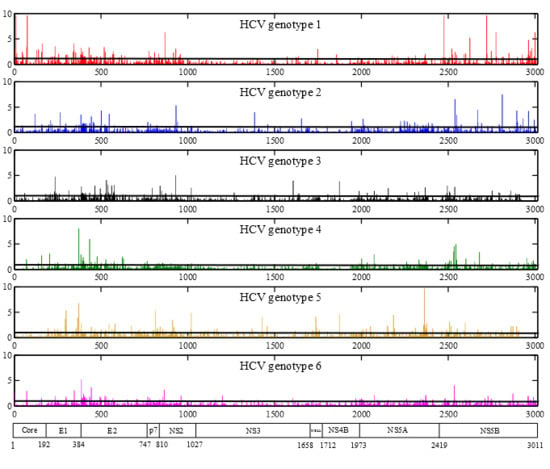
2.1. HCV Genome-Wide Sequence Diversity


2.2. Frequency of Consensus Nucleotides and Amino Acids

| Proportion of Total Positions | Core | E1 | E2 | p7 | NS2 | NS3 | NS4A | NS4B | NS5A | NS5B | Full-Genome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pan-genotypic consensus positions | 80.6 | 38.5 | 60.3 | 25.4 | 39.6 | 70.4 | 53.7 | 55.6 | 46.4 | 55.3 | 56.5 |
| Pan-genotypic conserved (95% ≤ x < 99%) | 33.0 | 14.1 | 20.7 | 4.8 | 15.2 | 31.4 | 20.4 | 27.2 | 20.4 | 24.8 | 23.9 |
| Pan-genotypic highly conserved (x ≥ 99%) | 31.4 | 12.5 | 15.2 | 6.3 | 11.1 | 22.0 | 14.8 | 12.3 | 7.4 | 12.1 | 15.0 |
2.3. Positions under Positive Selective Pressure
2.4. Large-Scale Analysis of Amino Acid Variability at Positions Important for DAA Therapy
| NS3 | 36 | 41 | 42 | 43 | 54 | 55 | 56 | 57 | 80 | 81 | 107 | 117 | 122 | 132 | 136 | 137 | 138 | 139 | 155 | 156 | 157 | 158 | 159 | 168 | 170 | 174 | 175 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H77 | V | Q | T | F | T | V | Y | H | Q | D | V | R | S | I | K | G | S | S | R | A | A | V | C | D | I | S | L |
| HCV1 | V97.9 | Q98.7 | T60.7 | F99.2 | T97.3 | V97.6 | Y92.4 | H99.3 | Q72.1 | D99.2 | V99.3 | R97.5 | S88.5 | I70.2 | K99.1 | G99.3 | S100 | S100 | R98.7 | A100 | A99.3 | V99.3 | C99.3 | D98.7 | I72.3 | S59.8 | L61 |
| L1.0 | T0.7 | S38.3 | L0.7 | S1.9 | F6.8 | L0.7 | T0.7 | C1.6 | G7.6 | V28.8 | G0.7 | S0.7 | A0.7 | V0.7 | C0.7 | F0.7 | V27.1 | N36.3 | M38.3 | ||||||||
| S0.7 | H0.6 | F0.7 | S0.1 | V0.7 | I1.2 | H0.7 | G0.7 | K24.2 | Q0.1 | H0.8 | T1.8 | L3.8 | R0.2 | K0.4 | T0.7 | E0.5 | P0.7 | G2.0 | E0.7 | ||||||||
| M0.3 | A0.3 | X0.1 | A0.5 | X0.1 | L1.9 | Q0.1 | N1.3 | S0.7 | P 0.2 | G0.1 | A0.8 | X0.1 | |||||||||||||||
| I0.1 | Y0.7 | D0.8 | R0.7 | L0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| N0.6 | X0.1 | T0.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| R0.3 | D0.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| M0.1 | F0.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H0.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HCV2 | L99.4 | Q100 | S92.6 | F100 | T98.2 | V99.4 | Y77.8 | H100 | G100 | D100 | V100 | R100 | R77.2 | L91.4 | K100 | G99.4 | S100 | S100 | R100 | A100 | A100 | V95.1 | C100 | D100 | I95.7 | S72.2 | L98.1 |
| M0.6 | T7.4 | X1.2 | G0.6 | F22.2 | K21 | I7.4 | R0.6 | I3.1 | V3.1 | T17.9 | I1.9 | ||||||||||||||||
| A0.6 | T1.2 | V0.7 | M1.2 | X1.2 | A9.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| X0.7 | X0.7 | A0.6 | M0.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HCV3 | L100 | Q100 | T100 | F100 | T98.1 | V100 | Y100 | H100 | Q100 | D100 | V94.2 | R100 | S100 | L82.7 | K100 | G100 | S100 | S100 | R100 | A100 | A100 | V98.1 | C96.1 | Q100 | I92.3 | T88.5 | L100 |
| S1.9 | I5.8 | I15.4 | I1.9 | V7.7 | A5.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| V1.9 | V3.9 | S3.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| X1.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HCV4 | L100 | Q100 | S71.4 | F100 | T96.4 | V100 | Y98.2 | H100 | Q100 | D100 | V89.3 | R100 | T87.5 | I94.6 | K100 | G100 | S98.2 | S100 | R100 | A100 | A100 | V98.2 | C100 | D100 | V96.4 | S87.5 | L100 |
| T28.6 | X3.6 | X1.8 | I7.1 | S10.7 | L3.6 | F1.8 | L1.8 | I3.6 | A7.1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| X3.6 | X1.8 | V1.8 | N3.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| X1.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HCV5 | L100 | Q100 | T100 | F100 | T100 | V66.7 | F100 | H100 | K100 | D100 | V100 | R100 | T100 | I100 | K100 | G100 | S100 | S100 | R100 | A100 | A100 | V100 | C100 | E66.7 | I66.7 | N100 | L100 |
| L33.3 | D33.3 | V33.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HCV6 | V83.9 | Q100 | S56.8 | F100 | T100 | V98.8 | Y90.1 | H97.5 | Q71.6 | D100 | R100 | N44.4 | I82.7 | K98.8 | G98.8 | S97.5 | S100 | R100 | A100 | A100 | V95.1 | C100 | D96.3 | V58 | N60.5 | M100 | |
| L16.1 | T43.2 | X1.2 | F9.9 | K25.9 | T30.9 | L17.3 | R1.2 | A1.2 | F2.5 | I4.9 | E3.7 | I39.5 | S32.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Y2.5 | L2.5 | S24.7 | A2.5 | A4.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| G2.5 |
| NS5A Inhibitors | 23 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 35 | 36 | 37 | 54 | 56 | 58 | 62 | 92 | 93 | 95 | 97 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference H77 | L | M | P | Q | L | P | P | F | V | H | R | P | E | A | Y | T | P |
| HCV1 | L99.1 | M58.5 | P99.3 | Q62.5 | L97.2 | P99.3 | P99.3 | F94.4 | V57.9 | H71.5 | R60.6 | H57.8 | E60.3 | A98 | Y97.2 | T99.0 | P98.4 |
| K0.7 | L37.5 | Q0.7 | R35.4 | M2.0 | G0.7 | F0.6 | L4.8 | L21.8 | Q24.7 | T36.7 | P37.9 | Q37.2 | Y0.7 | H1.8 | G0.6 | S0.8 | |
| I0.1 | V2.7 | L0.9 | P0.7 | L0.1 | V0.7 | F15.7 | Y1.6 | I1.2 | S1.3 | D1.2 | T0.5 | T0.7 | A0.2 | C0.7 | |||
| M0.1 | P0.7 | H0.8 | I0.1 | I0.1 | I2.3 | N0.9 | C0.7 | C1 | I0.6 | V0.3 | C0.3 | V0.2 | H0.1 | ||||
| T0.3 | K0.3 | M1.3 | T0.7 | V0.3 | T0.7 | K0.3 | P0.3 | ||||||||||
| I0.2 | M0.1 | S0.7 | L0.4 | N0.2 | Q0.3 | R0.2 | G0.2 | ||||||||||
| F0.1 | Y0.3 | C0.2 | A0.1 | L0.3 | A0.1 | S0.1 | |||||||||||
| S0.1 | N0.2 | S0.1 | |||||||||||||||
| L0.1 | Y0.2 | ||||||||||||||||
| D0.2 | |||||||||||||||||
| A0.1 | |||||||||||||||||
| HCV2 | L100 | L61.1 | P99.4 | K97.5 | M72.8 | P100 | P100 | F96.3 | I84.5 | T98.8 | R96.3 | P95.7 | N85.8 | C93.8 | Y100 | E98.2 | P58.7 |
| F35.2 | L0.6 | R2.5 | L27.2 | L3.1 | V12.4 | V1.2 | K2.5 | S3.7 | A3.7 | S4.9 | D0.6 | Q37.7 | |||||
| C1.9 | S0.6 | L3.1 | Q1.2 | H0.6 | S3.1 | A1.2 | G0.6 | H1.8 | |||||||||
| I1.2 | T3.1 | V0.6 | S1.2 | ||||||||||||||
| S0.6 | V1.2 | A0.6 | |||||||||||||||
| D0.6 | |||||||||||||||||
| E0.6 | |||||||||||||||||
| H0.6 | |||||||||||||||||
| L0.6 | |||||||||||||||||
| Y0.6 | |||||||||||||||||
| HCV3 | L100 | M96.2 | P100 | A76.9 | L88.5 | P100 | P100 | F100 | I71.2 | S80.8 | R100 | P98.1 | S46.1 | E98.1 | Y100 | T96.1 | P100 |
| L1.9 | K17.4 | M7.7 | L25 | T19.2 | R1.9 | T28.8 | G1.9 | V3.9 | |||||||||
| I1.9 | L1.9 | V3.8 | F3.8 | M7.7 | |||||||||||||
| S1.9 | A3.8 | ||||||||||||||||
| V1.9 | D3.9 | ||||||||||||||||
| E3.9 | |||||||||||||||||
| L3.9 | |||||||||||||||||
| P1.9 | |||||||||||||||||
| HCV4 | L98.2 | L83.9 | P100 | R68.1 | M83.9 | P100 | P100 | F100 | L69.8 | H100 | T62.5 | P85.7 | E64.4 | A92.9 | Y89.2 | T89.3 | P92.8 |
| X1.8 | M10.7 | L10.7 | L16.1 | F19.6 | V16.1 | T10.7 | N8.9 | X5.4 | H5.4 | S10.7 | X3.6 | ||||||
| I3.6 | S10.7 | Y8.9 | I10.7 | R1.8 | S8.9 | T1.8 | R1.8 | S1.8 | |||||||||
| V1.8 | Q5.4 | I1.8 | K7.1 | X1.8 | Q7.1 | S1.8 | A1.8 | ||||||||||
| T3.4 | Q1.8 | R7.1 | T1.8 | ||||||||||||||
| A1.7 | R1.8 | D3.6 | |||||||||||||||
| HCV5 | L100 | L100 | P100 | Q100 | L100 | P100 | P100 | F100 | L55.6 | S88.9 | K100 | P100 | T88.9 | A100 | T100 | T100 | P100 |
| F44.4 | Y11.1 | A11.1 | |||||||||||||||
| HCV6 | L100 | V54.5 | P100 | S42.0 | L97.5 | P100 | P100 | F100 | L58.0 | H81.5 | T95.0 | T49.4 | V37.0 | A100 | T69.2 | T98.8 | P100 |
| F22.9 | R32.1 | I2.5 | F23.5 | T9.9 | K2.5 | P45.7 | D16.1 | S29.6 | A1.2 | ||||||||
| L20.7 | A23.5 | I11.1 | N4.9 | S2.5 | S2.5 | Q12.4 | I1.2 | ||||||||||
| M1.9 | N2.4 | Y7.4 | R3.7 | X2.5 | N9.9 | ||||||||||||
| E7.4 | |||||||||||||||||
| S4.9 | |||||||||||||||||
| M4.9 | |||||||||||||||||
| K3.7 | |||||||||||||||||
| A2.5 | |||||||||||||||||
| T1.2 |
| NS5B | 48 | 96 | 149 | 159 | 160 | 162 | 168 | 172 | 220 | 225 | 282 | 291 | 316 | 319 | 321 | 367 | 368 | 386 | 394 | 411 | 414 | 421 | 448 | 495 | 553 | 554 | 556 | 559 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H77 | R | S | P | L | I | F | R | K | D | D | S | N | C | D | V | S | S | R | R | N | M | A | Y | P | A | G | S | D |
| HCV1 | R99.3 | S99.3 | P99.2 | L97.3 | I99.2 | F93.3 | R99.3 | K99.3 | D99.2 | D99.2 | S99.1 | N99.3 | C86.8 | D99.3 | V99.7 | S99.8 | S99,1 | R99.0 | R99.1 | N99.1 | M99.0 | A88.2 | Y99.0 | P99.1 | A93.4 | G93.5 | S89.0 | D93.1 |
| S0.7 | A0.6 | E0.7 | F2.0 | V0.7 | Y5.9 | V0.7 | M0.7 | T0.7 | S0.7 | G0.7 | N12.2 | L0.7 | I0.3 | - 0.2 | N0.7 | A0.7 | I0.7 | F0.7 | V10.0 | G0.7 | -0.1 | -6.1 | -6.1 | -6.1 | -6.5 | |||
| T0.1 | A0.1 | I0.7 | F0.1 | P0.7 | C0.1 | E0.1 | R0.1 | T0.7 | G0.7 | -0.2 | D0.6 | −0.2 | -0.2 | -0.2 | -0.8 | -0.2 | G0.4 | Y0.3 | G3.9 | I0.3 | ||||||||
| S0.1 | T0.1 | H0.1 | P0.1 | I0.1 | R0.7 | C0.1 | V0.1 | X0.1 | N0.7 | N0.1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| R0.1 | −0.2 | V0.1 | T0.2 | H0.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Y0.1 | H0.1 | M0.1 | D0.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| X0.1 | S0.1 | X0.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Y0.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HCV2 | R100 | S100 | P100 | L100 | I100 | Y90.7 | R100 | K100 | D100 | D100 | S100 | N100 | C99.4 | D100 | V98.1 | S99.4 | S99.4 | R98.8 | R99.4 | N97.5 | Q94.4 | V81.5 | Y98.8 | P98.1 | -100 | -100 | -100 | -100 |
| F9.3 | W0.6 | F0.6 | - 0.6 | -0.6 | −0.6 | T1.2 | L4.3 | A17.3 | X0.6 | -2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| I0.6 | K0.6 | -0.6 | S0.6 | -0.6 | -0.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| X0.6 | -0.6 | D0.6 | -0.6 | X0.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HCV3 | R100 | S100 | P100 | L100 | I100 | Y96.1 | R100 | K100 | D100 | D100 | S98.1 | N100 | C100 | D100 | V100 | S98.1 | S100 | R100 | R100 | N96.2 | M100 | V100 | Y100 | P94.2 | V71.2 | G69.2 | G69.2 | D71.2 |
| F3.9 | R1.9 | A1.9 | S3.8 | -5.8 | -28.8 | -28.8S1.9 | -28.8 | -28.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S1.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HCV4 | R100 | S100 | P100 | L98.2 | I100 | Y89.3 | R98.2 | K100 | D100 | D100 | S100 | N100 | C75 | D100 | V94.6 | S100 | S100 | R100 | R100 | N100 | L48.2 | V89.3 | Y100 | P100 | V87.5 | G89.3 | G80.4 | D87.5 |
| X1.8 | F10.7 | V1.8 | N17.9 | I5.4 | I25 | A10.7 | -10.7 | -10.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| H5.4 | V23.2 | X1.8 | -10.7 | -12.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| X1.8 | Q3.6 | N7.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A1.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HCV5 | R100 | S100 | P100 | L100 | I100 | Y100 | R100 | K100 | D100 | D100 | S100 | N100 | C100 | D100 | V100 | S100 | S100 | R100 | R66.7 | N100 | M100 | A55.6 | Y100 | P66.7 | V66.7 | G66.7 | G66.7 | D66.7 |
| K33.3 | V44.4 | -22.2 | -33.3 | -33.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| X11.1 | -33.3 | -33.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HCV6 | R90.1 | S100 | P65.4 | L100 | I100 | Y85.2 | R100 | K100 | D100 | D100 | S97.5 | N100 | C100 | D100 | V100 | S100 | S92.6 | R100 | R100 | N100 | M100 | V100 | Y100 | P97.5 | A64.2 | G100 | S60.5 | D100 |
| T11.1 | F14.8 | C2.5 | A7.4 | L2.5 | S33.3 | D30.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| K9.9 | V8.6 | V2.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S7.4 | R6.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| M4.9 | G2.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A2.6 |
| Variants | HCV1 | HCV1a | HCV1b | HCV2 | HCV3 | HCV4 | HCV5 | HCV6 | DAA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NS3 | |||||||||
| V36L | 1% | 1.2% | 0.5% | 99.4% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 83.9% | Telaprevir |
| 1% | 1.2% | 0.5% | 99.4% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 83.9% | Asunaprevir | |
| 1% | 1.2% | 0.5% | 99.4% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 83.9% | Boceprevir | |
| Q80K | 24.2% | 39.3% | 0.25% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | Simeprevir |
| 24.2% | 39.3% | 0.25% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | Asunaprevir | |
| S122T | 1.8% | 0% | 4.7% | 1.2% | 0% | 87.5% | 100% | 30.9% | Simeprevir/Asunaprevir |
| S122R | 0.7% | 1.1% | 0% | 77.2% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | Simeprevir |
| S122N | 1.3% | 0% | 3.4% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 44.4% | Asunaprevir |
| D168Q | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 100% | 0% | 0% | 0% | Simeprevir |
| D168E | 0.5% | 0.2% | 1% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 66.7% | 3.7% | Simeprevir/Asunaprevir/Paritaprevir |
| I170V | 27.1% | 2.8% | 65.6% | 3.1% | 7.7% | 96.4% | 33.3% | 58% | Boceprevir |
| M175L | 61% | 98% | 1% | 98.1% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 0% | Boceprevir |
| NS5A | |||||||||
| L28M | 58.5% | 94% | 2.5% | 0% | 96.2% | 10.7% | 0% | 1.9% | Daclatasvir |
| M28V | 2.7% | 4.2% | 0.25% | 0% | 0% | 1.8% | 0% | 54.5% | Daclatasvir/Ombitasvir |
| R30Q | 62.5% | 97.5% | 7% | 0% | 0% | 5.4% | 100% | 0% | Daclatasvir |
| Q30K | 0.3% | 0% | 1% | 97.5% | 17.4% | 0% | 0% | 0% | Daclatasvir |
| Q30R | 35.4% | 0.3% | 91% | 2.5% | 0% | 68.1% | 0% | 32.1% | Daclatasvir/Ledipasvir/Ombitasvir |
| L30S | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 1.9% | 10.7% | 0% | 0% | Daclatasvir |
| L31M | 2% | 1.1% | 3.4% | 72.8% | 7.7% | 83.9% | 0% | 0% | Daclatasvir/Ledipasvir |
| NS5B | |||||||||
| A421V | 10% | 12.7% | 5.7% | 81.5% | 100% | 89.3% | 44.4% | 100% | Beclabuvir |
| S556G | 3.9% | 1.1% | 8.4% | 0% | 69.2% | 80.4% | 66.7% | 2.5% | Dasabuvir |

3. Discussion
3.1. The Highly Diverse Nature of the HCV Genome
3.2. Implications for the Development of DAAs
3.3. Implications for Drug Resistance Testing
3.4. Implications for the Development of Genotyping Assays and Epidemiological Surveys
3.5. Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Full-Length Genome Sequence Dataset
4.2. Diversity and Consensus Residues
4.3. Positive Selective Pressure
4.4. Drug Susceptibility-Related Positions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Hauri, A.M.; Armstrong, G.L.; Hutin, Y.J. The global burden of disease attributable to contaminated injections given in health care settings. Int. J. STD AIDS 2004, 15, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartosch, B.; Dubuisson, J.; Cosset, F.L. Infectious hepatitis C virus pseudo-particles containing functional E1–E2 envelope protein complexes. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Hakeem, M.S.; Shoukry, N.H. Protective immunity against hepatitis C: Many shades of gray. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.B.; Bukh, J.; Kuiken, C.; Muerhoff, A.S.; Rice, C.M.; Stapleton, J.T.; Simmonds, P. Expanded classification of hepatitis C virus into 7 genotypes and 67 subtypes: Updated criteria and genotype assignment web resource. J. Hepatol. 2014, 59, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, P. Variability of hepatitis C virus. Hepatology 1995, 21, 570–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukh, J.; Miller, R.H.; Purcell, R.H. Genetic heterogeneity of hepatitis C virus: Quasispecies and genotypes. Semin. Liver Dis. 1995, 15, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, J.P.; Humphreys, I.; Flaxman, A.; Brown, A.; Cooke, G.S.; Pybus, O.G.; Barnes, E. Global distribution and prevalence of hepatitis C virus genotypes. Hepatology 2015, 61, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guillou-Geuillemette, H.; Vallet, S.; Gaudy-Graffin, C.; Payan, C.; Pivert, A.; Goudeau, A.; Lunel-Fabiani, F. Genetic diversity of the hepatitis C virus: Impact and issues in the antiviral therapy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 2416–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummer, H.E. Challenges to the development of vaccines to hepatitis C virus that elicit neutralizing antibodies. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.J. Current progress in development of hepatitis C virus vaccines. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swadling, L.; Capone, S.; Antrobus, R.D.; Brown, A.; Richardson, R.; Newell, E.W.; Halliday, J.; Kelly, C.; Bowen, D.; Fergusson, J.; et al. A human vaccine strategy based on chimpanzee adenoviral and MVA vectors that primes, boosts, and sustains functional HCV-specific T cell memory. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, W.P.; Zeuzem, S. A new standard of care for the treatment of chronic HCV infection. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeuzem, S.; Andreone, P.; Pol, S.; Lawitz, E.; Diago, M.; Roberts, S.; Focaccia, R.; Younossi, Z.; Foster, G.R.; Horban, A.; et al. Telaprevir for retreatment of HCV infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2417–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, J.C.; De Meyer, S.; Bartels, D.J.; Dierynck, I.; Zhang, E.Z.; Spanks, J.; Tigges, A.M.; Thys, A.; Dorrian, J.; Adda, N.; et al. Evolution of treatment-emergent resistant variants in telaprevir phase 3 clinical trials. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlotsky, J.-M. EASL Recommendations on Treatment of Hepatitis C; ILC2015: Vienna, Austria, 24 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, I.M.; Dore, G.J.; Foster, G.R.; Fried, M.W.; Radu, M.; Rafalsky, V.V.; Moroz, L.; Craxi, A.; Peeters, M.; Lenz, O.; et al. Simeprevir with pegylated interferon alpha 2a plus ribavirin in treatment-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection (QUEST-1): A phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawitz, E.; Mangia, A.; Wyles, D.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Hassanein, T.; Gordon, S.C.; Schultz, M.; Davis, M.N.; Kayali, Z.; Reddy, K.R.; et al. Sofosbuvir for previously untreated chronic hepatitis C infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1878–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, D.R.; Cooper, J.N.; Lalezari, J.P.; Lawitz, E.; Pockros, P.J.; Gitlin, N.; Freilich, B.F.; Younes, Z.H.; Harlan, W.; Ghalib, R.; et al. All-oral 12-week treatment with daclatasvir plus sofosbuvir in patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 3 infection: ALLY-3 phase III study. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, S.; Tural, C.; Nevot, M.; Molto, J.; Rockstroh, J.K.; Clotet, B.; Martinez, M.A. Detection of a sexually transmitted hepatitis C virus protease inhibitor-resistance variant in a human immunodeficiency virus-infected homosexual man. Gastroenterology 2014, 174, 599–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, A.S.; Kretzschmar, M.E.E. Benefits of hepatitis C virus treatment: A balance of preventing onward transmission and re-infection. Math. Biosci. 2014, 258, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, T.C.; Martin, N.K.; Hickman, M.; Vickerman, P.; Page, E.E.; Everett, R.; Gazzard, B.G.; Nelson, M. Hepatitis C virus reinfection incidence and treatment outcome among HIV-positive MSM. AIDS 2013, 27, 2551–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micallef, J.M.; Macdonald, V.; Jauncey, M.; Amin, J.; Rawlinson, W.; van Beek, I.; Kaldor, J.M.; White, P.A.; Dore, G.J. High incidence of hepatitis C virus reinfection within a cohort of injecting drug users. J. Viral. Hepat. 2007, 14, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandamme, A.M.; Camacho, R.J.; Ceccherini Silberstein, F.; De Luca, A.; Palmisano, L.; Paraskevis, D.; Paredes, R.; Poljak, M.; Schmit, J.-C.; Soriano, V.; et al. European recommendations for the clinical use of HIV drug resistance testing: 2011 update. AIDS Rev. 2011, 13, 77–108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sarrazin, C.; Kieffer, T.L.; Bartels, D.; Hanzelka, B.; Müh, U.; Welker, M.; Wincheringer, D.; Zhou, Y.; Chu, H.M.; Lin, C. Dynamic hepatitis C virus genotypic and phenotypic changes in patients treated with the protease inhibitor telaprevir. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1767–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartels, D.J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, E.Z.; Marcial, M.; Byrn, R.A.; Pfeiffer, T.; Tigges, A.M.; Adiwijaya, B.S.; Lin, C.; Kwong, A.D. Natural prevalence of hepatitis C virus variants with decreased sensitivity to NS3.4A protease inhibitors in treatment-naïve subjects. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 198, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, O.; Verbinnen, T.; Fevery, B.; Tambuyzer, L.; Vijgen, L.; Peeters, M.; Buelens, A.; Ceulemans, H.; Beumont, M.; Picchio, G. Virology analyses of HCV isolates from genotype 1-infected patients treated with simeprevir plus peginterferon/ribavirin in Phase IIb/III studies. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarrazin, C.; Lathouwers, E.; Peeters, M.; Daems, B.; Buelens, A.; Witek, J.; Wyckmans, Y.; Fevery, B.; Verbinnen, T.; Ghys, A.; et al. Prevalence of the hepatitis C virus NS3 polymorphism Q80K in genotype 1 patients in the European region. Antivir. Res. 2015, 116, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afdhal, N.; Reddy, K.R.; Nelson, D.R.; Lawitz, E.; Gordon, S.C.; Schiff, E.; Nahass, R.; Ghalib, R.; Gitlin, N.; Herring, R. Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir for previously treated HCV genotype 1 infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1483–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, E.F.; Harrington, P.R.; O’Rear, J.J.; Naeger, L.K. Clinical evidence and bioinformatics characterization of potential hepatitis C virus resistance pathways for sofosbuvir. Hepatology 2015, 61, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukh, J.; Purcell, R.H.; Miller, R.H. Importance of primer selection for the detection of hepatitis C virus RNA with the polymerase chain reaction assay. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacka, B.; Lamoury, F.; Simmonds, P.; Dore, G.J.; Grebely, J.; Applegate, T. Sequencing of the hepatitis C virus: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salemi, M.; Vandamme, A.M. Hepatitis C virus evolutionary patterns studied through analysis of full-genome sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 2002, 54, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Piampongsant, S.; Faria, N.R.; Voet, A.; Pineda-Peña, A.C.; Khouri, R.; Lemey, P.; Vandamme, A.M.; Theys, K. An integrated map of HIV genome-wide variation from a population perspective. Retrovirology 2015, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, H. Hepatitis C virus: Is it time to say goodbye yet? Perspectives and challenges for the next decade. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Verheyen, J.; Rhee, S.Y.; Voet, A.; Vandamme, A.M.; Theys, K. Functional conservation of HIV-1 Gag: Implications for rational drug design. Retrovirology 2013, 10, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcantara, L.C.; Cassol, S.; Libin, P.; Deforche, K.; Pybus, O.G.; van Ranst, M.; Galvão-Castro, B.; Vandamme, A.M.; de Oliveira, T. A standardized framework for accurate, high-throughput genotyping of recombinant and non-recombinant viral sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W634–W642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margeridon-Thermet, S.; Shafer, R.W. Comparison of the mechanisms of drug resistance among HIV, Hepatitis B, and Hepatitis C. Viruses 2010, 2, 2696–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echevarría, J.M.; Avellón, A. Hepatitis B virus genetic diversity. J. Med. Virol. 2006, 78 (Suppl. 1), 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusim, K.; Fisher, W.; Yoon, H.; Thurmond, J.; Fenimore, P.W.; Lauer, G.; Korber, B.; Kuiken, C. Genotype 1 and global hepatitis C T-cell vaccines designed to optimize coverage of genetic diversity. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1194–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Gojobori, T. Positively selected amino acid sites in the entire coding region of hepatitis C virus subtype 1b. Gene 2001, 279, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, I.; Phybus, O.G.; Holmes, E.C.; Klenerman, P. High-resolution phylogenetic analysis of hepatitis C virus adaptation and its relationship to disease progression. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 3447–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, R.R.; Parker, J.; Lemey, P.; Salemi, M.; Katzourakis, A.; Pybus, O.G. The mode and tempo of hepatitis C virus evolution within and among hosts. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, E.C.; Smith, J.A.; Klenerman, P. The natural history of early hepatitis C virus evolution; lessons from a global outbreak in human immunodeficiency virus-1-infected individuals. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 2227–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackard, J.T.; Yang, Y.; Bordoni, P.; Sherman, K.E.; Chung, R.T. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) diversity in HIV-HCV-coinfected subjects initiating highly active antiretroviral therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 1472–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. Evolutionary rate at the molecular level. Nature 1968, 217, 624–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, E.C. Error thresholds and the constraints to RNA virus evolution. Trends Microbiol. 2003, 11, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snoeck, J.; Fellay, J.; Bartha, I.; Douek, D.C.; Telenti, A. Mapping of positive selection sites in the HIV-1 genome in the context of RNA and protein structural constraints. Retrovirology 2011, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashfaq, U.A.; Javed, T.; Rehman, S.; Nawaz, Z.; Riazuddin, S. An overview of HCV molecular biology, replication and immune responses. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.-L. Chapter 1: Hepatitis C viruses: genomes and molecular biology. Horiz. Biosci. 2006, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pantua, H.; Diao, J.; Ultsch, M.; Hazen, M.; Mathieu, M.; McCutcheon, K.; Takeda, K.; Date, S.; Cheung, T.K.; Phung, Q.; et al. Glycan shifting on hepatitis C virus (HCV) E2 glycoprotein is a mechanism for escape from broadly neutralizing antibodies. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 1899–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penin, F.; Combet, C.; Germanidis, G.; Frainais, P.O.; Deléage, G.; Pawlostky, J.M. Conservation of the conformation and positive charges of hepatitis C virus E2 envelope glycoprotein hypervariable region 1 points to a role in cell attachment. J. Virol. 2011, 75, 5703–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, V.C.; Peter, J.A.; Nelson, D.R. New therapeutic strategies in HCV: Second-Generation protease inhibitors. Liver Int. 2013, 33 (Suppl. 1), 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL recommendations on treatment of hepatitis C 2015. J. Hepatol. 2015, S0168–S8278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol, S.; Vallet-Pichard, A.; Corouge, M. Treatment of hepatitis C virus genotype 3-infection. Liver Int. 2014, 34 (Suppl. 1), 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatel-Chaix, L.; Baril, M.; Lamarre, D. Hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protease inhibitors: A light at the end of the tunnel. Viruses 2010, 2, 1752–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascher, D.B.; Wielens, J.; Nero, T.L.; Doughty, L.; Morton, C.J.; Parker, M.W. Potent hepatitis C inhibitors bind directly to NS5A and reduce its affinity for RNA. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, S.M.; Langley, D.R.; Garnett, J.A.; Angell, R.; Hedgethorne, K.; Meanwell, N.A.; Matthews, S.J. The crystal structure of NS5A domain 1 from genotype 1a reveals new clues to the mechanism of action for dimeric HCV inhibitors. Protein Sci. 2014, 23, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nettles, J.H.; Stanton, R.A.; Broyde, J.; Amblard, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, L.; Shi, J.; McBrayer, T.R.; Whitaker, T.; Coats, S.J.; et al. Asymmetric binding to NS5A by daclatasvir (BMS-790052) and analogues suggests two novel modes of HCV inhibition. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 10031–10043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, L.H.T.; Arcuri, H.A.; Jardim, A.C.G.; Bittar, C.; de Caravalho-Mello, I.M.V.G.; Rahal, P. New insights regarding HCV-NS5A structure/function and indication of genotypic differences. Virol. J. 2012, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nettles, R.E.; Gao, M.; Bifano, M.; Chung, E.; Persson, A.; Marbury, T.C.; Goldwater, R.; DeMicco, M.P.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Vutikullird, A.; et al. Multiple ascending dose study of BMS-790052, a nonstructural protein 5A replication complex inhibitor, in patients infected with hepatitis C virus genotype 1. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridell, R.A.; Qiu, D.; Wang, C.; Valera, L.; Gao, M. Resistance analysis of the hepatitis C virus NS5A inhibitor BMS-790052 in an in vitro replicon system. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3641–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bressanelli, S.; Tomei, L.; Roussel, A.; Incitti, I.; Vitale, R.L.; Mathieu, M.; De Francesco, R.; Rey, F.A. Crystal structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of hepatitis C virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 13034–13039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poveda, E.; Wyles, D.L.; Mena, Á.; Pedreira, J.D.; Castro-Inglesias, Á.; Cachay, E. Update on hepatitis C virus resistance to direct-acting antiviral agents. Antivir. Res. 2014, 108, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lontok, E.; Harrington, P.; Howe, A.; Kieffer, T.; Lennerstrand, J.; Lenz, O.; McPhee, F.; Mo, H.; Parkin, N.; Pilot-Matias, T.; et al. Hepatitis C virus drug resistance-associated substitutions: State of the art summary. Hepatology 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, P.; Cai, X.-Y.; Wang, L.; Greene, J.R.; Malcolm, B. Hepatitis C virus whole genome position weight matrix and robust primer design. BMC Microbiol. 2002, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirotsu, Y.; Kanda, T.; Matsumura, H.; Moriyama, M.; Yokosuka, O.; Omata, M. HCV NS5A resistance-associated variants in a group of real-world Japanese patients chronically infected with HCV genotype 1b. Hepatol. Int. 2015, 9, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Kanda, T.; Nakamoto, S.; Jiang, X.; Miyamura, T.; Nakatani, S.M.; Ono, S.K.; Takahashi-Nakaguchi, A.; Gonoi, T.; Yokosuka, O. Prevalence of hepatitis C virus subgenotypes 1a and 1b in Japanese patients: Ultra-Deep sequencing analysis of HCV NS5B genotype-specific region. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiken, C.; Hraber, P.; Thurmond, J.; Yusim, K. The hepatitis C sequence database in Los Alamos. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D512–D516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zein, N.N. Clinical significance of hepatitis C virus genotypes. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouy, M.; Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. SeaView version 4: A multiplatform graphical user interface for sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree building. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, B.G. Building phylogenetic trees from molecular data with MEGA. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struck, D.; Lawyer, G.; Ternes, A.M.; Schmit, J.C.; Bercoff, D.P. COMET: Adaptive context-based modeling for ultrafast HIV-1 subtype identification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, e144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, G.; Ying, M. Fuzzy Logic, Soft Computing and Computational Intelligence; Tsinghua University Press Springer. Eleventh International Fuzzy Systems Association World Congress: Beijing, China; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2005; Volume III, p. 1288. [Google Scholar]
- Eddy, S.R. Where did the BLOSUM62 alignment score matrix come from? Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 1035–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brocchieri, L.; Karlin, S. Conservation among HSP60 sequences in relation to structure, function and evolution. Protein Sci. 2000, 9, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, J.; Grishin, N.V. AL2CO: calculation of positional conservation in a protein sequence alignment. Boinformatics 2001, 17, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roebuck, K. Biochips: High-Impact Strategies—What You Need to Know: Definitions, Adoptions, Impact, Benefits, Maturity, Vendors; Emereo publishing: Aspley, Queensland, Australia, 2011; pp. 205–207. [Google Scholar]
- Pond, S.L.; Frost, S.D.; Muse, S.V. HyPhy: Hypothesis testing using phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, R.; Yang, Z. Likelihood models for detecting positively selected amino acid sites and applications to the HIV-1 envelope gene. Genetics 1998, 148, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Frost, S.D. Not so different after all: A comparison of methods for detecting amino acid sites under selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 5, 1208–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Poon, A.F.Y.; Frost, S.D.W. Chapter 14: Estimating selection pressures on alignments of coding sequences: Practice. In The Phylogenetic Handbook: A Practical Approach to Phylogenetic Analysis and Hypothesis Testing, 2nd ed.; Lemey, P., Salemi, M., Vandamme, A.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 477–478. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, M.D.; Lindberg, J.; Lin, T.-I.; de Kock, H.; Lenz, O.; Lilja, E.; Felländer, S.; Baraznenok, V.; Nyström, S.; Nilsson, M.; et al. Induced-fit binding of the macrocyclic noncovalent inhibitor TMC435 to its HCV NS3/NS4A protease target. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 1652–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, K.P.; Ali, A.; Royer, W.E.; Schiffer, C.A. Drug resistance against HCV NS3/4A inhibitors is defined by the balance of substrate recognition versus inhibitor binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20986–20991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, K.P.; Ali, A.; Aydin, C.; Soumana, D.; Özen, A.; Deveau, L.M.; Silver, C.; Cao, H.; Newton, A.; Petropoulos, C.J.; et al. The molecular basis of drug resistance against hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protease inhibitors. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeprasert, A.; Hannongbua, S.; Rungrotmongkol, T. Key binding and susceptibility of NS3/4A serine protease inhibitors against hepatitis C virus. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Boyle li, D.R.; Sun, J.H.; Nower, P.T.; Lemm, J.A.; Fridell, R.A.; Wang, C.; Romine, J.L.; Belema, M.; Nguyen, V.N.; Laurent, D.R.; et al. Characterizations of HCV NS5A replication complex inhibitors. Virology 2013, 444, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, W.; Jiao, P.; Yao, X. Molecular modeling and residue interaction network studies on the mechanism of binding and resistance of the HCV NS5B polymerase mutants to VX-222 and ANA598. Antivir. Res. 2014, 104, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfiky, A.A.; Elshemey, W.M.; Gawad, W.A.; Desoky, O.S. Molecular modeling comparison of the performance of NS5B polymerase inhibitor (PSI-7977) on prevalent HCV genotypes. Protein J. 2013, 32, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Ng, K.K.; Cherney, M.M.; Chan, L.; Yannopoulos, C.G.; Bedard, J.; Morin, N.; Nguyen-Ba, N.; Alaoui-Ismaili, M.H.; Bethell, R.C.; et al. Non-nucleoside analogue inhibitors bind to an allosteric site on HCV NS5B polymerase. Crystal structures and mechanism of inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9489–9495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cuypers, L.; Li, G.; Libin, P.; Piampongsant, S.; Vandamme, A.-M.; Theys, K. Genetic Diversity and Selective Pressure in Hepatitis C Virus Genotypes 1–6: Significance for Direct-Acting Antiviral Treatment and Drug Resistance. Viruses 2015, 7, 5018-5039. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7092857
Cuypers L, Li G, Libin P, Piampongsant S, Vandamme A-M, Theys K. Genetic Diversity and Selective Pressure in Hepatitis C Virus Genotypes 1–6: Significance for Direct-Acting Antiviral Treatment and Drug Resistance. Viruses. 2015; 7(9):5018-5039. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7092857
Chicago/Turabian StyleCuypers, Lize, Guangdi Li, Pieter Libin, Supinya Piampongsant, Anne-Mieke Vandamme, and Kristof Theys. 2015. "Genetic Diversity and Selective Pressure in Hepatitis C Virus Genotypes 1–6: Significance for Direct-Acting Antiviral Treatment and Drug Resistance" Viruses 7, no. 9: 5018-5039. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7092857
APA StyleCuypers, L., Li, G., Libin, P., Piampongsant, S., Vandamme, A.-M., & Theys, K. (2015). Genetic Diversity and Selective Pressure in Hepatitis C Virus Genotypes 1–6: Significance for Direct-Acting Antiviral Treatment and Drug Resistance. Viruses, 7(9), 5018-5039. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7092857