Heat Shock Enhances the Expression of the Human T Cell Leukemia Virus Type-I (HTLV-I) Trans-Activator (Tax) Antigen in Human HTLV-I Infected Primary and Cultured T Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture and Heat Shock (HS)
2.3. Flow Cytometry (FCM) Analysis
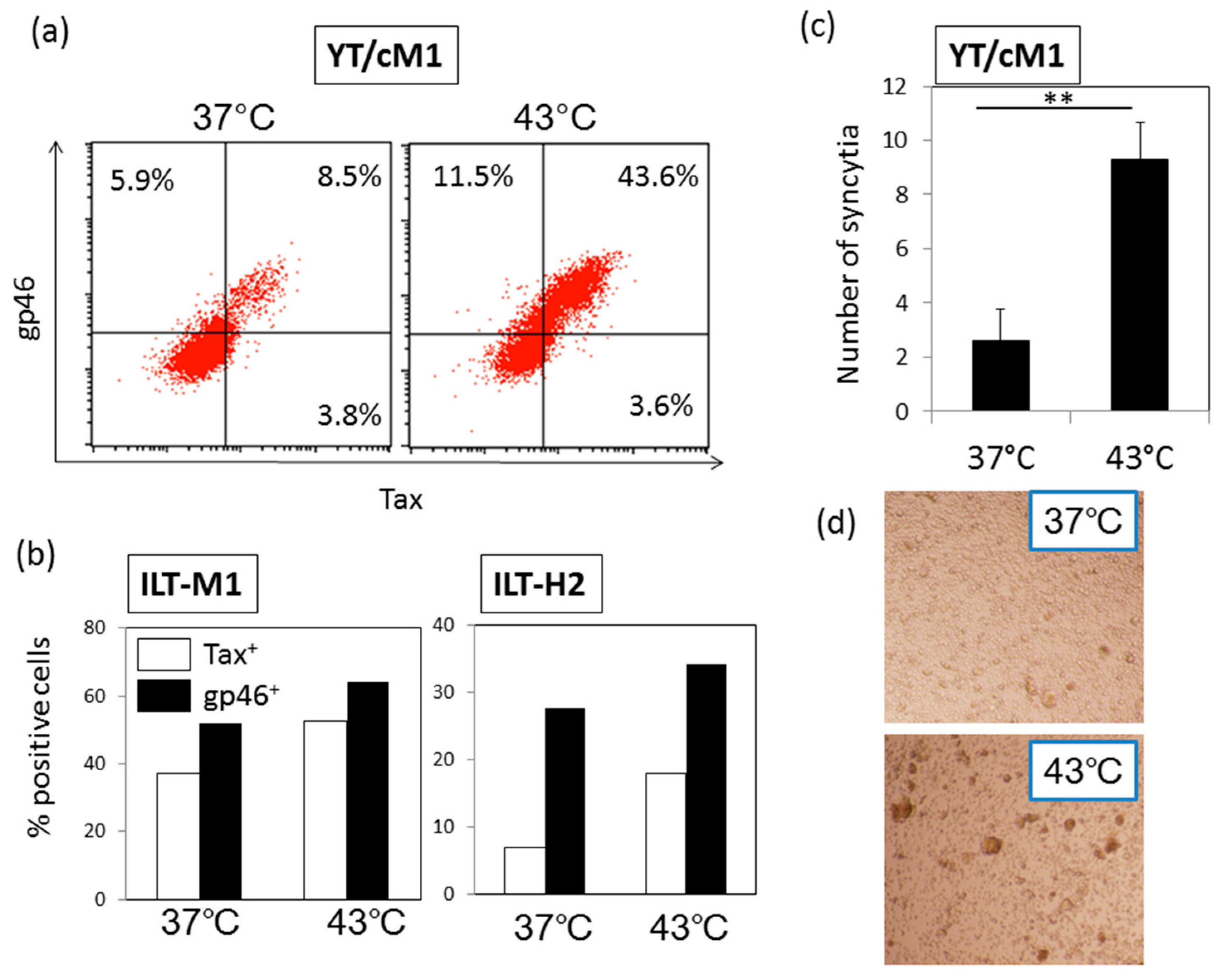
2.4. Syncytium Formation Assay
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
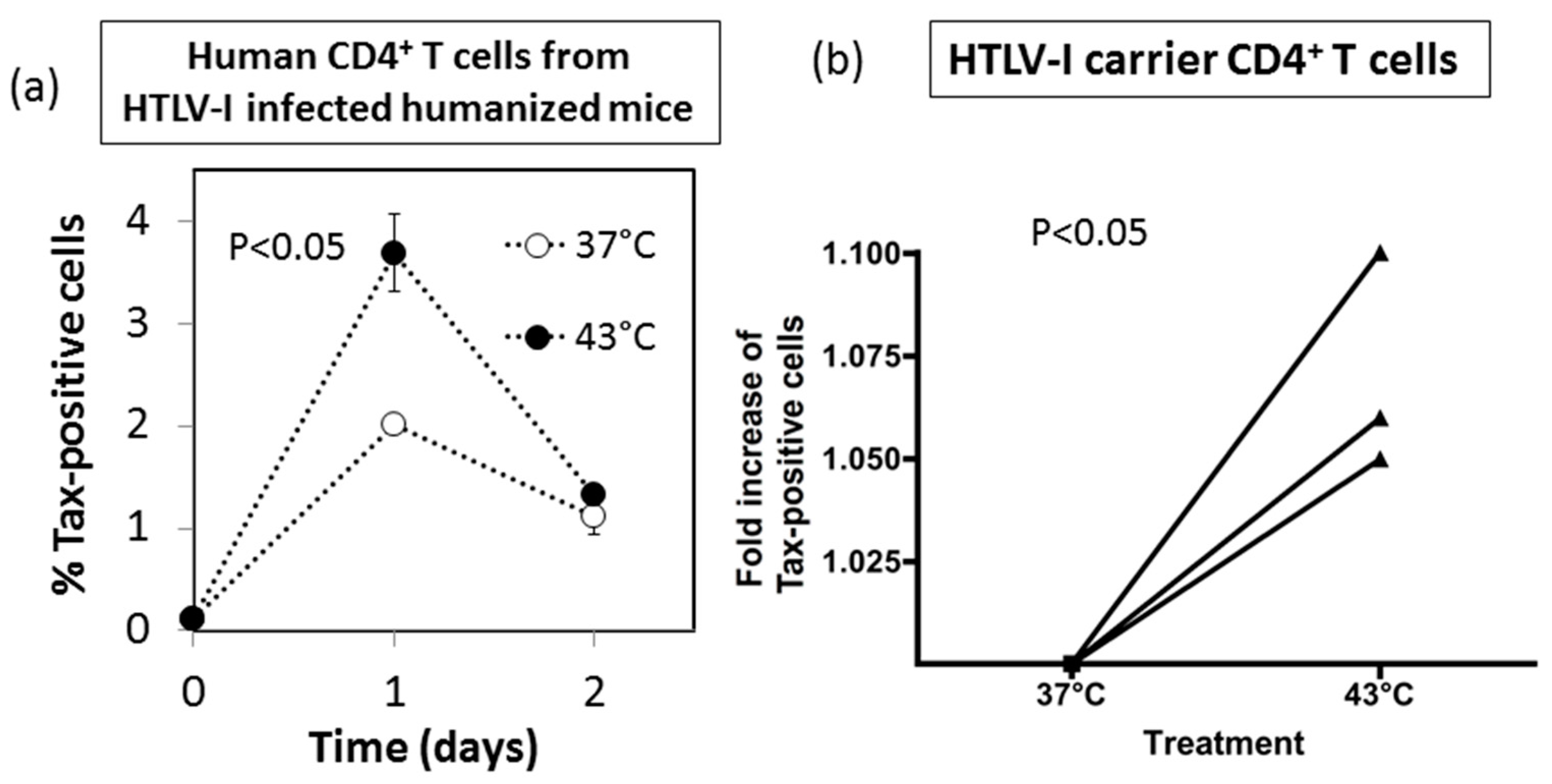
2.6. Primary human CD4+ T Cells Infected with Human T Cell Leukemia Virus Type-I (HTLV-I)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HS Up-Regulates the Expression of the HTLV-I Trans-Activator (Tax) Antigen
3.2. HS Increases the Total Amount of Tax Protein
3.3. HS Up-Regulates a Functional Form of Envelope gp46.
3.4. Time Course Effects of HS
3.5. A Possible Involvement of Heat Shock Protein 70 (HSP70)
3.6. Effect of HS on Tax-Inducible Host Antigens CD83 and OX40
3.7. Effect of HS Exposure on Primary Human CD4+ T Cells Infected with HTLV-I
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hinuma, Y.; Nagata, K.; Hanaoka, M.; Nakai, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Kinoshita, K.I.; Shirakawa, S.; Miyoshi, I. Adult T-cell leukemia: Antigen in an ATL cell line and detection of antibodies to the antigen in human sera. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 6476–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poiesz, B.J.; Ruscetti, F.W.; Reitz, M.S.; Kalyanaraman, V.S.; Gallo, R.C. Isolation of a new type C retrovirus (HTLV) in primary uncultured cells of a patient with sezary T-cell leukaemia. Nature 1981, 294, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, S.; Raine, C.S.; Mingioli, E.S.; McFarlin, D.E. Isolation of an HTLV-1-like retrovirus from patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Nature 1988, 331, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessain, A.; Cassar, O. Epidemiological Aspects and World Distribution of HTLV-1 Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T. Current status of HTLV-1 infection. Int. J. Hematol. 2011, 94, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arisawa, K.; Soda, M.; Endo, S.; Kurokawa, K.; Katamine, S.; Shimokawa, I.; Koba, T.; Takahashi, T.; Saito, H.; Doi, H.; Shirahama, S. Evaluation of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma incidence and its impact on non-Hodgkin lymphoma incidence in southwestern Japan. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 85, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, M.; Watanabe, T.; Utsunomiya, A.; Okayama, A.; Uchimaru, K.; Koh, K.R.; Ogata, M.; Kikuchi, H.; Sagara, Y.; Uozumi, K.; et al. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-1) proviral load and disease progression in asymptomatic HTLV-1 carriers: A nationwide prospective study in japan. Blood 2010, 116, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurihara, K.; Harashima, N.; Hanabuchi, S.; Masuda, M.; Utsunomiya, A.; Tanosaki, R.; Tomonaga, M.; Ohashi, T.; Hasegawa, A.; Masuda, T.; et al. Potential immunogenicity of adult T cell leukemia cells in vivo. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 114, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriuchi, M.; Moriuchi, H. A milk protein lactoferrin enhances human T cell leukemia virus type I and suppresses HIV-1 infection. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 4231–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriuchi, M.; Inoue, H.; Moriuchi, H. Reciprocal interactions between human t-lymphotropic virus type 1 and prostaglandins: Implications for viral transmission. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyot, D.J.; Newbound, G.C.; Lairmore, M.D. Signaling via the CD2 receptor enhances HTLV-1 replication in T lymphocytes. Virology 1997, 234, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.C.; Dezzutti, C.S.; Lal, R.B.; Rabson, A.B. Activation of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 TAX gene expression in chronically infected T cells. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 6264–6270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.C.; Hickey, M.; Hsu, L.; Medina, D.; Rabson, A.B. Activation of human T cell leukemia virus type 1 LTR promoter and cellular promoter elements by T cell receptor signaling and HTLV-1 TAX expression. Virology 2005, 339, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, J.M.; Oglesbee, M.J.; Trevino, A.V.; Guyot, D.J.; Newbound, G.C.; Lairmore, M.D. Enhanced human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 expression following induction of the cellular stress-response. Virology 1995, 208, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatza, M.; Marriott, S. Genotoxic stress and cellular stress alter the subcellular distribution of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 TAX through a CRM1-dependent mechanism. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 6657–6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.Y.; Oglesbee, M. Virus-heat shock protein interaction and a novel axis for innate antiviral immunity. Cells 2012, 1, 646–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.; Shin, M.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Seo, J.-E.; Lee, Y.M.; Park, C.-H.; Chung, J.H. Effects of infrared radiation and heat on human skin aging in vivo. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2009, 14, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Mizuguchi, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Fujii, H.; Tanaka, R.; Fukushima, T.; Tomoyose, T.; Ansari, A.A.; Nakamura, M. Human T-cell leukemia virus type-1 TAX induces the expression of CD83 on T cells. Retrovirology 2015, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Harhaj, E.W. HSP90 protects the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) tax oncoprotein from proteasomal degradation to support NF-kappa B activation and HTLV-1 replication. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 13640–13654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Cenciarelli, C.; Shao, Z.P.; Vidal, M.; Parks, W.P.; Pagano, M.; Cheng-Mayer, C. Human T cell leukemia virus type 1 TAX associates with a molecular chaperone complex containing HTID-1 and HSP70. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, 1771–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Zeng, L.; Shiraki, H.; Shida, H.; Tozawa, H. Identification of a neutralization epitope on the envelope gp46 antigen of human T cell leukemia virus type I and induction of neutralizing antibody by peptide immunization. J. Immunol. 1991, 147, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Tanaka, R.; Yamamoto, N.; Tanaka, Y. Enhancement of OX40-induced apoptosis by TNF coactivation in OX40-expressing T cell lines in vitro leading to decreased targets for HIV type 1 production. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2008, 24, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Yamashita, A.; Koyanagi, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Yamamoto, N. OX40 stimulation by gp34/OX40 ligand enhances productive human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 6748–6757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnishi, K.; Ohkura, S.; Nakahata, E.; Ishisaka, A.; Kawai, Y.; Terao, J.; Mori, T.; Ishii, T.; Nakayama, T.; Kioka, N.; et al. Non-specific protein modifications by a phytochemical induce heat shock response for self-defense. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goloudina, A.R.; Demidov, O.N.; Garrido, C. Inhibition of HSP70: A challenging anti-cancer strategy. Cancer Lett. 2012, 325, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Tanaka, R.; Kodama, A.; Fujii, H.; Hasegawa, A.; Kannagi, M.; Ansari, A.A.; Saito, M. Elimination of Human T cell Leukemia Virus Type-1-Infected Cells by Neutralizing and Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity-Inducing Antibodies Against Human T cell Leukemia Virus Type-1 Envelope gp46. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2014, 30, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Yoshida, A.; Tozawa, H.; Shida, H.; Nyunoya, H.; Shimotohno, K. Production of a recombinant human T-cell leukemia virus type-1 trans-activator (TAX1) antigen and its utilization for generation of monoclonal antibodies against various epitopes on the TAX1 antigen. Int. J. Cancer 1991, 48, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Masuda, M.; Yoshida, A.; Shida, H.; Nyunoya, H.; Shimotohno, K.; Tozawa, H. An antigenic structure of the trans-activator protein encoded by human T-cell leukemia virus type-1 (HTLV-1), as defined by a panel of monoclonal antibodies. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 1992, 8, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Inoi, T.; Tozawa, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Hinuma, Y. A glycoprotein antigen detected with new monoclonal antibodies on the surface of human lymphocytes infected with human T-cell leukemia virus type-1 (HTLV-1). Int. J. Cancer 1985, 36, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Tanaka, R.; Fujii, H.; Kodama, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Matsuzaki, T.; Takashima, H.; Tanaka, Y. The neutralizing function of the anti-HTLV-1 antibody is essential in preventing in vivo transmission of HTLV-1 to human T cells in NOD-SCID/γcnull (NOG) mice. Retrovirology 2014, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunihiro, M.; Tanaka, Y. Transient upregulation of Tax and gp46 by heat shock. Unpublished.
- Andrews, J.M.; Newbound, G.C.; Oglesbee, M.; Brady, J.N.; Lairmore, M.D. The cellular stress response enhances human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 basal gene expression through the core promotor region of the long terminal repeat. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andrews, J.M.; Oglesbee, M.; Lairmore, M.D. The effect of the cellular stress response on human T-lymphotropic virus type I envelope protein expression. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 2905–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, D.; Tanimoto, K.; Nakayama, K. CREB is activated by ER stress and modulates the unfolded protein response by regulating the expression of IRE1α and PERK. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 469, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Tan, H.; Gu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Geng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tong, H.; Tang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Su, L. Heat stress induces apoptosis through a Ca2+-mediated mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luscher, B.; Eisenman, R. c-Myc and c-Myb protein degradation: Effect of metabolic inhibitors and heat shock. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1988, 8, 2504–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangham, C.R.M.; Osame, M. Cellular immune response to HTLV-1. Oncogene 2005, 24, 6035–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannagi, M. Immunologic control of human T-cell leukemia virus type I and adult T-cell leukemia. Int. J. Hematol. 2007, 86, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, A.; Torigoe, T.; Tamura, Y.; Kanaseki, T.; Tsukahara, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Kameshima, H.; Tsuruma, T.; Hirata, K.; Tokino, T.; et al. Heat shock enhances the expression of cytotoxic granule proteins and augments the activities of tumor-associated antigen-specific cytotoxic t lymphocytes. Cell Stress Chaperones 2012, 17, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, H.; Murakami, T.; Tea, S.S.; Takeuchi, A.; Koga, T.; Okada, S.; Suico, M.A.; Shuto, T.; Kai, H. Heat shock suppresses human NK cell cytotoxicity via regulation of perforin. Int. J. Hyperth. 2007, 13, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunihiro, M.; Tanaka, Y. Heat shock inactivated ADCC activity of PBMC to HTLV-I infected cells. (unpublished; manuscript in preparation).
- Jing, Y.K.; Dai, J.; Chalmers-Redman, R.M.E.; Tatton, W.G.; Waxman, S. Arsenic trioxide selectively induces acute promyelocytic leukemia cell apoptosis via a hydrogen peroxide-dependent pathway. Blood 1999, 94, 2102–2111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nabeshi, H.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kamada, H.; Shibata, H.; Sugita, T.; Abe, Y.; Nagano, K.; Nomura, T.; Minowa, K.; Yamashita, T.; et al. Arsenic trioxide inhibits human T cell-lymphotropic virus-1-induced syncytiums by down-regulating gp46. Biol. Pharma. Bull. 2009, 32, 1286–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutsvunguma, L.Z.; Moetlhoa, B.; Edkins, A.L.; Luke, G.A.; Blatch, G.L.; Knox, C. Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus infection induces a redistribution of heat shock proteins 70 and 90 in BHK-21 cells, and is inhibited by novobiocin and geldanamycin. Cell Stress Chaperones 2011, 16, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khachatoorian, R.; Ganapathy, E.; Ahmadieh, Y.; Wheatley, N.; Sundberg, C.; Jung, C.L.; Arumugaswami, V.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Dasgupta, A.; French, S.W. The ns5a-binding heat shock proteins HSC70 and HSP70 play distinct roles in the hepatitis c viral life cycle. Virology 2014, 454–455, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Kang, K.; Ning, P.; Peng, Y.; Lin, Z.; Cui, H.; Cao, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Heat shock protein 70 is associated with CSFV NS5A protein and enhances viral rna replication. Virology 2015, 482, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, K.; Ide, Y.; Takagi, T.; Ohtani, K.; Aoshima, M.; Tozawa, H.; Nakamura, M.; Sugamura, K. Complex formation of human T-cell leukemia virus type I p40tax transactivator with cellular polypeptides. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fang, D.; Haraguchi, Y.; Jinno, A.; Soda, Y.; Shimizu, N.; Hoshino, H. Heat shock cognate protein 70 is a cell fusion-enhancing factor but not an entry factor for human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 261, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, H.; Tomita, M.; Okudaira, T.; Ishikawa, C.; Matsuda, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Nakazato, T.; Taira, N.; Ohshiro, K.; Mori, N. Inhibition of heat shock protein-90 modulates multiple functions required for survival of human T-cell leukemia virus type I-infected T-cell lines and adult T-cell leukemia cells. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 1811–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallouh, H.; Mahana, W. Antibody to heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) inhibits human T-cell lymphoptropic virus type I (HTLV-I) production by transformed rabbit T-cell lines. Toxins 2012, 4, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barolet, D.; Christiaens, F.; Hamblin, M.R. Infrared and skin: Friend or foe. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2016, 155, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roesch, F.; Meziane, O.; Kula, A.; Nisole, S.; Porrot, F.; Anderson, I.; Mammano, F.; Fassati, A.; Marcello, A.; Benkirane, M.; et al. Hyperthermia Stimulates HIV-1 Replication. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kunihiro, M.; Fujii, H.; Miyagi, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Tanaka, R.; Fukushima, T.; Ansari, A.A.; Tanaka, Y. Heat Shock Enhances the Expression of the Human T Cell Leukemia Virus Type-I (HTLV-I) Trans-Activator (Tax) Antigen in Human HTLV-I Infected Primary and Cultured T Cells. Viruses 2016, 8, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8070191
Kunihiro M, Fujii H, Miyagi T, Takahashi Y, Tanaka R, Fukushima T, Ansari AA, Tanaka Y. Heat Shock Enhances the Expression of the Human T Cell Leukemia Virus Type-I (HTLV-I) Trans-Activator (Tax) Antigen in Human HTLV-I Infected Primary and Cultured T Cells. Viruses. 2016; 8(7):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8070191
Chicago/Turabian StyleKunihiro, Marie, Hideki Fujii, Takuya Miyagi, Yoshiaki Takahashi, Reiko Tanaka, Takuya Fukushima, Aftab A. Ansari, and Yuetsu Tanaka. 2016. "Heat Shock Enhances the Expression of the Human T Cell Leukemia Virus Type-I (HTLV-I) Trans-Activator (Tax) Antigen in Human HTLV-I Infected Primary and Cultured T Cells" Viruses 8, no. 7: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8070191
APA StyleKunihiro, M., Fujii, H., Miyagi, T., Takahashi, Y., Tanaka, R., Fukushima, T., Ansari, A. A., & Tanaka, Y. (2016). Heat Shock Enhances the Expression of the Human T Cell Leukemia Virus Type-I (HTLV-I) Trans-Activator (Tax) Antigen in Human HTLV-I Infected Primary and Cultured T Cells. Viruses, 8(7), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8070191




