The Role of Infected Cell Proliferation in the Clearance of Acute HBV Infection in Humans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Data
2.2. Mathematical Models
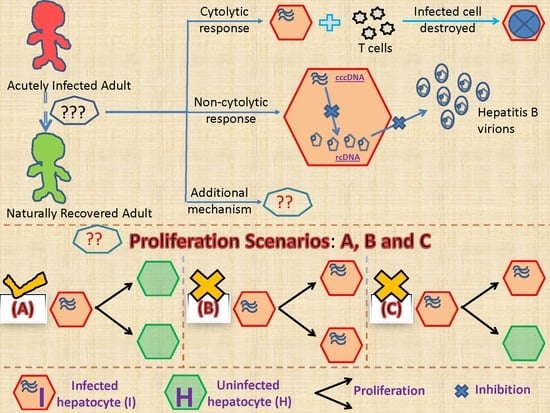
2.2.1. Models Characterizing Different Outcomes of the Cellular Proliferation of Infected Cells
2.2.2. Model Incorporating Cytokine-Mediated Cure of Infected Cells
2.3. Parameter Values and Simulation Procedure
2.4. Criteria to Determine the Biological Plausibility of the Model
3. Results
3.1. Fitting to Viral Load Data Alone Does Not Differentiate Models
3.2. Biological Constraints Indicate that Proliferation of Infected Cells is More Likely to Produce Two Uninfected Cells
3.3. Cytokine-Mediated Cure of Infected Cells is Insufficient to Achieve Non-Destructive Clearance of Acute HBV Infection
3.4. Cytokine-Mediated Cure of Infected Cells and cccDNA Loss during Cellular Proliferation
3.5. Model Robustness
3.5.1. Sensitivity to Viral Infectivity
3.5.2. Sensitivity to the Initial Infected Cell Population
3.6. Optimal Parameter Values for the 6 Acutely HBV Infected Patients
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Locarnini, S.; Hatzakis, A.; Chen, D.S.; Lok, A. Strategies to control hepatitis B: Public policy, epidemiology, vaccine and drugs. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S76–S86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandri, M.; Lutgehetmann, M.; Petersen, J. Experimental models and therapeutic approaches for HBV. Semin. Immunopathol. 2013, 35, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandri, M.; Petersen, J. Latest developments in the treatment of hepatitis B. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2016, 62, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chisari, F.V. Rous-Whipple Award Lecture. Viruses, immunity, and cancer: Lessons from hepatitis B. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 1117–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciupe, S.M.; Ribeiro, R.M.; Perelson, A.S. Antibody responses during hepatitis B viral infection. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whalley, S.A.; Murray, J.M.; Brown, D.; Webster, G.J.; Emery, V.C.; Dusheiko, G.M.; Perelson, A.S. Kinetics of acute hepatitis B virus infection in humans. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 193, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kock, J.; Schlicht, H.J. Analysis of the earliest steps of hepadnavirus replication: Genome repair after infectious entry into hepatocytes does not depend on viral polymerase activity. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 4867–4874. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fourel, I.; Cullen, J.M.; Saputelli, J.; Aldrich, C.E.; Schaffer, P.; Averett, D.R.; Pugh, J.; Mason, W.S. Evidence that hepatocyte turnover is required for rapid clearance of duck hepatitis B virus during antiviral therapy of chronically infected ducks. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 8321–8330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Rochford, R.; Chung, J.; Shapiro, M.; Purcell, R.; Chisari, F.V. Viral clearance without destruction of infected cells during acute HBV infection. Science 1999, 284, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandri, M.; Burda, M.R.; Will, H.; Petersen, J. Increased hepatocyte turnover and inhibition of woodchuck hepatitis B virus replication by adefovir in vitro do not lead to reduction of the closed circular DNA. Hepatology 2000, 32, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, K.A.; Joyce, M.A.; Addison, W.R.; Fischer, K.P.; Tyrrell, D.L. Superinfection exclusion in duck hepatitis B virus infection is mediated by the large surface antigen. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 7925–7937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, Y.C.; Jeng, K.S.; Chen, M.L.; Liu, H.H.; Liu, T.L.; Chen, Y.L.; Liu, Y.C.; Hu, C.P.; Chang, C. Evaluation of transcriptional efficiency of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA by reverse transcription-PCR combined with the restriction enzyme digestion method. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1813–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.M.; Purcell, R.H.; Wieland, S.F. The half-life of hepatitis B virions. Hepatology 2006, 44, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, W.S.; Litwin, S.; Xu, C.; Jilbert, A.R. Hepatocyte turnover in transient and chronic hepadnavirus infections. J. Viral Hepat. 2007, 14, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ugo, E.; Canitano, A.; Catone, S.; Argentini, C.; Giuseppetti, R.; Orobello, S.; Palmieri, G.; Rapicetta, M. Kinetics of WHV-HDV replication in acute fatal course of woodchuck hepatitis. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 2069–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hantz, O.; Parent, R.; Durantel, D.; Gripon, P.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C.; Zoulim, F. Persistence of the hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA in HepaRG human hepatocyte-like cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delius, H.; Gough, N.M.; Cameron, C.H.; Murray, K. Structure of the hepatitis B virus genome. J. Virol. 1983, 47, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, B.H.; Theele, D.; Litwin, S.; Toll, E.; Summers, J. Single-cell analysis of covalently closed circular DNA copy numbers in a hepadnavirus-infected liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12372–12377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutgehetmann, M.; Mancke, L.V.; Volz, T.; Helbig, M.; Allweiss, L.; Bornscheuer, T.; Pollok, J.M.; Lohse, A.W.; Petersen, J.; Urban, S.; et al. Humanized chimeric uPA mouse model for the study of hepatitis B and D virus interactions and preclinical drug evaluation. Hepatology 2012, 55, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassal, M. HBV cccDNA: viral persistence reservoir and key obstacle for a cure of chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2015, 64, 1972–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, H.C.; Lok, A.S.F.; Locarnini, S.A.; Zuckerman, A.J. Viral Hepatitis, 4th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; p. 624. [Google Scholar]
- Wieland, S.F.; Spangenberg, H.C.; Thimme, R.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. Expansion and contraction of the hepatitis B virus transcriptional template in infected chimpanzees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2129–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.M.; Stancevic, O.; Lutgehetmann, M.; Wursthorn, K.; Petersen, J.; Dandri, M. Variability in long-term hepatitis B virus dynamics under antiviral therapy. J. Theor. Biol. 2016, 391, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.M.; Goyal, A. In silico single cell dynamics of hepatitis B virus infection and clearance. J. Theor. Biol. 2015, 366, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, A.; Murray, J.M. Modelling the impact of cell-to-cell transmission in hepatitis B virus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.M.; Wieland, S.F.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. Dynamics of hepatitis B virus clearance in chimpanzees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 17780–17785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perelson, A.S. Modelling viral and immune system dynamics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perelson, A.S.; Ribeiro, R.M. Hepatitis B virus kinetics and mathematical modeling. Semin. Liver Dis. 2004, 24, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahari, H.; Shudo, E.; Ribeiro, R.M.; Perelson, A.S. Modeling complex decay profiles of hepatitis B virus during antiviral therapy. Hepatology 2009, 49, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, L.; Perelson, A.S. Modeling latently infected cell activation: Viral and latent reservoir persistence, and viral blips in HIV-infected patients on potent therapy. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewin, S.R.; Ribeiro, R.M.; Walters, T.; Lau, G.K.; Bowden, S.; Locarnini, S.; Perelson, A.S. Analysis of hepatitis B viral load decline under potent therapy: Complex decay profiles observed. Hepatology 2001, 34, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciupe, S.M.; Ribeiro, R.M.; Nelson, P.W.; Dusheiko, G.; Perelson, A.S. The role of cells refractory to productive infection in acute hepatitis B viral dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5050–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahari, H.; Cotler, S.J.; Layden, T.J.; Perelson, A.S. Hepatitis B virus clearance rate estimates. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1779–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, R.M.; Germanidis, G.; Powers, K.A.; Pellegrin, B.; Nikolaidis, P.; Perelson, A.S.; Pawlotsky, J.M. Hepatitis B virus kinetics under antiviral therapy sheds light on differences in hepatitis B e antigen positive and negative infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Dailey, P.J.; He, T.; Gettie, A.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Perelson, A.S.; Ho, D.D. Rapid clearance of simian immunodeficiency virus particles from plasma of rhesus macaques. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rong, L.; Perelson, A.S. Treatment of hepatitis C virus infection with interferon and small molecule direct antivirals: Viral kinetics and modeling. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 30, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, M.; Lythe, G.; Molina-Paris, C.; Ribeiro, R.M. Mathematics in modern immunology. Interface Focus 2016, 6, 20150093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graw, F.; Perelson, A.S. Modeling viral spread. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2016, 3, 555–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, B.J. The natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2009, 49, S45–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganem, D.; Prince, A.M. Hepatitis B virus infection--natural history and clinical consequences. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandri, M.; Locarnini, S. New insight in the pathobiology of hepatitis B virus infection. Gut 2012, 61, i6–i17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoletti, A.; Ferrari, C. Innate and adaptive immune responses in chronic hepatitis B virus infections: towards restoration of immune control of viral infection. Gut 2012, 61, 1754–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, R.J.; Chen, X.W.; Lu, M.J. Control of hepatitis B virus replication by interferons and Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 11618–11629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Protzer, U. Control of hepatitis B virus by cytokines. Viruses 2017, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, S.; Chokshi, S.; Riva, A.; Evans, A.; Williams, R.; Naoumov, N.V. CD8(+) T cell control of hepatitis B virus replication: Direct comparison between cytolytic and noncytolytic functions. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Ishikawa, T.; Hobbs, M.V.; Matzke, B.; Schreiber, R.; Chisari, F.V. Intracellular inactivation of the hepatitis B virus by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunity 1996, 4, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, L.V.; Guidotti, L.G.; Ishikawa, T.; Chisari, F.V. Posttranscriptional clearance of hepatitis B virus RNA by cytotoxic T lymphocyte-activated hepatocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 12398–12402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeger, C.; Mason, W.S. HBV replication, pathobiology and therapy: Unanswered questions. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S1–S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Stadler, D.; Lucifora, J.; Reisinger, F.; Webb, D.; Hosel, M.; Michler, T.; Wisskirchen, K.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, K.; et al. Interferon-γ and tumor necrosis factor-α produced by T cells reduce the HBV persistence form, cccDNA, without cytolysis. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allweiss, L.; Volz, T.; Giersch, K.; Kah, J.; Raffa, G.; Petersen, J.; Lohse, A.W.; Beninati, C.; Pollicino, T.; Urban, S.; et al. Proliferation of primary human hepatocytes and prevention of hepatitis B virus reinfection efficiently deplete nuclear cccDNA in vivo. Gut 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, C.L.; Chen, M.L.; Wu, Y.C.; Tsai, K.N.; Huang, C.C.; Hu, C.P.; Jeng, K.S.; Chou, Y.C.; Chang, C. Dynamics of HBV cccDNA expression and transcription in different cell growth phase. J. Biomed. Sci. 2011, 18, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutgehetmann, M.; Volz, T.; Kopke, A.; Broja, T.; Tigges, E.; Lohse, A.W.; Fuchs, E.; Murray, J.M.; Petersen, J.; Dandri, M. In vivo proliferation of hepadnavirus-infected hepatocytes induces loss of covalently closed circular DNA in mice. Hepatology 2010, 52, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, W.S.; Xu, C.; Low, H.C.; Saputelli, J.; Aldrich, C.E.; Scougall, C.; Grosse, A.; Colonno, R.; Litwin, S.; Jilbert, A.R. The amount of hepatocyte turnover that occurred during resolution of transient hepadnavirus infections was lower when virus replication was inhibited with entecavir. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 1778–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoletti, A.; Gehring, A.J. The immune response during hepatitis B virus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, P.T.F.; Litwin, S.; Dolman, G.E.; Bertoletti, A.; Mason, W.S. Immune tolerant chronic hepatitis B: The unrecognized risks. Viruses 2017, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajino, K.; Jilbert, A.R.; Saputelli, J.; Aldrich, C.E.; Cullen, J.; Mason, W.S. Woodchuck hepatitis-virus infections - very rapid recovery after a prolonged viremia and infection of virtually every hepatocyte. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 5792–5803. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Cullen, J.; Saputelli, J.; Aldrich, C.E.; Miller, D.S.; Litwin, S.; Furman, P.A.; Jilbert, A.R.; Mason, W.S. Kinetics of hepadnavirus loss from the liver during inhibition of viral DNA synthesis. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucifora, J.; Xia, Y.; Reisinger, F.; Zhang, K.; Stadler, D.; Cheng, X.; Sprinzl, M.F.; Koppensteiner, H.; Makowska, Z.; Volz, T.; et al. Specific and nonhepatotoxic degradation of nuclear hepatitis B virus cccDNA. Science 2014, 343, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucifora, J.; Protzer, U. Attacking hepatitis B virus cccDNA—The holy grail to hepatitis B cure. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S41–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisari, F.V.; Mason, W.S.; Seeger, C. Virology. Comment on “Specific and nonhepatotoxic degradation of nuclear hepatitis B virus cccDNA”. Science 2014, 344, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reaiche-Miller, G.Y.; Thorpe, M.; Low, H.C.; Qiao, Q.; Scougall, C.A.; Mason, W.S.; Litwin, S.; Jilbert, A.R. Duck hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA appears to survive hepatocyte mitosis in the growing liver. Virology 2013, 446, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuntz, E.; Kuntz, H.-D. Morphology of the Liver. In Hepatology Textbook and Atlas: History·Morphology Biochemistry·Diagnostics Clinic·Therapy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock, S.; Dooley, J. Diseases of the Liver and Biliary System, 11th ed.; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Michalopoulos, G.K. Liver regeneration. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 213, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kmiec, Z. Cooperation of liver cells in health and disease. Adv. Anat. Embryol. Cell Biol. 2001, 161, 1–151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ciupe, S.M.; Ribeiro, R.M.; Nelson, P.W.; Perelson, A.S. Modeling the mechanisms of acute hepatitis B virus infection. J. Theor. Biol. 2007, 247, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandri, M.; Murray, J.M.; Lutgehetmann, M.; Volz, T.; Lohse, A.W.; Petersen, J. Virion half-life in chronic hepatitis B infection is strongly correlated with levels of viremia. Hepatology 2008, 48, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawelek, K.A.; Huynh, G.T.; Quinlivan, M.; Cullinane, A.; Rong, L.; Perelson, A.S. Modeling within-host dynamics of influenza virus infection including immune responses. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedj, J.; Rotman, Y.; Cotler, S.J.; Koh, C.; Schmid, P.; Albrecht, J.; Haynes-Williams, V.; Liang, T.J.; Hoofnagle, J.H.; Heller, T.; et al. Understanding early serum hepatitis D virus and hepatitis B surface antigen kinetics during pegylated interferon-α therapy via mathematical modeling. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furchtgott, L.A.; Chow, C.C.; Periwal, V. A model of liver regeneration. Biophys. J. 2009, 96, 3926–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reluga, T.C.; Dahari, H.; Perelson, A.S. Analysis of hepatitis C virus infection models with hepatocyte homeostasis. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2009, 69, 999–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahari, H.; Layden-Almer, J.E.; Kallwitz, E.; Ribeiro, R.M.; Cotler, S.J.; Layden, T.J.; Perelson, A.S. A mathematical model of hepatitis C virus dynamics in patients with high baseline viral loads or advanced liver disease. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 1402–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Vargas, E.A.; Wilk, E.; Canini, L.; Toapanta, F.R.; Binder, S.C.; Uvarovskii, A.; Ross, T.M.; Guzman, C.A.; Perelson, A.S.; Meyer-Hermann, M. Effects of aging on influenza virus infection dynamics. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 4123–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R.; Huyvaert, K.P. AIC model selection and multimodel inference in behavioral ecology: Some background, observations, and comparisons. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2011, 65, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabozzi, F.J.; Focardi, S.M.; Rachev, S.T.; Arshanapalli, B.G. Appendix E: Model selection criterion: AIC and BIC. In The Basics of Financial Econometrics; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 399–403. [Google Scholar]
- Kenneth, P.; Burnham, D.R.A. Information and Likelihood Theory: A Basis for Model Selection and Inference. In Model Selection and Multimodel Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach; Burnham, K.P., Anderson, D.R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 49–97. [Google Scholar]
- Summers, J.; Jilbert, A.R.; Yang, W.; Aldrich, C.E.; Saputelli, J.; Litwin, S.; Toll, E.; Mason, W.S. Hepatocyte turnover during resolution of a transient hepadnaviral infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11652–11659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhi, H.; Guicciardi, M.E.; Gores, G.J. Hepatocyte death: A clear and present danger. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 1165–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmi, A.; Ruzzenente, A.; Conci, S.; Valdegamberi, A.; Iacono, C. How much remnant is enough in liver resection? Dig. Surg. 2012, 29, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruttadauria, S.; Parikh, V.; Pagano, D.; Tuzzolino, F.; Cintorino, D.; Miraglia, R.; Spada, M.; Vizzini, G.; Luca, A.; Gridelli, B. Early regeneration of the remnant liver volume after right hepatectomy for living donation: a multiple regression analysis. Liver Transplant. 2012, 18, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishi, Y.; Abdalla, E.K.; Chun, Y.S.; Zorzi, D.; Madoff, D.C.; Wallace, M.J.; Curley, S.A.; Vauthey, J.N. Three hundred and one consecutive extended right hepatectomies: Evaluation of outcome based on systematic liver volumetry. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Unalp, A.; Creer, M.H. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network. Influence of local reference populations on upper limits of normal for serum alanine aminotransferase levels. Arch. Intern. Med. 2008, 168, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.R.; Flamm, S.L.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Bodenheimer, H.C. Public Policy Committee of the American Association for the Study of Liver, D. Serum activity of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) as an indicator of health and disease. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoletti, A.; Gehring, A.J. Immune therapeutic strategies in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: Virus or inflammation control? PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, C.; Penna, A.; Bertoletti, A.; Valli, A.; Antoni, A.D.; Giuberti, T.; Cavalli, A.; Petit, M.A.; Fiaccadori, F. Cellular immune response to hepatitis B virus-encoded antigens in acute and chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Immunol. 1990, 145, 3442–3449. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bertoletti, A.; Ferrari, C. Kinetics of the immune response during HBV and HCV infection. Hepatology 2003, 38, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, Q.; Xia, N. Detection of HBV covalently closed circular DNA. Viruses 2017, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allweiss, L.; Dandri, M. The role of cccDNA in HBV maintenance. Viruses 2017, 9, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, W.S.; Liu, C.; Aldrich, C.E.; Litwin, S.; Yeh, M.M. Clonal expansion of normal-appearing human hepatocytes during chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 8308–8315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, C.T.; Chiu, H.T.; Chu, C.M.; Liaw, Y.F. G1 phase dependent nuclear localization of relaxed-circular hepatitis B virus DNA and aphidicolin-induced accumulation of covalently closed circular DNA. J. Med. Virol. 1998, 55, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, A.; Khaoustov, V.I.; Mearns, M.; Lewis, D.E.; Genta, R.M.; Darlington, G.J.; Yoffe, B. Effect of hepatocyte proliferation and cellular DNA synthesis on hepatitis B virus replication. Gastroenterology 1996, 110, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandri, M.; Petersen, J. Mechanism of hepatitis B virus persistence in hepatocytes and its carcinogenic potential. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, S281–S288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiang, M.; Rooney, J.F.; Toole, J.J.; Gibbs, C.S. Biphasic clearance kinetics of hepatitis B virus from patients during adefovir dipivoxil therapy. Hepatology 1999, 29, 1863–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, M.A.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Hill, A.M.; Boehme, R.; Thomas, H.C.; McDade, H. Viral dynamics in hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 4398–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, B.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Kong, H.; Tian, L.; Chen, Y. T-cell exhaustion in chronic hepatitis B infection: Current knowledge and clinical significance. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.S.; Cox, M.A.; Zajac, A.J. T-cell exhaustion: Characteristics, causes and conversion. Immunology 2010, 129, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyaoka, Y.; Miyajima, A. To divide or not to divide: Revisiting liver regeneration. Cell Div. 2013, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasue, N.; Yukaya, H.; Ogawa, Y.; Kohno, H.; Nakamura, T. Human liver regeneration after major hepatic resection. A study of normal liver and livers with chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis. Ann. Surg. 1987, 206, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Model | Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 5 | Patient 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | ||||||
| HT | 1.26 | 0.72 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.78 | 0.82 |
| LCN | 52.6 | 91.8 | 69.3 | 72.4 | 79.3 | 75 |
| M2 | ||||||
| HT | 1.5 | 1.27 | 1.02 | 1.0 | 1.05 | 1.01 |
| LCN | 43.8 | 51.1 | 44.1 | 42.9 | 45.5 | 43.5 |
| M3 | ||||||
| HT | 1.34 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 1.0 | 0.98 | 0.99 |
| LCN | 49.6 | 83.5 | 98.3 | 64.8 | 66 | 68.5 |
| Model | Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 5 | Patient 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M4 | ||||||
| HT | 1.49 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 |
| LCN | 43.8 | 93.6 | 98.2 | 99.5 | 98.9 | 99.8 |
| NDT | 0.001 | 0.851 | 0.905 | 1.01 | 0.963 | 0.984 |
| M5 | ||||||
| HT | 1.26 | 0.69 | 0.7 | 0.84 | 0.62 | 0.79 |
| LCN | 52.7 | 92.3 | 98.5 | 72.1 | 98.8 | 76.7 |
| NDT | 0.002 | 0.047 | 0.008 | 0.006 | 0.113 | 0.029 |
| Patient | /Day | Vir/Cell·Day | /Day | /Day | HT | AICC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient 1 | 0.58 | 788 | 0.92 | 0.20 | 1.26 | 14.08 |
| Patient 2 | 0.03 | 5.7 | 0.83 | 0.24 | 0.72 | −29.31 |
| Patient 3 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.67 | 0.05 | 0.83 | −15.66 |
| Patient 4 | 0.09 | 5.30 | 0.67 | 0.10 | 0.84 | 9.94 |
| Patient 5 | 0.05 | 1.80 | 0.67 | 0.10 | 0.78 | 23.96 |
| Patient 6 | 0.07 | 3.8 | 0.87 | 0.10 | 0.82 | 19.77 |
| Median | 0.065 | 4.55 | 0.75 | 0.10 | 0.825 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goyal, A.; Ribeiro, R.M.; Perelson, A.S. The Role of Infected Cell Proliferation in the Clearance of Acute HBV Infection in Humans. Viruses 2017, 9, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9110350
Goyal A, Ribeiro RM, Perelson AS. The Role of Infected Cell Proliferation in the Clearance of Acute HBV Infection in Humans. Viruses. 2017; 9(11):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9110350
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoyal, Ashish, Ruy M. Ribeiro, and Alan S. Perelson. 2017. "The Role of Infected Cell Proliferation in the Clearance of Acute HBV Infection in Humans" Viruses 9, no. 11: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9110350
APA StyleGoyal, A., Ribeiro, R. M., & Perelson, A. S. (2017). The Role of Infected Cell Proliferation in the Clearance of Acute HBV Infection in Humans. Viruses, 9(11), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/v9110350