Hydrocolonic Sonography: Description of the Technique and Its Application in a Case of Intracolonic Lipoma: Report about a Case
Abstract
:1. Introduction
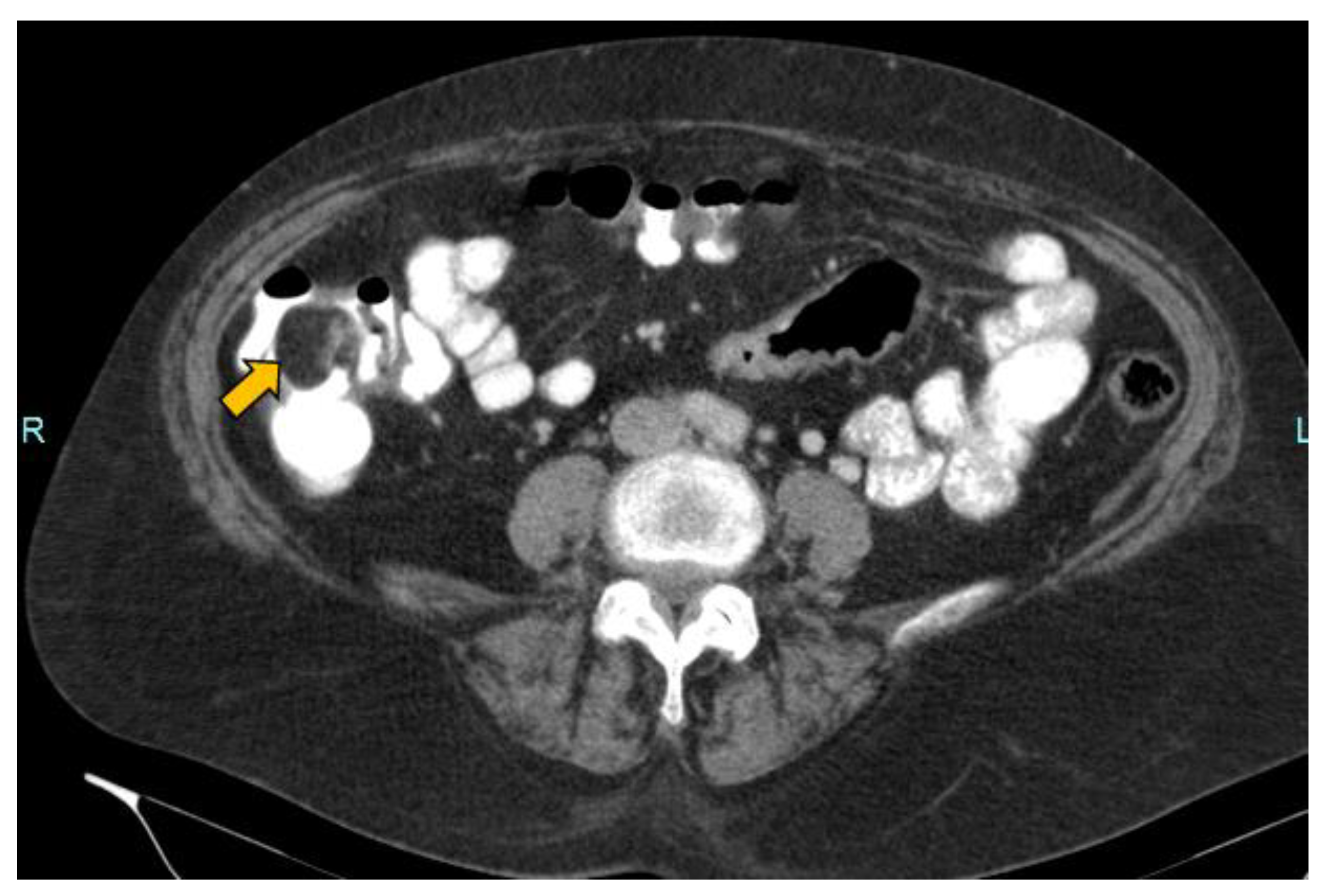
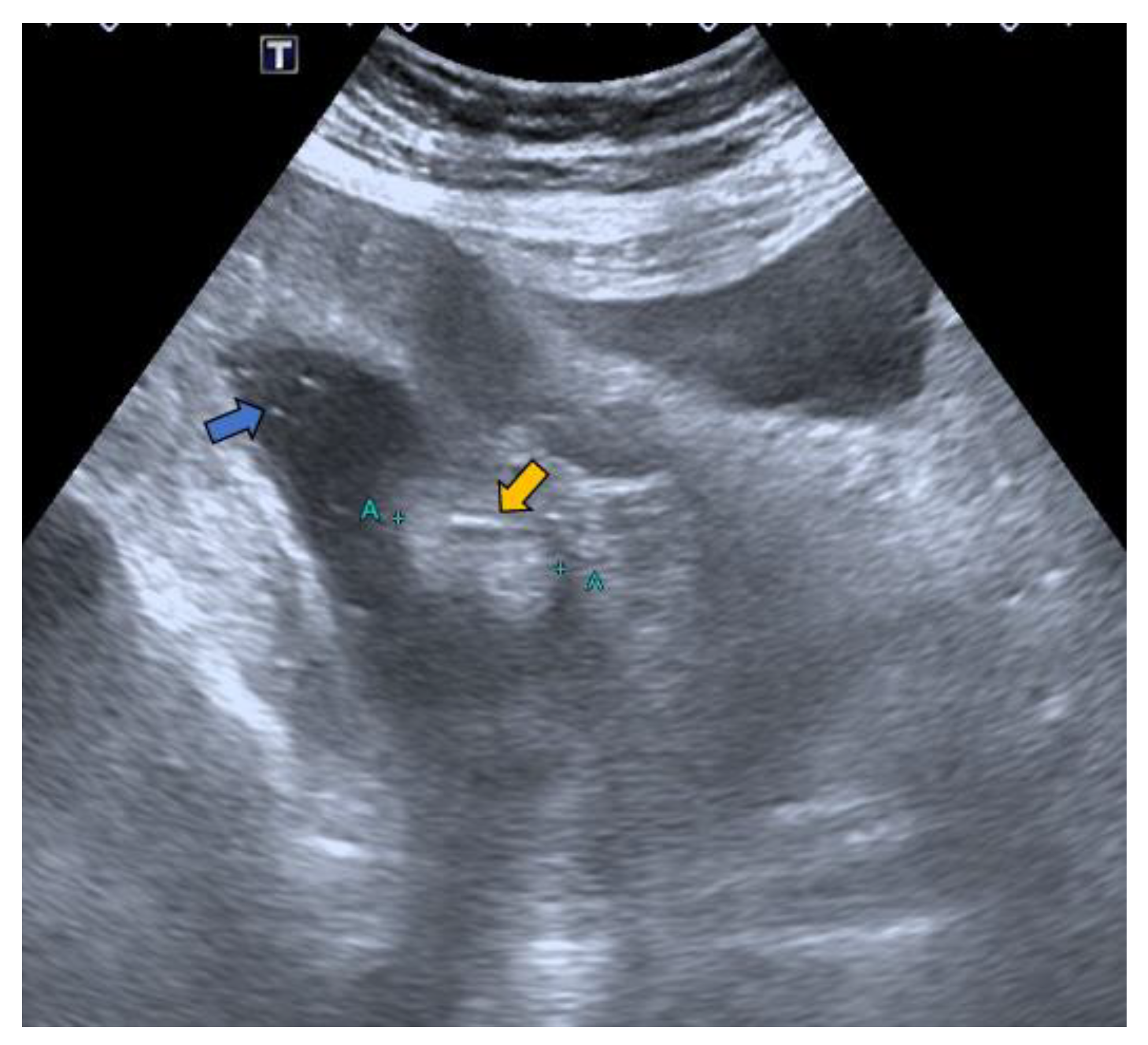
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
- Follow-up time: In a long-term follow-up in which the patient will undergo numerous check-ups, the use of a technique that does not include radiation is advisable. In this way, the patient’s exposure to radiation is reduced, and the time between check-ups can be shortened without fear of harming the patient.
- Lesion size: The sensitivity of HS in the detection of lesions larger than 10 mm is 93% [20]. In our case of a lesion size of 33 mm, it was possible to avoid the discomfort associated with the cleansing preparation. In a recent study, 18 mm lesions were detected with HS without using cleansing preparation [20].
- Lesion location: The segment of the colon in which the lesion is located is an important factor if HS is to be used in follow-up. The rectum is a non-assessable segment. The position of the sigma in the pelvis, the disposition of the transverse colon [20] or the existence of dolichomegalosigma [15,20] are factors that limit the study of these colonic segments. However, the cecum, and ascending and descending colon are more superficial segments and are easier to assess by HS. Our lesion located in the cecum is accessible by HS. However, studying the cecum has peculiarities. First, the presence of faecal remains. Faecal remains frequently accumulate in the right colon [14,15,20]. Faecal remains are observed in the lumen of the colon during retrograde instillation of saline solution and can be moved by using the transducer to compress the abdomen rapidly and lightly [10,11,14,20]. Moving the patient sideways also allows the faecal matter to be displaced, allowing better visualisation. However, they can sometimes be abundant. The concentration of faecal matter can be reduced by increasing the infusion of saline solution [14] if the patient can tolerate it. It is also possible to decrease the faecal concentration by emptying and refilling the colon [20]. Thus, the saline solution together with the faecal remains return to the bag and a new bag of saline solution is used. Second, the ileocecal valve can also be mistaken for a lipoma. The ileocecal valve is seen as a pseudopolyp image projecting into the colon lumen from the ileocecal junction [38] (Figure 4). A lipoma in the cecum may be confused with lipomatosis of the ileocecal valve, which is a more common entity than lipoma [7,36].
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crocetti, D.; Sapienza, P.; Sterpetti, A.V.; Paliotta, A.; De Gori, A.; Pedulla, G.; De Toma, G. Surgery for syntomatic colon lipoma: A systematic review of the literature. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 6271–6276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rogers, S.O., Jr.; Lee, M.C.; Ashley, S.W. Giant colonic lipoma as lead point for intermittent colo-colonic intussusception. Surgery 2002, 131, 687–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nallamothu, G.; Adler, D.G. Large colonic lipomas. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 7, 490–492. [Google Scholar]
- Rogy, M.A.; Mirza, D.; Berlakovich, G.; Winkellbauer, F.; Rauhs, R. Submucous large-bowell lipomas presentation and management: An 18-year study. Eur. J. Surg. 1991, 157, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Law, Y.Y.; Patel, R.; Cusick, M.; Van Eps, J.L. A case of colonic intussception and obstruction secondary to giant colonic lipoma. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2020, 10, rjaa429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsinelos, P.; Chatzimavroudis, G.; Zavos, C.; Pilpilidis, I.; Lazaraki, G.; Papaziogas, B.; Paroutoglou, G.; Kountouras, J.; Paikos, D. Cecal lipoma with psuedomalignant features. A case report and review of the literature. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 2510–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, M.M.; Win, T.T.; Rasheed, S. A Cecal lipoma causing intussuscepction, detected on routine outpatient abdominal ultrasound. J. Med. Ultrasound 2020, 28, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Jiang, L.S.; Li, F.Y.; Ye, H.; Li, N.; Cheng, N.S.; Zhou, Y. Giant submubosal lipoma located in the descending colon: A case report and review of the literature. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 5664–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsiaousidou, A.; Chatzitheoklitos, E.; Hatzis, I.; Alatsakis, M.; Katsourakis, A. Giant transmural lipoma of the sigmoid colon. Hippokratia 2012, 16, 278–279. [Google Scholar]
- Limberg, B. Diagnosis of large bowell tumors by colonic sonography. Lancet 1990, 335, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limberg, B. Diagnosis and staging of colonic tumors by conventional abdominal sonography as compared with hydrocolonic sonography. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 327, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Socorro, C.R.; Guerra, C.; Hernández-Romero, J.; Rey, A.; López-Facal, P.; Alvaréz-Santullano, V. Colorectal carninomas: Diagnosis and preoperative staging by hydrocolonic sonography. Surgery 1995, 117, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candia, C.; Ciacci, V.; Di Segni, R.; Santini, E. Hydrocolonic sonography in the study of colonic diseases: Comparision with double-contrast enema. Radiol. Med. 1995, 89, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ling, U.P.; Chen, J.Y.; Hwang, C.J.; Lin, C.K.; Chang, M.H. Hydrosonography in the evaluation of colorectal polyps. Arch. Dis. Child. 1995, 73, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segura, J.M.; Molina, E.; Herrera, A.; Berges, M.A.; Erdozain, J.C.; Arjonilla, A.; Suárez, J.M. Hidrocolonic ultrasonography in the detection of tumoral processes in the inferior gastrointestinal tract. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 1998, 90, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dixit, R.; Chowdhury, V.; Kumar, N. Hydrocolonic sonography in the evaluation of colonic lesions. Abdom. Imaging 1999, 24, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maconi, G.; Radice, E.; Bareggi, E.; Porro, G.B. Hydronosonography of the gastrointestinal tract. AJR 2009, 193, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira, A.; Pereira, E.; Baldaque-Silva, F.; Pereira, B.; Sousa, R.; Tristan, J.; Banhudo, A. Role of hydrocolonic sonography in the detection of colonic neoplastic lesions. J. Diagn. Med. Sonogr. 2011, 27, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siripongsakun, S.; Charoenvisal, L.; Pantongrag-Brown, L.; Dusitanond, N.; Siripongpreeda, B. Hydrocolonic sonography: A complete corectal evaluation technique with preliminary results. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2013, 41, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez García, D.; Maria, T.B.A.; Javier, E.B.M.; Jose, M.L.L.; Carlos, B.R.; Francisco, J.M.P.; Miguel Angel, M.R.; Maria Luz, P.M.; Mihaela Alina, G.; Paula, R.E. Hydrocolonic sonography. A Forgotten technique. Jpn. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Carl Rubin, D.O.; Alfred, B.; Kurtz, M.D.; Barry, B.; Goldberg, M.D. Water enema: A new ultrasound technique in defining pelvic anatomy. J. Clin. Ultrasound 1978, 6, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limberg, B.; Osswald, B. Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease by hydrocolonic sonography. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1994, 89, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar]
- Bru, C.; Sans, M.; Defelitto, M.M.; Gilabert, R.; Fuster, D.; Llach, J.; Lomeña, F.; Bordas, J.M.; Piqué, J.M.; Panés, J. Hydrocolonic sonography for evaluating inflammatory bowel disease. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2001, 177, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parente, F.; Greco, S.; Molteni, M.; Cucino, C.; Maconi, G.; Sampietro, G.M.; Danelli, P.G.; Cristaldi, M.; Bianco, R.; Gallus, S.; et al. Role of early ultrasound in detecting inflammatory intestinal disorders and identifying their anatomical location within the bowel. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 18, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düx, M. Hydrocolonic sonography. Abdom. Imaging 1999, 24, 506–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, D.W.; Gooding, G.A.; McQuaid, K.R.; Griswold, V.; Grendell, J.H. Hydrocolonic ultrasonography in the detection of colonic polyps and tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 332, 1685–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düx, M.; Roeren, T.; Kuntz, C.; Ritcher, G.M.; Kauffmann, G.W. TNM staging of gastrointestinal tumors by hydrosonography: Results of a histopathologically controlled study in 60 patients. Abdom. Imaging 1997, 22, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulhall, B.P.; Veerappan, G.R.; Jackson, J.L. Meta-analysis: Computed tomographic colonography. Ann. Intern. Med. 2005, 142, 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, D.R.; Mehrzad, H.; Patel, R.; Dadds, J.; Pallan, A.; Karandikar, S.S.; Roy-Choudhury, S. CT colonography for synchronous colorectal lesions in patients with colorectal cancer: Initial experience. Eur. Radiol. 2010, 20, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, E.; Faggioni, L.; Cerri, F.; Turini, F.; Angeli, S.; Cini, L.; Perrone, F.; Paolicchi, F.; Bartolozzi, C. CT colonography versus double-contrast barium enema for screening of colorectal cancer: Comparison of radiation burden. Abdom. Imaging 2010, 35, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, D.F.; Govil, S.; Korula, A.; William, R.R.; Chandy, G. Pedunculated colonic polyp diagnosed by colonic sonography. Pediatr. Radiol. 1992, 22, 148–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagita, A.; Amemoto, K.; Yoden, A.; Yamazaki, T.; Mino, M.; Miyoshi, H. Ultrasonographic diagnosis of juvenile colonic polyps. J. Pediatr. 1994, 124, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, A.J.; Thomas, M.L.; Roediger, E.W.; Hewett, P.J. Localization of the nonpalpable colonic lesion with intraoperative ultrasound. Surg. Endosc. 1999, 13, 526–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luck, A.; Copley, J.; Hewett, P. Ultrasound of colonic neoplasia. An operative tool? Surg. Endosc. 2000, 14, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greif, F.; Belenky, A.; Aranovich, D.; Yampolski, I.; Hannanel, N. Intraoperative ultrasonography: A tool for localizing small colonic colonic polyps. Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 2005, 20, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, W.M. Imaging and findings of lipomas of the gastrointestinal tract. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2005, 184, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinis, A.; Yiallourou, A.; Samanides, L.; Dafnios, N.; Anastasopoulos, G.; Vassiliou, I.; Theodosopoulos, T. Intussusception of the bowell in adults: A rewiew. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limberg, B. Diagnosis of inflammatory and tumorous changes of the large intestine using colonic sonography. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 1986, 111, 1273–1276. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Indications |
|
| Limitations |
|
| Limiting Factors |
|
| Advantages |
|
| Procedure Description |
|
| Materials |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García, D.M.; Alcaráz, M.T.B.; Gonzalez, G.M.; Molina, J.E.B.; Rosique, C.B.; Pina, F.J.M.; Rodenas, M.Á.M. Hydrocolonic Sonography: Description of the Technique and Its Application in a Case of Intracolonic Lipoma: Report about a Case. Gastroenterol. Insights 2022, 13, 173-181. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent13020018
García DM, Alcaráz MTB, Gonzalez GM, Molina JEB, Rosique CB, Pina FJM, Rodenas MÁM. Hydrocolonic Sonography: Description of the Technique and Its Application in a Case of Intracolonic Lipoma: Report about a Case. Gastroenterology Insights. 2022; 13(2):173-181. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent13020018
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía, Diego Martínez, Maria Teresa Belmonte Alcaráz, Guilda Morell Gonzalez, Javier Emilio Brugal Molina, Carlos Ballester Rosique, Francisco Jose Menarguez Pina, and Miguel Ángel Morcillo Rodenas. 2022. "Hydrocolonic Sonography: Description of the Technique and Its Application in a Case of Intracolonic Lipoma: Report about a Case" Gastroenterology Insights 13, no. 2: 173-181. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent13020018
APA StyleGarcía, D. M., Alcaráz, M. T. B., Gonzalez, G. M., Molina, J. E. B., Rosique, C. B., Pina, F. J. M., & Rodenas, M. Á. M. (2022). Hydrocolonic Sonography: Description of the Technique and Its Application in a Case of Intracolonic Lipoma: Report about a Case. Gastroenterology Insights, 13(2), 173-181. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastroent13020018






