Abstract
The bidirectional communication network between the gut and the brain, known as the gut–brain axis, plays a crucial role in health and disease. This review explores the mechanisms underlying gut–brain interaction disorders and highlights translational therapies bridging neurology and gastroenterology. Mechanisms encompass anatomical, endocrine, humoral, metabolic, and immune pathways, with the gut microbiota exerting profound influence. Clinical evidence links gut microbiota fluctuations to mood disorders, GI disruptions, and neurodevelopmental conditions, emphasizing the microbiome’s pivotal role in shaping brain–gut interactions. Pharmacological therapies such as amitriptyline and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors modulate neurotransmitter activity, offering relief in functional gastrointestinal disorders like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Non-pharmacological interventions like cognitive–behavioral therapy and hypnotherapy address maladaptive thoughts and induce relaxation, alleviating gastrointestinal symptoms exacerbated by stress. Emerging therapies include gut microbiota modulation, dietary interventions, vagus nerve stimulation, and intestinal barrier modulation, offering novel approaches to manage neurological disorders via the gastrointestinal tract. Understanding and harnessing the gut–brain axis holds promise for personalized therapeutic strategies in neurogastroenterology.
1. Introduction
The gut–brain axis constitutes a bidirectional communication network bridging the enteric and central nervous systems, encompassing anatomical, endocrine, humoral, metabolic, and immune pathways [1]. Interactions between the autonomic nervous system, hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis, and GI tract nerves facilitate mutual influence, with the brain modulating intestinal activities and the gut impacting mood, cognition, and mental health. Enteric microbiota profoundly affect this relationship, influencing emotional regulation, neuromuscular function, and HPA regulation [2]. Clinical evidence highlights associations between gut microbiota fluctuations and mood disorders, GI disruptions, and neurodevelopmental conditions, emphasizing the pivotal role of the microbiome in shaping gut-brain interactions and cognitive function [3].
Recent preclinical studies have underscored the bidirectional interactions between the brain, gut, and microbiome (BGM), shedding light on their role in health and disease. Notably, alterations in these interactions have been implicated in a spectrum of disorders ranging from irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) to psychiatric and neurological conditions such as affective disorders, autism spectrum disorders (ASD), Parkinson’s disease, and chronic pain [4]. Understanding the intricate mechanisms governing gut–brain interactions is of paramount importance due to their profound implications for behavior, physiology, and overall health. The bidirectional nature of the gut–brain axis stems from the ability of gut microbes to not only respond to, but also actively shape, neuronal activity and plasticity [5]. Various pathways, including neurological, endocrine, humoral/metabolic, and immune routes, orchestrate this complex communication network. Microbiota-derived metabolites, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and lipopolysaccharides (LPS), play pivotal roles in modulating neurotransmitter activity, stress responsiveness, and inflammatory processes, thereby impacting behavior and mood regulation. Dysbiosis, characterized by microbial imbalance, contributes to chronic inflammation implicated in conditions like depression and autoimmune diseases [1]. Moreover, the integrity of the intestinal barrier, regulated by the microbiome, is crucial for systemic health, with disruptions implicated in various gastrointestinal and systemic disorders. Promisingly, interventions targeting the microbiome offer potential therapeutic avenues for restoring barrier function and alleviating inflammation, highlighting the translational significance of gut–brain axis research for neurological and psychiatric disorders. Continued investigation into microbiota-based interventions holds promise for advancing our understanding and treatment of these complex conditions [6].
However, not only do the gut microbiota influence the nervous system, but also, a vast array of neuromodulating substances are able to relieve many gastrointestinal complaints [7]. The aim of this comprehensive review is to delve into the intricate interactions between the nervous and gastrointestinal systems, exploring emerging therapies that target both systems, leveraging the potential of neuromodulating substances and microbiome-based interventions.
2. Search Strategy
For the literature review, comprehensive searches were conducted across multiple databases, including PubMed/MEDLINE, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, PsycINFO, Cochrane Library, and Google Scholar. The search strategy utilized a combination of Medical Subject Headings (MESH) terms and free-text words. The search strings were constructed using Boolean operators to combine relevant terms, such as (“Gut-brain axis” AND “Neurological disorders”) OR (“Neurogastroenterology” AND “Gastrointestinal disorders”) OR (“Mucosal immune system” AND “Enteric nervous system”) OR (“Microbiota-gut-brain axis” AND “Functional gastrointestinal disorders”). Articles were retrieved by systematically screening the search results based on predefined inclusion criteria, including peer-reviewed journals, relevance to mechanisms and translational therapies of gut–brain interaction disorders, incorporation of both neurological and gastrointestinal perspectives, and publication within the last 10–15 years to ensure inclusion of recent advancements. Additionally, relevant articles from the reference lists of included studies and key review articles were hand-searched to identify additional relevant literature. However, our aim was to provide a broad overview of the topic while guiding readers to specific references for more detailed information.
3. Mechanisms of Gut–Brain Interaction
The gut–brain axis encompasses a multifaceted network of communication pathways involving neural, microbial, immune, and endocrine signaling. Understanding the mechanisms underlying gut–brain interactions is essential for clarifying the pathophysiology of various disorders and developing targeted therapeutic interventions aimed at restoring homeostasis within this complex system. While animal models, particularly in mice, have elucidated key aspects of this interaction, their translation to human therapeutics remains challenging, prompting a critical examination of how to enhance the translational value of preclinical research [8].
3.1. Neural Pathways
Neural pathways play a crucial role in the gut–brain axis, facilitating communication between the gut and the brain through the vagus nerve, which serves as a major conduit for this bidirectional signaling. Recent findings highlight its role in regulating peripheral regulatory T cells (pTregs) in the gut, influenced by the vago–vagal reflex mediated by gut microbiota information. Understanding this gut–brain axis mechanism could lead to the development of neurostimulatory therapies targeting the complex gut–brain association [9] This bi-directional conduit carries sensory information from the gut to the brainstem’s nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS), where it undergoes integration and processing. The nucleus solitarius (NTS) emerges as a critical hub in the intricate neural circuits that govern feeding behavior and energy balance regulation. By employing advanced techniques such as optogenetics and neural activity monitoring, researchers have uncovered specific subsets of NTS neurons, particularly those expressing prodynorphin, that exert profound effects on appetite suppression and energy expenditure [10]. Subsequently, efferent signals are sent back to the gut, influencing various gastrointestinal functions, including motility, secretion and visceral perception [5]. This neural communication pathway plays a significant role in regulating appetite, satiety and digestive processes [11]. All of this intricate process ensures metabolic homeostasis and efficient digestion [12].
3.2. Microbiota–Brain Axis
The gut microbiota consist of trillions of microorganisms residing in the gastrointestinal tract that exert profound effects on the brain function through the microbiota–brain axis. Microbial metabolites, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), neurotransmitters, and immunomodulatory molecules, can influence neural activity and neurotransmitter synthesis within the brain [13,14]. The brain exerts significant influence on the gut microbiota through efferent signals, which are mediated by both the autonomic nervous system and the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis. These signals, triggered by various psychological stressors, lead to alterations in gut microbial composition and biomass, impacting the microbiotic profile and reducing the relative proportions of main phyla. Additionally, the brain modulates gut functions crucial for microbial habitat maintenance, such as motility, secretion, and mucosal immune response, which can indirectly affect microbiota composition and function. Furthermore, stress-induced changes in intestinal permeability impact systemic inflammation and neuronal function. By also affecting immune responses, this disintegration of the intestinal barrier may facilitate the expression of virulent bacteria, highlighting the intricate interplay between the brain, gut, and microbiota in response to stress [5,15]. The dysregulation of the microbiota–brain axis has been implicated in exacerbating the course of various neurological and psychiatric disorders spanning conditions such as depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, autism spectrum disorders (ASD), Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease. Dysfunctions in the gut microbiota composition and function can influence symptoms of these disorders through several interconnected mechanisms. These include the dysregulation of immune responses leading to chronic inflammation, alterations in neurotransmitter levels affecting mood and cognition, and disruptions in the gut barrier integrity, allowing pathogenic substances to enter the bloodstream and affect brain function. These findings highlight the importance of maintaining a balanced gut microbiome for optimal brain health. The microbiota–gut–brain axis plays a crucial role in the pathophysiology of various neuropsychiatric disorders [16]. Furthermore, emerging evidence suggests that alterations in the gut microbiota composition and function can contribute to the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [17].
3.3. Immune System Modulation
The gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) plays a crucial role in immune system modulation, and serves as a link between the gut and the brain [18]. Immune cells within the gastrointestinal tract (such as T cells, B cells, and dendritic cells) communicate with the central nervous system through cytokines and other immune mediators. In the intricate network of the intestinal neuro-immune axis, communication occurs between neurons, immune cells, and microorganisms. The crosstalk between these components underscores the dynamic interplay shaping gut health and immune responses. Understanding these interactions is pivotal for elucidating the mechanisms underlying gastrointestinal disorders and developing targeted interventions for therapeutic benefit [19]. The activation of the immune system in the gut can trigger systemic inflammation and immune responses that impact brain function and behavior. Conversely, alterations in brain function, such as stress, can modulate immune activity in the gut, leading to changes in gut permeability and microbial composition [20]. This bidirectional communication between the immune system and the brain is integral to maintaining adequate adaptation in responding to environmental challenges.
3.4. Link with Endocrine System
The endocrine system plays a crucial role in mediating communication between the gut and the brain through the release of hormones and neuropeptides [21]. The gut–brain axis orchestrates a complex interplay between the gastrointestinal tract, the brain, and the endocrine system, allowing it to regulate appetite and satiety. Hormones like ghrelin, known as the “hunger hormone”, are produced in the stomach and signal the brain to stimulate appetite. Conversely, leptin, produced by adipose tissue, acts as a “satiety hormone” by signaling to the brain when the body has had enough food. Additionally, peptide YY, released by cells in the intestines in response to food intake, promotes feelings of fullness and suppresses appetite. Understanding the intricate neuroendocrine mechanisms involved in appetite regulation provides valuable insights into combating obesity and metabolic disorders [22]. These hormones bind to specific receptors in the hypothalamus, triggering neuronal pathways that regulate food intake, energy expenditure and metabolic processes [23]. Additionally, hormones like cortisol and adrenaline can influence gut motility, barrier function and immune responses [24]. Metabolic syndrome induces dysregulation in the gut–brain axis, characterized by altered communication between the gut microbiota, the endocrine system, and the central nervous system. This disruption contributes to systemic inflammation, insulin resistance, and dyslipidemia, which in turn affect gastrointestinal function and neuroinflammation. Ultimately, these disturbances in the gut–brain axis can lead to cognitive impairment, neurodegenerative diseases, and compromised integrity of the blood–brain barrier, highlighting the intricate interplay between metabolic health and neurological function [25].
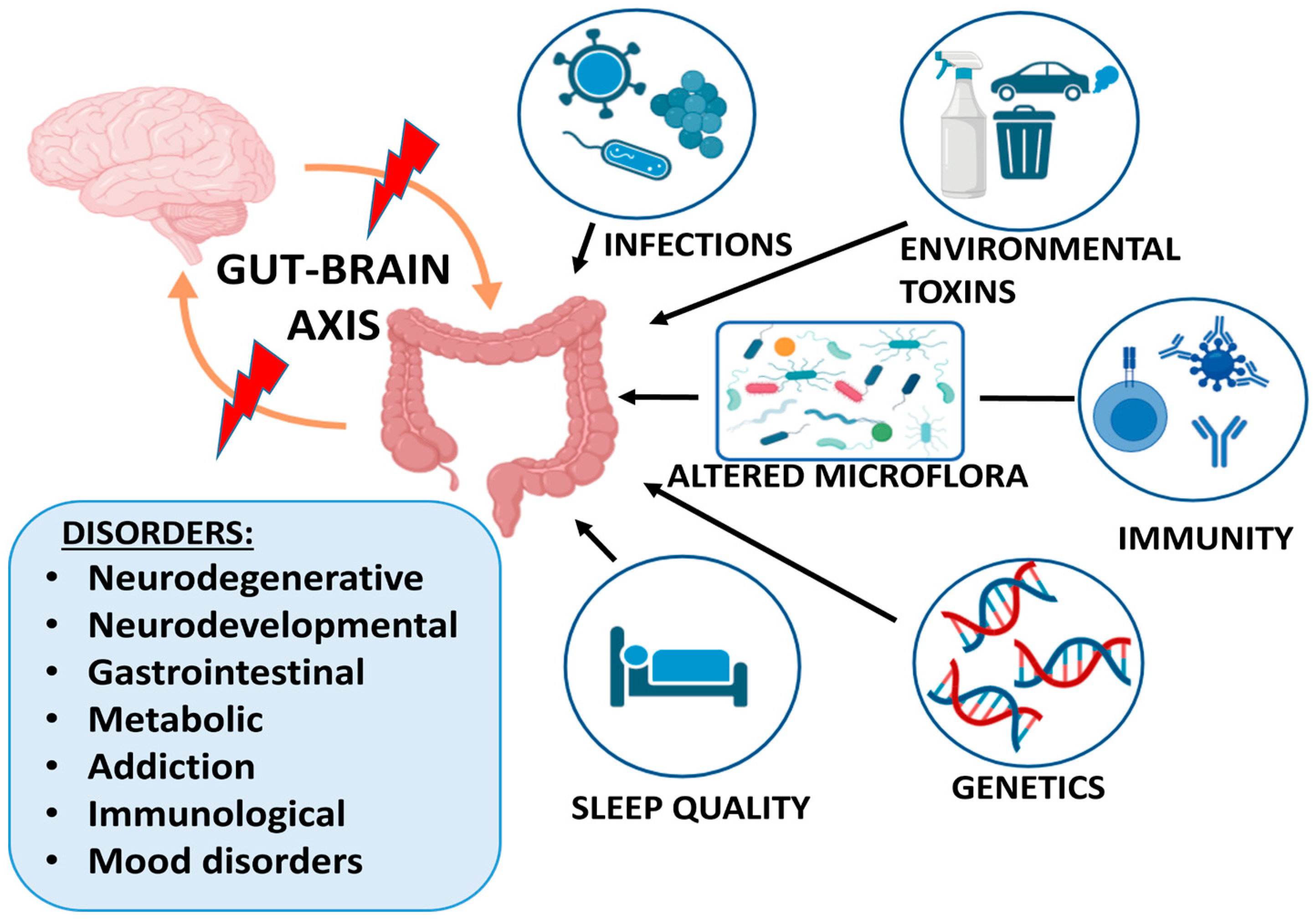
Figure 1 presents the main factors affecting the gut–brain interaction and the related groups of disorders.
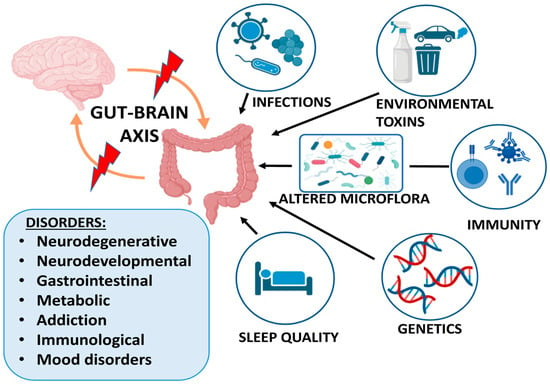
Figure 1.
Factors affecting gut–brain axis and related disorders. Created with BioRender.com.
4. Gut–Brain-Associated Disorders in Focus
The gut–brain axis is discussed in relation to many GI conditions, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), functional dyspepsia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, functional dysphagia, gastroparesis, functional constipation, fecal incontinence, and even inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) and other disorders [26].
The gut–brain axis’ bidirectional communication driven by neuronal, hormonal, metabolic, immunological, and microbial signals has been researched intensively in some chronic inflammatory conditions, where the pathogenesis is still elusive, such as IBD. As a result, mounting data point to a connection between neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disorders and IBD. In this regard, clinical, epidemiological, and experimental evidence has shown that IBD predisposes one to the development of CNS diseases. Similarly, alterations in intestinal neuronal signaling are linked to certain GI disorders [27].
The CNS and the GI tract may be affected in tandem by the disruption of ENS function [28]. In this regard, persistent pain and visceral hypersensitivity are prevalent, incapacitating symptoms of IBD that point to a connection between the intestines, the ENS, and the central nervous system. According to current theory, pain—including neuro–immune interactions in the inflammatory gut—mediates a rise in intestinal permeability, which in turn causes disease activity to worsen. Resolving inflammation is also linked to a decrease in abdominal pain [29]. Additionally, severe neurologic and neuropsychiatric symptoms, such as funicular myelosis or psychosis, can result from intestinal malabsorption diseases (such as vitamin B12 insufficiency) [30].
Crucially, statistics about the individual risk for neurodegeneration among CD and UC patients vary widely, and the risk of acquiring CNS diseases among IBD patients differs greatly depending on the study group. The age of diagnosis is one crucial factor to consider: people with IBD onset before the age of 60 had a greater incidence of Parkinson’s disease (PD), primarily due to the age-related nature of PD, as previously indicated. Elderly individuals are frequently given a wide range of medications, which raises the possibility of drug-induced neurological disorders. In summary, epidemiological studies unequivocally show that people with IBD are at risk for PD, multiple sclerosis (MS), or other CNS illnesses; nevertheless, precise statistics need to be determined [27].
Data on the incidence of intestinal inflammation among patients with PD are few and still under debate. However, clinical and preclinical research strongly indicates the possibility that individuals with IBD would have extraintestinal manifestations in the CNS. This could be partly explained by the fact that neurodegeneration is uncommon in persons under 50, but IBD is typically diagnosed in younger people. On the other hand, as there is evidence of a higher frequency of IBD among MS and of MS among IBD, the relationship between MS and IBD is bidirectional [27].
On the other hand, it is assumed that IBS is the most prevalent disorder of the brain–gut axis (prevalence 5–10% of the worldwide population) [31].
A comprehensive disease model of brain–gut–microbiome interactions for IBS has emerged, which can explain the altered bowel habits, chronic abdominal pain, and psychiatric comorbidities. This model is based on a large body of reported information about genetic factors involved in the pathophysiology of IBS symptoms. Furthermore, relationships between brain networks and characteristics associated with the gut microbiota, immunology, gastrointestinal tract, and genetics have been described [31].
IBS-related malfunctions in ENS circuits may be caused by disrupted communication between intestinal glia and neurons [32]. Recent research has demonstrated the neuronal–glia signaling of the ENS about visceral discomfort, IBS, and other GI diseases [32], where genes such as CADM2 and NCAM1 play a critical role.
Specific cognitive/psychiatric symptoms, such as overall cognitive capacity, risk-taking behavior, intellect, and neuroticism, have been associated with NCAM1 and CADM2 [33].
5. Genetic and Environmental Factors and Novel Diagnostic Approaches
5.1. Genetic Factors in Gut–Brain Disorders
Many studies suggest the role of different risk factors in gut–brain disorders, although the molecular mechanisms they are involved in are poorly understood [34,35,36]. To date, a lot of arguments state the role of the host genes and the gut microbiome in the interdependency regulation of certain phenotypes of neurodevelopmental and gastrointestinal disorders [37,38].
A series of research has shown that the intestinal microbiome could be involved in bidirectionally regulating the activity of the central nervous system through metabolic pathways [34,35,39,40]. The accumulating data on the host genetic–gut microbial interaction suggest that the host’s genetic variants may prevent the presence of certain bacterial species in their gut. Such remodeling of the intestinal microbiome may affect brain development and behavioral function [41,42]. Studies on germ-free (GF) animals demonstrate that the absence of bacterial colonization of the intestine results in the altered expression of the genes controlling the synthesis and transport of neurotransmitters and muscle contractile proteins [5]. Therefore, gut dysbiosis has an impact on both the central nervous system (CNS) and gut-innervating neurons through neurotransmitters and some other metabolites, leading to neurogenetic disorders and gastrointestinal diseases [43]. For example, early metagenomic and metabolic evidence shows that gut dysbiosis accompanies autism spectrum disorder (ASD), and recent studies confirm the direct involvement of ASD risk genes in the regulation of gut nutrition processing. It is known that a mutation in the validated ASD risk gene, CHD8 (14p11.2), is associated with a range of gastrointestinal symptoms [44], and the mutations in the MECP2 in an autism-like mouse model lead to changes in the microbiota and related metabolic changes [39,40,41].
Cumulative genome-wide association studies (GWAS) may highlight the relationship between common genetic risk variants and neurogenetic and gastrointestinal diseases [45]. The systematic post-GWAS analyses of the identified multiple genetic variants, such as single-nucleotide variations (SNVs) and single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), associated with the psychiatric and gastrointestinal phenotypes, point out the large degree of genetic overlap between them [38,45]. A few loci, such as INAVA (1q32.1), LRP8 (1p32.3), NCAM1 (11q23.2), FUT2 (19q13.33), EP300 (22q13.2), etc., display a pleiotropic potential for both types of disorders, and may be used as shared genetic risk determinants for brain–gut interaction disorders [38,46]. The two pleiotropic loci EP300 and LRP8 are the main risk factors for IBS, which suggests a large degree of polygenic overlap with psychiatric disorders. The common EP300 SNP rs20551 is involved in the regulation of molecular processes of neuronal plasticity, the differentiation of intestinal epithelial cells and the expression of gut antimicrobial peptides [45]. The other locus, LRP8, which encodes the receptor protein ApoER2 from the RELN-ApoER2 pathway, regulates the neurodevelopmental processes in the central and peripheral nervous system, as well as the maintenance of the intestinal epithelial barrier [45].
Understanding the role of genetics in gut–brain disorders is crucial for researchers to identify individuals at higher risk, explore potential therapeutic targets, and develop personalized interventions for improving gut and overall health.
In recent years, researchers have begun to pay more attention to the role of epigenetics in host-microbe interactions which alter their cellular functions through several mechanisms [47]. It is hypothesized that gut microbial products can affect chromatin structure in host brain cells, which in turn leads to transcriptional changes in neurons, and hence changes host behavior. In addition, the microbiota are believed to be an important mediator of gene–environment interactions [48].
5.2. Environmental Triggers
The bidirectional communication network between the enteric and the central nervous system has been studied intensively in recent years, looking for factors that disrupt it. The composition of the gut microbiota depends on individual genetic predispositions, nutrition, physical activity, age, environmental factors, infections, drug use and stress [1,49,50]. In the last 10 years, research has focused on the link between the emotional, behavioral and cognitive centers of the brain and gut microbiota. The composition of the gut microbiota depends on an individual’s genetic predisposition, age, nutrition, physical activity, environmental factors, stress, infection, other diseases, and use of antibiotics [5,51,52,53].
Although environmental pollutants have a huge impact on public health, little is known about their role in gut dysbiosis and mental health [54]. Diseases of the host (gastrointestinal, immunological, and neurological) can occur because of changes in the microbiota that favor the development of more pathogenic organisms and chronic inflammation [55,56]. Hormonal imbalance, bacterial metabolites, and genetic and epigenetic mutations are potential mechanisms by which intestinal dysbiosis can affect the host. However, it has been shown that exposure to environmental pollutants can lead to systemic consequences, including changes in brain functions and behavior [57,58,59]. Heavy metals, air pollutants, drugs, alcohol, unbalanced nutrition, sleep quality and stress are among the most well-studied factors implicated in human psychiatric disorders and behavior [49,60].
During the prenatal period, the maternal resident flora impacts the gut microbiota. Evidence shows that different environmental factors such as antibiotics, infection, diet, stress, mode of birth, breast milk quality, and even type of infant feeding can disrupt the colonization of the microbiota in the offspring, influencing brain development [61].
The role and harmful effects of heavy metals in the progression of different mental disorders are known [62,63,64,65,66,67]. Intestinal dysbiosis induced by heavy metal intake also plays a role in the pathology of these diseases [49,68,69]. They are absorbed into the body much faster than they are eliminated, and before reaching the brain, may interact with gut microorganisms [70,71].
Numerous studies have shown that exposure to di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate and bisphenol A can affect gut microbiota and metabolites that are important for the gut–brain axis [72,73,74,75,76,77].
Air pollutants such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, dust and other substances change the composition of the intestinal microorganisms, leading to the synthesis of dangerous metabolites and inflammation, which can lead to brain dysfunctions [78,79,80,81,82,83].
Nutritional status and diet also prove to be critical factors. If they are disturbed, they can have an impact on neurological functions [84]. The link between diet, gut microbiota and the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease has been shown [85,86]. The disruption of the composition and quantity of some bacteria affects the amount of some important metabolites that directly affect the body, the microbiota and brain [87,88].
Sleep is a critical factor in human physical and mental health. In recent years, evidence has shown that the microbiota–gut–brain axis contributes to sleep regulation and may play a role in the pathology of sleep and neuropsychiatric disorders [89,90,91].
Dysbiosis leads to the production of potentially harmful products in the gut that can reach the brain and affect sleep quality [92]. Some of the neuromodulators involved in the sleep–wake cycle are produced and metabolized by gut microbes, thus directly or indirectly reaching the CNS [13,93,94].
5.3. Diagnostic Approaches—Biomarkers
All the evidence clearly shows that neurological disorders are closely related to the gut microbiome. Depression, schizophrenia, epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease and migraine are among the many examples of this connection [16,95]. All microbiome-based tools may be useful in the diagnosis and treatment of gut microbiome disorders and neurological disorders.
Culture-based methods have been used for years in clinical microbiology. These methods are widely used in clinical practice, but are too labor-intensive for extensive characterization of the microbiome. They are limited in diagnosis when it comes to the low abundance of microbes. This method is very useful when looking for antibiotic-resistant pathogens contained in the microbiome of hospitalized patients [96,97].
Multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR), quantitative PCR (qPCR) or flow cytometry panels are much more informative and applicable for microbiome diagnostics. Both next-generation sequencing (NGS) and shotgun metagenomic sequencing (MGS) are very useful when reporting on the relative abundance of microorganisms [98,99,100].
Total RNA (transcriptome), proteins (proteome), metabolites (metabolome) and other indicators of the microbiota have enormous potential to be used as diagnostic biomarkers. They would require standardization and calibration, but their application in clinical diagnostics seems achievable and very useful. Volatile organic compounds such as ethane, methane, ammonia, dimethylamine, etc., are produced by bacteria. They can be measured in human fluids, and if there is a change in their levels, they can be used as biomarkers.
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) are one of the most important gut microbial products, and influence various processes in the host [101,102,103,104]. They are natural inhibitors of histone deacetylases, and an imbalance in the quantity in HDAC has been found in Parkinson’s disease, depression, and schizophrenia [105,106,107]. They also would be a good diagnostic tool for disorders in the microbiome.
A study showed that the gut microbiome can also influence neurotransmitters [108]. Isovaleric acid can cross the blood–brain barrier and affect the release of neurotransmitters in the CNS. Another example of the influence of bacterial products on brain function was shown by Collins and Bercik, 2009 [109]. Factor-S is extracted from the bacterial cell wall, but accumulates in the brains of sleep-deprived people. Intestinal bacteria produce many different metabolites with potential encephalotoxicity, which can be used as a diagnostic tool in neurological dysfunction [110,111,112,113].
The use of different diagnostic methods, as well as the use of biomarkers, will reveal the expression of genes, different products and metabolites that can contribute to clarifying the association of the gut microbiome with the gut–brain axis, and how this affects the development of neurological diseases.
6. Imaging Techniques for Gut–Brain Visualization
In patients with brain–gut interaction disruption (BGID), the gastrointestinal symptoms are typical, but the neurological changes are not specific, presenting with various cognitive, emotional and memory disturbances, necessitating the study of methods that objectify the neurological disturbances. The assessment of the interaction between the brain and the gastrointestinal tract is possible owing to modern imaging methods and, above all, functional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The disruption of brain–gut interaction is present when there is a combination of GIT disorders with disorders in the function of the central nervous system. For a long time, specific brain functions, such as pain processing, were thought to occur in isolated areas of the brain, but nowadays the process is seen as a dynamic interaction between several brain areas. These findings were established thanks to functional MRI, and in particular MR spectroscopy, which clarified the role of the neurotransmitters and the brain metabolites [114,115]. Another method that allows the assessment of brain–gut interactions is positron emission tomography (PET) using radiolabeled ligands at sub pharmacological doses [116]. MRI scans study the presence of certain receptor/transporter systems by scanning patients with BGID and comparing them to healthy control groups. A study by Jarcho et al. investigated neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R), finding that in patients with BGID, this type of receptor was reduced, with these changes being demonstrated mostly in the hippocampus, amygdala, the cingulate region and the basal nuclei [117]. Another receptor studied is the cannabinoid-1 receptor (CB1-R), which in the functional magnetic resonance imaging of patients with BGID is increased compared to healthy controls [118]. MRI spectroscopy allows in vivo quantification of the neurotransmitters glutamate and GABA, as well as the inflammatory mediator myo-inositol. In patients with impaired brain–gut interactions, a reduction in glutamate-glutamine in the hippocampus region has been demonstrated [119].
Other MR studies of patients with brain–gut interactions include structural scanning for measuring the portion of the cerebral cortex, as well as diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), which allows the measurement of microstructural integrity and connectivity. MRI allows the assessment of brain white matter, brain topology and gray matter morphometry, and also depicts anatomical and functional connectivity [120].
7. Translational Therapies
A wide array of neuromodulating substances, classically used in neurology and psychiatry, can be precisely utilized to treat gastroenterological conditions. Amitriptyline, a tricyclic antidepressant, is a cornerstone medication in gastroenterology due to its ability to modulate neurotransmitter activity in both the brain and gastrointestinal tract. It exerts its therapeutic effects in gastrointestinal conditions through multiple mechanisms. By inhibiting the reuptake of neurotransmitters serotonin and norepinephrine, it enhances their availability in the central nervous system, thereby modulating pain perception and reducing visceral hypersensitivity. This analgesic action makes it particularly effective in alleviating abdominal pain associated with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), functional dyspepsia, and non-cardiac chest pain [121,122].
Moreover, amitriptyline’s ability to modulate neurotransmitter levels also influences gastrointestinal motility, potentially reducing symptoms of bloating and altered bowel habits commonly seen in IBS. However, its use in gastrointestinal conditions is not without considerations; side effects such as drowsiness, dry mouth, and constipation are common, and may limit tolerability. Therefore, careful dosing and monitoring are essential in clinical practice to balance therapeutic benefits with potential adverse effects. Despite these drawbacks, amitriptyline remains a valuable option for managing gastrointestinal symptoms, particularly in cases refractory to conventional therapies, highlighting its broad utility in gastroenterology [122]. What makes it even more appealing is that the dosages that are used to treat gastrointestinal conditions are substantially lower, on average 10–25 mg daily, in comparison to those used in psychiatric disorders [121].
IBS is a chronic functional bowel disorder marked by abdominal pain and changes in stool frequency. Its prevalence globally ranges from 5% to 10%. Despite its chronic and fluctuating nature, there is no cure, and treatment focuses on managing symptoms. IBS significantly impacts both individuals and society, with patients experiencing impairments in quality of life comparable to those with conditions like Crohn’s disease, and worse than those with non-gastrointestinal diseases such as diabetes or heart failure [123]. Amitriptyline stands out for its comprehensive effects on both neurological and gastrointestinal systems, making it a preferred choice for many clinicians in the management of functional gastrointestinal disorders. The findings from the trial ATLANTIS indicate that low-dose amitriptyline, administered at 10 mg to 30 mg once daily, effectively alleviates symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) in a primary care setting. The study, encompassing 463 participants, demonstrated a significant decrease in IBS symptom severity scores over a 6-month period compared to baseline. Notably, amitriptyline’s efficacy persisted irrespective of the duration of disease or symptom severity. While adverse events, particularly anticholinergic effects, were more frequent with amitriptyline, they were generally mild and did not significantly affect trial adherence. These findings suggest that low-dose amitriptyline represents a safe and well-tolerated second-line therapy for patients with IBS who do not respond to first-line treatments. The results underscore the importance of updating management guidelines to include low-dose amitriptyline as a recommended option for IBS management in primary care settings [122]. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are another class of medications used in gastroenterology. They primarily regulate serotonin levels in the brain, thereby influencing gastrointestinal function as well as numerous serotonin receptors in the GI tract. SSRIs have shown efficacy in managing symptoms of IBS and inflammatory bowel disease [124]. Antipsychotic medications, such as olanzapine and quetiapine, as well as the pro-kinetic and anti-emetic medication metoclopramide, may be used off-label to address gastroparesis and associated nausea and vomiting. These medications act on dopamine receptors and serotonin pathways, offering relief from gastrointestinal symptoms [125].
Emerging gastrointestinal therapies for neurological disorders primarily focus on interventions that target the GI tract to influence neurological function. These therapies include gut microbiota modulation, which involves manipulating the gut microbiota composition through probiotics, prebiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT). In the realm of treating neurological disorders, harnessing the therapeutic potential of the gut microbiota holds immense promise. Probiotics, which are live microorganisms with potential health benefits, have gained attention for their ability to restore gut microbial balance and promote neuroprotective effects. By introducing beneficial bacteria into the gut, probiotics can enhance immune function, reduce inflammation, and influence neurotransmitter production, thereby exerting positive effects on neurological health. Prebiotics, on the other hand, are non-digestible fibers that serve as food for beneficial gut bacteria. By promoting the growth of these beneficial microbes, prebiotics contribute to a healthier gut microbiota composition, which in turn can modulate immune responses, reduce inflammation, and improve brain function. Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) represents a more direct approach to modulating gut microbiota composition by transferring fecal matter from a healthy donor to a recipient with dysbiosis. While primarily used to treat gastrointestinal conditions such as Clostridium difficile infection, emerging research suggests its potential efficacy in addressing neurological disorders by restoring microbial balance and improving gut–brain axis function [126].
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is another emerging therapy with applications in both gastrointestinal and neurological disorders. By modulating neural signaling between the gut and the brain, VNS may offer therapeutic benefits for conditions like gastroparesis and inflammatory bowel disease, indirectly influencing neurological function, which offers a form of unique epilepsy treatment [127]. Furthermore, interventions aimed at strengthening the intestinal barrier, such as certain medications or dietary supplements, may prevent the translocation of pathogenic substances from the gut into the bloodstream, reducing systemic inflammation and potentially benefiting neurological conditions [128].
Personalized medicine in gut–brain interaction disorders represents a promising frontier, leveraging mechanistic understanding and genetic insights to tailor therapies for individual patients. By elucidating the intricate interplay between the gut and the brain, personalized approaches can address the unique molecular and physiological factors contributing to each patient’s condition [129]. Tailoring therapies based on mechanistic understanding involves identifying specific pathways or targets implicated in gut–brain disorders and developing interventions that directly modulate these mechanisms. For example, targeting neurotransmitter imbalances or immune dysregulation in the gut can help alleviate symptoms of neuro-psychiatric disorders such as depression, anxiety, and autism spectrum disorders. By understanding the underlying mechanisms driving these conditions, clinicians can select interventions that are the most likely to be effective for each patient [130]. Genetic and biomarker-guided approaches offer further opportunities for personalized medicine in gut–brain interaction disorders. Genetic testing and biomarker analysis can identify individuals who may be predisposed to certain conditions or who are likely to respond favorably to specific treatments. For instance, genetic markers associated with gut microbiota composition or neurotransmitter metabolism can inform treatment decisions, guiding the selection of probiotics, dietary interventions, or pharmacological therapies tailored to an individual’s genetic profile [131].
By integrating mechanistic understanding, genetic insights, and biomarker-guided approaches, clinicians can optimize therapeutic strategies, enhance treatment efficacy, and ultimately improve patient care and quality of life.
These interventions impact neurotransmitter production and immune function, potentially affecting conditions such as depression, anxiety, and autism spectrum disorders by restoring microbial balance in the gut and modulating the gut–brain axis [126].
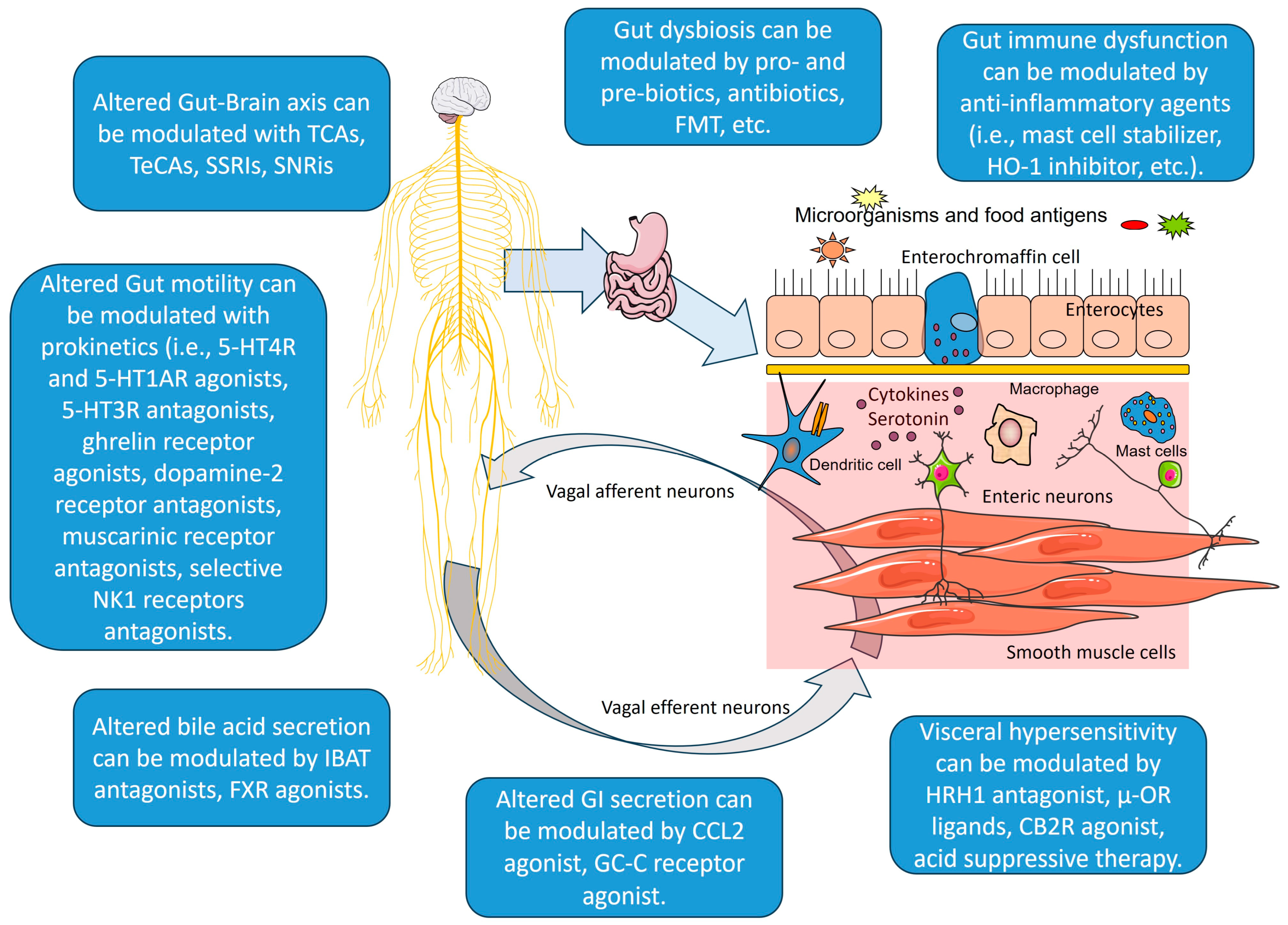
In Figure 2, we present an overview of gut–brain pathways and mechanisms, and how we can intervene into them.
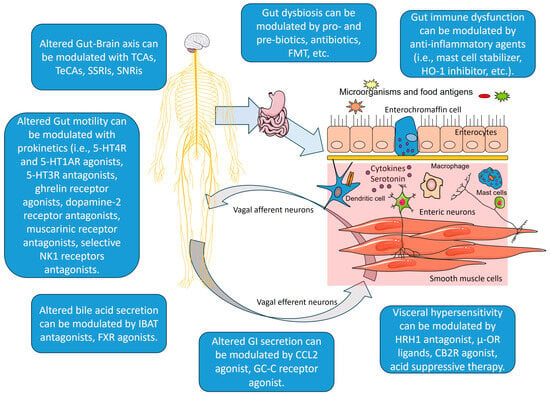
Figure 2.
Gut–brain axis pathways and mechanisms, and therapeutic approaches. Created with Servier Medical Art, licensed under CC BY 4.0. Legend: TCAs—tricyclic antidepressants; TeCAs—tetracyclic antidepressants; SSRs—selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors; SNRis—serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors; 5-HT4R—5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 4; 5-HT1AR—5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1A; 5-HT3R—5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 3; NK1—neurokinin 1 receptor; IBAT—ileal bile acid transporter; FXR—Farnesoid X receptor; CCL2—CC chemokine ligand-2; GC-C—Receptor guanylyl cyclase C; HRH1—histamine and histamine receptor H1; CB2R—cannabinoid receptor 2; μ-OR—μ-opioid receptors; FMT—fecal microbiota transplantation; HO-1—heme oxygenase-1. Parts of the figure were created using Servier Medical Art, licensed under CC BY 4.0.
8. Dietary Interventions
Diet plays a significant role in modulating inflammation associated with neurological diseases, which involves crucial interactions between the gut and the brain.
Kurowska et al. explored the significant role of diet in modulating inflammation related to neurological diseases, emphasizing gut–brain interaction [132]. Various diets can influence this interaction by affecting the gut microbiome and inflammation processes, which are crucial in the development and progression of neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, schizophrenia, depression, and multiple sclerosis.
The Mediterranean diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, and includes the moderate consumption of fish and poultry. It is known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties due to high levels of omega-3 fatty acids, polyphenols, and other bioactive compounds. This diet has been associated with reduced risks of cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s due to its ability to modulate the gut microbiome and reduce systemic inflammation [132,133].
The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting saturated fats, sugars, and sodium. Originally designed to combat high blood pressure, the DASH diet also offers anti-inflammatory benefits that support brain health. By promoting the intake of nutrient-dense foods, the DASH diet helps reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, which are critical factors in the prevention and management of neurological diseases. This diet’s balanced approach ensures a steady supply of essential nutrients that support overall brain function [132].
The ketogenic diet (KD) is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate, and adequate-protein diet that has shown significant therapeutic potential in various neurological disorders [132]. One of the most established benefits of the KD is its effectiveness in reducing seizures in drug-resistant epilepsy. Studies have demonstrated that this diet can significantly decrease seizure frequency in many patients, especially in children, with some experiencing a complete cessation of seizures. This diet’s anti-seizure properties are believed to stem from its ability to stabilize neuronal activity and reduce excitotoxicity [132,134].
The ketogenic diet has shown potential benefits in managing Alzheimer’s disease by targeting several underlying mechanisms associated with the disease. The KD works primarily by shifting the brain’s energy source from glucose to ketone bodies, such as beta-hydroxybutyrate. This metabolic switch enhances mitochondrial function and reduces oxidative stress by decreasing the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and increasing the efficiency of the electron transport chain through the expression of uncoupling proteins [135,136]. Additionally, ketone bodies activate the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), which boosts the brain’s antioxidant defenses [136].
Another critical aspect of the ketogenic diet is its anti-inflammatory effects. The diet inhibits the activation of nuclear factor kappa light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) and the nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome. These actions help reduce neuroinflammation, a significant contributor to the progression of AD. Furthermore, the diet’s modulation of histone deacetylases (HDACs) enhances memory encoding and cognitive functions [136].
Studies in animal models of AD have shown that the ketogenic diet can improve cognitive performance and reduce the deposition of amyloid plaques, a hallmark of AD pathology [137]. These findings suggest that the ketogenic diet’s neuroprotective effects are mediated through its ability to stabilize synaptic functions and enhance neurotransmitter pathways.
Overall, the ketogenic diet presents a promising non-pharmacological intervention for Alzheimer’s disease by improving mitochondrial function, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, and supporting cognitive health [132,135].
Research has shown that a diet rich in antioxidants, like vitamins C and E, and beta-carotene, may lower the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease [138]. The Mediterranean diet has also been linked to a reduced risk of PD, while diets high in saturated fat and cholesterol may increase the risk [132]. Additionally, the Mediterranean diet has been shown to reduce inflammatory markers and improve motor function in PD patients [132]. Probiotics, found in foods like yogurt and kimchi, have been associated with improved metabolic state in PD patients [139]. The ketogenic diet has also shown promising results in improving symptoms and reducing inflammation in PD patients [132].
In Huntington’s disease (HD), oxidative stress and inflammation play critical roles in disease progression. A diet enriched with antioxidants, such as elderberry, has been shown to improve motor function and reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in animal models of HD [140]. A moderate Mediterranean diet has been associated with improved mobility and quality of life, and reduced psychiatric impairment in HD patients [141]. Higher dairy consumption and caloric intake have been linked to a higher risk of disease progression in HD patients, while adherence to the Mediterranean diet has been associated with a higher quality of life [142]. Additionally, a ketogenic diet has shown potential benefits in improving symptoms and body weight management in HD, although high-fat diets may exacerbate symptoms and disease progression [132]. Overall, dietary interventions hold promise in managing symptoms and potentially slowing the progression of neurodegenerative diseases like PD and HD.
Personalized nutritional interventions are proposed as a non-invasive and effective strategy for managing these conditions through targeted dietary modifications [132].
9. Conclusions
In conclusion, our review highlights the complex interplay between the gut and the brain, shedding light on the bidirectional communication pathways pivotal in health and disease. Through synthesizing diverse research findings, we emphasize the significant impact of gut–brain interactions on a spectrum of disorders, from gastrointestinal to neurological conditions. These insights have profound implications for clinical practice, emphasizing the necessity of personalized medicine approaches. Furthermore, collaborative efforts among multidisciplinary healthcare teams and researchers are crucial to validate emerging therapies and advance our understanding of gut–brain interaction disorders. A collective call to action for continued research and collaboration is warranted to address existing gaps, validate findings, and translate discoveries into impactful clinical interventions, ultimately improving patient well-being and quality of life.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.V.V. and T.V.; methodology, D.M.; software, M.K.; validation, G.V.V., D.M. and T.V.; formal analysis, M.G.; investigation, L.C.; resources, M.G.; data curation, M.K.; writing—original draft preparation, G.V.V., D.M., M.K., M.G., L.C.; writing—review and editing, T.V.; visualization, D.M.; supervision, T.V.; project administration, T.V.; funding acquisition, T.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is financed by the European Union-NextGenerationEU through the National Recovery and Resilience Plan of the Republic of Bulgaria, project No BG-RRP-2.004-0008.
Acknowledgments
This study is financed by the European Union-NextGenerationEU through the National Recovery and Resilience Plan of the Republic of Bulgaria, project No BG-RRP-2.004-0008.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Appleton, J. The Gut-Brain Axis: Influence of Microbiota on Mood and Mental Health. Integr. Med. 2018, 17, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rusch, J.A.; Layden, B.T.; Dugas, L.R. Signalling cognition: The gut microbiota and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1130689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mhanna, A.; Martini, N.; Hmaydoosh, G.; Hamwi, G.; Jarjanazi, M.; Zaifah, G.; Kazzazo, R.; Haji Mohamad, A.; Alshehabi, Z. The correlation between gut microbiota and both neurotransmitters and mental disorders: A narrative review. Medicine 2024, 103, e37114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Martin, C.R.; Osadchiy, V.; Kalani, A.; Mayer, E.A. The Brain-Gut-Microbiome Axis. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gieryńska, M.; Szulc-Dąbrowska, L.; Struzik, J.; Mielcarska, M.B.; Gregorczyk-Zboroch, K.P. Integrity of the Intestinal Barrier: The Involvement of Epithelial Cells and Microbiota-A Mutual Relationship. Animals 2022, 12, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chaudhry, T.S.; Senapati, S.G.; Gadam, S.; Mannam, H.P.S.S.; Voruganti, H.V.; Abbasi, Z.; Abhinav, T.; Challa, A.B.; Pallipamu, N.; Bheemisetty, N.; et al. The Impact of Microbiota on the Gut-Brain Axis: Examining the Complex Interplay and Implications. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schächtle, M.A.; Rosshart, S.P. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Health and Disease and Its Implications for Translational Research. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2021, 15, 698172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kanai, T.; Teratani, T. Role of the Vagus Nerve in the Gut-Brain Axis: Development and Maintenance of Gut Regulatory T Cells via the Liver-Brain-Gut Vago-Vagal Reflex. Brain Nerve 2022, 74, 971–977. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Cheng, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Xu, D.; Cao, P.; Wang, F.; Herzog, H.; Song, S.; Zhan, C. A Vagal-NTS Neural Pathway that Stimulates Feeding. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 3986–3998.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahima, R.S.; Antwi, D.A. Brain regulation of appetite and satiety. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 37, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wachsmuth, H.R.; Weninger, S.N.; Duca, F.A. Role of the gut-brain axis in energy and glucose metabolism. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Parker, A.; Fonseca, S.; Carding, S.R. Gut microbes and metabolites as modulators of blood-brain barrier integrity and brain health. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- O’Riordan, K.J.; Collins, M.K.; Moloney, G.M.; Knox, E.G.; Aburto, M.R.; Fülling, C.; Morley, S.J.; Clarke, G.; Schellekens, H.; Cryan, J.F. Short chain fatty acids: Microbial metabolites for gut-brain axis signalling. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2022, 546, 111572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takiishi, T.; Fenero, C.I.M.; Câmara, N.O.S. Intestinal barrier and gut microbiota: Shaping our immune responses throughout life. Tissue Barriers 2017, 5, e1373208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, Y.K.; Shin, C. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Novel Treatments. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Loh, J.S.; Mak, W.Q.; Tan, L.K.S.; Ng, C.X.; Chan, H.H.; Yeow, S.H.; Foo, J.B.; Ong, Y.S.; How, C.W.; Khaw, K.Y. Microbiota-gut-brain axis and its therapeutic applications in neurodegenerative diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasarello, K.; Cudnoch-Jedrzejewska, A.; Czarzasta, K. Communication of gut microbiota and brain via immune and neuroendocrine signaling. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1118529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jacobson, A.; Yang, D.; Vella, M.; Chiu, I.M. The intestinal neuro-immune axis: Crosstalk between neurons, immune cells, and microbes. Mucosal Immunol. 2021, 14, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karl, J.P.; Hatch, A.M.; Arcidiacono, S.M.; Pearce, S.C.; Pantoja-Feliciano, I.G.; Doherty, L.A.; Soares, J.W. Effects of Psychological, Environmental and Physical Stressors on the Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wei, P.; Keller, C.; Li, L. Neuropeptides in gut-brain axis and their influence on host immunity and stress. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yeung, A.Y.; Tadi, P. Physiology, Obesity Neurohormonal Appetite And Satiety Control. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.D. Appetite Regulation: Hormones, Peptides, and Neurotransmitters and Their Role in Obesity. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2017, 13, 586–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Foster, J.A.; Rinaman, L.; Cryan, J.F. Stress & the gut-brain axis: Regulation by the microbiome. Neurobiol. Stress. 2017, 7, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Van Dyken, P.; Lacoste, B. Impact of Metabolic Syndrome on Neuroinflammation and the Blood-Brain Barrier. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mukhtar, K.; Nawaz, H.; Abid, S. Functional gastrointestinal disorders and gut-brain axis: What does the future hold? World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 552–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Günther, C.; Rothhammer, V.; Karow, M.; Neurath, M.; Winner, B. The Gut-Brain Axis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease-Current and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Drokhlyansky, E.; Smillie, C.S.; Van Wittenberghe, N.; Ericsson, M.; Griffin, G.K.; Eraslan, G.; Dionne, D.; Cuoco, M.S.; Goder-Reiser, M.N.; Sharova, T.; et al. The Human and Mouse Enteric Nervous System at Single-Cell Resolution. Cell 2020, 182, 1606–1622.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, A.; Roesch, J.; Saake, M.; Sergeeva, M.; Hirschmann, S.; Neumann, H.; Dorfler, A.; Neurath, M.F.; Atreya, R. Functional Brain Imaging Reveals Rapid Blockade of Abdominal Pain Response Upon Anti-TNF Therapy in Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 864–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stabler, S.P. Clinical practice. Vitamin B12 deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.A.; Ryu, H.J.; Bhatt, R.R. The neurobiology of irritable bowel syndrome. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 1451–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguella, L.; Gulbransen, B.D. Enteric glial biology, intercellular signalling and roles in gastrointestinal disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eraslan, G.; Drokhlyansky, E.; Anand, S.; Fiskin, E.; Subramanian, A.; Slyper, M.; Wang, J.; Van Wittenberghe, N.; Rouhana, J.; Regev, A. Single-nucleus cross-tissue molecular reference maps toward understanding disease gene function. Science 2022, 376, eabl4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.; Riordan, K.; Cowan, C.; Sandhu, K.; Bastiaanssen, T.; Boehme, M. The microbiota-gut-brain axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuolo, J.; Gliozzi, M.; Musolino, V.; Carresi, C.; Scarano, F.; Nucera, S.; Scicchitano, M.; Oppedisano, F.; Bosco, F.; Ruga, S.; et al. The Contribution of Gut Microbiota–Brain Axis in the Development of Brain Disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 23, 616883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zia, J.; Lenhart, A.; Yang, P.-L.; Heitkemper, M.; Baker, J.; Keefer, L.; Saps, M.; Cuff, C.; Hungria, G.; Videlock, E.J.; et al. Risk Factors for Abdominal Pain–Related Disorders of Gut–Brain Interaction in Adults and Children: A Systematic Review. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 995–1023.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, J.; Cryan, J.F. Host genetics, the microbiome & behaviour-a H‘olobiont’ perspective. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 832–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gong, W.; Guo, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Yan, R.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Xue, F.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, Z. Role of the Gut-Brain Axis in the Shared Genetic Etiology between Gastrointestinal Tract Diseases and Psychiatric Disorders: A Genome-Wide Pleiotropic Analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2023, 80, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.; Surette, M.; Bercik, P. The interplay between the intestinal microbiota and the brain. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hu, Q.; Rao, X.; Zhao, H.; Tang, H.; Wang, Y. Gut microbiome and metabolic profiles of mouse model for MeCP2 duplication syndrome. Brain Res. Bull. 2024, 206, 110862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Zeng, B.; Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Pan, J.; Han, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, K.; Zhou, C.; Wang, H.; et al. The gut microbiome from patients with schizophrenia modulates the glutamate-glutamine-GABA cycle and schizophrenia-relevant behaviors in mice. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaay2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Wu, H.; Chen, Z.; Hao, H.; Zheng, X. Gut microbiome at the crossroad of genetic variants and behavior disorders. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2201156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Dawson, T.; Kulkarni, S. Neurodegenerative disorders and gut-brain interactions. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e143775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, I.; Getselter, D.; Ghanayem, N.; Harari, R.; Davis, L.; Bel, S.; Elliott, E. CHD8 regulates gut epithelial cell function and affects autism-related behaviors through the gut-brain axis. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, M.; Jaholkowski, P.; Hindley, G.; Shadrin, A.; Rahman, Z.; Bahrami, S.; Lin, A.; Holen, B.; Parker, N.; Cheng, W.; et al. Shared genetic architecture between irritable bowel syndrome and psychiatric disorders reveals molecular pathways of the gut-brain axis. Genome Med. 2023, 15, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Eve, M.; Gandawijaya, J.; Yang, L.; Oguro-Ando, A. Neuronal Cell Adhesion Molecules May Mediate Neuroinflammation in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 842755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rajeev, R.; Dwivedi, A.; Sinha, A.; Agarwaal, V.; Dev, R.; Kar, A.; Khosla, S. Epigenetic interaction of microbes with their mammalian hosts. J. Biosci. 2021, 46, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stilling, R.; Dinan, T.; Cryan, J. Microbial genes, brain & behaviour–epigenetic regulation of the gut–brain axis. Genes. Brain Behav. 2014, 13, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Sharma, P.; Pal, N.; Kumawat, M.; Shubham, S.; Sarma, D.K.; Tiwari, R.R.; Kumar, M.; Nagpal, R. Impact of Environmental Pollutants on Gut Microbiome and Mental Health via the Gut-Brain Axis. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, N.; Mandhare, A.; Tryphena, K.P.; Srivastava, S.; Shaikh, M.F.; Singh, S.B.; Khatri, D.K. Epigenetics in depression and gut-brain axis: A molecular crosstalk. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 1048333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustí, A.; García-Pardo, M.P.; López-Almela, I.; Campillo, I.; Maes, M.; Romani-Pérez, M.; Sanz, Y. Interplay between the Gut-Brain Axis, Obesity and Cognitive Function. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaisas, S.; Maher, J.; Kanthasamy, A. Gut microbiome in health and disease: Linking the microbiome-gut-brain axis and environmental factors in the pathogenesis of systemic and neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 158, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paton, S.E.; Solano, J.L.; Coulombe-Rozon, F.; Lebel, M.; Menard, C. Barrier–environment interactions along the gut–brain axis and their influence on cognition and behaviour throughout the lifespan. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. May 2023, 48, E190–E208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventriglio, A.; Bellomo, A.; di Gioia, I.; Di Sabatino, D.; Favale, D.; De Berardis, D.; Cianconi, P. Environmental pollution and mental health: A narrative review of literature. CNS Spectr. 2020, 26, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simkin, D.R. Microbiome and Mental Health, Specifically as It Relates to Adolescents. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2019, 21, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obrenovich, M.E.M. Leaky Gut, Leaky Brain? Microorganisms 2018, 6, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, H.S.; Pothoulakis, C.; Mayer, E.A. Principles and clinical implications of the brain–gut–enteric microbiota axis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 6, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.M.; Bercik, P. The Relationship Between Intestinal Microbiota and the Central Nervous System in Normal Gastrointestinal Function and Disease. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Mind-altering microorganisms: The impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silbergeld, E.K.; Goldberg, A. Pharmacological and neurochemical investigations of lead-induced hyperactivity. Neuropharmacology 1975, 14, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tochitani, S. Vertical transmission of gut microbiota: Points of action of environmental factors influencing brain development. Neurosci. Res. 2021, 168, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opler, M.G.; Buka, S.L.; Groeger, J.; McKeague, I.; Wei, C.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Bresnahan, M.; Graziano, J.; Goldstein, J.M.; Seidman, L.J.; et al. Prenatal exposure to lead, delta-aminolevulinic acid, and schizophrenia: Further evidence. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1586–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, P.; Hossain, M.I.; Sadat, A.N.; Nahar, Z.; Hossain, M.K.; Hasnat, A. Serum levels of cadmium, calcium, lead and iron in schizophrenic patients. Dhaka Univ. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 5, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, M.F.; Bellinger, D.C.; Weuve, J.; Matthews-Bellinger, J.; Gilman, S.; Wright, R.O.; Schwartz, J.; Weisskopf, M.G. Blood Lead Levels and Major Depressive Disorder, Panic Disorder, and Generalized Anxiety Disorder in US Young Adults. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurczak, A.; Brodowska, A.; Szkup, M.; Prokopowicz, A.; Karakiewicz, B.; Łój, B.; Kotwas, A.; Brodowska, A.; Grochans, E. Influence of Pb and Cd levels in whole blood of postmenopausal women on the incidence of anxiety and depressive symptoms. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2018, 25, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiue, I. Urinary heavy metals, phthalates and polyaromatic hydrocarbons independent of health events are associated with adult depression: USA NHANES, 2011–2012. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res 2015, 22, 17095–17103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahouaoui, H.; Aimrane, A.; Khamsi, Y.; Zouhairi, N.; Benammi, H.; El Hidan, M.A.; Draoui, A.; Alahyane, H.; Bouazza, A. Handbook of Research on Global Environmental Changes and Human Health; IGI Global: Pennsylvania, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 305–321, Depression and Anxiety Emerging from Heavy Metals: What Relationship? [Google Scholar]
- Tizabi, Y.; Bennani, S.; El Kouhen, N.; Getachew, B.; Aschner, M. Interaction of Heavy Metal Lead with Gut Microbiota: Implications for Autism Spectrum Disorder. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayuso-Álvarez, A.; Simón, L.; Nuñez, O.; Rodríguez-Blázquez, C.; Martín-Méndez, I.; Bel-Lán, A.; López-Abente, G.; Merlo, J.; Fernandez-Navarro, P.; Galán, I. Association between heavy metals and metalloids in topsoil and mental health in the adult population of Spain. Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshala-Katumbay, D.; Mwanza, J.-C.; Rohlman, D.S.; Maestre, G.E.; Oriá, R. A global perspective on the influence of environmental exposures on the nervous system. Nature 2015, 527, S187–S192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; He, L.; Wang, L.; Chang, D.; Cui, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, C.; et al. Acute oral methylmercury exposure perturbs the gut microbiome and alters gut-brain axis related metabolites in rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Han, H.; Li, Y.; Xu, B.; Dai, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Ma, H. PeiDi-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate exposure induces female reproductive toxicity and alters the intestinal microbiota community structure and fecal metabolite profile in mice. Environ. Toxicol. 2021, 36, 1226–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Shu, R.; Xie, X.; Fu, Z. Exposure to dibutyl phthalate impairs lipid metabolism and causes inflammation via disturbing microbiota-related gut–liver axis. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2020, 52, 1382–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-W.; Kim, M.-S.; Lim, Y.-H.; Lee, N.; Hong, Y.-C. Prenatal and postnatal exposure to di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and neurodevelopmental outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2018, 167, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, F.; Nolte, E.L.R.; Wang, Y.; Margolis, A.E.; Calafat, A.M.; Wang, S.; Garcia, W.; Hoepner, L.A.; Peterson, B.S.; Rauh, V.; et al. Bisphenol A exposure and symptoms of anxiety and depression among inner city children at 10–12 years of age. Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sarma, D.K.; Shubham, S.; Kumawat, M.; Verma, V.; Prakash, A.; Tiwari, R. Environmental Endocrine-Disrupting Chemical Exposure: Role in Non-Communicable Diseases. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 553850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.-H.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.H.; Bae, S.; Park, H.Y.; Hong, Y.-C. Air Pollution and Symptoms of Depression in Elderly Adults. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borroni, E.; Pesatori, A.C.; Bollati, V.; Buoli, M.; Carugno, M. Air pollution exposure and depression: A comprehensive updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 292, 118245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SShin, J.; Park, J.Y.; Choi, J. Long-term exposure to ambient air pollutants and mental health status: A nationwide population-based cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195607. [Google Scholar]
- Bakian, A.V.; Huber, R.S.; Coon, H.; Gray, D.; Wilson, P.; McMahon, W.M.; Renshaw, P.F. Acute Air Pollution Exposure and Risk of Suicide Completion. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 181, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, L.M.; Calderón-Garcidueñas, L. Air pollution: Mechanisms of neuroinflammation and CNS disease. Trends Neurosci. 2009, 32, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, E.M. Air Pollution, Stress, and Allostatic Load: Linking Systemic and Central Nervous System Impacts. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 69, 597–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fang, J.; Tang, S.; Du, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Deng, F.; Liu, Y.; Du, Y.; Cui, L.; et al. PM2.5 exposure associated with microbiota gut-brain axis: Multi-omics mechanistic implications from the BAPE study. Innovation 2022, 3, 100213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larroya-García, A.; Navas-Carrillo, D.; Orenes-Piñero, E. Impact of gut microbiota on neurological diseases: Diet composition and novel treatments. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 3102–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villumsen, M.; Aznar, S.; Pakkenberg, B.; Jess, T.; Brudek, T. Inflammatory bowel disease increases the risk of Parkinson’s disease: A Danish nationwide cohort study 1977–2014. Gut 2019, 68, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallen, Z.D.; Appah, M.; Dean, M.N.; Sesler, C.L.; Factor, S.A.; Molho, E.; Zabetian, C.P.; Standaert, D.G.; Payami, H. Characterizing dysbiosis of gut microbiome in PD: Evidence for overabundance of opportunistic pathogens. NPJ Park. Dis. 2020, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Pardo, P.; Kliest, T.; Dodiya, H.B.; Broersen, L.M.; Garssen, J.; Keshavarzian, A.; Kraneveld, A.D. The gut-brain axis in Parkinson’s disease: Possibilities for food-based therapies. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 817, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnik, W.; Fularski, P.; Gajewska, A.; Jakubowska, P.; Uszok, Z.; Młynarska, E.; Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B. The Role of Intestinal Microbiota and Diet as Modulating Factors in the Course of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases. Nutrients 2024, 16, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Lu, T.; Chen, W.; Yan, W.; Yuan, K.; Shi, L.; Liu, X.; Zhou, X.; Shi, J.; et al. The microbiota-gut-brain axis in sleep disorders. Sleep. Med. Rev. 2022, 65, 101691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, A.; Galiè, S. The Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis in Metabolic Syndrome and Sleep Disorders: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, K.; Lu, X.; Yuan, G.; Yang, H.; Guo, H.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, T.; Hao, J.; et al. The Component and Functional Pathways of Gut Microbiota Are Altered in Populations with Poor Sleep Quality-A Preliminary Report. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2022, 71, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eban-Rothschild, A.; Appelbaum, L.; De Lecea, L. Neuronal Mechanisms for Sleep/Wake Regulation and Modulatory Drive. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 937–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.A.; Forsythe, P.; Chew, M.V.; Escaravage, E.; Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Cryan, J.F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16050–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Gutiérrez, L.; Vicente, L.S.; Barrón, L.J.R.; del Carmen Villarán, M.; Chavarri, M. Gamma-aminobutyric acid and probiotics: Multiple health benefits and their future in the global functional food and nutraceuticals market. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhanna, A.; Alshehabi, Z. The microbiota-gut-brain axis and three common neurological disorders: A mini-review. Ann. Med. Surg. 2023, 85, 1780–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, H. Controlling the spread of vancomycin-resistant enterococci. Is active screening worthwhile? J. Hosp. Infect. 2014, 88, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettigrew, M.M.; Gent, J.F.; Kong, Y.; Halpin, A.L.; Pineles, L.; Harris, A.D.; Johnson, J.K. Gastrointestinal microbiota disruption and risk of colonization with carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in intensive care unit patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damhorst, G.L.; Adelman, M.W.; Woodworth, M.H.; Kraft, C.S. Current Capabilities of Gut Microbiome-Based Diagnostics and the Promise of Clinical Application. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223 (Suppl. 3), S270–S275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, C.; Luukkonen, P.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Salonen, A.; Korpela, K. Quantitative PCR provides a simple and accessible method for quantitative microbiota profiling. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloor, G.B.; Macklaim, J.M.; Pawlowsky-Glahn, V.; Egozcue, J.J. Microbiome datasets are compositional: And this is not optional. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, G.; Gambino, R.; Cassader, M. Interactions between gut microbiota and host metabolism predisposing to obesity and diabetes. Annu. Rev. Med. 2011, 62, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenderov, B.A. Gut indigenous microbiota and epigenetics. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2012, 23, 17195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooks, M.G.; Garrett, W.S. Bacteria, food, and cancer. F1000 Biol. Rep. 2011, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Lahham, S.H.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Roelofsen, H.; Vonk, R.J.; Venema, K. Biological effects of propionic acid in humans; metabolism, potential applications and underlying mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1801, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, I.F.; Dexter, D.T. Epigenetic targeting of histone deacetylase: Therapeutic potential in Parkinson’s disease? Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 140, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahgoub, M.; Monteggia, L.M. Epigenetics and psychiatry. Neurotherapeutics 2013, 10, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haberland, M.; Montgomery, R.L.; Olson, E.N. The many roles of histone deacetylases in development and physiology: Implications for disease and therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 8, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczesniak, O.; Hestad, K.; Hanssen, J.F.; Rudi, K. Isovaleric acid in stool correlates with human depression. Nutr. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, J.; Borojevic, R.; Verdu, E.F.; Huizinga, J.D.; Ratcliffe, E.M. Intestinal microbiota influence the early postnatal development of the enteric nervous system. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheedy, J.R.; Wettenhall, R.E.; Scanlon, D.; Gooley, P.R.; Lewis, D.P.; Mcgregor, N.; Stapleton, D.I.; Butt, H.L.; De Meirleir, K.L. Increased d-lactic acid intestinal bacteria in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Vivo 2009, 23, 621–628. [Google Scholar]
- Skowrońska, M.; Albrecht, J. Alterations of blood brain barrier function in hyperammonemia: An overview. Neurotox. Res. 2012, 21, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galland, L. The gut microbiome and the brain. J. Med. Food. 2014, 17, 1261–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, L.H.; Schreiber, H.L., 4th; Mazmanian, S.K. The gut microbiota-brain axis in behaviour and brain disorders. Nature reviews. Microbiology 2021, 19, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, Q.; Thompson, D.G. Brain-gut axis in health and disease. Gastroenterology 1998, 114, 559–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drossman, D.A.; Hasler, W.L. Rome IV-Functional GI Disorders: Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hg, L.; Dupont, P.; Geeraerts, B.; Bormans, G.; Van Laere, K.; Tack, J.; Van Oudenhove, L. Lack of endogenous opioid release during sustained visceral pain: A [11C]carfentanil PET study. Pain 2013, 154, 2072–2077. [Google Scholar]
- Jarcho, J.M.; Feier, N.A.; Bert, A.; Labus, J.A.; Lee, M.; Stains, J.; Ebrat, B.; Groman, S.M.; Tillisch, K.; Brody, A.L.; et al. Diminished neurokinin-1 receptor availability in patients with two forms of chronic visceral pain. Pain 2013, 154, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hg, L.; Ceccarini, J.; Weltens, N.; Bormans, G.; Van Laere, K.; Tack, J.; Van Oudenhove, L. Increased cerebral cannabinoid-1 receptor availability is a stable feature of functional dyspepsia: A [FJMK-9470 PET study. Psychother Psychosom 2015, 84, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Niddam, D.M.; Tsai, S.Y.; Lu, C.L.; Ko, C.W.; Hsieh, J.C. Reduced hippocampal glutamate-glutamine levels in irritable bowel syndrome: Preliminary findings using magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 1503–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, E.A.; Labus, J.; Aziz, Q.; Tracey, I.; Kilpatrick, L.; Elsenbruch, S.; Schweinhardt, P.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Borsook, D. Role of brain imaging in disorders of brain-gut interaction: A Rome Working Team Report. Gut 2019, 68, 1701–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thour, A.; Marwaha, R. Amitriptyline. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537225/ (accessed on 23 March 2024).
- Ford, A.C.; Wright-Hughes, A.; Alderson, S.L.; Ow, P.L.; Ridd, M.J.; Foy, R.; Bianco, G.; Bishop, F.L.; Chaddock, M.; Cook, H.; et al. ATLANTIS trialists. Amitriptyline at Low-Dose and Titrated for Irritable Bowel Syndrome as Second-Line Treatment in primary care (ATLANTIS): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, A.C.; Sperber, A.D.; Corsetti, M.; Camilleri, M. Irritable bowel syndrome. Lancet 2020, 396, 1675–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatamnejad, M.R.; Baradaran Ghavami, S.; Shirvani, M.; Asghari Ahmadabad, M.; Shahrokh, S.; Farmani, M.; Sherkat, G.; Asadzadeh Aghdaei, H.; Zali, M.R. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and inflammatory bowel disease; Beneficial or malpractice. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 980189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Camilleri, M.; Atieh, J. New Developments in Prokinetic Therapy for Gastric Motility Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 711500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tiwari, P.; Dwivedi, R.; Bansal, M.; Tripathi, M.; Dada, R. Role of Gut Microbiota in Neurological Disorders and Its Therapeutic Significance. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Krahl, S.E. Vagus nerve stimulation for epilepsy: A review of the peripheral mechanisms. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2012, 3 (Suppl. 1), S47–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lu, K.H.; Cao, J.; Oleson, S.; Ward, M.P.; Phillips, R.J.; Powley, T.L.; Liu, Z. Vagus nerve stimulation promotes gastric emptying by increasing pyloric opening measured with magnetic resonance imaging. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2018, 30, e13380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chunduri, A.; Reddy, S.D.M.; Jahanavi, M.; Reddy, C.N. Gut-Brain Axis, Neurodegeneration and Mental Health: A Personalized Medicine Perspective. Indian J. Microbiol. 2022, 62, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Strandwitz, P. Neurotransmitter modulation by the gut microbiota. Brain Res. 2018, 1693 Pt B, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hajjo, R.; Sabbah, D.A.; Al Bawab, A.Q. Unlocking the Potential of the Human Microbiome for Identifying Disease Diagnostic Biomarkers. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kurowska, A.; Ziemichód, W.; Herbet, M.; Piątkowska-Chmiel, I. The Role of Diet as a Modulator of the Inflammatory Process in the Neurological Diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Loughrey, D.G.; Lavecchia, S.; Brennan, S.; Lawlor, B.A.; Kelly, M.E. The Impact of the Mediterranean Diet on the Cognitive Functioning of Healthy Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Martin-McGill, K.J.; Bresnahan, R.; Levy, R.G.; Cooper, P.N. Ketogenic diets for drug-resistant epilepsy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 6, CD001903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dyńka, D.; Kowalcze, K.; Paziewska, A. The Role of Ketogenic Diet in the Treatment of Neurological Diseases. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.; Bonucci, A.; Maggi, E.; Corsi, M.; Businaro, R. Anti-Oxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Ketogenic Diet: New Perspectives for Neuroprotection in Alzheimer’s Disease. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilamand, M.; Porte, B.; Cognat, E.; Hugon, J.; Mouton-Liger, F.; Paquet, C. Are ketogenic diets promising for Alzheimer’s disease? A translational review. Alz. Res. Ther. 2020, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-A.; Ellis, A.C. Dietary Antioxidants and Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Antioxidants 2020, 50, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Tamtaji, O.R.; Taghizadeh, M.; Kakhaki, R.D.; Kouchaki, E.; Bahmani, F.; Borzabadi, S.; Asemi, Z. Clinical and metabolic response to probiotic administration in people with Parkinson’s disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghaddam, M.H.; Bayat, A.H.; Eskandari, N.; Abdollahifar, M.A.; Fotouhi, F.; Forouzannia, A.; Rafiei, R.; Hatari, S.; Seraj, A.; Shahidi, A.; et al. Elderberry diet ameliorates motor function and prevents oxidative stress-induced cell death in rat models of Huntington’s disease. Brain Res. 2021, 1762, 147444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivadeneyra, J.; Cubo, E.; Gil, C.; Calvo, S.; Mariscal, N.; Martínez, A. Factors associated with Mediterranean diet adherence in Huntington’s disease. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2016, 12, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marder, K.; Zhao, H.; Eberly, S.; Tanner, C.M.; Oakes, D.; Shoulson, I. Dietary intake in adults at risk for Huntington disease: Analysis of PHAROS research participants. Neurology 2009, 73, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).