Risk of Thrombosis during and after a SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Pathogenesis, Diagnostic Approach, and Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Clinical Characteristics of COVID-19 Infections
3. Coagulopathy in COVID-19 Infections
3.1. Endothelial Injury and Dysfunction
3.2. Hyperinflammatory Response and Cytokine Storm
3.3. The Activation of Mononuclear Phagocytes, Complements, and NETs
3.4. Tissue Hypoxia
4. Clinical Manifestations of Thrombosis in COVID-19
4.1. Venous Thromboembolism
4.1.1. Deep-Vein Thrombosis
4.1.2. Pulmonary Embolism
4.2. Arterial Thromboembolism
4.2.1. Acute Myocardial Infarction
4.2.2. Ischemic Stroke
5. Diagnostic Markers of Thrombosis in COVID-19 Patients
5.1. Platelet Counts and Immature Platelet Fraction
5.2. D-Dimer
5.3. Von Willebrand Factor
5.4. Viscoelastic Test and Thromboelastography
5.5. Antiphospholipid Antibody
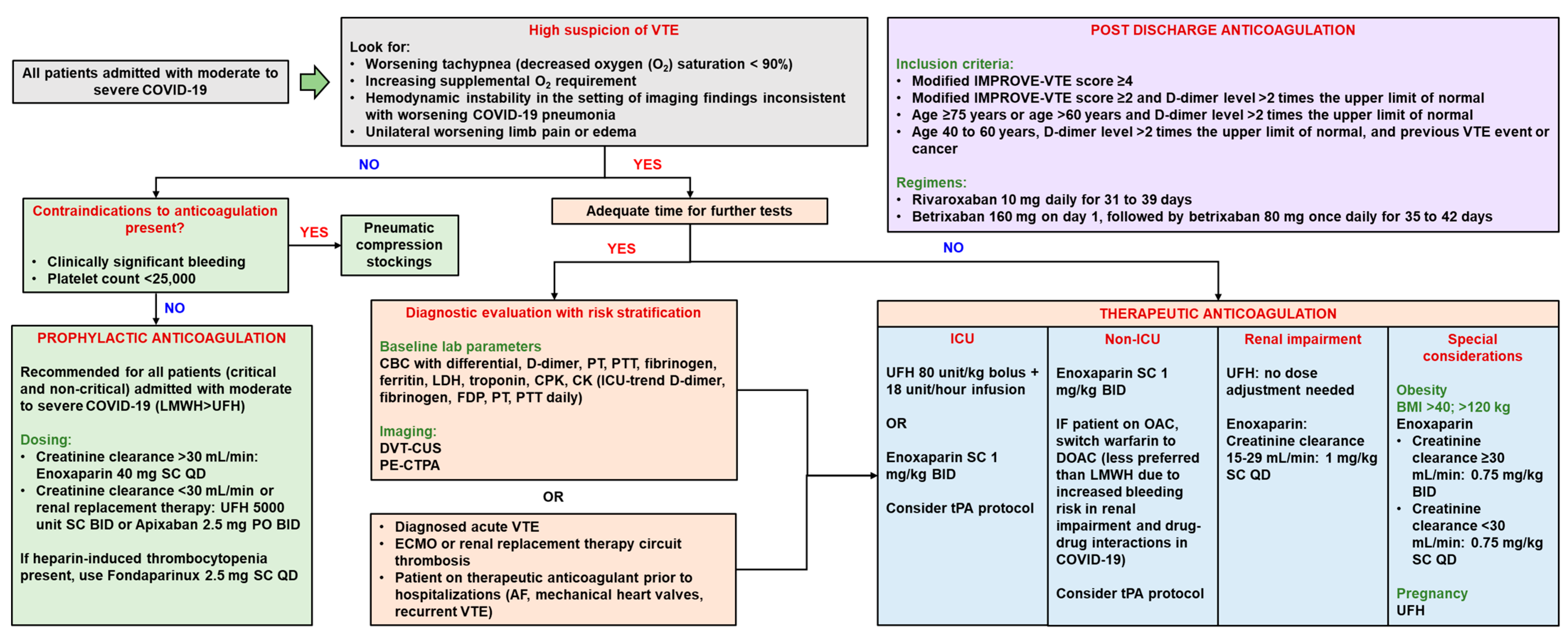
6. Prevention and Management of Thrombosis in COVID-19
6.1. Thrombosis Management
6.1.1. Anticoagulation
6.1.2. Tissue Plasminogen Activator (tPA)
6.1.3. Other Potential Therapies
6.2. Thrombosis Prevention
7. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Worldometers COVID Live—Coronavirus Statistics—Worldometer. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Elezkurtaj, S.; Greuel, S.; Ihlow, J.; Michaelis, E.G.; Bischoff, P.; Kunze, C.A.; Sinn, B.V.; Gerhold, M.; Hauptmann, K.; Ingold-Heppner, B.; et al. Causes of Death and Comorbidities in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichmann, D.; Sperhake, J.-P.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Steurer, S.; Edler, C.; Heinemann, A.; Heinrich, F.; Mushumba, H.; Kniep, I.; Schröder, A.S.; et al. Autopsy Findings and Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with COVID-19. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenner, W.J.; Gorog, D.A. Incidence of Thrombotic Complications in COVID-19. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 52, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burn, E.; Duarte-Salles, T.; Fernandez-Bertolin, S.; Reyes, C.; Kostka, K.; Delmestri, A.; Rijnbeek, P.; Verhamme, K.; Prieto-Alhambra, D. Venous or Arterial Thrombosis and Deaths among COVID-19 Cases: A European Network Cohort Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1142–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.K.; Mainbourg, S.; Friggeri, A.; Bertoletti, L.; Douplat, M.; Dargaud, Y.; Grange, C.; Lobbes, H.; Provencher, S.; Lega, J.-C. Arterial and Venous Thromboembolism in COVID-19: A Study-Level Meta-Analysis. Thorax 2021, 76, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruip, M.J.H.A.; Cannegieter, S.C.; ten Cate, H.; van Gorp, E.C.M.; Juffermans, N.P.; Klok, F.A.; Maas, C.; Vonk-Noordegraaf, A. Caging the Dragon: Research Approach to COVID-19–Related Thrombosis. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 5, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, S.R.; Ducruet, T.; Lamping, D.L.; Arsenault, L.; Miron, M.J.; Roussin, A.; Desmarais, S.; Joyal, F.; Kassis, J.; Solymoss, S.; et al. Prospective Evaluation of Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Deep Venous Thrombosis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, S.R.; Akaberi, A.; Granton, J.T.; Anderson, D.R.; Wells, P.S.; Rodger, M.A.; Solymoss, S.; Kovacs, M.J.; Rudski, L.; Shimony, A.; et al. Quality of Life, Dyspnea, and Functional Exercise Capacity Following a First Episode of Pulmonary Embolism: Results of the ELOPE Cohort Study. Am. J. Med. 2017, 130, 990.e9–990.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katsoularis, I.; Fonseca-Rodríguez, O.; Farrington, P.; Jerndal, H.; Lundevaller, E.H.; Sund, M.; Lindmark, K.; Connolly, A.-M.F. Risks of Deep Vein Thrombosis, Pulmonary Embolism, and Bleeding after COVID-19: Nationwide Self-Controlled Cases Series and Matched Cohort Study. BMJ 2022, 377, e069590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Health Clinical Spectrum. Available online: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/overview/clinical-spectrum/ (accessed on 17 December 2022).
- Deng, G.; Yin, M.; Chen, X.; Zeng, F. Clinical Determinants for Fatality of 44,672 Patients with COVID-19. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhong, X.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Luo, T.; Liu, Q. Clinical Determinants of the Severity of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertanto, D.M.; Sutanto, H.; Adi, S. Case Report: Diabetic Nephropathy Aggravates the Progression and Prognosis of COVID-19-Associated Acute Limb Ischemia. F1000Research 2021, 10, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Rosa Mesquita, R.; Francelino Silva Junior, L.C.; Santos Santana, F.M.; Farias de Oliveira, T.; Campos Alcântara, R.; Monteiro Arnozo, G.; Rodrigues da Silva Filho, E.; Galdino dos Santos, A.G.; Oliveira da Cunha, E.J.; Salgueiro de Aquino, S.H.; et al. Clinical Manifestations of COVID-19 in the General Population: Systematic Review. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2021, 133, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Xin, Y.; Li, H.; Mu, W.; Wu, Q.; Xu, L.; Zhao, M.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of 310 SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant Patients and Comparison with Delta and Beta Variant Patients in China. Virol. Sin. 2022, 37, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.-H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Renner, D.M.; Comar, C.E.; Whelan, J.N.; Reyes, H.M.; Cardenas-Diaz, F.L.; Truitt, R.; Tan, L.H.; Dong, B.; Alysandratos, K.D.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Induces Double-Stranded RNA-Mediated Innate Immune Responses in Respiratory Epithelial-Derived Cells and Cardiomyocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2022643118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, M.M.; Haagmans, B.L. SARS-CoV-2 Pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Lou, X.; Chen, S.; Deng, H.; Shi, L.; Xie, J.; Tang, D.; Zhao, J.; et al. Damaged Lung Gas Exchange Function of Discharged COVID-19 Patients Detected by Hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabc8180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, J.P.; Vladar, E.K.; Huang, H.; Mason, R.J. Respiratory Epithelial Cell Responses to SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19. Thorax 2022, 77, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Ismail, M.Y.; Diamond, A.; Kapoor, S.; Arafah, Y.; Nayak, L. The Hypercoagulable State in COVID-19: Incidence, Pathophysiology, and Management. Thromb. Res. 2020, 194, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, J.; MacArthur, T.A.; Sridharan, M.; Pruthi, R.K.; McBane, R.D.; Witzig, T.E.; Park, M.S. A Review of Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, and Management Options of COVID-19 Associated Coagulopathy. Shock 2021, 55, 700–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadyen, J.D.; Stevens, H.; Peter, K. The Emerging Threat of (Micro)Thrombosis in COVID-19 and Its Therapeutic Implications. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaventura, A.; Vecchié, A.; Dagna, L.; Martinod, K.; Dixon, D.L.; Van Tassell, B.W.; Dentali, F.; Montecucco, F.; Massberg, S.; Levi, M.; et al. Endothelial Dysfunction and Immunothrombosis as Key Pathogenic Mechanisms in COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Schiavon, C.R.; He, M.; Chen, L.; Shen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, Q.; Cho, Y.; Andrade, L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Impairs Endothelial Function via Downregulation of ACE 2. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 1323–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, Z.; Flammer, A.J.; Steiger, P.; Haberecker, M.; Andermatt, R.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Mehra, M.R.; Schuepbach, R.A.; Ruschitzka, F.; Moch, H. Endothelial Cell Infection and Endotheliitis in COVID-19. Lancet 2020, 395, 1417–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targosz-Korecka, M.; Kubisiak, A.; Kloska, D.; Kopacz, A.; Grochot-Przeczek, A.; Szymonski, M. Endothelial Glycocalyx Shields the Interaction of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein with ACE2 Receptors. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Han, K.; Blair, R.; Kenst, K.; Qin, Z.; Upcin, B.; Wörsdörfer, P.; Midkiff, C.C.; Mudd, J.; Belyaeva, E.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infects Endothelial Cells In Vivo and In Vitro. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 701278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCracken, I.R.; Saginc, G.; He, L.; Huseynov, A.; Daniels, A.; Fletcher, S.; Peghaire, C.; Kalna, V.; Andaloussi-Mäe, M.; Muhl, L.; et al. Lack of Evidence of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Expression and Replicative Infection by SARS-CoV-2 in Human Endothelial Cells. Circulation 2021, 143, 865–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhl, L.; He, L.; Sun, Y.; Andaloussi Mäe, M.; Pietilä, R.; Liu, J.; Genové, G.; Zhang, L.; Xie, Y.; Leptidis, S.; et al. The SARS-CoV-2 Receptor ACE2 Is Expressed in Mouse Pericytes but Not Endothelial Cells: Implications for COVID-19 Vascular Research. Stem Cell Rep. 2022, 17, 1089–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zuo, W. Single-Cell RNA Expression Profiling of ACE2, the Receptor of SARS-CoV-2. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, 756–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, S.E.; Curley, G.F.; Lavin, M.; Fogarty, H.; Karampini, E.; McEvoy, N.L.; Clarke, J.; Boylan, M.; Alalqam, R.; Worrall, A.P.; et al. Von Willebrand Factor Propeptide in Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Evidence of Acute and Sustained Endothelial Cell Activation. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 192, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.O.; Reyat, J.S.; Hill, H.; Bourne, J.H.; Colicchia, M.; Newby, M.L.; Allen, J.D.; Crispin, M.; Youd, E.; Murray, P.G.; et al. Preferential Uptake of SARS-CoV-2 by Pericytes Potentiates Vascular Damage and Permeability in an Organoid Model of the Microvasculature. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 3085–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Paz, L.; Capodanno, D.; Montalescot, G.; Angiolillo, D.J. Coronavirus Disease 2019–Associated Thrombosis and Coagulopathy: Review of the Pathophysiological Characteristics and Implications for Antithrombotic Management. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e019650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.; Verleden, S.E.; Kuehnel, M.; Haverich, A.; Welte, T.; Laenger, F.; Vanstapel, A.; Werlein, C.; Stark, H.; Tzankov, A.; et al. Pulmonary Vascular Endothelialitis, Thrombosis, and Angiogenesis in COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Feng, Y.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Bai, X.; Jiao, L. Prognostic Value of von Willebrand Factor and ADAMTS13 in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Thromb. Res. 2022, 218, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, A.; Marco, P. Von Willebrand Factor and ADAMTS13 Activity as Clinical Severity Markers in Patients with COVID-19. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 52, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guervilly, C.; Burtey, S.; Sabatier, F.; Cauchois, R.; Lano, G.; Abdili, E.; Daviet, F.; Arnaud, L.; Brunet, P.; Hraiech, S.; et al. Circulating Endothelial Cells as a Marker of Endothelial Injury in Severe COVID-19. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 1789–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, S.; Mendes, M.C.; Camargo Martins, A.P.; Borges, N.H.; Godoy, T.M.; dos Santos Miggiolaro, A.F.R.; da Silva Dezidério, F.; Machado-Souza, C.; de Noronha, L. Endothelial Dysfunction and Thrombosis in Patients with COVID-19—Brief Report. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 2404–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Salvo, E.; Di Gioacchino, M.; Tonacci, A.; Casciaro, M.; Gangemi, S. Alarmins, COVID-19 and Comorbidities. Ann. Med. 2021, 53, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savla, S.R.; Prabhavalkar, K.S.; Bhatt, L.K. Cytokine Storm Associated Coagulation Complications in COVID-19 Patients: Pathogenesis and Management. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2021, 19, 1397–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hottz, E.D.; Azevedo-Quintanilha, I.G.; Palhinha, L.; Teixeira, L.; Barreto, E.A.; Pão, C.R.R.; Righy, C.; Franco, S.; Souza, T.M.L.; Kurtz, P.; et al. Platelet Activation and Platelet-Monocyte Aggregate Formation Trigger Tissue Factor Expression in Patients with Severe COVID-19. Blood 2020, 136, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albornoz, E.A.; Amarilla, A.A.; Modhiran, N.; Parker, S.; Li, X.X.; Wijesundara, D.K.; Aguado, J.; Zamora, A.P.; McMillan, C.L.D.; Liang, B.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Drives NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Human Microglia through Spike Protein. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Shen, M.; Yu, Z.; Ge, W.; Chen, K.; Tian, M.; Xiao, F.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Jia, Y.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 N Protein Promotes NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation to Induce Hyperinflammation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setua, S.; Thangaraju, K.; Dzieciatkowska, M.; Wilkerson, R.B.; Nemkov, T.; Lamb, D.R.; Tagaya, Y.; Boyer, T.; Rowden, T.; Doctor, A.; et al. Coagulation Potential and the Integrated Omics of Extracellular Vesicles from COVID-19 Positive Patient Plasma. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbi, C.; Burrello, J.; Bolis, S.; Lazzarini, E.; Biemmi, V.; Pianezzi, E.; Burrello, A.; Caporali, E.; Grazioli, L.G.; Martinetti, G.; et al. Circulating Extracellular Vesicles Are Endowed with Enhanced Procoagulant Activity in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. eBioMedicine 2021, 67, 103369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görlach, A.; Diebold, I.; Schini-Kerth, V.B.; Berchner-Pfannschmidt, U.; Roth, U.; Brandes, R.P.; Kietzmann, T.; Busse, R. Thrombin Activates the Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Signaling Pathway in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Circ. Res. 2001, 89, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waheed, S.M.; Kudaravalli, P.; Hotwagner, D.T. Deep Vein Thrombosis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, Y.J.; Hong, H.; Ohana, M.; Bompard, F.; Revel, M.-P.; Valle, C.; Gervaise, A.; Poissy, J.; Susen, S.; Hékimian, G.; et al. Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Radiology 2021, 298, E70–E80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, R.; Walker, V.; Ip, S.; Cooper, J.A.; Bolton, T.; Keene, S.; Denholm, R.; Akbari, A.; Abbasizanjani, H.; Torabi, F.; et al. Association of COVID-19 With Major Arterial and Venous Thrombotic Diseases: A Population-Wide Cohort Study of 48 Million Adults in England and Wales. Circulation 2022, 146, 892–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, V.; Goyal, A. Acute Pulmonary Embolism. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Riyahi, S.; Dev, H.; Behzadi, A.; Kim, J.; Attari, H.; Raza, S.I.; Margolis, D.J.; Jonisch, A.; Megahed, A.; Bamashmos, A.; et al. Pulmonary Embolism in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Multicenter Study. Radiology 2021, 301, E426–E433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauvel, C.; Weizman, O.; Trimaille, A.; Mika, D.; Pommier, T.; Pace, N.; Douair, A.; Barbin, E.; Fraix, A.; Bouchot, O.; et al. Pulmonary Embolism in COVID-19 Patients: A French Multicentre Cohort Study. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 3058–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanaroff, A.C.; Garcia, S.; Giri, J. Myocardial Infarction During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA 2021, 326, 1916–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, M.; Kennedy, K.F.; Imran, H.; Louis, D.W.; Shippey, E.; Poppas, A.; Wood, K.E.; Abbott, J.D.; Aronow, H.D. Association Between COVID-19 Diagnosis and In-Hospital Mortality in Patients Hospitalized With ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. JAMA 2021, 326, 1940–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Chang, J.; Xian, Y.; Wang, D.; Mao, L.; Jin, H.; Hu, B. Acute Cerebrovascular Disease Following COVID-19: A Single Center, Retrospective, Observational Study. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2020, 5, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannoni, S.; de Groot, R.; Bell, S.; Markus, H.S. Stroke in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Stroke 2021, 16, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, G.; Plebani, M.; Henry, B.M. Thrombocytopenia Is Associated with Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Infections: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 506, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorog, D.A.; Storey, R.F.; Gurbel, P.A.; Tantry, U.S.; Berger, J.S.; Chan, M.Y.; Duerschmied, D.; Smyth, S.S.; Parker, W.A.E.; Ajjan, R.A.; et al. Current and Novel Biomarkers of Thrombotic Risk in COVID-19: A Consensus Statement from the International COVID-19 Thrombosis Biomarkers Colloquium. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2022, 19, 475–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thachil, J.; Tang, N.; Gando, S.; Falanga, A.; Cattaneo, M.; Levi, M.; Clark, C.; Iba, T. ISTH Interim Guidance on Recognition and Management of Coagulopathy in COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wool, G.D.; Miller, J.L. The Impact of COVID-19 Disease on Platelets and Coagulation. PAT 2021, 88, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Mullier, F.; Favaloro, E.J. D-Dimer: Old Dogmas, New (COVID-19) Tricks. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudatsir, M.; Fajar, J.K.; Wulandari, L.; Soegiarto, G.; Ilmawan, M.; Purnamasari, Y.; Mahdi, B.A.; Jayanto, G.D.; Suhendra, S.; Setianingsih, Y.A.; et al. Predictors of COVID-19 Severity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. F1000Research 2021, 9, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auditeau, C.; Khider, L.; Planquette, B.; Sanchez, O.; Smadja, D.M.; Gendron, N. D-Dimer Testing in Clinical Practice in the Era of COVID-19. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 6, e12730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, E.S.; McClelland, P.H.; Cheng, O.; Kim, Y.; Hu, J.; Zenilman, M.E.; D’Ayala, M. Utility of D-Dimer for Diagnosis of Deep Vein Thrombosis in Coronavirus Disease-19 Infection. J. Vasc. Surg. Venous Lymphat. Disord. 2021, 9, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivan, M.A.; Rigatti, B.; da Cunha, S.V.; Frison, G.C.; Antoniazzi, L.Q.; de Oliveira, P.H.K.; Oliveira, J.P.S.; Fontanari, C.; Seligman, B.G.S.; Seligman, R. Pulmonary Embolism in Patients with COVID-19 and D-Dimer Diagnostic Value: A Retrospective Study. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 26, 102702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logothetis, C.N.; Weppelmann, T.A.; Jordan, A.; Hanna, C.; Zhang, S.; Charkowick, S.; Oxner, A. D-Dimer Testing for the Exclusion of Pulmonary Embolism Among Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2128802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalay, B.; Cesur, A.; Agirbasli, M. Discrepancy between Biomarkers of Lung Injury and 1-Year Mortality in COVID-19. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 52, e13827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhao, W.; Kaatz, S.; Latack, K.; Schultz, L.; Poisson, L. Factors Associated with Risk of Postdischarge Thrombosis in Patients with COVID-19. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2135397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshua, G.; Pine, A.B.; Meizlish, M.L.; Chang, C.-H.; Zhang, H.; Bahel, P.; Baluha, A.; Bar, N.; Bona, R.D.; Burns, A.J.; et al. Endotheliopathy in COVID-19-Associated Coagulopathy: Evidence from a Single-Centre, Cross-Sectional Study. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e575–e582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escher, R.; Breakey, N.; Lämmle, B. Severe COVID-19 Infection Associated with Endothelial Activation. Thromb. Res. 2020, 190, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortus, J.R.; Manek, S.E.; Brubaker, L.S.; Loor, M.; Cruz, M.A.; Trautner, B.W.; Rosengart, T.K. Thromboelastographic Results and Hypercoagulability Syndrome in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Who Are Critically Ill. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2011192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, N.; Atallah, B.; El Nekidy, W.S.; Sadik, Z.G.; Park, W.M.; Mallat, J. Thromboelastography Findings in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 51, 961–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvi, T.K.; Stubblefield, W.B.; Tillman, B.F.; Tenforde, M.W.; Patel, M.M.; Lindsell, C.J.; Self, W.H.; Grijalva, C.G.; Rice, T.W.; Influenza and Other Viruses in the Acutely Ill (IVY) Network. Serial Thromboelastography and the Development of Venous Thromboembolism in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19. Crit. Care Explor. 2022, 4, e0618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gkrouzman, E.; Andrade, D.C.O.; Andreoli, L.; Barbhaiya, M.; Belmont, H.M.; Branch, D.W.; de Jesús, G.R.; Efthymiou, M.; Ríos-Garcés, R.; et al. COVID-19 and Antiphospholipid Antibodies: A Position Statement and Management Guidance from AntiPhospholipid Syndrome Alliance for Clinical Trials and InternatiOnal Networking (APS ACTION). Lupus 2021, 30, 2276–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iba, T.; Nisio, M.D.; Levy, J.H.; Kitamura, N.; Thachil, J. New Criteria for Sepsis-Induced Coagulopathy (SIC) Following the Revised Sepsis Definition: A Retrospective Analysis of a Nationwide Survey. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e017046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hajra, A.; Mathai, S.V.; Ball, S.; Bandyopadhyay, D.; Veyseh, M.; Chakraborty, S.; Lavie, C.J.; Aronow, W.S. Management of Thrombotic Complications in COVID-19: An Update. Drugs 2020, 80, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute of Health Antithrombotic Therapy. Available online: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/therapies/antithrombotic-therapy/ (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- Goyal, A.; Saigal, S.; Niwariya, Y.; Sharma, J.; Singh, P. Successful Use of TPA for Thrombolysis in COVID Related ARDS: A Case Series. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 51, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hajizadeh, N.; Moore, E.E.; McIntyre, R.C.; Moore, P.K.; Veress, L.A.; Yaffe, M.B.; Moore, H.B.; Barrett, C.D. Tissue Plasminogen Activator (TPA) Treatment for COVID-19 Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): A Case Series. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1752–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whyte, C.S.; Morrow, G.B.; Mitchell, J.L.; Chowdary, P.; Mutch, N.J. Fibrinolytic Abnormalities in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) and Versatility of Thrombolytic Drugs to Treat COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Mitre, M.P.; Tong, S.Y.C.; Denholm, J.T.; Dore, G.J.; Bowen, A.C.; Lewin, S.R.; Venkatesh, B.; Hills, T.E.; McQuilten, Z.; Paterson, D.L.; et al. Nafamostat Mesylate for Treatment of COVID-19 in Hospitalised Patients: A Structured, Narrative Review. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2022, 61, 1331–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, T.M.; Gaughan, E.E.; Bruce, A.; Antonelli, J.; O’Connor, R.; Li, F.; McNamara, S.; Koch, O.; MacKintosh, C.; Dockrell, D.; et al. Randomised Controlled Trial of Intravenous Nafamostat Mesylate in COVID Pneumonitis: Phase 1b/2a Experimental Study to Investigate Safety, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics. EBioMedicine 2022, 76, 103856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravel, S.V.; Khmelnitskiy, O.K.; Burlaka, O.O.; Gritsan, A.I.; Goloshchekin, B.M.; Kim, S.; Hong, K.Y. Nafamostat in Hospitalized Patients with Moderate to Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Randomised Phase II Clinical Trial. eClinicalMedicine 2021, 41, 101169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, S.; Sholzberg, M.; Spyropoulos, A.C.; Zarychanski, R.; Resnick, H.E.; Bradbury, C.A.; Broxmeyer, L.; Connors, J.M.; Falanga, A.; Iba, T.; et al. ISTH Guidelines for Antithrombotic Treatment in COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 20, 2214–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sutanto, H.; Soegiarto, G. Risk of Thrombosis during and after a SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Pathogenesis, Diagnostic Approach, and Management. Hematol. Rep. 2023, 15, 225-243. https://doi.org/10.3390/hematolrep15020024
Sutanto H, Soegiarto G. Risk of Thrombosis during and after a SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Pathogenesis, Diagnostic Approach, and Management. Hematology Reports. 2023; 15(2):225-243. https://doi.org/10.3390/hematolrep15020024
Chicago/Turabian StyleSutanto, Henry, and Gatot Soegiarto. 2023. "Risk of Thrombosis during and after a SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Pathogenesis, Diagnostic Approach, and Management" Hematology Reports 15, no. 2: 225-243. https://doi.org/10.3390/hematolrep15020024
APA StyleSutanto, H., & Soegiarto, G. (2023). Risk of Thrombosis during and after a SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Pathogenesis, Diagnostic Approach, and Management. Hematology Reports, 15(2), 225-243. https://doi.org/10.3390/hematolrep15020024







