Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Mild COVID-19: Case Series and Analysis of the Literature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- age between 18 and 65 years;
- diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection, through a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay on oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal (OP/NP) swab test [25];
- asymptomatic to mild clinical presentation of COVID-19, according to NIH Guidelines [26];
- compliance with the therapy and adherence to the follow-up.
- previous HL and/or tinnitus;
- previous ear pathology and/or otologic surgery;
- cerebello-pontine angle pathology or congenital ear malformations;
- head and/or neck trauma or barotrauma within the last 3 months.
- complete recovery (CR): final hearing better than 25 dB;
- partial recovery (PR): more than 15 dB gain, final hearing 25–45 dB;
- slight improvement (SI): more than 15 dB gain, final hearing poorer than 45 dB;
- no improvement (NO): less than 15 dB gain, final hearing poorer than 75 dB.
3. Results—Case Series
3.1. Patient #1
3.2. Patient #2
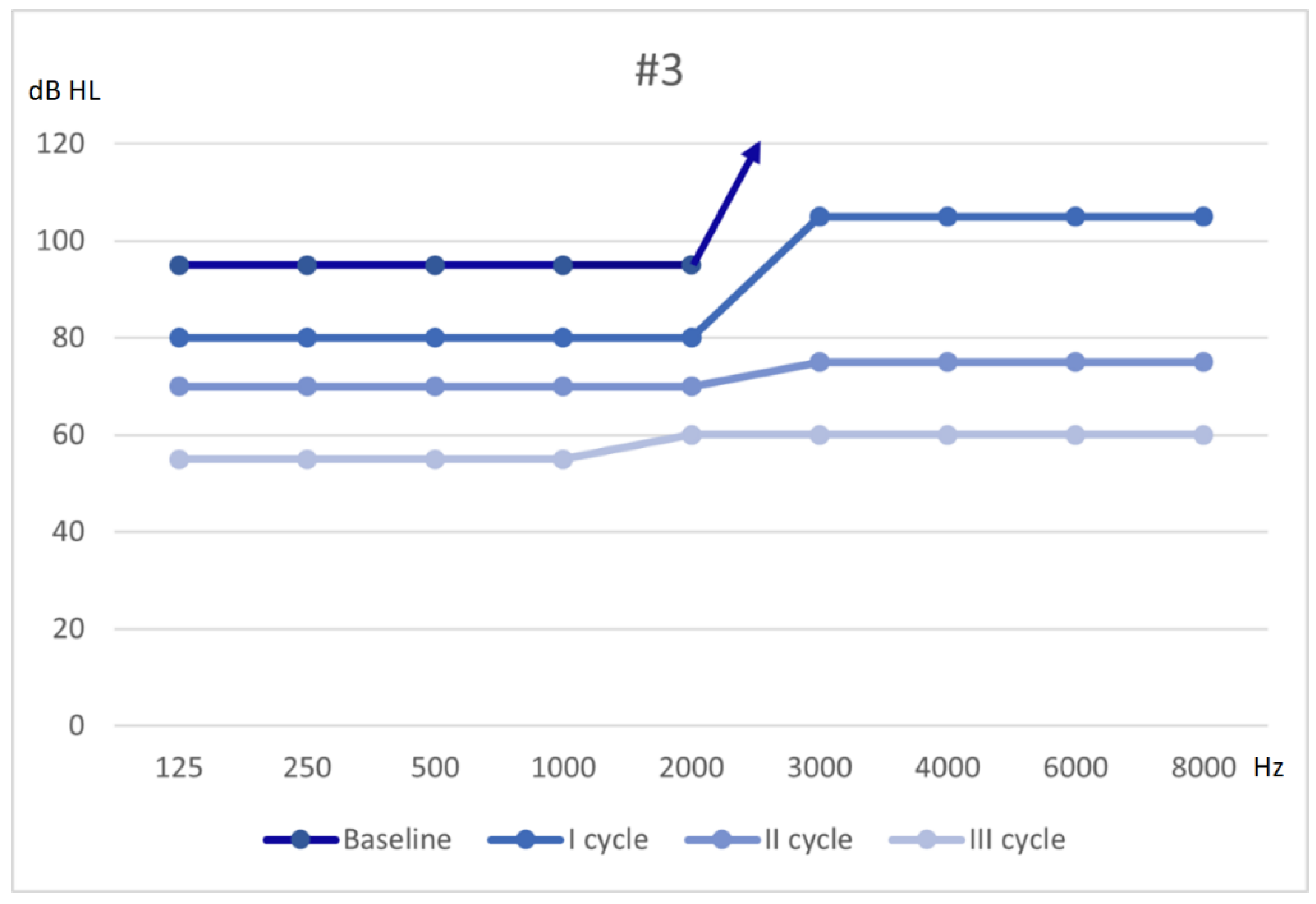
3.3. Patient #3
3.4. Patient #4
3.5. Patient #5
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schreiber, B.E.; Agrup, C.; Haskard, D.O.; Luxon, L.M. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Lancet 2010, 375, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosrati-Zarenoe, R.; Hultcrantz, E. Corticosteroid Treatment of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Otol. Neurotol. 2012, 33, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quaranta, N.; De Ceglie, V.; D’Elia, A. Endothelial Dysfunction in Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Review. Audiol. Res. 2016, 6, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yigider, A.P.; Keskin, M.; Kufeciler, L.; Kocak, H.E. Topography of the lesion in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2020, 140, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciancalepore, P.I.; De Robertis, V.; Sardone, R.; Quaranta, N. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: What factors influence the response to therapy? Audiol. Res. 2020, 10, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.M.; Jung, S.W.; Rhee, C.K. Vestibular diagnosis as prognostic indicator in sudden hearing loss with vertigo. Acta Oto-Laryngol. Suppl. 2001, 545, 11677749. [Google Scholar]
- Prince, A.D.P.; Stucken, E.Z. Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Emergency. J. Am. Board Fam. Med. 2021, 34, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, P.G. Herpes simplex virus type 1 and Bell’s palsy—A current assessment of the controversy. J. Neurovirol. 2010, 16, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, B.E.; Durstenfeld, A.; Roehm, P.C. Viral Causes of Hearing Loss: A Review for Hearing Health Professionals. Trends Hear. 2014, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateer, E.J.; Huang, C.; Shehu, N.Y.; Paessler, S. Lassa fever–induced sensorineural hearing loss: A neglected public health and social burden. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, W.R. The Relationship of the Herpesvirus Family to Sudden Hearing Loss: A Prospective Clinical Study and Literature Review. Laryngoscope 1986, 96, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, Y.; Kurata, T.; Saito, K. Cochlear Changes after Herpes Simplex Virus Infection. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1985, 99, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esaki, S.; Goshima, F.; Kimura, H.; Ikeda, S.; Katsumi, S.; Kabaya, K.; Watanabe, N.; Hashiba, M.; Nishiyama, Y.; Murakami, S. Auditory and vestibular defects induced by experimental labyrinthitis following herpes simplex virus in mice. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2011, 131, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficenec, S.C.; Schieffelin, J.S.; Emmett, S.D. A Review of Hearing Loss Associated with Zika, Ebola, and Lassa Fever. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 101, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, N.E.; Ronca, S.; Tamura, A.; Koma, T.; Seregin, A.V.; Dineley, K.T.; Miller, M.; Cook, R.; Shimizu, N.; Walker, A.G.; et al. Animal Model of Sensorineural Hearing Loss Associated with Lassa Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 2920–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cashman, K.A.; Wilkinson, E.R.; Zeng, X.; Cardile, A.P.; Facemire, P.R.; Bell, T.M.; Bearss, J.J.; Shaia, C.I.; Schmaljohn, C.S. Immune-Mediated Systemic Vasculitis as the Proposed Cause of Sudden-Onset Sensorineural Hearing Loss following Lassa Virus Exposure in Cynomolgus Macaques. mBio 2018, 9, e01896-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Haro-Licer, J.; Roura-Moreno, J.; Vizitiu, A.; González-Fernández, A.; González-Ares, J.A. Resfriado-gripe: Pérdida grave del olfato a largo plazo. Acta Otorrinolaringológica Española 2013, 64, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Saito, K.; Min, W.-P.; Vladau, C.; Toida, K.; Itoh, H.; Murakami, S. Identification of Viruses in Patients With Postviral Olfactory Dysfunction. Laryngoscope 2007, 117, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumari, P.; Rothan, H.; Natekar, J.; Stone, S.; Pathak, H.; Strate, P.; Arora, K.; Brinton, M.; Kumar, M. Neuroinvasion and Encephalitis Following Intranasal Inoculation of SARS-CoV-2 in K18-hACE2 Mice. Viruses 2021, 13, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viola, P.; Ralli, M.; Pisani, D.; Malanga, D.; Sculco, D.; Messina, L.; Laria, C.; Aragona, T.; Leopardi, G.; Ursini, F.; et al. Tinnitus and equilibrium disorders in COVID-19 patients: Preliminary results. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narozny, W.; Tretiakow, D.; Skorek, A. Tinnitus in COVID-19 Pandemic. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021, 100, 197S–198S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadera, L.; Viola, P.; Pisani, D.; Scarpa, A.; Malanga, D.; Sorrentino, G.; Madini, E.; Laria, C.; Aragona, T.; Leopardi, G.; et al. Sudden olfactory loss as an early marker of COVID-19: A nationwide Italian survey. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2021, 278, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarella, G.; Pizzolato, R.; Malanga, D.; Pisani, D.; Abenavoli, L.; Viola, P. Prevention of COVID-19 Infection in the Medical Population: Possible Help from Anosmia? Rev. Recent Clin. Trials 2020, 15, 244–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, A.S.; Joshi, S.V.; Naik, S.; Sangle, S.; Abraham, N.M. Quantitative assessment of olfactory dysfunction accurately detects asymptomatic COVID-19 carriers. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marty, F.M.; Chen, K.; Verrill, K.A. How to Obtain a Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimen. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/overview/clinical-spectrum/ (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- De Luca, P.; Scarpa, A.; De Bonis, E.; Cavaliere, M.; Viola, P.; Gioacchini, F.M.; Ralli, M.; Ettore, C.; Claudia, C. Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine ototoxicity; potential implications for SARS-CoV-2 treatment. A brief review of the literature. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2021, 42, 102640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altissimi, G.; Colizza, A.; Cianfrone, G.; de Vincentiis, M.; Greco, A.; Taurone, S.; Musacchio, A.; Ciofalo, A.; Turchetta, R.; Angeletti, D.; et al. Drugs inducing hearing loss, tinnitus, dizziness and vertigo: An updated guide. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 7946–7952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monzani, D.; Genovese, E.; Marrara, A.; Gherpelli, C.; Pingani, L.; Forghieri, M.; Rigatelli, M.; Guadagnin, T.; Arslan, E. Validity of the Italian adaptation of the Tinnitus Handicap Inventory; focus on quality of life and psychological distress in tinnitus-sufferers. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2008, 28, 126–134. [Google Scholar]
- Nola, G.; Mostardini, C.; Salvi, C.; Ercolani, A.; Ralli, G. Validity of Italian adaptation of the Dizziness Handicap Inventory (DHI) and evaluation of the quality of life in patients with acute dizziness. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2010, 30, 190. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, B.P.C.; Stathopoulos, D.; O’Leary, S. Steroids for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, J.H.; Bs, J.A.Z.; Gandhi, K.R.; Flaherty, A.; Barber, W.; Bs, M.A.L.; Burgess, L.P. Oral and intratympanic steroid therapy for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 2018, 3, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mirian, C.; Ovesen, T. Intratympanic vs Systemic Corticosteroids in First-line Treatment of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. JAMA Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2020, 146, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufano, A.; Arturo, C.; Cimino, E.; Di Minno, M.N.D.; Di Capua, M.; Cerbone, A.M.; Di Minno, G. Mesoglycan: Clinical Evidences for Use in Vascular Diseases. Int. J. Vasc. Med. 2010, 2010, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neri, G.; Marcelli, V.; Califano, L. Glicover Investigators Assessment of the effect of mesoglycan in the treatment of audiovestibular disorders of vascular origin. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2018, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Do, B.S.T.; Schwartz, S.R.; Bontempo, L.J.; Faucett, E.A.; Finestone, S.A.; Hollingsworth, D.B.; Kelley, D.M.; Kmucha, S.T.; Moonis, G.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Sudden Hearing Loss (Update). Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2019, 161, S1–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Legros, T.L.; Murphy-Lavoie, H. HBO2 for sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2020, 271–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.H.; Kertesz, T.; Perleth, M.; Yeung, P.; Lehm, J. Hyperbaric oxygen for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss and tinnitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 10, CD004739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayoumy, A.B.; De Ru, J.A. The use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in acute hearing loss: A narrative review. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2019, 276, 1859–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.-F.; Chu, Y.-C.; Tu, T.-Y.; Shiao, A.-S.; Wu, S.-L.; Liao, W.-H. Modified Siegel’s criteria for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Reporting recovery outcomes with matched pretreatment hearing grades. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2018, 81, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desforges, M.; Favreau, D.J.; Brison, É.; Desjardins, J.; Meessen-Pinard, M.; Jacomy, H.; Talbot, P.J. Human Coronaviruses Respiratory Pathogens Revisited as Infectious Neuroinvasive, Neurotropic, and Neurovirulent Agents; Informa UK Limited: London, UK, 2013; pp. 93–121. [Google Scholar]
- Arabi, Y.M.; Balkhy, H.H.; Hayden, F.G.; Bouchama, A.; Luke, T.; Baillie, J.K.; Al-Omari, A.; Hajeer, A.H.; Senga, M.; Denison, M.R.; et al. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.; Zhang, C.; Israelow, B.; Lu-Culligan, A.; Prado, A.V.; Skriabine, S.; Lu, P.; Weizman, O.-E.; Liu, F.; Dai, Y.; et al. Neuroinvasion of SARS-CoV-2 in human and mouse brain. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armocida, D.; Palmieri, M.; Frati, A.; Santoro, A.; Pesce, A. How SARS-Cov-2 can involve the central nervous system. A systematic analysis of literature of the department of human neurosciences of Sapienza University, Italy. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 79, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlman, S.; Wheeler, D.L. Neurotropic Coronavirus Infections. In Neurotropic Viral Infections; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 115–148. [Google Scholar]
- Natoli, S.; Oliveira, V.; Calabresi, P.; Maia, L.; Pisani, A. Does SARS-Cov-2 invade the brain? Translational lessons from animal models. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 1764–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamounier, P.; Franco, V.; Ramos, H.V.L.; Gobbo, D.A.; Teixeira, R.P.; Dos Reis, P.C.; Bahmad, F., Jr.; Cândido, C.C. A 67-Year-Old Woman with Sudden Hearing Loss Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Am. J. Case Rep. 2020, 21, e927519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degen, C.; Lenarz, T.; Willenborg, K. Acute Profound Sensorineural Hearing Loss After COVID-19 Pneumonia. In Proceedings of the Mayo Clinic Proceedings; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 95, pp. 1801–1803. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, N.; Abe, R.; Hattori, N.; Matsumura, Y.; Oshima, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Igari, H.; Nakada, T.-A. Clinical course of a critically ill patient with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). J. Artif. Organs 2020, 23, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumpa, F.S.; Forde, C.T.; Manjaly, J.G. Sudden irreversible hearing loss post COVID-19. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e238419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunay, E.; Kozan, G.; Yuksel, E.; Mizrakli, A.; Aslan, O.; Kavak, S.; Kaya, S.; Yilmaz, Z. A case of peritoneal dialysis in which SARS-CoV-2 was diagnosed by sudden hearing loss. Ren. Fail. 2021, 43, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chern, A.; Famuyide, A.; Moonis, G.; Lalwani, A.K. Bilateral Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Intralabyrinthine Hemorrhage in a Patient With COVID-19. Otol. Neurotol. 2021, 42, e10–e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, O.; Kalcioglu, M.T.; Cag, Y.; Tuysuz, O.; Pektas, E.; Caskurlu, H.; Cetın, F. Could sudden sensorineural hearing loss be the sole manifestation of COVID-19? An investigation into SARS-COV-2 in the etiology of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 97, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, B.; Hintze, J.; Conlon, B. Coronavirus disease 2019 and sudden sensorineural hearing loss. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2020, 134, 1026–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, S.; Toros, S.Z. Vascular Occlusion Role in the Etiopathohegenesis of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Risk Analysis with Hematological Parameters. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2020, 30, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, W.; Song, S.-P.; Jiang, Y.-D. Association between routine hematological parameters and sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A meta-analysis. J. Otol. 2021, 16, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almulhim, A. Sensorineural hearing loss with macrolide antibiotics exposure: A meta-analysis of the association. Int. J. Pharm. Pr. 2021, 29, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Etminan, M.; Westerberg, B.D.; Kozak, F.K.; Guo, M.Y.; Carleton, B.C. Risk of sensorineural hearing loss with macrolide antibiotics: A nested case-control study. Laryngoscope 2016, 127, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alrwisan, A.; Antonelli, P.J.; Brumback, B.A.; Wei, Y.-J.; Winterstein, A.G. Azithromycin and Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Adults: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Otol. Neurotol. 2018, 39, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ricciardiello, F.; Pisani, D.; Viola, P.; Cristiano, E.; Scarpa, A.; Giannone, A.; Longo, G.; Russo, G.; Bocchetti, M.; Coppola, C.; et al. Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Mild COVID-19: Case Series and Analysis of the Literature. Audiol. Res. 2021, 11, 313-326. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres11030029
Ricciardiello F, Pisani D, Viola P, Cristiano E, Scarpa A, Giannone A, Longo G, Russo G, Bocchetti M, Coppola C, et al. Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Mild COVID-19: Case Series and Analysis of the Literature. Audiology Research. 2021; 11(3):313-326. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres11030029
Chicago/Turabian StyleRicciardiello, Filippo, Davide Pisani, Pasquale Viola, Elisabetta Cristiano, Alfonso Scarpa, Antonio Giannone, Giuseppe Longo, Giuseppe Russo, Marco Bocchetti, Ciro Coppola, and et al. 2021. "Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Mild COVID-19: Case Series and Analysis of the Literature" Audiology Research 11, no. 3: 313-326. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres11030029
APA StyleRicciardiello, F., Pisani, D., Viola, P., Cristiano, E., Scarpa, A., Giannone, A., Longo, G., Russo, G., Bocchetti, M., Coppola, C., Perrella, M., Oliva, F., & Chiarella, G. (2021). Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Mild COVID-19: Case Series and Analysis of the Literature. Audiology Research, 11(3), 313-326. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres11030029







