Congenital Nonprofound Bilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Children: Comprehensive Characterization of Auditory Function and Hearing Aid Benefit
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.1.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.1.2. Exclusion Criteria
2.1.3. Eligible Subjects
2.1.4. Participating Subjects
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Stimulus and Recording Equipment
2.4. Hearing Dynamic Range for Pure Tones
2.4.1. Pure-Tone Threshold (PTT)
2.4.2. Uncomfortable Loudness Level for Pure Tones (UCL)
2.5. Otoacoustic Emissions (OAEs)
2.5.1. Transient Evoked Otoacoustic Emission (TEOAE)
2.5.2. Distortion Product Otoacoustic Emission (DPOAE)
2.6. Psychophysical Tuning Curve (PTC)
2.7. Wideband Acoustic Stapedius Reflex Threshold (WBART)
2.8. Click-Evoked ABR
2.9. Recognition of Speech in Spatially Separate Competing Speech
2.10. Aided Frequency-Modulated Tone Threshold in Sound Field
2.11. Questionnaires
2.12. Imaging
- Transversal high-resolution 3D T2-weighted images over IAC, inner ear, reconstructed in coronar and oblique sagittal plane.
- Coronar 3D FLAIR over brain including IAC, inner ear, reconstructed in coronar and oblique sagittal plane.
- Transversal high resolution 2D T2-weighted fast spin-echo images over brain, IAC.
- Transversal high resolution 2D T1-weighted fast spin-echo images over brain, IAC.
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Hearing Dynamic Range for Pure Tones
3.1.1. Pure-Tone Threshold (PTT)
3.1.2. Uncomfortable Loudness Level for Pure Tones (UCL)
3.2. Effects of Ear and Sex on Pure-Tone Thresholds
3.3. Otoacoustic Emissions (OAEs)
3.4. Psychophysical Tuning Curve (PTC)
3.5. Wideband Tympanogram and Acoustic Stapedius Reflex Threshold (WBART)
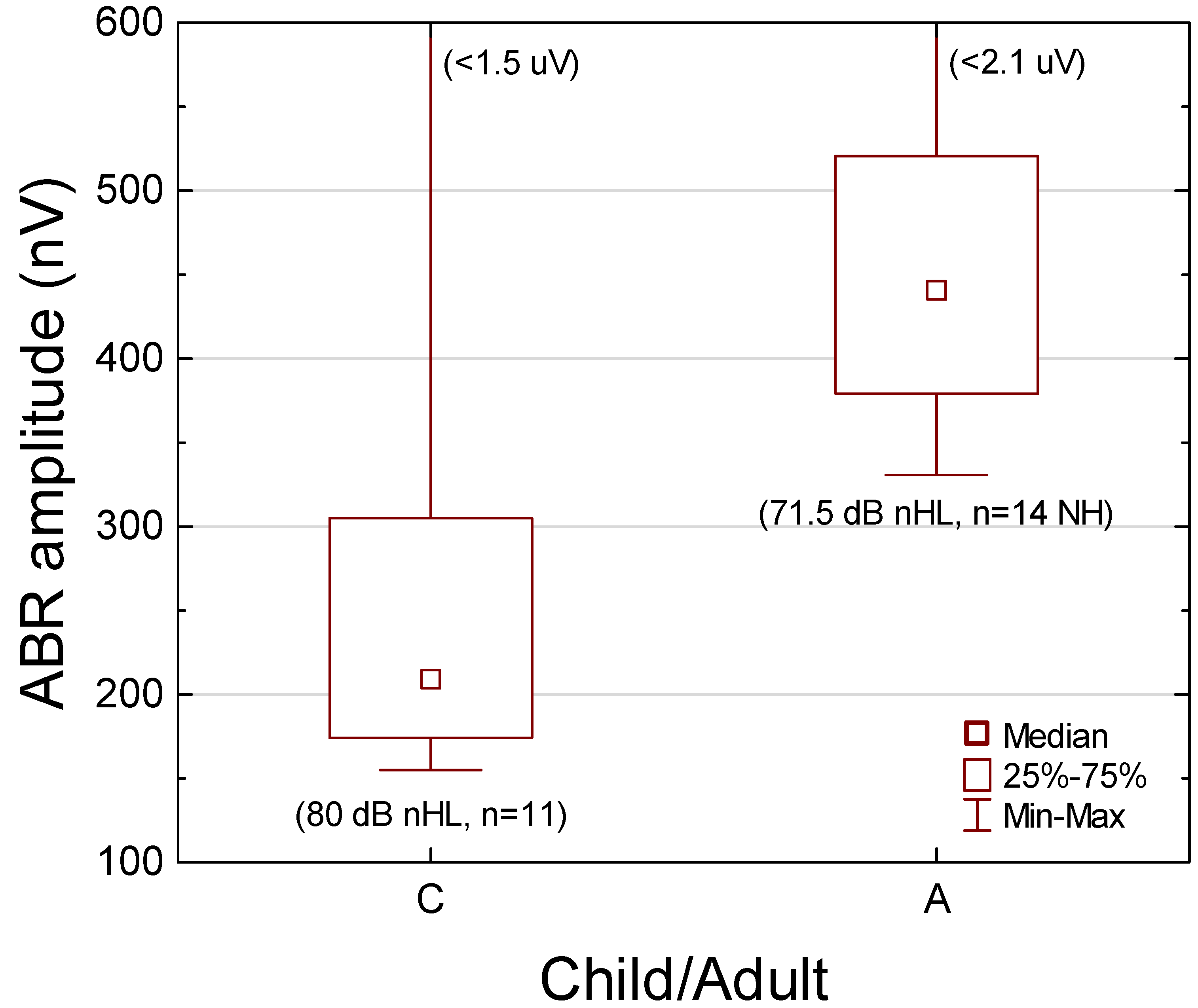
3.6. Click-Evoked Entire ABR RMS Amplitude
Comparison with Young Normal-Hearing Adults
3.7. Click-Evoked ABR Wave Amplitudes and I-V Latency
Comparison with Young Normal-Hearing Adults
3.8. Click-Evoked ABR Threshold
3.9. Aided Frequency-Modulated Tone Threshold in Sound Field
3.10. Age at First Hearing Aid Fit and Daily Usage Time
3.11. Recognition of Speech in Spatially Separate Competing Speech
3.12. Questionnaires
3.13. Imaging
4. Discussion
4.1. Hearing Dynamic Range
4.2. Effects of Ear and Sex on Hearing Thresholds
4.3. Function of the Cochlear Amplifier
4.4. Main Sites for Functional Deficiency
4.5. Hearing Aid Benefit
4.6. Strengths and Limitations
4.7. Future Research and Clinical Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Materials and Methods
Appendix A.1. Subjects
Eligible Subjects
Appendix A.2. Study Design
Appendix A.3. Hearing Dynamic Range for Pure Tones
Pure-Tone Threshold (PTT)
References
- Morton, C.C.; Nance, W.E. Newborn hearing screening--a silent revolution. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2151–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erenberg, A.; Lemons, J.; Sia, C.; Trunkel, D.; Ziring, P. Newborn and infant hearing loss: Detection and intervention. American Academy of Pediatrics. Task Force on Newborn and Infant Hearing, 1998–1999. Pediatrics 1999, 103, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mehl, A.L.; Thomson, V. Newborn hearing screening: The great omission. Pediatrics 1998, 101, E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wroblewska-Seniuk, K.E.; Dabrowski, P.; Szyfter, W.; Mazela, J. Universal newborn hearing screening: Methods and results, obstacles, and benefits. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 81, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vohr, B.; Jodoin-Krauzyk, J.; Tucker, R.; Johnson, M.J.; Topol, D.; Ahlgren, M. Early language outcomes of early-identified infants with permanent hearing loss at 12 to 16 months of age. Pediatrics 2008, 122, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshinaga-Itano, C.; Sedey, A.L.; Coulter, D.K.; Mehl, A.L. Language of early- and later-identified children with hearing loss. Pediatrics 1998, 102, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshinaga-Itano, C.; Sedey, A.L.; Wiggin, M.; Chung, W. Early Hearing Detection and Vocabulary of Children With Hearing Loss. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20162964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, H.L.; Neely, S.T.; Gorga, M.P. Using benefit-cost ratio to select Universal Newborn Hearing Screening test criteria. Ear Hear. 2009, 30, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, D.A.; Chan, D.K. Diagnosis and Treatment of Congenital Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Curr. Otorhinolaryngol. Rep. 2017, 5, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Beeck Calkoen, E.A.; Engel, M.S.D.; van de Kamp, J.M.; Yntema, H.G.; Goverts, S.T.; Mulder, M.F.; Merkus, P.; Hensen, E.F. The etiological evaluation of sensorineural hearing loss in children. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2019, 178, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berninger, E.; Westling, B. Outcome of a universal newborn hearing-screening programme based on multiple transient-evoked otoacoustic emissions and clinical brainstem response audiometry. Acta Otolaryngol. 2011, 131, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, B. An update on the external ear resonance in infants and young children. Ear Hear. 1987, 8, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisch, L. Integrated development and maturation of the hearing system. A critical review article. Br. J. Audiol. 1983, 17, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, L.A.; Folsom, R.C.; Mancl, L.R. The relationship between auditory brainstem response and behavioral thresholds in normal hearing infants and adults. Hear. Res. 1993, 68, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berninger, E. Characteristics of normal newborn transient-evoked otoacoustic emissions: Ear asymmetries and sex effects. Int. J. Audiol. 2007, 46, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berninger, E. Letter to the Editor regarding “Otoacoustic emissions in newborn hearing screening: A systematic review of the effects of different protocols on test outcomes”. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 78, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, H. An active process in cochlear mechanics. Hear. Res. 1983, 9, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobili, R.; Mammano, F.; Ashmore, J. How well do we understand the cochlea? Trends Neurosci. 1998, 21, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudspeth, A.J. Integrating the active process of hair cells with cochlear function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 600–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglione, A.; Möller, C. Usher Syndrome. Audiol. Res. 2022, 12, 42–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.J.H.; Iwasa, Y.; Schaefer, A.M. Pendred Syndrome/Nonsyndromic Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct, in GeneReviews(®); Adam, M.P., Ed.; University of Washington: Seattle, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 8253-1; Acoustics–Audiometric Test Methods—Part 1: Pure-Tone Air and Bone Conduction Audiometry. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- Berninger, E.; Olofsson, A.; Leijon, A. Analysis of click-evoked auditory brainstem responses using time domain cross-correlations between interleaved responses. Ear Hear. 2014, 35, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 60318-4; Electroacoustics-Simulators of Human Head and Ear-Part 4: Occluded-Ear Simulator for the Measurement of Earphones Coupled to the Ear by Means of Ear Inserts. International Electrotechnical Commision: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- ISO 389-2; Acoustics—Reference Zero for the Calibration of Audiometric Equipment—Part 2: Reference Equivalent Threshold Sound Pressure Levels for Pure Tones and Insert Earphones. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994.
- McFadden, D. A speculation about the parallel ear asymmetries and sex differences in hearing sensitivity and otoacoustic emissions. Hear. Res. 1993, 68, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swedish Audiometry Methods Group. Uncomfortable Loudness Level (UCLL) for Pure Tones. In Practical Aspects of Audiology. Manual of Practical Audiometry; Arlinger, S., Ed.; Whurr Publishers Ltd.: London, UK, 1990; pp. 70–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ohlms, L.A.; Lonsbury-Martin, B.L.; Martin, G.K. Acoustic-distortion products: Separation of sensory from neural dysfunction in sensorineural hearing loss in human beings and rabbits. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1991, 104, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verpy, E.; Weil, D.; Leibovici, M.; Goodyear, R.J.; Hamard, G.; Houdon, C.; Lefevre, G.M.; Hardelin, J.P.; Richardson, G.P.; Avan; et al. Stereocilin-deficient mice reveal the origin of cochlear waveform distortions. Nature 2008, 456, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shera, C.A.; Guinan, J.J., Jr. Evoked otoacoustic emissions arise by two fundamentally different mechanisms: A taxonomy for mammalian OAEs. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 105, 782–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinan, J.J., Jr. Olivocochlear efferents: Their action, effects, measurement and uses, and the impact of the new conception of cochlear mechanical responses. Hear. Res. 2018, 362, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, D.T.; Ryan, S.; Bray, P. A guide to the effective use of otoacoustic emissions. Ear Hear. 1990, 11, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonsbury-Martin, B.L.; Harris, F.P.; Stagner, B.B.; Hawkins, M.D.; Martin, G.K. Distortion product emissions in humans. I. Basic properties in normally hearing subjects. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol.-Suppl. 1990, 147, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonsbury-Martin, B.L.; Martin, G.K. The clinical utility of distortion-product otoacoustic emissions. Ear Hear. 1990, 11, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, L.H.; Popelka, G.R.; Rasmussen, A.N.; Osterhammel, P.A. Clinical significance of probe-tone frequency ratio on distortion product otoacoustic emissions. Scand. Audiol. 1993, 22, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smoorenburg, G.F. Audibility region of combination tones. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1972, 52, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berninger, E. Quinine as a Model for the Study of Cochlear Hearing Loss in Humans; Karolinska Institutet: Stockholm, Sweden, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Berninger, E.; Karlsson, K.K.; Alvan, G. Quinine reduces the dynamic range of the human auditory system. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1998, 118, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson, K.K.; Berninger, E.; Gustafsson, L.L.; Alvan, G. Pronounced quinine-induced cochlear hearing loss. A mechanistic study in one volunteer at multiple stable plasma concentrations. J. Audiol. Med. 1995, 4, 12–24. [Google Scholar]
- Berninger, E.; Karlsson, K.K.; Hellgren, U.; Eskilsson, G. Magnitude changes in transient evoked otoacoustic emissions and high-level 2f1-f2 distortion products in man during quinine administration. Scand. Audiol. 1995, 24, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sek, A.; Moore, B.C. Implementation of a fast method for measuring psychophysical tuning curves. Int. J. Audiol. 2011, 50, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwicker, E.; Schorn, K. Psychoacoustical tuning curves in audiology. Audiology 1978, 17, 120–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.C. Perceptual consequences of cochlear hearing loss and their implications for the design of hearing aids. Ear Hear. 1996, 17, 133–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keefe, D.H.; Fitzpatrick, D.; Liu, Y.W.; Sanford, C.A.; Gorga, M.P. Wideband acoustic-reflex test in a test battery to predict middle-ear dysfunction. Hear. Res. 2009, 263, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefe, D.H.; Simmons, J.L. Energy transmittance predicts conductive hearing loss in older children and adults. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 114, 3217–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, L.L.; Keefe, D.H.; Feeney, M.P.; Fitzpatrick, D.F. Pressurized Wideband Acoustic Stapedial Reflex Thresholds: Normal Development and Relationships to Auditory Function in Infants. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2017, 18, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggermont, J.J. Electrocochleography and recruitment. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1977, 86, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakay, W.M.H.; Anderson, L.A.; Garcia-Lazaro, J.A.; McAlpine, D.; Schaette, R. Hidden hearing loss selectively impairs neural adaptation to loud sound environments. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawa, S.G.; Liberman, M.C. Adding insult to injury: Cochlear nerve degeneration after “temporary” noise-induced hearing loss. J. Neurosci 2009, 29, 14077–14085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Badry, M.M.; McFadden, S.L. Evaluation of inner hair cell and nerve fiber loss as sufficient pathologies underlying auditory neuropathy. Hear. Res. 2009, 255, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 389-6; Acoustics—Reference Zero for the Calibration of Audiometric Equipment—Part 6: Reference Threshold of Hearing for Test Signals of Short Duration. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- Eggermont, J.J.; Salamy, A. Maturational time course for the ABR in preterm and full term infants. Hear. Res. 1988, 33, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coenraad, S.; van Immerzeel, T.; Hoeve, L.J.; Goedegebure, A. Fitting model of ABR age dependency in a clinical population of normal hearing children. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. Soc. (EUFOS) Affil. Ger. Soc. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 267, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jiang, Z.D. Intensity effect on amplitude of auditory brainstem responses in human. Scand. Audiol 1991, 20, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpanos, Y.C. ABR and DPOAE indices of normal loudness in children and adults. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2004, 15, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamy, A.; Fenn, C.B.; Bronshvag, M. Ontogenesis of human brainstem evoked potential amplitude. Dev. Psychobiol. 1979, 12, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.; Asp, F.; Berninger, E. Children With Congenital Unilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Effects of Late Hearing Aid Amplification-A Pilot Study. Ear Hear. 2020, 41, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moodie, S.T.F.; Scollie, S.D.; Bagatto, M.P.; Keene, K. Fit-to-Targets for the Desired Sensation Level Version 5.0a Hearing Aid Prescription Method for Children. Am. J. Audiol. 2017, 26, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, C.V. Derivation of primary parameters and procedures for use in speech intelligibility predictions. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1987, 82, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 389-7; Acoustics—Reference Zero for the Calibration of Audiometric Equipment—Part 7: Reference Threshold of Hearing under Free-Field and Diffuse-Field Listening Conditions. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- Cox, R.M.; Alexander, G.C. The abbreviated profile of hearing aid benefit. Ear Hear. 1995, 16, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.A.; Cox, R.M.; Alexander, G.C. Development of APHAB norms for WDRC hearing aids and comparisons with original norms. Ear Hear. 2010, 31, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berninger, E.; Karlsson, K.K. Clinical study of Widex Senso on first-time hearing aid users [published erratum appears in Scand Audiol 2000;29(1):60]. Scand. Audiol. 1999, 28, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoe, D.P. Clinical Measurements of the Auditory Dynamic Range and their Relation to Formulas for Hearing Aid Gain. In Hearing aid Fitting. Theoretical and Practical Views. 13th Danavox Symposium; Jensen, J.H., Ed.; GN ReSound Audiological Library: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1988; pp. 129–152. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, R.D. Estimation of surviving spiral ganglion cells in the deaf rat using the electrically evoked auditory brainstem response. Hear. Res. 1990, 49, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.D. Estimation of surviving spiral ganglion cells in the deaf rat using the electrically evoked auditory brainstem response. Hear. Res. 1990, 45, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coats, A.C.; Martin, J.L. Human auditory nerve action potentials and brain stem evoked responses: Effects of audiogram shape and lesion location. Arch. Otolaryngol. (Chic. Ill. 1960) 1977, 103, 605–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, K.; Blegvad, B. Brain stem responses in patients with sensorineural hearing loss. Monaural versus binaural stimulation. The significance of the audiogram configuration. Scand. Audiol. 1976, 5, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asp, F.; Jakobsson, A.M.; Berninger, E. The effect of simulated unilateral hearing loss on horizontal sound localization accuracy and recognition of speech in spatially separate competing speech. Hear. Res. 2018, 357, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plomp, R. Auditory handicap of hearing impairment and the limited benefit of hearing aids. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1978, 63, 533–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagerman, B. Clinical measurements of speech reception threshold in noise. Scand. Audiol. 1984, 13, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smoorenburg, G.F.; de Laat, J.A.; Plomp, R. The effect of noise-induced hearing loss on the intelligibility of speech in noise. Scand. Audiol. Suppl. 1982, 16, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggermont, J.J.; Brown, D.K.; Ponton, C.W.; Kimberley, B.P. Comparison of distortion product otoacoustic emission (DPOAE) and auditory brain stem response (ABR) traveling wave delay measurements suggests frequency-specific synapse maturation. Ear Hear. 1996, 17, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, D.R.; Zobay, O.; Ferguson, M.A. Minimal and Mild Hearing Loss in Children: Association with Auditory Perception, Cognition, and Communication Problems. Ear Hear. 2020, 41, 720–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olusanya, B.O.; Newton, V.E. Global burden of childhood hearing impairment and disease control priorities for developing countries. Lancet 2007, 369, 1314–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.; Olofsson, Å.; Berninger, E. Twin study of neonatal transient-evoked otoacoustic emissions. Hear. Res. 2020, 398, 108108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, D.; Loehlin, J.C.; Pasanen, E.G. Additional findings on heritability and prenatal masculinization of cochlear mechanisms: Click-evoked otoacoustic emissions. Hear. Res. 1996, 97, 102–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, D.; Pasanen, E.G. Spontaneous otoacoustic emissions in heterosexuals, homosexuals, and bisexuals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 105, 2403–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, D.; Pasanen, E.G.; Callaway, N.L. Changes in otoacoustic emissions in a transsexual male during treatment with estrogen. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 104, 1555–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutman, M.E.; Coles, R.R. Asymmetric sensorineural hearing thresholds in the non-noise-exposed UK population: A retrospective analysis. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2009, 34, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, T. A review of the effectiveness of otoacoustic emissions for evaluating hearing status after newborn screening. Otol. Neurotol. 2013, 34, 1058–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, K.A.; Guo, D.; Micucci, S.; De Gruttola, V.; Liberman, M.C.; Kujawa, S.G. Noise-induced Cochlear Synaptopathy with and Without Sensory Cell Loss. Neuroscience 2020, 427, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramhall, N.F.; Konrad-Martin, D.; McMillan, G.P.; Griest, S.E. Auditory Brainstem Response Altered in Humans With Noise Exposure Despite Normal Outer Hair Cell Function. Ear Hear. 2017, 38, e1–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramhall, N.; Beach, E.F.; Epp, B.; Le Prell, C.G.; Lopez-Poveda, E.A.; Plack, C.J.; Schaette, R.; Verhulst, S.; Canlon, B. The search for noise-induced cochlear synaptopathy in humans: Mission impossible? Hear. Res. 2019, 377, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, H.; Wedenberg, E. Audiometric identification of normal hearing carriers of genes for deafness. Acta Otolaryngol. 1968, 65, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefe, D.H.; Archer, K.L.; Schmid, K.K.; Fitzpatrick, D.F.; Feeney, M.P.; Hunter, L.L. Identifying Otosclerosis with Aural Acoustical Tests of Absorbance, Group Delay, Acoustic Reflex Threshold, and Otoacoustic Emissions. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2017, 28, 838–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvan, G.; Berninger, E.; Gustafsson, L.L.; Karlsson, K.K.; Paintaud, G.; Wakelkamp, M. Concentration-Response Relationship of Hearing Impairment Caused by Quinine and Salicylate: Pharmacological Similarities but Different Molecular Mechanisms. Basic Clin. Pharm. Toxicol. 2017, 120, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan-Heggen, C.M.; Bierer, A.O.; Shearer, A.E.; Kolbe, D.L.; Nishimura, C.J.; Frees, K.L.; Ephraim, S.S.; Shibata, S.B.; Booth, K.T.; Campbell, C.A.; et al. Comprehensive genetic testing in the clinical evaluation of 1119 patients with hearing loss. Hum. Genet. 2016, 135, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buran, B.N.; Sarro, E.C.; Manno, F.A.; Kang, R.; Caras, M.L.; Sanes, D.H. A sensitive period for the impact of hearing loss on auditory perception. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 2276–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, E.I. Sensitive periods in the development of the brain and behavior. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2004, 16, 1412–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kral, A. Auditory critical periods: A review from system’s perspective. Neuroscience 2013, 247, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neil, J.N.; Connelly, C.J.; Limb, C.J.; Ryugo, D.K. Synaptic morphology and the influence of auditory experience. Hear. Res. 2011, 279, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.; Karltorp, E.; Edholm, K.; Drott, M.; Berninger, E. A Prospective Study of Etiology and Auditory Profiles in Infants with Congenital Unilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carraro, M.; Almishaal, A.; Hillas, E.; Firpo, M.; Park, A.; Harrison, R.V. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Infection Causes Degeneration of Cochlear Vasculature and Hearing Loss in a Mouse Model. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2016, 19, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

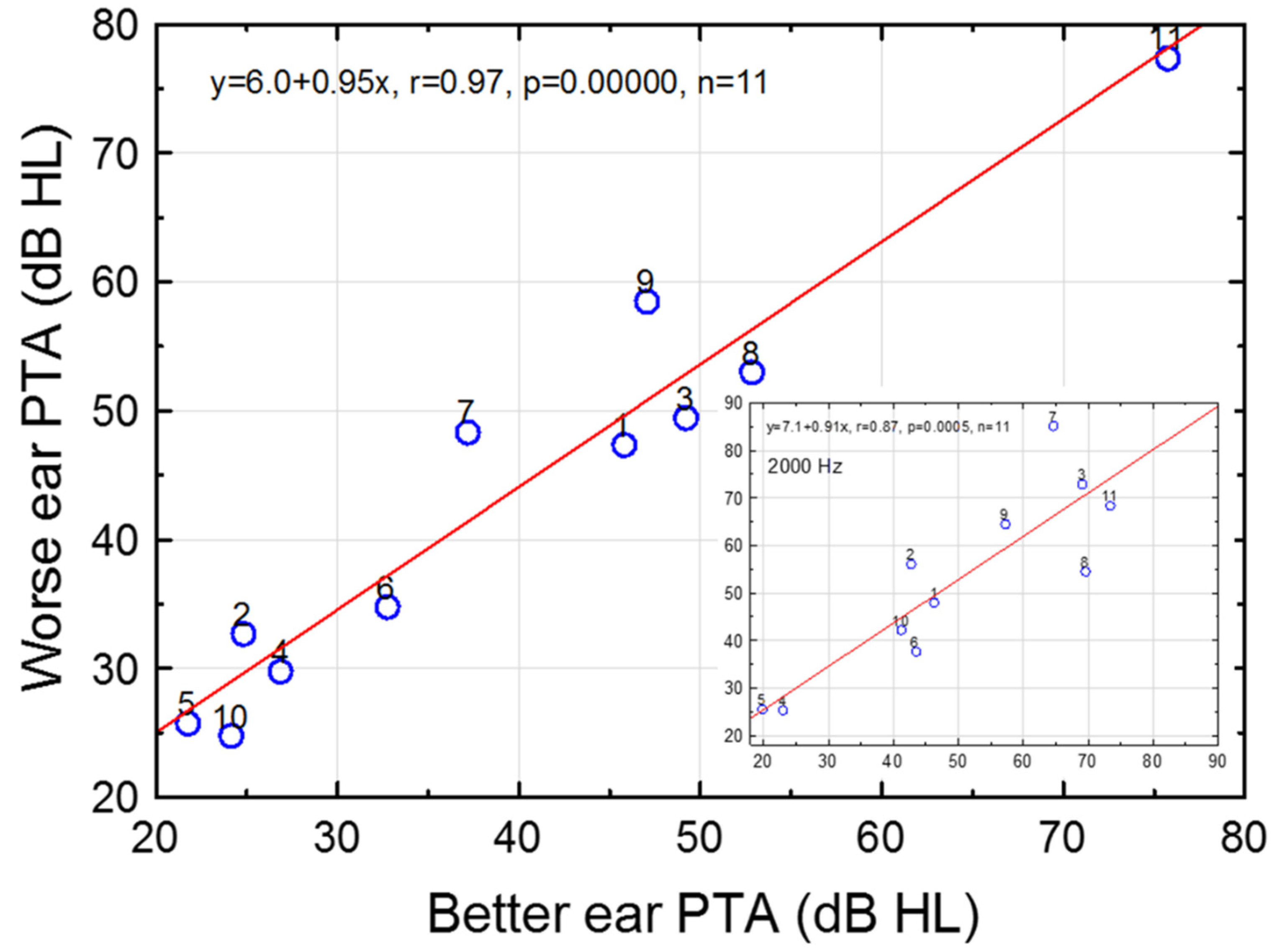



| Frequency (Hz) | Regression Line | r | p | n | Regression Line | r | p | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | y = 13.1 − 0.25x | −0.49 | 0.18 | 9 | y = 20.0 − 0.26x | −0.47 | 0.20 | 9 |
| 1500 | y = 16.6 − 0.39x | −0.80 | 0.05 | 6 | y = 31.2 − 0.45x | −0.80 | 0.06 | 6 |
| 2000 | y = 23.9 − 0.70x | −0.95 | 0.01 | 5 | y = 31.9 − 0.61x | −0.96 | 0.01 | 5 |
| 3000 | y = 16.3 − 0.37x | −0.68 | 0.13 | 6 | y = 31.1 − 0.37x | −0.65 | 0.16 | 6 |
| 4000 | y = 16.8 − 0.40x | −0.85 | 0.03 | 6 | y = 33.0 − 0.48x | −0.90 | 0.01 | 6 |
| 6000 | y = 31.7 − 0.74x | −0.95 | 0.01 | 5 | y = 49.8 − 0.83x | −0.97 | 0.01 | 5 |
| Min | Lower Quartile | Median | Upper Quartile | Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amplitude wave I | 32 | 50 | 101 | 162 | 207 |
| Amplitude wave III | 36 | 169 | 235 | 407 | 462 |
| Amplitude wave V | 71 | 255 | 355 | 431 | 570 |
| Latency I–V | 3.38 | 3.82 | 4.10 | 4.20 | 5.26 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berninger, E.; Drott, M.; Romanitan, M.; Tranebjærg, L.; Hellström, S. Congenital Nonprofound Bilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Children: Comprehensive Characterization of Auditory Function and Hearing Aid Benefit. Audiol. Res. 2022, 12, 539-563. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres12050054
Berninger E, Drott M, Romanitan M, Tranebjærg L, Hellström S. Congenital Nonprofound Bilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Children: Comprehensive Characterization of Auditory Function and Hearing Aid Benefit. Audiology Research. 2022; 12(5):539-563. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres12050054
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerninger, Erik, Maria Drott, Mircea Romanitan, Lisbeth Tranebjærg, and Sten Hellström. 2022. "Congenital Nonprofound Bilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Children: Comprehensive Characterization of Auditory Function and Hearing Aid Benefit" Audiology Research 12, no. 5: 539-563. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres12050054
APA StyleBerninger, E., Drott, M., Romanitan, M., Tranebjærg, L., & Hellström, S. (2022). Congenital Nonprofound Bilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Children: Comprehensive Characterization of Auditory Function and Hearing Aid Benefit. Audiology Research, 12(5), 539-563. https://doi.org/10.3390/audiolres12050054






