Hormonal Contraception and Massive Pulmonary Embolism in a COVID-19 Ambulatory Patient: A Case Report
Abstract
:1. Introduction
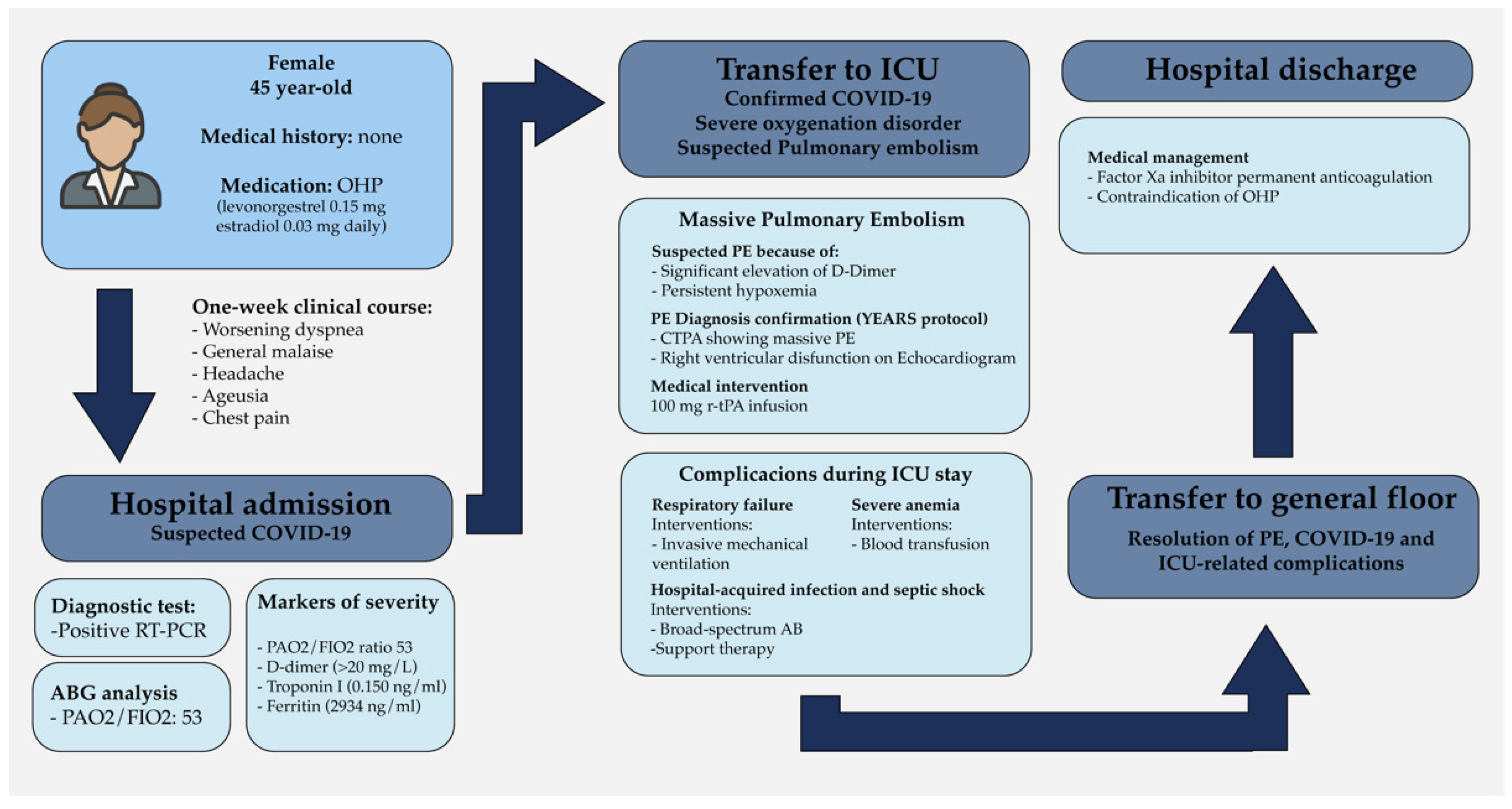
2. Case Description
2.1. Emergency Room Consultation and COVID-19 Diagnosis
2.2. Massive Pulmonary Embolism and Initial ICU Stay
2.3. ICU-Related Complications
2.4. Discharge and Outpatient Plan
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wiersinga, W.J.; Rhodes, A.; Cheng, A.C.; Peacock, S.J.; Prescott, H.C. Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA 2020, 324, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharthy, A.; Balhamar, A.; Faqihi, F.; Alshaya, R.; Noor, A.; Alaklobi, F.; Memish, Z.A.; Karakitsos, D. Insidious development of pulmonary embolism in asymptomatic patients with COVID-19: Two rare case-reports. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2020, 31, 101186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauvel, C.; Weizman, O.; Trimaille, A.; Mika, D.; Pommier, T.; Pace, N.; Douair, A.; Barbin, E.; Fraix, A.; Bouchot, O.; et al. Pulmonary embolism in COVID-19 patients: A French multicentre cohort study. Eur. Hear. J. 2020, 41, 3058–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scudiero, F.; Silverio, A.; Di Maio, M.; Russo, V.; Citro, R.; Personeni, D.; Cafro, A.; D’Andrea, A.; Attena, E.; Pezzullo, S.; et al. Pulmonary embolism in COVID-19 patients: Prevalence, predictors and clinical outcome. Thromb. Res. 2021, 198, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bavaro, D.; Diella, L.; Fabrizio, C.; Sulpasso, R.; Bottalico, I.; Calamo, A.; Santoro, C.; Brindicci, G.; Bruno, G.; Mastroianni, A.; et al. Peculiar clinical presentation of COVID-19 and predictors of mortality in the elderly: A multicentre retrospective cohort study. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 105, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitruk-Ware, R. Hormonal contraception and thrombosis. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sugiura, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Ojima, T. The epidemiological characteristics of thromboembolism related to oral contraceptives in Japan: Results of a national survey. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2021, 47, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vechi, H.T.; Maia, L.R.; Alves, M.D.M. Late acute pulmonary embolism after mild Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A case series. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 2020, 62, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwanwongse, K.; Shabarek, N. Bilateral Popliteal Vein Thrombosis, Acute Pulmonary Embolism and Mild COVID-19. Cureus 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, J.W.; Roberts, J.C.; Weaver, C.N.; Anderson, J.S.; Wong, M.L. Patients with Mild COVID-19 Symptoms and Coincident Pulmonary Embolism: A Case Series. Clin. Pr. Cases Emerg. Med. 2020, 4, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorini, N.B.; Garagoli, F.; Bustamante, R.C.; Pizarro, R. Acute pulmonary embolism in a patient with mild COVID-19 symptoms: A case report. Eur. Hear. J. Case Rep. 2021, 5, ytaa563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Xiao, J.; Yi, Q. Assessment of the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism in Medical Inpatients using the Padua Prediction Score and Caprini Risk Assessment Model. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2018, 25, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ozen, M.; Yilmaz, A.; Cakmak, V.; Beyoglu, R.; Oskay, A.; Seyit, M.; Senol, H. D-Dimer as a potential biomarker for disease severity in COVID-19. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 40, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuker, A.; Tseng, E.K.; Nieuwlaat, R.; Angchaisuksiri, P.; Blair, C.; Dane, K.; Davila, J.; DeSancho, M.T.; Diuguid, D.; Griffin, D.O.; et al. American Society of Hematology 2021 guidelines on the use of anticoagulation for thromboprophylaxis in patients with COVID-19. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 872–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moores, L.K.; Tritschler, T.; Brosnahan, S.; Carrier, M.; Collen, J.F.; Doerschug, K.; Holley, A.B.; Jimenez, D.; Le Gal, G.; Rali, P.; et al. Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment of VTE in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019. Chest 2020, 158, 1143–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaptein, F.; Stals, M.; Grootenboers, M.; Braken, S.; Burggraaf, J.; van Bussel, B.; Cannegieter, S.; Cate, H.T.; Endeman, H.; Gommers, D.; et al. Incidence of thrombotic complications and overall survival in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in the second and first wave. Thromb. Res. 2021, 199, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capell, W.H.; Barnathan, E.S.; Piazza, G.; Spyropoulos, A.C.; Hsia, J.; Bull, S.; Lipardi, C.; Sugarmann, C.; Suh, E.; Rao, J.P.; et al. Rationale and design for the study of rivaroxaban to reduce thrombotic events, hospitalization and death in outpatients with COVID-19: The PREVENT-HD study. Am. Hear. J. 2021, 235, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Maria, E.; Latini, A.; Borgiani, P.; Novelli, G. Genetic variants of the human host influencing the coronavirus-associated phenotypes (SARS, MERS and COVID-19): Rapid systematic review and field synopsis. Hum. Genom. 2020, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragoman, M.V.; Tepper, N.K.; Fu, R.; Curtis, K.M.; Chou, R.; Gaffield, M.E. A systematic review and meta-analysis of venous thrombosis risk among users of combined oral contraception. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2018, 141, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valenzuela-Vallejo, L.; Corredor-Orlandelli, D.; Alzate-Ricaurte, S.; Hernández-Santamaría, V.; Aguirre-Ruiz, J.F.; Peña-Peña, A. Hormonal Contraception and Massive Pulmonary Embolism in a COVID-19 Ambulatory Patient: A Case Report. Clin. Pract. 2021, 11, 914-918. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11040105
Valenzuela-Vallejo L, Corredor-Orlandelli D, Alzate-Ricaurte S, Hernández-Santamaría V, Aguirre-Ruiz JF, Peña-Peña A. Hormonal Contraception and Massive Pulmonary Embolism in a COVID-19 Ambulatory Patient: A Case Report. Clinics and Practice. 2021; 11(4):914-918. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11040105
Chicago/Turabian StyleValenzuela-Vallejo, Laura, David Corredor-Orlandelli, Sergio Alzate-Ricaurte, Valentina Hernández-Santamaría, Juan Felipe Aguirre-Ruiz, and Adwar Peña-Peña. 2021. "Hormonal Contraception and Massive Pulmonary Embolism in a COVID-19 Ambulatory Patient: A Case Report" Clinics and Practice 11, no. 4: 914-918. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11040105
APA StyleValenzuela-Vallejo, L., Corredor-Orlandelli, D., Alzate-Ricaurte, S., Hernández-Santamaría, V., Aguirre-Ruiz, J. F., & Peña-Peña, A. (2021). Hormonal Contraception and Massive Pulmonary Embolism in a COVID-19 Ambulatory Patient: A Case Report. Clinics and Practice, 11(4), 914-918. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract11040105






