Usefulness of Collaborative Work in the Evaluation of Prostate Cancer from MRI
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Database
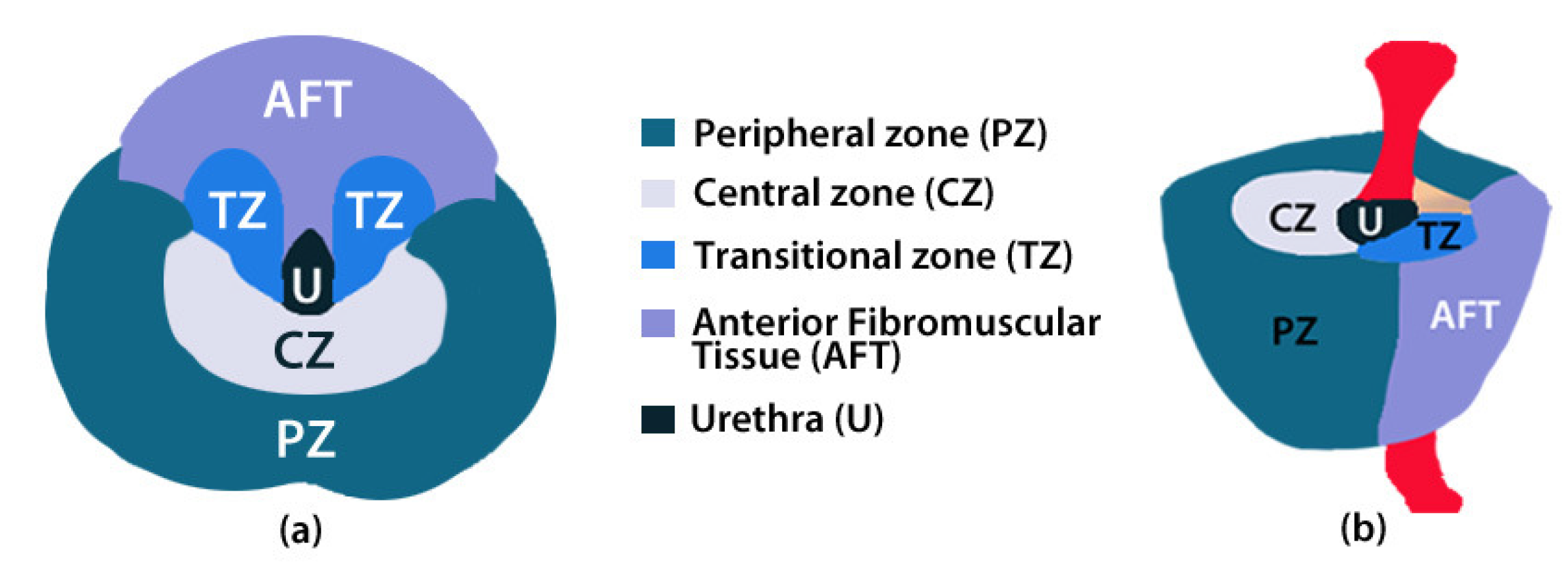
2.2. ROIs of Prostate Anatomy
2.3. Evaluation Procedure
2.4. Evaluation Parameters
3. Results
3.1. Anatomic Parameters
3.2. Contour Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCa | prostate cancer |
| ICD-O | International Classification of Diseases for Oncology |
| ICCC | International Classification of Childhood Cancer |
| EU | European Union |
| CT | computed tomography |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| ROI | region of interest |
| T2WI | T2-weighted imaging |
| DWI | diffusion weighted imaging |
| DCE | perfusion based on the dynamic contrast enhancement |
| MRS | magnetic resonance spectroscopy |
| PI-RADS | prostate imaging-reporting and data system |
| LGG | low-grade glioma |
| CZ | central zone |
| PZ | peripheral zone |
| TZ | transition zone |
| AFT | anterior fibromuscular tissue |
| Tum | tumour lesion |
| E1 | experiment 1 |
| E2 | experiment 2 |
| E3 | experiment 3 |
References
- Dalmartello, G.; Bertuccio, P.; Boffetta, P.; Levi, F.; La Vecchia, C.; Negri, E.; Malvezzi, M. European cancer mortality predictions for the year 2022 with focus on ovarian cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorow, P.F.; Varvakis, G.; Trzeciak, D.S.; Souza, L.F.N. Collaborative learning in the production of diagnostic imaging: Detailing group practices. Gestão Produção 2020, 27, e4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, D.B.; Langlotz, C.P. The Role of Radiology in the Diagnostic Process: Information, Communication, and Teamwork. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 209, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wajswol, E.; Winoker, J.S.; Anastos, H.; Falagario, U.; Okhawere, K.; Martini, A.; Treacy, P.J.; Voutsinas, N.; Knauer, C.J.; Sfakianos, J.P.; et al. A cohort of transperineal electromagnetically tracked magnetic resonance imaging/ultrasonography fusion-guided biopsy: Assessing the impact of inter-reader variability on cancer detection. BJU Int. 2020, 125, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Dang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, C.; Li, S.; Wang, W. Prostate cancer detection: Comparison of t2-weighted imaging, diffusion-weighted imaging, proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging, and the three techniques combined. Acta Radiol. 2008, 49, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.R.; Johnson, T.D.; McLennan, G.; Aberle, D.R.; Kazerooni, E.A.; MacMahon, H.; Mullan, B.F.; Yankelevitz, D.F.; van Beek, E.J.; Armato, S.G.; et al. Evaluation of lung MDCT nodule annotation across radiologists and methods. Acad. Radiol. 2006, 13, 1254–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Dang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, C.; Li, S.; Wang, W. Intravascular Imaging and Computer Assisted Stenting, and Large-Scale Annotation of Biomedical Data and Expert Label Synthesis. In Proceedings of the LABELS: International Workshop on Large-Scale Annotation of Biomedical Data and Expert Label Synthesis, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 10–14 September 2017. LNCS (10552). [Google Scholar]
- Pupulim, L.F.; Ronot, M.; Paradis, V.; Chemouny, S.; Vilgrain, V. Volumetric measurement of hepatic tumours: Accuracy of manual contouring using CT with volumetric pathology as the reference method. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2018, 99, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bø, H.K.; Solheim, O.; Jakola, A.S.; Kvistad, K.A.; Reinertsen, I.; Berntsen, E.M. Intra-rater variability in low-grade glioma segmentation. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2017, 131, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, C.; Walker, P.; Oliver, A.; Brunotte, F.; Martí, J.; Lalande, A. Prostateanalyzer: Web-based medical application for the management of prostate cancer using multiparametric mr images. Inf. Health Soc. Care 2015, 87, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagosa, J.; Benitez, R.; Mata, C. ProstateAnnotation: Web-Based Application for Medical Imaging. IEEE EMBS International Conference on Biomedical and Health Informatics (BHI). 2021. Available online: https://www.bhi-bsn-2021.org/?page_id=2336 (accessed on 29 July 2021).
- Brancato, V.; Di Costanzo, G.; Basso, L.; Tramontano, L.; Puglia, M.; Ragozzino, A.; Cavaliere, C. Assessment of DCE Utility for PCa Diagnosis Using PI-RADS v2.1: Effects on Diagnostic Accuracy and Reproducibility. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Marzo, A.; Platz, E.; Sutcliffe, S.; Xu, J.; Grönberg, H.; Drake, C.; Nakay, Y. Inflammation in prostate carcinogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bitar, R.; Leung, G.; Perng, R.; Tadros, S.; Moody, A.; Sarrazin, J.; McGregor, C.; Christakis, M.; Symons, S.; Nelson, A.; et al. Mr pulse sequences: What every radioogist wants to know but is afraid to ask. RAD 2006, 26, 513–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalande, A.; Garreau, M.; Frouin, F. Evaluation of cardiac structure segmentation in cine magnetic resonance imaging. In Multi-Modality Cardiac Imaging; Clarysse, P., Friboulet, D., Eds.; ISTE-Wiley: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2015; pp. 171–215. [Google Scholar]
- Altmant, D.G.; Bland, J.M. Measurement in medicine: The analysis of method comparison studies. Statistician 1983, 32, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986, 327, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.A. Mathematical Statistics and Data Analysis, 3rd ed.; Duxbury Press: Würzburg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rote, G. Computing the minimum hausdorff distance between two point sets on a line under translation. Inform. Proces. Lett. 1991, 38, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockafellar, R.; Tyrrell, W.; Roger, J.-B. Variational Analysis; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005; p. 117. [Google Scholar]
- Guang-Zhong, Y.; Tianz, J. Medical Imaging and Augmented Reality: Second International Workshop, MIAR 2004; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 3150. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, C.; Bell, D. Variational Analysis. Radiopaedia Artif. Intell. 2020, 75056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, S.; Oliver, O.; Martí, J.; Lladó, X.; Vilanova, J.; Freixenet, J. A survey of prostate segmentation methodologies in ultrasound, magnetic resonance and computed tomography images. RAD 2012, 108, 262–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bosch, B.; Mansell, H. Interprofessional collaboration in health care: Lessons to be learned from competitive sports. Can. Pharm. J. 2015, 148, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falagario, U.G.; Jambor, I.; Lantz, A.; Ettala, O.; Stabile, A.; Taimen, P.; Aronen, H.J.; Knaapila, J.; Perez, I.M.; Gandaglia, G.; et al. Combined Use of Prostate-specific Antigen Density and Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Prostate Biopsy Decision Planning: A Retrospective Multi-institutional Study Using the Prostate Magnetic Resonance Imaging Outcome Database (PROMOD). Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2020, 4, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanec, S.H.; Lazar, M.; Wengert, G.J.; Bickel, H.; Spick, C.; Susani, M.; Shariat, S.; Clauser, P.; Baltzer, P.A.T. 3D T2-weighted imaging to shorten multiparametric prostate MRI protocols. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rauschecker, A.M.; Rudie, J.D.; Xie, L.; Wang, J.; Duong, M.T.; Botzolakis, E.J.; Kovalovich, A.M.; Egan, J.; Cook, T.C.; Bryan, R.N.; et al. Artificial Intelligence System Approaching Neuroradiologist-level Differential Diagnosis Accuracy at Brain MRI. Radiology 2020, 295, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkon, A.H.; Labib, M.; Hasan, T.; Mozamal, H.; Jannat, M. Deep learning in prostate cancer diagnosis and Gleason grading in histopathology images: An extensive study. Inf. Med. Unlocked 2021, 24, 100582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tătaru, O.S.; Vartolomei, M.D.; Rassweiler, J.J.; Virgil, O.; Lucarelli, G.; Porpiglia, F.; Amparore, D.; Manfredi, M.; Carrieri, G.; Falagario, U.; et al. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Prostate Cancer Patient Management-Current Trends and Future Perspectives. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, M.; Saha, A.; Brand, P.; Slootweg, I.; de Rooij, M.; Huisman, H. Deep learning-assisted prostate cancer detection on bi-parametric MRI: Minimum training data size requirements and effect of prior knowledge. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 11, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmarakeby, H.A.; Hwang, J.; Arafeh, R. Biologically informed deep neural network for prostate cancer discovery. Nature 2021, 598, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardis, M.; Houshyar, R.; Chantaduly, C.; Tran-Harding, K.; Ushinsky, A.; Chahine, C.; Rupasinghe, M.; Chow, D.; Chang, P. Segmentation of the Prostate Transition Zone and Peripheral Zone on MR Images with Deep Learning. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2021, 3, e200024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Patient | Processed Slides | CZ | PZ | TUM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| vs. | vs. | vs. | vs. | vs. | vs. | ||
| Patient 1 | 18 | 6% | 6% | 11% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Patient 2 | 21 | 10% | 10% | 10% | 10% | 0% | 0% |
| Patient 3 | 25 | 8% | 0% | 8% | 0% | 12% | 4% |
| Patient 4 | 30 | 7% | 0% | 7% | 0% | 17% | 0% |
| Patient 5 | 24 | 13% | 0% | 13% | 8% | 13% | 0% |
| Patient 6 | 17 | 18% | 0% | 12% | 0% | 65% | 0% |
| Patient 7 | 26 | 12% | 4% | 8% | 0% | 19% | 0% |
| Patient 8 | 31 | 19% | 10% | 3% | 6% | 0% | 0% |
| Patient 9 | 21 | 14% | 0% | 14% | 0% | 5% | 0% |
| Patient 10 | 25 | 16% | 0% | 8% | 0% | 8% | 0% |
| r | Regression Line | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| vs. | vs. | vs. | vs. | |
| CZ | 0.95 | 0.98 | y = 0.9x − 166 | y = x − 12 |
| PZ | 0.91 | 0.94 | y = 0.9x − 96 | y = 0.9x + 21 |
| TUM | 0.96 | 0.98 | y = 0.7x − 3 | y = x + 3 |
| Bland–Altman | t-Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| vs. | vs. | vs. | vs. | |
| CZ | −261.13 ± 168.20 | −13.07 ± 118.09 | 0.01 | 0.36 |
| PZ | −156.50 ± 95.71 | −10.73 ± 84.60 | 0.01 | 0.32 |
| TUM | −54.93 ± 64.34 | −0.08 ± 27.13 | 0.02 | 0.47 |
| Hausdorff Distance | Dice Index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| vs. | vs. | vs. | vs. | |
| CZ | 8 ± 3 | 4 ± 1 | 0.70 ± 0.20 | 0.90 ± 0.10 |
| PZ | 11 ± 5 | 5 ± 2 | 0.60 ± 0.20 | 0.90 ± 0.10 |
| TUM | 10 ± 4 | 8 ± 11 | 0.70 ± 0.10 | 0.90 ± 0.10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mata, C.; Walker, P.; Oliver, A.; Martí, J.; Lalande, A. Usefulness of Collaborative Work in the Evaluation of Prostate Cancer from MRI. Clin. Pract. 2022, 12, 350-362. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract12030040
Mata C, Walker P, Oliver A, Martí J, Lalande A. Usefulness of Collaborative Work in the Evaluation of Prostate Cancer from MRI. Clinics and Practice. 2022; 12(3):350-362. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract12030040
Chicago/Turabian StyleMata, Christian, Paul Walker, Arnau Oliver, Joan Martí, and Alain Lalande. 2022. "Usefulness of Collaborative Work in the Evaluation of Prostate Cancer from MRI" Clinics and Practice 12, no. 3: 350-362. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract12030040
APA StyleMata, C., Walker, P., Oliver, A., Martí, J., & Lalande, A. (2022). Usefulness of Collaborative Work in the Evaluation of Prostate Cancer from MRI. Clinics and Practice, 12(3), 350-362. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract12030040








