Readability Metrics in Patient Education: Where Do We Innovate?
Abstract
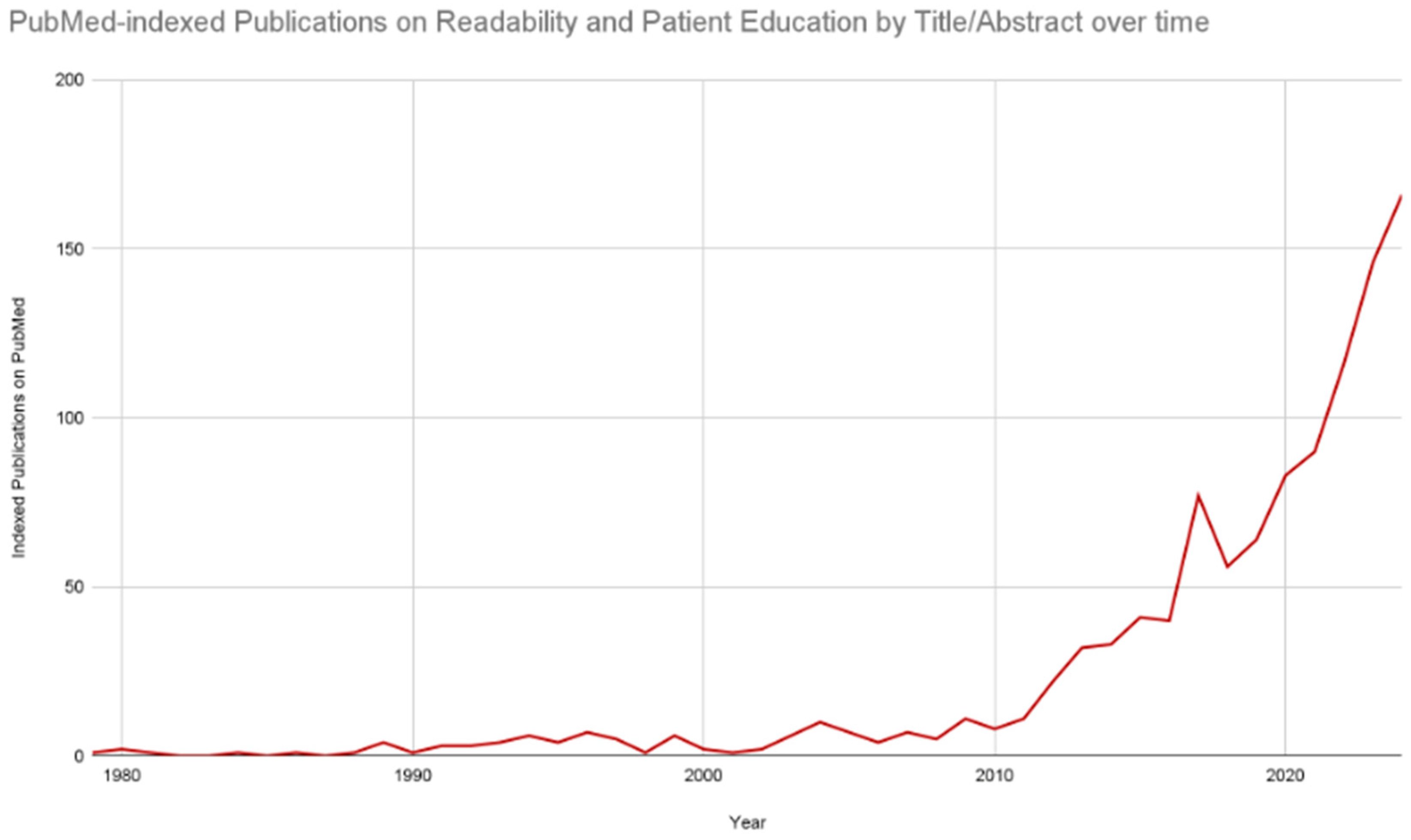
1. Introduction
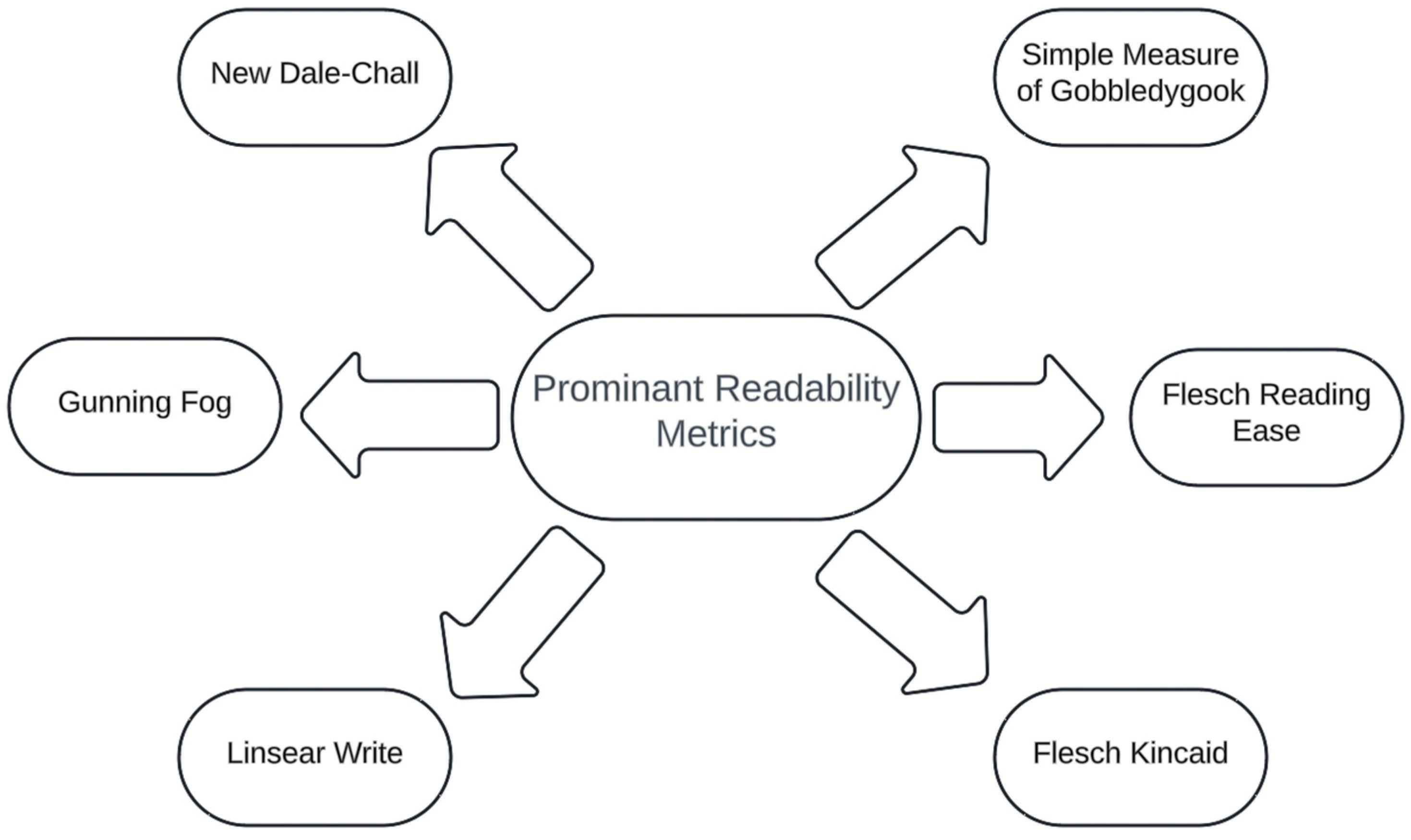
Readability
2. Readability and Patient Education in Adult Internal Medicine
3. Readability and Patient Education in Pediatric Medicine
4. Readability and Patient Education in Preventative Medicine
5. Readability and Patient Education in Surgery
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Honavar, S.G. Electronic Medical Records—The Good, the Bad and the Ugly. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 68, 417–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, R.S. Electronic Health Records: Then, Now, and in the Future. Yearb. Med. Inform. 2016, 25, S48–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carini, E.; Villani, L.; Pezzullo, A.M.; Gentili, A.; Barbara, A.; Ricciardi, W.; Boccia, S. The Impact of Digital Patient Portals on Health Outcomes, System Efficiency, and Patient Attitudes: Updated Systematic Literature Review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e26189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shank, J.C.; Murphy, M.; Schulte-Mowry, L. Patient Preferences Regarding Educational Pamphlets in the Family Practice Center. Fam. Med. 1991, 23, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giguère, A.; Zomahoun, H.T.V.; Carmichael, P.-H.; Uwizeye, C.B.; Légaré, F.; Grimshaw, J.M.; Gagnon, M.-P.; Auguste, D.U.; Massougbodji, J. Printed Educational Materials: Effects on Professional Practice and Healthcare Outcomes. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 31, CD004398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, R.; Shoker, M.; Chu, L.M.; Frehlick, R.; Ward, H.; Pahwa, P. Impact of Low Health Literacy on Patients’ Health Outcomes: A Multicenter Cohort Study. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2022, 22, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasu, R.S.; Bawa, W.A.; Suminski, R.; Snella, K.; Warady, B. Health Literacy Impact on National Healthcare Utilization and Expenditure. Int. J. Health Policy Manag. 2015, 4, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickren, S.E.; Stacy, M.; Del Tufo, S.N.; Spencer, M.; Cutting, L.E. The Contribution of Text Characteristics to Reading Comprehension: Investigating the Influence of Text Emotionality. Read. Res. Q. 2022, 57, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBay, W.H. The Principles of Readability; Online Submiss; ERIC: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Klare, G.R. Measurement of Readability; Wageningen University and Research Library Catalog: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1963; Available online: https://library.wur.nl/WebQuery/titel/495567 (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Rooney, M.K.; Santiago, G.; Perni, S.; Horowitz, D.P.; McCall, A.R.; Einstein, A.J.; Jagsi, R.; Golden, D.W. Readability of Patient Education Materials From High-Impact Medical Journals: A 20-Year Analysis. J. Patient Exp. 2021, 8, 2374373521998847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noblin, A.M.; Zraick, R.I.; Miller, A.N.; Schmidt-Owens, M.; Deichen, M.; Tran, K.; Patel, R. Readability and Suitability of Information Presented on a University Health Center Website. Perspect. Health Inf. Manag. 2022, 19, 1f. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Lin, F.; Duan, T. Exploring Two Decades of Research on Online Reading by Using Bibliometric Analysis. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2024, 29, 12831–12862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-W.; Miller, M.J.; Schmitt, M.R.; Wen, F.K. Assessing Readability Formula Differences with Written Health Information Materials: Application, Results, and Recommendations. Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm. RSAP 2013, 9, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanci, V.; Otlu, B.; Biyikoğlu, A.S. Assessment of the Readability of the Online Patient Education Materials of Intensive and Critical Care Societies. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 52, e47–e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliffe, M.; Thompson, E.; Johnston, J.; Freeman, D.; Bagga, H.; Wong, P.K.K. Assessing the Readability and Patient Comprehension of Rheumatology Medicine Information Sheets: A Cross-Sectional Health Literacy Study. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e024582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kher, A.; Johnson, S.; Griffith, R. Readability Assessment of Online Patient Education Material on Congestive Heart Failure. Adv. Prev. Med. 2017, 2017, 9780317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mac, O.; Ayre, J.; Bell, K.; McCaffery, K.; Muscat, D.M. Comparison of Readability Scores for Written Health Information Across Formulas Using Automated vs Manual Measures. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2246051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, P.; MacDermid, J.C. Assessing Reading Levels of Health Information: Uses and Limitations of Flesch Formula. Educ. Health 2017, 30, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrigley Kelly, N.E.; Murray, K.E.; McCarthy, C.; O’Shea, D.B. An Objective Analysis of Quality and Readability of Online Information on COVID-19. Health Technol. 2021, 11, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Qureshi, F.M.; Borthwick, K.G.; Singh, S.; Menon, S.; Barthel, B. Comprehension Profile of Patient Education Materials in Endocrine Care. Kans. J. Med. 2022, 15, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Jamal, A.; Qureshi, F.; Zaidi, R.; Qureshi, F. Leveraging Generative Artificial Intelligence Models in Patient Education on Inferior Vena Cava Filters. Clin. Pract. 2024, 14, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chall, J.S.; Dale, E. Readability Revisited: The New Dale-Chall Readability Formula; CiNii Research; Brookline Books: Brookline, MA, USA, 1995; Available online: https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1130282268845043712 (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Perni, S.; Rooney, M.K.; Horowitz, D.P.; Golden, D.W.; McCall, A.R.; Einstein, A.J.; Jagsi, R. Assessment of Use, Specificity, and Readability of Written Clinical Informed Consent Forms for Patients With Cancer Undergoing Radiotherapy. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, e190260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battineni, G.; Baldoni, S.; Chintalapudi, N.; Sagaro, G.G.; Pallotta, G.; Nittari, G.; Amenta, F. Factors Affecting the Quality and Reliability of Online Health Information. Digit. Health 2020, 6, 2055207620948996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabtree, L.; Lee, E. Assessment of the Readability and Quality of Online Patient Education Materials for the Medical Treatment of Open-Angle Glaucoma. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2022, 7, e000966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boroumand, M.A.; Sedghi, S.; Adibi, P.; Panahi, S.; Rahimi, A. Patients’ Perspectives on the Quality of Online Patient Education Materials: A Qualitative Study. J. Educ. Health Promot. 2022, 11, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansberry, D.R.; D’Angelo, M.; White, M.D.; Prabhu, A.V.; Cox, M.; Agarwal, N.; Deshmukh, S. Quantitative Analysis of the Level of Readability of Online Emergency Radiology-Based Patient Education Resources. Emerg. Radiol. 2018, 25, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, B.D.; Mollon, L.; Lee, J.K. Readability of Patient Education Information on the American Geriatrics Society Foundation’s Health-in-Aging Website. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2013, 61, 1845–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakos, J.; Samoil, D.; Giannopoulos, E.; Jain, P.; McBain, S.; Mittmann, N.; Papadakos, T.; Fox, C.; Moody, L.; McLeod, R. The Cost of Patient Education Materials Development: Opportunities to Identify Value and Priorities. J. Cancer Educ. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Educ. 2022, 37, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cureus. Can Generative Artificial Intelligence Enhance Health Literacy About Lateral Epicondylitis? Available online: https://www.cureus.com/articles/257423-can-generative-artificial-intelligence-enhance-health-literacy-about-lateral-epicondylitis#!/ (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Rouhi, A.D.; Ghanem, Y.K.; Yolchieva, L.; Saleh, Z.; Joshi, H.; Moccia, M.C.; Suarez-Pierre, A.; Han, J.J. Can Artificial Intelligence Improve the Readability of Patient Education Materials on Aortic Stenosis? A Pilot Study. Cardiol. Ther. 2024, 13, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.; Condren, M. Communication Strategies for Empowering and Protecting Children. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. JPPT 2016, 21, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freda, M.C. The Readability of American Academy of Pediatrics Patient Education Brochures. J. Pediatr. Health Care Off. Publ. Natl. Assoc. Pediatr. Nurse Assoc. Pract. 2005, 19, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuhara, T.; Ishikawa, H.; Ueno, H.; Okada, H.; Kato, M.; Kiuchi, T. Readability Assessment of Vaccine Information: A Systematic Review for Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy. Patient Educ. Couns. 2022, 105, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, S.; Malone, E.; Lekiachvili, A.; Briss, P. Health Care Industry Insights: Why the Use of Preventive Services Is Still Low. Prev. Chron. Dis. 2019, 16, E30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, F.; Ngo, S.; Baird, G.; Balla, S.; Miles, R.; Garg, M. Readability of Online Patient Educational Materials for Coronary Artery Calcium Scans and Implications for Health Disparities. J. Am. Heart Assoc. Cardiovasc. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 9, e017372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.P.; Ramprasad, A.; Luu, A.; Zaidi, R.; Siddiqui, Z.; Pham, T. Health Literacy Analytics of Accessible Patient Resources in Cardiovascular Medicine: What Are Patients Wanting to Know? Kans. J. Med. 2023, 16, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrzypczak, T.; Mamak, M. Assessing the Readability of Online Health Information for Colonoscopy—Analysis of Articles in 22 European Languages. J. Cancer Educ. 2023, 38, 1865–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagne, S.M.; Fintelmann, F.J.; Flores, E.J.; McDermott, S.; Mendoza, D.P.; Petranovic, M.; Price, M.C.; Stowell, J.T.; Little, B.P. Evaluation of the Informational Content and Readability of US Lung Cancer Screening Program Websites. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e1920431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, L.R.; Baird, G.L.; Roy, I.T.; Choi, P.H.S.; Lehman, C.D.; Miles, R.C. Are English-Language Online Patient Education Materials Related to Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Understandable, Readable, and Actionable? Breast 2022, 61, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.Z.; Baird, G.L.; Escamilla Guevara, A.; Sohn, Y.-J.; Lydston, M.; Doyle, C.; Tevis, S.E.A.; Miles, R.C. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of English Language Online Patient Education Materials in Breast Cancer: Is Readability the Only Story? Breast Edinb. Scotl. 2024, 75, 103722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlKhalili, R.; Shukla, P.A.; Patel, R.H.; Sanghvi, S.; Hubbi, B. Readability Assessment of Internet-Based Patient Education Materials Related to Mammography for Breast Cancer Screening. Acad. Radiol. 2015, 22, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, M.J.; Dowdle, T.S.; Steadman, J.N.; Guerra, T.R.; Cox, K.L. Pap Smear Readability on Google: An Analysis of Online Articles Regarding One of the Most Routine Medical Screening Tests. Int. J. Med. Stud. 2020, 8, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, S.; Asirvatham, R.; Baird, G.L.; Sarraju, A.; Maron, D.J.; Rodriguez, F. Readability and Reliability of Online Patient Education Materials about Statins. Am. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2023, 16, 100594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.; Thornton, I.; Turrin, D.; Hipskind, J.E. Informed Consent. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.T.; Mitchell, M.B.; Hammack-Aviran, C.; Gao, Y.; Liu, D.; Langerman, A. Content and Readability of US Procedure Consent Forms. JAMA Intern. Med. 2024, 184, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massie, P.L.; Arshad, S.A.; Auyang, E.D. Readability of American Society of Metabolic Surgery’s Patient Information Publications. J. Surg. Res. 2024, 293, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Earp, B.E.; Kilgallen, E.E.; Blazar, P. Readability of Online Hand Surgery Patient Educational Materials: Evaluating the Trend Since 2008. J. Hand Surg. 2021, 47, 186.E1–186.E8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltorai, A.E.M.; Ghanian, S.; Adams, C.A.; Born, C.T.; Daniels, A.H. Readability of Patient Education Materials on the American Association for Surgery of Trauma Website. Arch. Trauma Res. 2014, 3, e18161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behmer Hansen, R.; Gold, J.; Lad, M.; Gupta, R.; Ganapa, S.; Mammis, A. Health Literacy among Neurosurgery and Other Surgical Subspecialties: Readability of Online Patient Materials Found with Google. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2020, 197, 106141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A.; Ali, R.; Johansen, P.M. Readability of Neurosurgical Patient Education Resources by the American Association of Neurological Surgeons. World Neurosurg. 2024, 186, e734–e739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherla, D.V.; Sanghvi, S.; Choudhry, O.J.; Liu, J.K.; Eloy, J.A. Readability Assessment of Internet-Based Patient Education Materials Related to Endoscopic Sinus Surgery. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.S.; McDermott, L.E.; Thor, S. The Readability of Patient Education Materials Pertaining to Gastrointestinal Procedures. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 2021, 7532905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Connolly, I.D.; Tang, O.Y.; Mirza, F.N.; Johnston, B.; Abdulrazeq, H.F.; Lim, R.K.; Galamaga, P.F.; Libby, T.J.; Sodha, N.R.; et al. Bridging the Literacy Gap for Surgical Consents: An AI-Human Expert Collaborative Approach. NPJ Digit Med. 2024, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, J.L.; Morales, L.S.; Liu, H.; Hays, R.D. Variation in the Readability of Items Within Surveys. Am. J. Med. Qual. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med. Qual. 2006, 21, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, C.; Dijanic, C.; Abdelmalek, G.; Sudah, S.; Kerrigan, D.; Gorgy, G.; Yalamanchili, P. Readability Assessment of Patient Educational Materials for Pediatric Spinal Deformity from Top Academic Orthopedic Institutions. Spine Deform. 2022, 10, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackos, J.T.; Stevens, D.M. Standards for Online Communication: Publishing Information for the Internet, World Wide Web, Help Systems, Corporate Intranets; Wiley Computer Pub.: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Available online: https://demo.locate.ebsco.com/instances/af424a0f-0ee2-4d56-a732-396ed28edda0?option=subject&query=Invisibility (accessed on 13 August 2024).
- Golan, R.; Ripps, S.J.; Reddy, R.; Loloi, J.; Bernstein, A.P.; Connelly, Z.M.; Golan, N.S.; Ramasamy, R. ChatGPT’s Ability to Assess Quality and Readability of Online Medical Information: Evidence From a Cross-Sectional Study. Cureus 2023, 15, e42214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moons, P.; Van Bulck, L. Using ChatGPT and Google Bard to Improve the Readability of Written Patient Information: A Proof of Concept. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2024, 23, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, S.; Jamal, A.; Qureshi, F. Readability Metrics in Patient Education: Where Do We Innovate? Clin. Pract. 2024, 14, 2341-2349. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14060183
Singh S, Jamal A, Qureshi F. Readability Metrics in Patient Education: Where Do We Innovate? Clinics and Practice. 2024; 14(6):2341-2349. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14060183
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Som, Aleena Jamal, and Fawad Qureshi. 2024. "Readability Metrics in Patient Education: Where Do We Innovate?" Clinics and Practice 14, no. 6: 2341-2349. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14060183
APA StyleSingh, S., Jamal, A., & Qureshi, F. (2024). Readability Metrics in Patient Education: Where Do We Innovate? Clinics and Practice, 14(6), 2341-2349. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14060183





