Dose and Exposure Time-Dependent Renal and Hepatic Effects of Intraperitoneally Administered Fumonisin B1 in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Feed Intake, Body and Organ Weights
2.2. Blood Clinical Chemistry
2.2.1. Enzymes
2.2.2. Nitrogenous Metabolites
2.2.3. Lipids
2.2.4. Glucose
2.2.5. Dose-Dependence of the Plasma Clinical Chemical Compounds
2.3. Antioxidant and Lipid Peroxidation Parameters
2.3.1. Liver
2.3.2. Kidney
2.3.3. Lung
2.3.4. Plasma
2.4. Genotoxicity
2.5. Histopathology
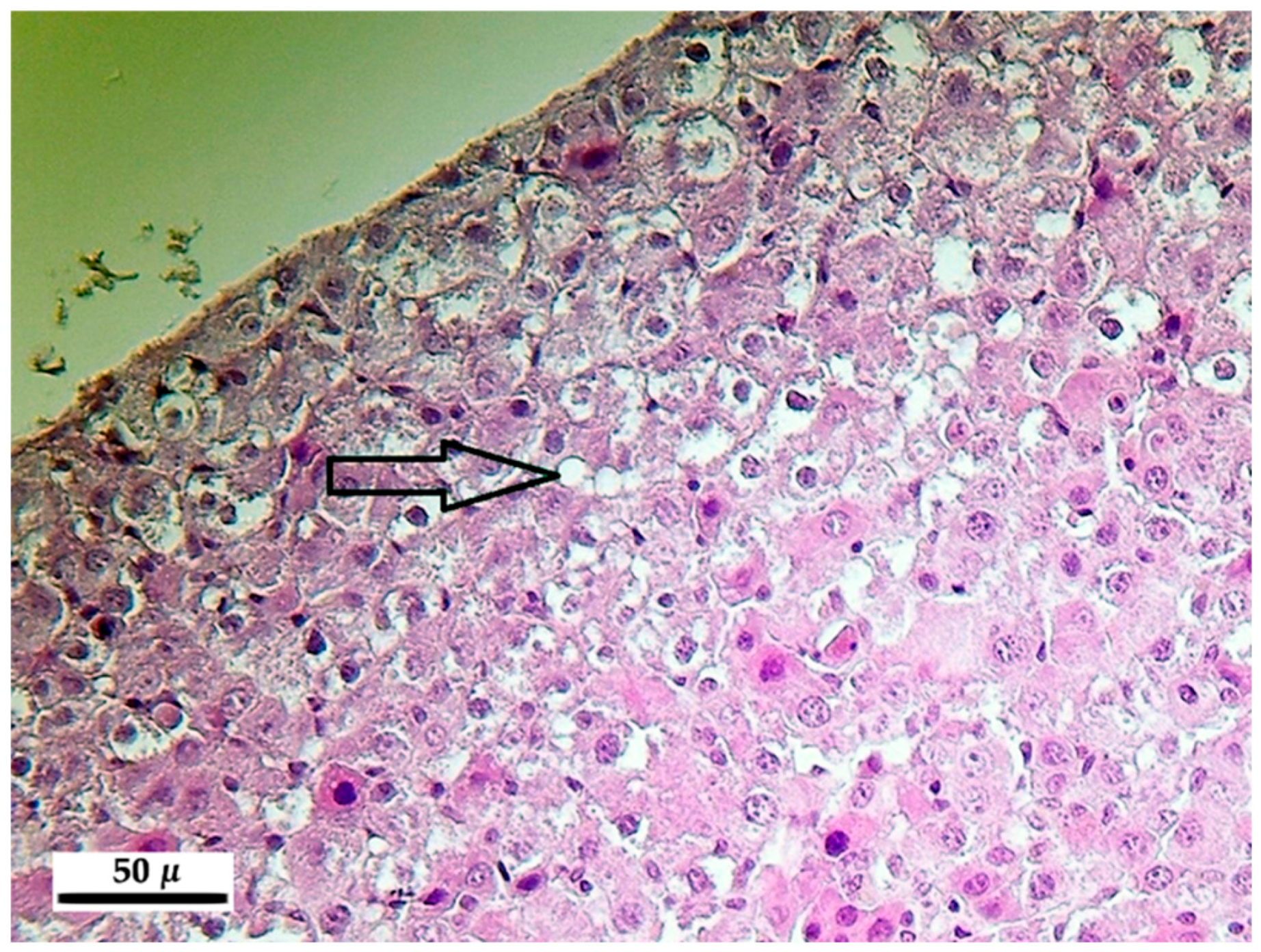
2.5.1. Liver
2.5.2. Kidney
2.5.3. Lung
3. Discussion
3.1. Feed Intake, Body and Organ Weights
3.2. Serum Clinical Chemistry
3.2.1. Enzymes
3.2.2. Nitrogenous Metabolites
3.2.3. Lipids
3.2.4. Glucose
3.3. Antioxidant and Lipid Peroxidation Parameters
3.3.1. Liver
3.3.2. Kidney
3.3.3. Lung
3.3.4. Blood Plasma
3.4. Genotoxicity
3.5. Histopathological Analysis
3.5.1. Liver
3.5.2. Kidney
3.5.3. Lung
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Animals and Feeding
5.2. Ethical Permission
5.3. Clinical Chemical Parameters
5.4. Antioxidant Status and Lipid Peroxidation
5.5. Comet Assay of Lymphocytes
5.6. Histopathological Analysis
5.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rheeder, J.P.; Marasas, W.F.O.; Vismer, H.F. Production of fumonisin analogs by Fusarium species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 2101–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission (2003) Updated opinion of the Scientific Committee on Food (SCF) on Fumonisin B1, BIOMIN Mycotoxin Survey, (2017): BIOMIN Holding GmbH, Getzersdorf, Austria. Available online: https://info.biomin.net/acton/attachment/14109/f-0463/1/-/-/l-0009/l-0009/MAG_MTXsurveyReport_2016_EN_0117_PKO.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2018.).
- Kubena, L.; Edrington, T.; Harvey, R.; Buckley, S.; Phillips, T.; Rottinghaus, G.; Casper, H. Individual and combined effects of fumonisin B1 present in Fusarium moniliforme culture material and T-2 toxin or deoxynivalenol in broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 1997, 76, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Månsson, M.; Klejnstrup, M.L.; Phipps, R.K.; Nielsen, K.F.; Frisvad, J.C.; Gotfredsen, C.H.; Larsen, T.O. Isolation and NMR characterization of fumonisin B2 and a new fumonisin B6 from Aspergillus niger. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candlish, A.; Aidoo, K.; Smith, J.; Pearson, S. A limited survey of aflatoxins and fumonisins in retail maizebased products in the UK using immunoassay detection. Mycotoxin Res. 2000, 16, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Arco, G.; Fernández-Franzón, M.; Font, G.; Damiani, P.; Mañes, J. Survey of fumonisins B1, B2 and B3 in conventional and organic retail corn products in Spain and Italy and estimated dietary exposure. Food Addit. Contam. Part B Surveill. 2009, 2, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano-Sancho, G.; Ramos, A.J.; Marín, S.; Sanchis, V. Occurrence of fumonisins in Catalonia (Spain) and an exposure assessment of specific population groups. Food Addit. Contam. Part A. Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 2012, 29, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakšić, S.; Abramović, B.; Jajić, I.; Baloš, M.Ž.; Mihaljev, Ž.; Despotović, V.; Šojić, D. Co-occurrence of fumonisins and deoxynivalenol in wheat and maize harvested in Serbia. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 89, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christofidou, M.; Kafouris, D.; Christodoulou, M.; Stefani, D.; Christoforou, E.; Nafti, G.; Christou, E.; Aletrari, M.; Ioannou-Kakouri, E. Occurrence, surveillance, and control of mycotoxins in food in Cyprus for the years 2004–2013. Food Agric. Immunol. 2015, 26, 880–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasas, W.F.; Kellerman, T.S.; Gelderblom, W.C.; Coetzer, J.A.; Thiel, P.G.; van der Lugt, J.J. Leukoencephalomalacia in a horse induced by fumonisin B1 isolated from Fusarium moniliforme. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1988, 55, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Colvin, B.M.; Harrison, L.R. Fumonisin-induced pulmonary edema and hydrothorax in swine. Mycopathologia 1992, 117, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelderblom, W.C.; Cawood, M.E.; Snyman, S.D.; Marasas, W.F. Fumonisin B1 dosimetry in relation to cancer initiation in rat liver. Carcinogenesis 1994, 15, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC (International Agency for Research on Cancer). Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans No 82; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2002; pp. 275–366. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, E.; Norred, W.P.; Bacon, C.W.; Riley, R.T.; Merrill, A.H. Inhibition of sphingolipid biosynthesis by fumonisins. Implications for diseases associated with Fusarium moniliforme. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 14486–14490. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abbès, S.; Ben Salah-Abbès, J.; Jebali, R.; Younes, R.B.; Oueslati, R. Interaction of aflatoxin B1 and fumonisin B1 in mice causes immunotoxicity and oxidative stress: Possible protective role using lactic acid bacteria. J. Immunotoxicol. 2016, 13, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, A.; Szabó-Fodor, J.; Fébel, H.; Mézes, M.; Repa, I.; Kovács, M. Acute hepatic effects of low-dose fumonisin B(1) in rats. Acta Vet. Hung. 2016, 64, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, A.; Szabó-Fodor, J.; Fébel, H.; Mézes, M.; Bajzik, G.; Kovács, M. Oral administration of fumonisin B 1 and T-2 individually and in combination affects hepatic total and mitochondrial membrane lipid profile of rabbits. Physiol. Int. 2016, 103, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedel, S.; Abel, S.; Burger, H.-M.; van der Westhuizen, L.; Swanevelder, S.; Gelderblom, W.C.A. Differential modulation of the lipid metabolism as a model for cellular resistance to fumonisin B1-induced cytotoxic effects in vitro. Prostaglandins. Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2016, 109, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mary, V.S.; Theumer, M.G.; Arias, S.L.; Rubinstein, H.R. Reactive oxygen species sources and biomolecular oxidative damage induced by aflatoxin B1 and fumonisin B1 in rat spleen mononuclear cells. Toxicology 2012, 302, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Q.; Wan, D.; Liu, Q.; Chen, D.; Liu, Z.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; Martínez, M.A.; Anadón, A.; Yuan, Z. Fumonisins: Oxidative stress-mediated toxicity and metabolism in vivo and in vitro. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 81–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehm, O.; Zur, B.; Koch, A.; Tran, N.; Freyenhagen, R.; Hartmann, M.; Zacharowski, K. Clinical chemistry reference database for Wistar rats and C57/BL6 mice. Biol. Chem. 2007, 388, 1255–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, O.; Romero, I.; González, J.E.; Mandina, T. Measurements of DNA damage on silver stained comets using free Internet software. Mutat. Res. 2007, 627, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Safety Evaluation of Certain Mycotoxins in Food; IPCS: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001; Volume 47. [Google Scholar]
- NTP Technical Report on the Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of Fumonisin B1 (CAS No. 116355-83-0) in F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice (Feed Studies); US Department of Health and Human Service, National Toxicology Program: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 1999.
- Bondy, G.S.; Barker, M.G.; Lombaert, G.A.; Armstrong, C.L.; Fernie, S.M.; Gurofsky, S.; Huzel, V.; Savard, M.E.; Curran, I.H. A comparison of clinical, histopathological and cell-cycle markers in rats receiving the fungal toxins fumonisin B1 or fumonisin B2 by intraperitoneal injection. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2000, 38, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondy, G.; Suzuki, C.; Barker, M.; Armstrong, C.; Fernie, S.; Hierlihy, L.; Rowsell, P.; Mueller, R. Toxicity of fumonisin B1 administered intraperitoneally to male Sprague-Dawley rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1995, 33, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiseau, N.; Polizzi, A.; Dupuy, A.; Therville, N.; Rakotonirainy, M.; Loy, J.; Viadere, J.-L.; Cossalter, A.-M.; Bailly, J.-D.; Puel, O.; et al. New insights into the organ-specific adverse effects of fumonisin B1: Comparison between lung and liver. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 1619–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondy, G.S.; Suzuki, C.A.; Mueller, R.W.; Fernie, S.M.; Armstrong, C.L.; Hierlihy, S.L.; Savard, M.E.; Barker, M.G. Gavage administration of the fungal toxin fumonisin B1 to female Sprague-Dawley rats. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health. A 1998, 53, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bucci, T.J.; Howard, P.C.; Tolleson, W.H.; Laborde, J.B.; Hansen, D.K. Renal Effects of Fumonisin Mycotoxins in Animals. Toxicol. Pathol. 1998, 26, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bondy, G.; Barker, M.; Mueller, R.; Fernie, S.; Miller, J.D.; Armstrong, C.; Hierlihy, S.L.; Rowsell, P.; Suzuki, C. Fumonisin B1 toxicity in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1996, 392, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.W.; Parker, H.M.; Vesonder, R.F.; Haschek, W.M. Intravenous fumonisin B1 induces cell proliferation and apoptosis in the rat. Nat. Toxins 1996, 4, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, C.A.M.; Hierlihy, L.; Barker, M.; Curran, I.; Mueller, R.; Bondy, G.S. The Effects of Fumonisin B1 on Several Markers of Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1995, 133, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, K.A.; Chamberlain, W.J.; Bacon, C.W.; Norred, W.P. A preliminary investigation on renal and hepatic toxicity in rats fed purified fumonisin B1. Nat. Toxins 1993, 1, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance, D.E.; Vance, J.E. Biochemistry of Lipids, Lipoproteins and Membranes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; ISBN 9780080559889. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, H.M.; Abel, S.; Gelderblom, W.C.A. Modulation of key lipid raft constituents in primary rat hepatocytes by fumonisin B1—Implications for cancer promotion in the liver. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 115, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeni, F.; Migliorati, L.; Terzano, G.M.; Capelletti, M.; Gallo, A.; Masoero, F.; Pirlo, G. Effects of two different blends of naturally mycotoxin-contaminated maize meal on growth and metabolic profile in replacement heifers. Animal 2014, 8, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turpin, S.M.; Lancaster, G.I.; Darby, I.; Febbraio, M.A.; Watt, M.J. Apoptosis in skeletal muscle myotubes is induced by ceramides and is positively related to insulin resistance. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2006, 291, E1341–E1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abel, S.; Gelderblom, W.C. Oxidative damage and fumonisin B1-induced toxicity in primary rat hepatocytes and rat liver in vivo. Toxicology 1998, 131, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domijan, A.-M.; Peraica, M.; Vrdoljak, A.L.; Radić, B.; Žlender, V.; Fuchs, R. The involvement of oxidative stress in ochratoxin A and fumonisin B1 toxicity in rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 1147–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdellatef, A.A.; Khalil, A.A. Ameliorated effects of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. lactis DSM 20076 and Pediococcus acidilactici NNRL B-5627 on Fumonisin B1-induced Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity in rats. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 11, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J.; Alexander, J.M. Alterations of the glutathione redox cycle status in fumonisin B1-treated pig kidney cells. J. Biochem. Toxicol. 1996, 11, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, B.F.; Kadlubar, F.F. Human alpha class glutathione S-transferases: Genetic polymorphism, expression, and susceptibility to disease. Methods Enzymol. 2005, 401, 9–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, M.; Gomi, F.; Dooley, M.M. Age-related alterations in antioxidant capacity and lipid peroxidation in brain, liver, and lung homogenates of normal and vitamin E-deficient rats. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1992, 64, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrache, I.; Natarajan, V.; Zhen, L.; Medler, T.R.; Richter, A.T.; Cho, C.; Hubbard, W.C.; Berdyshev, E.V.; Tuder, R.M. Ceramide upregulation causes pulmonary cell apoptosis and emphysema-like disease in mice. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hafner, D.; Szabó, A.; D’Costa, L.; Szabó-Fodor, J.; Tornyos, G.; Blochné Bodnár, Z.; Ölbeiné Horvatovich, K.; Baloghné Zándoki, E.; Bóta, B.; Kovács, M. Individual and combined effects of feed artificially contaminated with with fumonisin B1 and T-2 toxin in weaned rabbits. World Mycotoxin J. 2016, 9, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragan, Y.P.; Bidlack, W.R.; Cohen, S.M.; Goldsworthy, T.L.; Hard, G.C.; Howard, P.C.; Riley, R.T.; Voss, K.A. Implications of apoptosis for toxicity, carcinogenicity, and risk assessment: Fumonisin B(1) as an example. Toxicol. Sci. 2001, 61, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.S.; Groopman, J.D. DNA damage by mycotoxins. Mutat. Res. 1999, 424, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theumer, M.G.; Cánepa, M.C.; López, A.G.; Mary, V.S.; Dambolena, J.S.; Rubinstein, H.R. Subchronic mycotoxicoses in Wistar rats: Assessment of the in vivo and in vitro genotoxicity induced by fumonisins and aflatoxin B1, and oxidative stress biomarkers status. Toxicology 2010, 268, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelderblom, W.C.; Kriek, N.P.; Marasas, W.F.; Thiel, P.G. Toxicity and carcinogenicity of the Fusarium moniliforme metabolite, fumonisin B1, in rats. Carcinogenesis 1991, 12, 1247–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, K.A.; Smith, G.W.; Haschek, W.M. Fumonisins: Toxicokinetics, mechanism of action and toxicity. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2007, 137, 299–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venancio, J.C.; Emerich, S.S.; Branquinho, N.T.D.; de Sousa, F.C.; Natali, M.R.M.; Baroni, E.A. Effect of administering a diet contamined with fumonisins on the kidneys of wistar rats. Acta Sci. Biol. Sci. 2014, 36, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kócsó, D.J.; Szabó-Fodor, J.; Mézes, M.; Balogh, K.; Ferenczi, S.; Szabó, A.; Bóta, B.; Kovács, M. Fumonisin B1 exposure increases Hsp70 expression in the lung and kidney of rats without inducing significant oxidative stress. Acta Vet. Hung. 2018, 66, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salam, G.A.; Mehlab, E.; Shishtawy, M. Fumonisin Lung Toxicity: Gross and microscopic changes are dose and time dependent. J. Am. Sci. 2012, 8, 729–736. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Larranaga, M.R.; Anadon, A.; Diaz, M.J.; Fernandez-Cruz, M.L.; Martinez, M.A.; Frejo, M.T.; Martinez, M.; Fernandez, R.; Anton, R.M.; Morales, M.E.; et al. Toxicokinetics and oral bioavailability of fumonisin B1. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 1999, 41, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Botsoglou, N.A.; Fletouris, D.J.; Papageorgiou, G.E.; Vassilopoulos, V.N.; Mantis, A.J.; Trakatellis, A.G. Rapid, Sensitive, and Specific Thiobarbituric Acid Method for Measuring Lipid Peroxidation in Animal Tissue, Food, and Feedstuff Samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 1931–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Arlington, 14th ed.; AOAC: Arlington, VA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Sedlak, J.; Lindsay, R.H. Estimation of total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent. Anal. Biochem. 1968, 25, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, R.A.; Burk, R.F. Species, tissues and subcellular distribution of non-selenium dependent glutathione peroxidase activity. J. Nutr. 1978, 108, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD Environmental Health and Safety Publications. OECD Principles of Good Laboratory Practice (as Revised in 1997). Available online: https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/iccvam/suppdocs/feddocs/oecd/oecd_glpcm.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2018.).
- SPSS. SPSS for Windows ver. 20; SPSS: Chicago, IL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bright, J.; Aylott, M.; Bate, S.; Geys, H.; Jarvis, P.; Saul, J.; Vonk, R. Recommendations on the statistical analysis of the Comet assay. Pharm. Stat. 2011, 10, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Group | Days in Treatment | Control | 20 ppm | 50 ppm | 100 ppm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BW_initial (g) | 5 | 326.7 ± 15.2 | 323.6 ± 10.7 | 324.0 ± 9.60 | 331.1 ± 9.93 |
| 10 | 325.5 ± 13.9 | 329.4 ± 6.9 | 336.9 ± 15.6 | 329.8 ± 20.6 | |
| BW_final (g) | 5 | 346.7 ± 14.6 b | 316.9 ± 17.5 a | 315.5 ± 17.2 a | 308.1 ± 15.1 a |
| 10 | 368.0 ± 11.6 b | 321.8 ± 28.5 ab | 283.4 ± 36.1 a | 270.7 ± 47.9 a | |
| BW_gain (g) | 5 | 19.9 ± 2.29 c | -6.73 ± 7.97 b | −8.55 ± 7.95 b | −23 ± 10.7 a |
| 10 | 42.5 ± 13.4 c | -7.58 ± 30.0 b | −53.5 ± 29.0 ab | −59.1 ± 34.1 a | |
| liver (g) | 5 | 14.1 ± 1.18 b | 10.1 ± 1.37 a | 10.1 ± 0.87 a | 8.97 ± 0.41 a |
| 10 | 15.2 ± 1.14 b | 9.12 ± 2.55 a | 7.83 ± 1.66 a | 7.45 ± 1.41 a | |
| rel. liver (%) | 5 | 4.07 ± 0.28 b | 3.15 ± 0.29 a | 3.22 ± 0.21 a | 2.92 ± 0.08 a |
| 10 | 4.12 ± 0.22 b | 2.92 ± 0.52 a | 2.73 ± 0.32 a | 2.80 ± 0.19 a | |
| kidney (g) | 5 | 2.33 ± 0.19 | 2.07 ± 0.12 | 2.27 ± 0.27 | 2.07 ± 0.16 |
| 10 | 2.47 ± 0.21 ab | 2.42 ± 0.22 ab | 2.30 ± 0.22 a | 2.77 ± 0.39 b | |
| rel. kidney (%) | 5 | 0.68 ± 0.04 | 0.63 ± 0.05 | 0.72 ± 0.10 | 0.67 ± 0.08 |
| 10 | 0.67 ± 0.05 a | 0.78 ± 0.15 a | 0.83 ± 0.10 ab | 1.05 ± 0.21 b | |
| lung (g) | 5 | 2.35 ± 0.28 b | 1.82 ± 0.40 a | 1.60 ± 0.22 a | 1.52 ± 0.12 a |
| 10 | 1.73 ± 0.14 | 1.60 ± 0.13 | 1.55 ± 0.14 | 1.58 ± 0.13 | |
| rel. lung. % | 5 | 0.68 ±0.07 b | 0.57 ± 0.13 ab | 0.51 ± 0.07 a | 0.49 ± 0.04 a |
| 10 | 0.47 ± 0.04 a | 0.52 ± 0.04 ab | 0.55 ± 0.06 ab | 0.60 ± 0.07 b |
| Serum Parameters | Days in Treatment | Control | 20 ppm | 50 ppm | 100 ppm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AST (IU/L) | 5 | 181.0 ± 19.8 a | 553.3 ± 116.2 b | 570.0 ± 54.0 b | 691.5 ± 189.7 b |
| 10 | 170.5 ± 16.7 a | 406.0 ± 171.4 ab | 736.8 ± 432.8 bc | 1028.0 ± 418.0 c | |
| ALT (IU/L) | 5 | 46.2 ± 5.27 a | 128 ± 36.72 b * | 208.8 ± 29.6 c * | 205.5 ± 52.7 c * |
| 10 | 43.2 ± 4.17 a | 126.7 ± 29.47 ab* | 202.8 ± 102.5 bc* | 248.3 ± 81.3 c * | |
| Total protein (g/L) | 5 | 57.0 ± 1.79 a | 58.2 ± 4.17 a | 62.8 ± 1.92 b | 59.3 ± 1.97 ab |
| 10 | 58.8 ± 1.47 | 57.5 ± 3.62 | 59.2 ± 2.93 | 60.5 ± 1.76 | |
| Albumin (g/L) | 5 | 32.7 ± 0.52 a | 33.2 ± 1.94 ab | 35.0 ± 1.22 b | 33.5 ± 1.05 ab |
| 10 | 33.0 ± 0.63 | 33.5 ± 1.38 | 34.3 ± 1.63 | 34.0 ± 1.26 | |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 5 | 8.87 ± 1.15 c | 6.43 ± 1.92 b | 4.32 ± 0.61 a | 4.95 ± 0.64 ab |
| 10 | 7.15 ± 1.23 b | 6.52 ± 2.25 ab | 4.13 ± 1.01 a | 4.55 ± 0.92 a | |
| Total Chol. (mmol/L) | 5 | 2.60 ± 0.3 a | 4.63 ± 0.63 ab | 5.30 ± 0.45 ab | 6.43 ± 0.83 b |
| 10 | 2.38 ± 0.15 a | 4.43 ± 0.52 b | 5.18 ± 0.91b | 5.92 ± 1.58 b | |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 5 | 8.85 ± 0.53 a | 10.1 ± 1.62 a * | 10.5 ± 0.86 ab * | 12.7 ± 2.11 b * |
| 10 | 8.42 ± 0.35 a | 12.2 ± 5.18 a * | 13.0 ± 5.12 ab * | 22.9 ± 11.1 b * | |
| Creatinine (micromol/L) | 5 | 30.3 ± 4.23 a | 47.2 ± 8.3 b | 57.0 ± 7.78 bc * | 64.5 ± 7.4 c * |
| 10 | 26.3 ± 1.63 a | 56.2 ± 12.6 b * | 60.7 ± 9.03 bc * | 81.5 ± 25.1 c * |
| Parameters | 5 Days | 10 Days | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope | Constant | R2 | Slope | Constant | R2 | |
| AST | 154.8 | 11.9 | 0.82 | 290.3 | −140.5 | 0.996 |
| ALT | 55.9 | 7.42 | 0.88 | 69.2 | 17.7 | 0.984 |
| total_chol. | 1.22 | 1.7 | 0.95 | 1.13 | 1.64 | 0.93 |
| urea | 1.19 | 7.58 | 0.93 | 4.44 | 3.04 | 0.86 |
| creatinine | 11.2 | 21.7 | 0.97 | 17 | 13.7 | 0.93 |
| Liver | Days in Treatment | Control | 20 ppm | 50 ppm | 100 ppm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSH (micromol/g) | 5 | 2.72 ± 0.76 | 3.01 ± 0.41 | 3.06 ± 0.71 | 2.95 ± 1.15 |
| 10 | 3.2 ± 0.27 | 4.12 ± 1.19 | 3.52 ± 1 | 3.98 ± 1.14 | |
| GSHPx (IU/g prot.) | 5 | 1.39 ± 0.31 ab | 1.11 ± 0.1 a | 1.82 ± 0.42 b | 1.6 ± 0.36 ab |
| 10 | 1.42 ± 0.2 | 2.01 ± 1.02 | 1.05 ± 0.53 | 1.61 ± 1.06 | |
| MDA (nmol/g) | 5 | 55.6 ± 3.19 a | 69.9 ± 4.09 b | 64.9 ± 7.57ab | 68.9 ± 8.52 b |
| 10 | 47.3 ± 14.2 a | 74.7 ± 12.4 b | 61.5 ± 13.2ab | 63.6 ± 3.94 ab | |
| CD (Abs. 232 nm) | 5 | 0.57 ± 0.02 | 0.58 ± 0.03 | 0.59 ± 0.02 | 0.56 ± 0.04 |
| 10 | 0.6 ± 0.03 | 0.62 ± 0.02 | 0.63 ± 0.04 | 0.64 ± 0.12 | |
| CT (Abs. 268 nm) | 5 | 0.22 ± 0.01 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 0.22 ± 0.01 | 0.21 ± 0.01 |
| 10 | 0.22 ± 0.01 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 0.25 ± 0.07 |
| Kidney | Days in Treatment | Control | 20 ppm | 50 ppm | 100 ppm |
| GSH (micromol/g) | 5 | 2.65 ± 0.44 a | 4.26 ± 1.09 ab | 6.65 ± 0.79 ab | 5.24 ± 1.00 b |
| 10 | 3.19 ± 0.47 a | 4.68 ± 0.21 b | 4.86 ± 0.46 b | 5.3 ± 0.61 b | |
| GSHPx (IU/g prot.) | 5 | 2.47 ± 0.38 ab | 1.99 ± 0.86 a | 3.13 ± 0.4 b | 2.5 ± 0.33 ab |
| 10 | 2.11 ± 0.1 a | 2.89 ± 0.35 b | 2.82 ± 0.18 b | 2.97 ± 0.51 b | |
| MDA (nmol/g) | 5 | 52.2 ± 8.0 ab | 57.7 ± 5.09 b | 44.3 ± 2.89 a | 63.4 ± 10.1 b |
| 10 | 66.5 ± 11.3 b | 55.0 ± 8.27 ab | 41.9 ± 6.24 a | 54.8 ± 9.75 ab | |
| Lung | Days in Treatment | Control | 20 ppm | 50 ppm | 100 ppm |
| GSH (micromol/g) | 5 | 3.44 ± 0.39 | 3.81 ± 0.54 | 3.4 ± 0.37 | 3.41 ± 0.33 |
| 10 | 3.49 ± 0.45 | 3.75 ± 0.47 | 2.94 ± 0.44 | 3.26 ± 0.58 | |
| GSHPx (IU/g prot.) | 5 | 2.97 ± 0.42 | 3.26 ± 0.68 | 3.16 ± 0.48 | 3.06 ± 0.36 |
| 10 | 2.69 ± 0.29 | 2.97 ± 0.63 | 2.56 ± 0.27 | 2.67 ± 0.48 | |
| MDA (nmol/g) | 5 | 28.6 ± 6.54 ab | 35.2 ± 6.67 b | 24.1 ± 3.16 a | 27.7 ± 4.28 ab |
| 10 | 35.3 ± 4.91 a | 55.6 ± 5.03 c | 39.1 ± 2.78 ab | 42.9 ± 4.25 b | |
| Plasma | Days in Treatment | Control | 20 ppm | 50 ppm | 100 ppm |
| GSH (micromol/g) | 5 | 3.34 ± 0.29 ab | 3.44 ± 0.34 b | 2.8 ± 0.34 a | 3.45 ± 0.38 b |
| 10 | 3.16 ± 0.25 a | 3.46 ± 0.29 ab | 3.32 ± 0.23 ab | 3.97 ± 0.83 b | |
| GSHPx (IU/g prot.) | 5 | 3.02 ± 0.35 b | 2.47 ± 0.17 a | 2.47 ± 0.36 a | 2.57 ± 0.33 ab |
| 10 | 2.69 ± 0.25 | 2.73 ± 0.19 | 2.83 ± 0.29 | 2.58 ± 0.34 | |
| MDA (nmol/g) | 5 | 12.4 ± 1.43 a | 14.1 ± 1.46 ab | 14.5 ± 1.3 ab | 15.3 ± 1.24 b |
| 10 | 12.4 ± 0.91 a | 14.5 ± 1.63 b | 12.4 ± 0.6 a | 16.7 ± 1.11 c |
| Number of Animals Showing the Respected Alteration in the Respective Group (n = 6/Group) | Total Score (Representing the Severity of the Alteration) 1 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group (ppm) | 0 (control) | 20 | 50 | 100 | 0 (control) | 20 | 50 | 100 | ||||||||
| length of exposure (day) | 5 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 10 |
| Liver | ||||||||||||||||
| Vacuolar degeneration | 0 | 0 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 12 | 9 | 14 | 13 | 16 |
| Cytoplasma fragmentation | 0 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 14 | 12 | 18 |
| Solitaire necrosis (Councilman bodies) | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 12 | 10 | 18 |
| MPS cell proliferation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 30 | 12 |
| Kidney | ||||||||||||||||
| Tubular degeneration | 0 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 10 | 6 | 13 | 12 | 17 |
| Tubular necrosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 1 | 12 |
| Detachment of tubular epithelial cells | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 12 |
| Tubular dilatation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 15 |
| Hyaline accumulation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 |
| Lung | ||||||||||||||||
| Any alteration | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szabó, A.; Szabó-Fodor, J.; Kachlek, M.; Mézes, M.; Balogh, K.; Glávits, R.; Ali, O.; Zeebone, Y.Y.; Kovács, M. Dose and Exposure Time-Dependent Renal and Hepatic Effects of Intraperitoneally Administered Fumonisin B1 in Rats. Toxins 2018, 10, 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10110465
Szabó A, Szabó-Fodor J, Kachlek M, Mézes M, Balogh K, Glávits R, Ali O, Zeebone YY, Kovács M. Dose and Exposure Time-Dependent Renal and Hepatic Effects of Intraperitoneally Administered Fumonisin B1 in Rats. Toxins. 2018; 10(11):465. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10110465
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzabó, András, Judit Szabó-Fodor, Mariam Kachlek, Miklós Mézes, Krisztián Balogh, Róbert Glávits, Omeralfaroug Ali, Yarsmin Yunus Zeebone, and Melinda Kovács. 2018. "Dose and Exposure Time-Dependent Renal and Hepatic Effects of Intraperitoneally Administered Fumonisin B1 in Rats" Toxins 10, no. 11: 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10110465
APA StyleSzabó, A., Szabó-Fodor, J., Kachlek, M., Mézes, M., Balogh, K., Glávits, R., Ali, O., Zeebone, Y. Y., & Kovács, M. (2018). Dose and Exposure Time-Dependent Renal and Hepatic Effects of Intraperitoneally Administered Fumonisin B1 in Rats. Toxins, 10(11), 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10110465







