Indoxyl Sulfate, a Uremic Toxin, Stimulates Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Erythrocyte Cell Death Supposedly by an Organic Anion Transporter 2 (OAT2) and NADPH Oxidase Activity-Dependent Pathways
Abstract
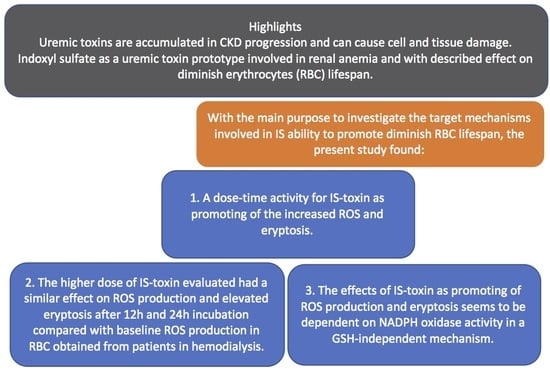
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. ROS Generation and Eryptosis
2.2. Glutathione Levels
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Subjects
4.2. Blood Samples and Red Blood Cells (RBCs) Preparations and Incubations
4.3. Measurement of Reactive Oxygen Species Production
4.4. Measurement of Eryptosis Levels by Annexin-V Binding
4.5. Measurement of Reduced Glutathione (GSH) Levels
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Georgatzakou, H.T.; Antonelou, M.H.; Papassideri, I.S.; Kriebardis, A.G. Red Blood Cell Abnormalities and the Pathogenesis of Anemia in End-Stage Renal Disease. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2016, 10, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamson, J.W. Hyporesponsiveness to Erythropoiesis Stimulating Agents in Chronic Kidney Disease: The Many Faces of Inflammation. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2009, 16, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, F.; Abed, M.; Lang, E.; Föller, M. Oxidative Stress and Suicidal Erythrocyte Death. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Föller, M.; Sopjani, M.; Mahmud, H.; Lang, F. Vanadate-Induced Suicidal Erythrocyte Death. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2008, 31, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.S.E.; Langer, H.; Abed, M.; Voelkl, J.; Lang, F. The Uremic Toxin Acrolein Promotes Suicidal Erythrocyte Death. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2013, 37, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolay, J.P.; Schneider, J.; Niemoeller, O.M.; Artunc, F.; Portero-Otin, M.; Haik, G.; Thornalley, P.J.; Schleicher, E.; Wieder, T.; Lang, F. Stimulation of Suicidal Erythrocyte Death by Methylglyoxal. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2006, 18, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, M.S.E.; Abed, M.; Voelkl, J.; Lang, F. Triggering of Suicidal Erythrocyte Death by Uremic Toxin Indoxyl Sulfate. BMC Nephrol. 2013, 14, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Ji, S.; Dong, W.; Qi, Y.; Song, W.; Cui, D.; Shi, J. Indolic Uremic Solutes Enhance Procoagulant Activity of Red Blood Cells through Phosphatidylserine Exposure and Microparticle Release. Toxins 2015, 7, 4390–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.-J.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lai, T.-S.; Wu, P.-C.; Chuang, C.-K.; Sun, F.-J.; Liu, H.-L.; Chen, H.-H.; Yeh, H.-I.; Lin, C.-S.; et al. The Role of Indoxyl Sulfate in Renal Anemia in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 83030–83037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, C.-K.; Tanaka, T.; Inagi, R.; Fujita, T.; Nangaku, M. Indoxyl Sulfate, a Representative Uremic Toxin, Suppresses Erythropoietin Production in a HIF-Dependent Manner. Lab. Investig. 2011, 91, 1564–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adelibieke, Y.; Shimizu, H.; Saito, S.; Mironova, R.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl Sulfate Counteracts Endothelial Effects of Erythropoietin through Suppression of Akt Phosphorylation. Circ. J. 2013, 77, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigam, S.K.; Wu, W.; Bush, K.T.; Hoenig, M.P.; Blantz, R.C.; Bhatnagar, V. Handling of Drugs, Metabolites, and Uremic Toxins by Kidney Proximal Tubule Drug Transporters. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 2039–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nigam, S.K. What Do Drug Transporters Really Do? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanWert, A.L.; Gionfriddo, M.R.; Sweet, D.H. Organic Anion Transporters: Discovery, Pharmacology, Regulation and Roles in Pathophysiology. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2007, 28, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sager, G.; Smaglyukova, N.; Fuskevaag, O.M. The Role of OAT2 (SLC22A7) in the Cyclic Nucleotide Biokinetics of Human Erythrocytes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 5972–5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enomoto, A.; Takeda, M.; Shimoda, M.; Narikawa, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Sekine, T.; Cha, S.H.; Niwa, T.; et al. Interaction of Human Organic Anion Transporters 2 and 4 with Organic Anion Transport Inhibitors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 301, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Enomoto, A.; Takeda, M.; Taki, K.; Takayama, F.; Noshiro, R.; Niwa, T.; Endou, H. Interactions of Human Organic Anion as Well as Cation Transporters with Indoxyl Sulfate. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 466, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelasco, A.K.; Raymond, J.R. Indoxyl Sulfate Induces Complex Redox Alterations in Mesangial Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2006, 290, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolati, D.; Shimizu, H.; Higashiyama, Y.; Nishijima, F.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl Sulfate Induces Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Rat Kidneys and Human Proximal Tubular Cells. Am. J. Nephrol. 2011, 34, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekine, T.; Cha, S.H.; Tsuda, M.; Apiwattanakul, N.; Nakajima, N.; Kanai, Y.; Endou, H. Identification of Multispecific Organic Anion Transporter 2 Expressed Predominantly in the Liver. FEBS Lett. 1998, 429, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoyamada, M.; Sekine, T.; Kanai, Y.; Endou, H. Molecular Cloning and Functional Expression of a Multispecific Organic Anion Transporter from Human Kidney. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.H.; Sekine, T.; Fukushima, J.I.; Kanai, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Goya, T.; Endou, H. Identification and Characterization of Human Organic Anion Transporter 3 Expressing Predominantly in the Kidney. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 59, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrissey, K.M.; Wen, C.C.; Johns, S.J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, S.M.; Giacomini, K.M. The UCSF-FDA Transportal: A Public Drug Transporter Database. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 92, 545–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, L.; Jourde-Chiche, N.; Faure, V.; Cerini, C.; Berland, Y.; Dignat-George, F.; Brunet, P. The Uremic Solute Indoxyl Sulfate Induces Oxidative Stress in Endothelial Cells. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, H.; Miyamoto, Y.; Honda, D.; Tanaka, H.; Wu, Q.; Endo, M.; Noguchi, T.; Kadowaki, D.; Ishima, Y.; Kotani, S.; et al. P-Cresyl Sulfate Causes Renal Tubular Cell Damage by Inducing Oxidative Stress by Activation of NADPH Oxidase. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambeth, J.D. NOX Enzymes and the Biology of Reactive Oxygen. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, A.; Pushkaran, S.; Konstantinidis, D.G.; Koochaki, S.; Malik, P.; Mohandas, N.; Zheng, Y.; Joiner, C.H.; Kalfa, T.A. Erythrocyte NADPH Oxidase Activity Modulated by Rac GTPases, PKC, and Plasma Cytokines Contributes to Oxidative Stress in Sickle Cell Disease. Blood 2013, 121, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muteliefu, G.; Enomoto, A.; Jiang, P.; Takahashi, M.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl Sulphate Induces Oxidative Stress and the Expression of Osteoblast-Specific Proteins in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockler-Pinto, M.B.; Saldanha, J.F.; Yi, D.; Mafra, D.; Fouque, D.; Soulage, C.O. The Uremic Toxin Indoxyl Sulfate Exacerbates Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Inflammation in 3T3-L1 Adipose Cells. Free Radic. Res. 2016, 50, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abed, M.; Artunc, F.; Alzoubi, K.; Honisch, S.; Baumann, D.; Föller, M.; Lang, F. Suicidal Erythrocyte Death in End-Stage Renal Disease. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 92, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonan, N.B.; Steiner, T.M.; Kuntsevich, V.; Virzì, G.M.; Azevedo, M.; Nakao, L.S.; Barreto, F.C.; Ronco, C.; Thijssen, S.; Kotanko, P.; et al. Uremic Toxicity-Induced Eryptosis and Monocyte Modulation: The Erythrophagocytosis as a Novel Pathway to Renal Anemia. Blood Purif. 2016, 41, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, I.-W.; Hsu, K.-H.; Lee, C.-C.; Sun, C.-Y.; Hsu, H.-J.; Tsai, C.-J.; Tzen, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-Y.; Wu, M.-S. P-Cresyl Sulphate and Indoxyl Sulphate Predict Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, J.B.; Butterfield, D.A. Measurement of Oxidized/Reduced Glutathione Ratio. In Protein Misfolding and Cellular Stress in Disease and Aging: Concepts and Protocols; Humana: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 648, pp. 269–277. [Google Scholar]
- Khazim, K.; Giustarini, D.; Rossi, R.; Verkaik, D.; Cornell, J.E.; Cunningham, S.E.D.; Mohammad, M.; Trochta, K.; Lorenzo, C.; Folli, F.; et al. Glutathione Redox Potential Is Low and Glutathionylated and Cysteinylated Hemoglobin Levels Are Elevated in Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients. Transl. Res. 2013, 162, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, N.D. Oxidative Stress in Uremia: Nature, Mechanisms, and Potential Consequences. Semin. Nephrol. 2004, 24, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceballos-picot, I.; Witko-sarsat, V.; Merad-Boudia, M.; Nguyen, A.T.; Thévenin, M.; Venin, M.T.H.; Jaudon, M.C.; Zingraff, J.; Verger, C.; Jungers, P.; Descamps-latscha, B. Glutathione Antioxidant System as a Marker of Oxidative Stress in Chronic Renal Faillure. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 21, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataille, S.; Pelletier, M.; Sallée, M.; Berland, Y.; McKay, N.; Duval, A.; Gentile, S.; Mouelhi, Y.; Brunet, P.; Burtey, S. Indole 3-Acetic Acid, Indoxyl Sulfate and Paracresyl-Sulfate Do Not Influence Anemia Parameters in Hemodialysis Patients. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duranton, F.; Cohen, G.; De Smet, R.; Rodriguez, M.; Jankowski, J.; Vanholder, R.; Argiles, A. Normal and Pathologic Concentrations of Uremic Toxins. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bi, Y.; Mathialagan, S.; Tylaska, L.; Fu, M.; Keefer, J.; Vildhede, A.; Costales, C.; Rodrigues, A.D.; Varma, M. Organic Anion Transporter 2 Mediates Hepatic Uptake of Tolbutamide, a Cytochrome P450 2C9 Probe Drug. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2018, 364, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Parameters | Healthy Subjects [n = 8] | HD Patients [n = 10] |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 33.1 ± 11 | 36.7 ± 4.5 |
| Gender (Male %) | 44.4 | 50 |
| Caucasians (%) | 100 | 93.3 |
| BMI (Kg/m²) | 22 ± 1.8 | 25.3 ± 3.7 |
| Hb (g/dL) | 14.1 ± 0.5 | 10.8 ± 1.2 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.9 ± 2 | 12.4 ± 2.1 |
| Urea normal or pre-HD (mg/dL) | 21 ± 0.5 | 164.4 ± 41 |
| Urea post HD (mg/dL) | NA | 54.1 ± 17.7 |
| CVD | 0 | 21.1 |
| DM | 0 | 33.3 |
| Hypertension | 0 | 46.6 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dias, G.F.; Bonan, N.B.; Steiner, T.M.; Tozoni, S.S.; Rodrigues, S.; Nakao, L.S.; Kuntsevich, V.; Pecoits Filho, R.; Kotanko, P.; Moreno-Amaral, A.N. Indoxyl Sulfate, a Uremic Toxin, Stimulates Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Erythrocyte Cell Death Supposedly by an Organic Anion Transporter 2 (OAT2) and NADPH Oxidase Activity-Dependent Pathways. Toxins 2018, 10, 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10070280
Dias GF, Bonan NB, Steiner TM, Tozoni SS, Rodrigues S, Nakao LS, Kuntsevich V, Pecoits Filho R, Kotanko P, Moreno-Amaral AN. Indoxyl Sulfate, a Uremic Toxin, Stimulates Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Erythrocyte Cell Death Supposedly by an Organic Anion Transporter 2 (OAT2) and NADPH Oxidase Activity-Dependent Pathways. Toxins. 2018; 10(7):280. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10070280
Chicago/Turabian StyleDias, Gabriela Ferreira, Natalia Borges Bonan, Thiago Maass Steiner, Sara Soares Tozoni, Silvia Rodrigues, Lia Sumie Nakao, Viktoriya Kuntsevich, Roberto Pecoits Filho, Peter Kotanko, and Andréa N. Moreno-Amaral. 2018. "Indoxyl Sulfate, a Uremic Toxin, Stimulates Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Erythrocyte Cell Death Supposedly by an Organic Anion Transporter 2 (OAT2) and NADPH Oxidase Activity-Dependent Pathways" Toxins 10, no. 7: 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10070280
APA StyleDias, G. F., Bonan, N. B., Steiner, T. M., Tozoni, S. S., Rodrigues, S., Nakao, L. S., Kuntsevich, V., Pecoits Filho, R., Kotanko, P., & Moreno-Amaral, A. N. (2018). Indoxyl Sulfate, a Uremic Toxin, Stimulates Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Erythrocyte Cell Death Supposedly by an Organic Anion Transporter 2 (OAT2) and NADPH Oxidase Activity-Dependent Pathways. Toxins, 10(7), 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10070280