Structural and Mechanistic Features of ClyA-Like α-Pore-Forming Toxins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Common Structural Topology of ClyA-Like Toxin Components
3. Homooligomeric ClyA and Cry6Aa Toxins
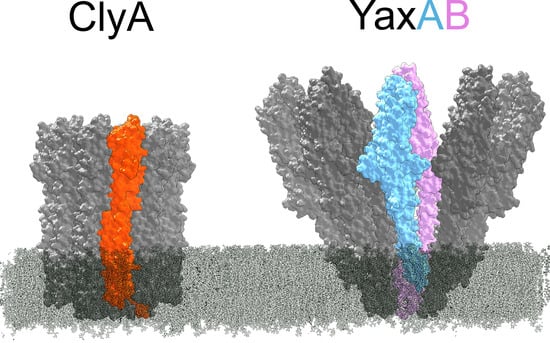
4. Two-Component Heterooligomeric ClyA-Like Toxins
5. Exposure of the Transmembrane Domains in ClyA-Like Toxins
6. Assembly Pathways of ClyA-Like Pores
7. Assembly of Three-Component Membrane Pores: Nhe and Hbl Toxins
8. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Los, F.C.O.; Randis, T.M.; Aroian, R.V.; Ratner, A.J. Role of pore-forming toxins in bacterial infectious diseases. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 173–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peraro, M.D.; Van Der Goot, F.G. Pore-forming toxins: Ancient, but never really out of fashion. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 14, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Pentelute, B.L.; Collier, R.J.; Zhou, Z.H. Atomic structure of anthrax protective antigen pore elucidates toxin translocation. Nature 2015, 521, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokori-Brown, M.; Martin, T.G.; Naylor, C.E.; Basak, A.K.; Titball, R.W.; Savva, C.G. Cryo-EM structure of lysenin pore elucidates membrane insertion by an aerolysin family protein. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudkina, N.V.; Spicer, B.A.; Reboul, C.F.; Conroy, P.J.; Lukoyanova, N.; Elmlund, H.; Law, R.H.P.; Ekkel, S.M.; Kondos, S.C.; Goode, R.J.A.; et al. Structure of the poly-C9 component of the complement membrane attack complex. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatsogiannis, C.; Merino, F.; Prumbaum, D.; Roderer, D.; Leidreiter, F.; Meusch, D.; Raunser, S. Membrane insertion of a Tc toxin in near-atomic detail. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bräuning, B.; Bertosin, E.; Praetorius, F.; Ihling, C.; Schatt, A.; Adler, A.; Richter, K.; Sinz, A.; Dietz, H.; Groll, M. Structure and mechanism of the two-component α-helical pore-forming toxin YaxAB. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, E.; Vetter, I.R.; Prumbaum, D.; Penczek, P.A.; Raunser, S. Membrane insertion of α-xenorhabdolysin in near-atomic detail. eLife 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, M.; Grauschopf, U.; Maier, T.; Glockshuber, R.; Ban, N. The structure of a cytolytic α-helical toxin pore reveals its assembly mechanism. Nature 2009, 459, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Caaveiro, J.M.M.; Morante, K.; González-Mañas, J.M.; Tsumoto, K. Structural basis for self-assembly of a cytolytic pore lined by protein and lipid. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dementiev, A.; Board, J.; Sitaram, A.; Hey, T.; Kelker, M.S.; Xu, X.; Hu, Y.; Vidal-Quist, C.; Chikwana, V.; Griffin, S.; et al. The pesticidal Cry6Aa toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis is structurally similar to HlyE-family alpha pore-forming toxins. BMC Biol. 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneux, F.; Zumbihl, R.; Jubelin, G.; Ribeiro, C.; Poncet, J.; Baghdiguian, S.; Givaudan, A.; Brehelin, M. The xaxAB Genes Encoding a New Apoptotic Toxin from the Insect Pathogen Xenorhabdus nematophila Are Present in Plant and Human Pathogens. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 9571–9580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, N.J.; Lin, C.P.; Borst, L.B.; Miller, V.L. YaxAB: A Yersinia enterocolitica pore-forming toxin regulated by Rova. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 4208–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madegowda, M.; Eswaramoorthy, S.; Burley, S.K.; Swaminathan, S. X-ray crystal structure of the B component of Hemolysin BL from Bacillus cereus. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2008, 71, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganash, M.; Phung, D.; Sedelnikova, S.E.; Lindbäck, T.; Granum, P.E.; Artymiuk, P.J. Structure of the NheA component of the Nhe toxin from Bacillus cereus: Implications for function. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindback, T.; Hardy, S.P.; Dietrich, R.; Sodring, M.; Didier, A.; Moravek, M.; Fagerlund, A.; Bock, S.; Nielsen, C.; Casteel, M.; et al. Cytotoxicity of the Bacillus cereus Nhe enterotoxin requires specific binding order of its three exoprotein components. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 3813–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, A.J.; Stillman, T.J.; Atkins, A.; Jamieson, S.J.; Bullough, P.A.; Green, J.; Artymiuk, P.J. E. coli hemolysin E (HlyE, ClyA, SheA): X-ray crystal structure of the toxin and observation of membrane pores by electron microscopy. Cell 2000, 100, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Soding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2014, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benke, S.; Roderer, D.; Wunderlich, B.; Nettels, D.; Glockshuber, R.; Schuler, B. The assembly dynamics of the cytolytic pore toxin ClyA. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roderer, D.; Glockshuber, R. Assembly mechanism of the α-pore-forming toxin cytolysin A from Escherichia coli. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 2017, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Bhatnagar, N.B.; Bhatnagar, R. Bacterial insecticidal toxins. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 30, 33–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, D.; Chai, L.; Wang, F.; Zhang, F.; Ruan, L.; Sun, M. Synergistic activity between Bacillus thuringiensis Cry6Aa and Cry55Aa toxins against Meloidogyne incognita. Microb. Biotechnol. 2011, 4, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adang, M.J.; Crickmore, N.; Jurat-Fuentes, J.L. Diversity of Bacillus thuringiensis crystal toxins and mechanism of action. Adv. Insect Physiol. 2014, 47, 39–87. [Google Scholar]
- Fortea, E.; Lemieux, V.; Potvin, L.; Chikwana, V.; Griffin, S.; Hey, T.; McCaskill, D.; Narva, K.; Tan, S.Y.; Xu, X.; et al. Cry6Aa1, a Bacillus thuringiensis nematocidal and insecticidal toxin, forms pores in planar lipid bilayers at extremely low concentrations and without the need of proteolytic processing. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 13122–13132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eifler, N.; Vetsch, M.; Gregorini, M.; Ringler, P.; Chami, M.; Philippsen, A.; Fritz, A.; Müller, S.A.; Glockshuber, R.; Engel, A.; et al. Cytotoxin ClyA from Escherichia coli assembles to a 13-meric pore independent of its redox-state. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 2652–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beecher, D.J.; Macmillan, J.D. Characterization of the components of hemolysin BL from Bacillus cereus. Infect. Immun. 1991, 59, 1778–1784. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beecher, D.J.; Schoeni, J.L.; Wong, A.C. Enterotoxic activity of hemolysin BL from Bacillus cereus. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 4423–4428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lund, T.; Granum, P.E. Characterisation of a non-haemolytic enterotoxin complex from Bacillus cereus isolated after a foodborne outbreak. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1996, 141, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindbäck, T.; Fagerlund, A.; Rødland, M.S.; Granum, P.E. Characterization of the Bacillus cereus Nhe enterotoxin. Microbiol. Read. Engl. 2004, 150, 3959–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeßberger, N.; Dietrich, R.; Bock, S.; Didier, A.; Märtlbauer, E. Bacillus cereus enterotoxins act as major virulence factors and exhibit distinct cytotoxicity to different human cell lines. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2014, 77, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeßberger, N.; Rademacher, C.; Krey, V.M.; Dietrich, R.; Mohr, A.K.; Böhm, M.E.; Scherer, S.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Märtlbauer, E. Simulating Intestinal Growth Conditions Enhances Toxin Production of Enteropathogenic Bacillus cereus. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Didier, A.; Dietrich, R.; Heilkenbrinker, U.; Waltenberger, E.; Jessberger, N.; Märtlbauer, E.; Benz, R. Formation of small transmembrane pores: An intermediate stage on the way to Bacillus cereus non-hemolytic enterotoxin (Nhe) full pores in the absence of NheA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 469, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tausch, F.; Dietrich, R.; Schauer, K.; Janowski, R.; Niessing, D.; Märtlbauer, E.; Jessberger, N. Evidence for Complex Formation of the Bacillus cereus Haemolysin BL Components in Solution. Toxins 2017, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastalla, I.; Fattah, R.; Coppage, N.; Nandy, P.; Crown, D.; Pomerantsev, A.P.; Leppla, S.H. The Bacillus cereus Hbl and Nhe tripartite enterotoxin components assemble sequentially on the surface of target cells and are not interchangeable. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didier, A.; Dietrich, R.; Märtlbauer, E. Antibody binding studies reveal conformational flexibility of the Bacillus cereus Non-Hemolytic Enterotoxin (Nhe) a-component. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serna, M.; Giles, J.L.; Morgan, B.P.; Bubeck, D. Structural basis of complement membrane attack complex formation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bräuning, B.; Groll, M. Structural and Mechanistic Features of ClyA-Like α-Pore-Forming Toxins. Toxins 2018, 10, 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10090343
Bräuning B, Groll M. Structural and Mechanistic Features of ClyA-Like α-Pore-Forming Toxins. Toxins. 2018; 10(9):343. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10090343
Chicago/Turabian StyleBräuning, Bastian, and Michael Groll. 2018. "Structural and Mechanistic Features of ClyA-Like α-Pore-Forming Toxins" Toxins 10, no. 9: 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10090343
APA StyleBräuning, B., & Groll, M. (2018). Structural and Mechanistic Features of ClyA-Like α-Pore-Forming Toxins. Toxins, 10(9), 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10090343