Crotoxin Conjugated to SBA-15 Nanostructured Mesoporous Silica Induces Long-Last Analgesic Effect in the Neuropathic Pain Model in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. CTX LD50 Increased When Adsorbed to SBA-15
2.2. CTX:SBA-15 Prolongs the Antinociceptive Effect of CTX in the PSNL Model
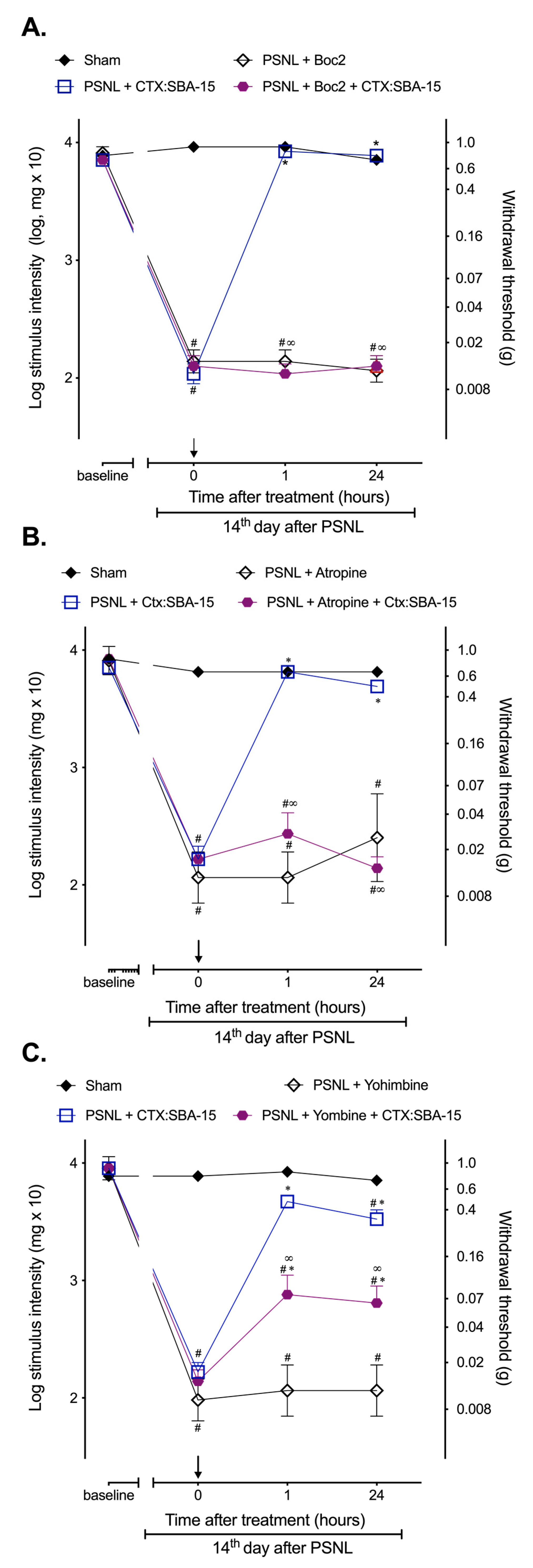
2.3. CTX:SBA-15 Complex Does Not Alter CTX Analgesic Mechanisms of Action Related to the Involvement of Formyl Peptide, α2-Adrenergic and Muscarinic Receptors
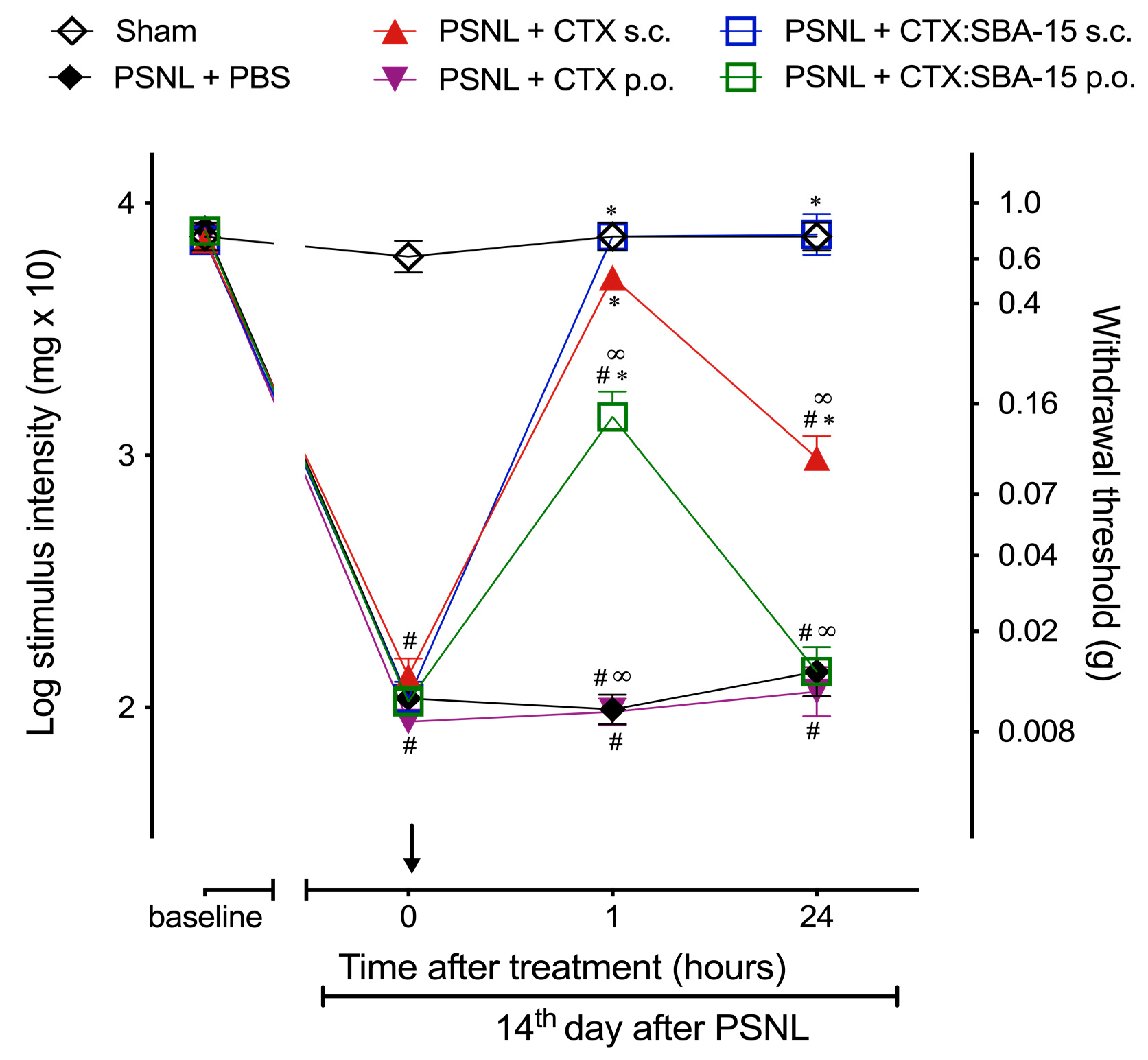
2.4. CTX Orally Administered Only Presents Analgesic Activity When Adsorbed to SBA-15
2.5. Both CTX and CTX:SBA-15 Treatments Reduce Iba-1 and GFAP Spinal Cord Expression Induced by PSNL
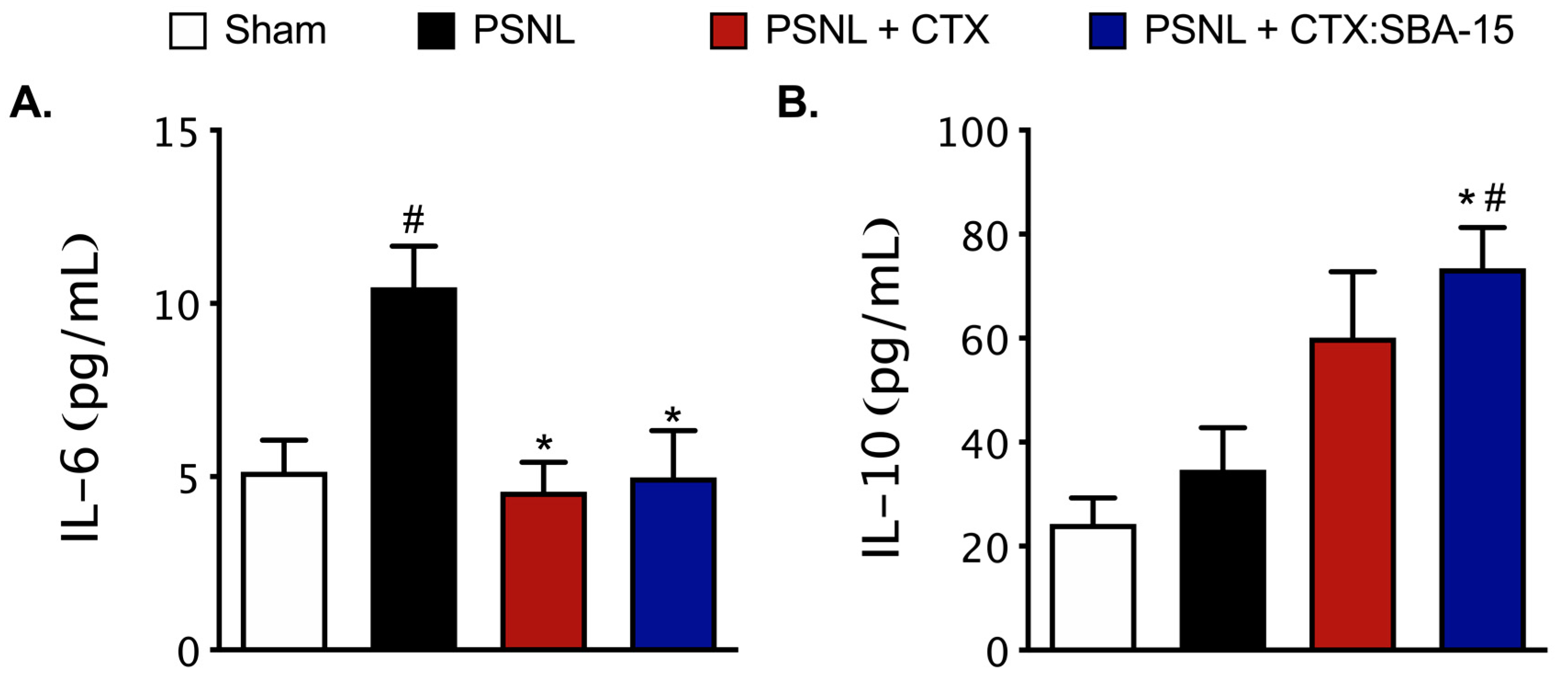
2.6. Both CTX and CTX:SBA-15 Modulate the Production and Release of Cytokines Induced by PSNL Model
2.7. Antibodies Produced after CTX:SBA-15 Immunization Protect Against CTX Lethality and Do Not Affect CTX or CTX:SBA-15 Analgesic Effect
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Animals
5.2. Crotoxin (CTX)
5.3. SBA-15 Synthesis
5.4. Preparation of the Complex (CTX:SBA-15)
5.5. Drug Administration
5.6. Lethal Dose (LD50) Determination
5.7. General Experimental Design
5.8. Neuropathic Pain Model—Partial Sciatic Nerve Ligation (PSNL)
5.9. Behavioural Test—Mechanical Hypernociception Assessment Using von Frey Filaments
5.10. Glia Cell Expression Evaluated by Western Blotting
5.11. Cytokine Level Evaluation
5.12. Anti-CTX Antibody Titration by ELISA and Passive Immunization
5.13. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Millan, M.J. The induction of pain: An integrative review. Prog. Neurobiol. 1999, 57, 1–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besson, J.M. The neurobiology of pain. Lancet 1999, 353, 1610–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, P.M.; Hutchinson, M.R.; Maier, S.F.; Watkins, L.R. Pathological pain and the neuroimmune interface. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, J.; Woolf, C.J. The neuropathic pain triad: Neurons, immune cells and glia. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, R.-D.; Suter, M.R.; Ji, R.-R.; Decosterd, I. Glial cells and chronic pain. Neuroscientist 2010, 16, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.-R.; Berta, T.; Nedergaard, M. Glia and pain: Is chronic pain a gliopathy? Pain 2013, 154, S10–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrance, N.; Smith, B.H.; Watson, M.C.; Bennett, M.I. Medication and treatment use in primary care patients with chronic pain of predominantly neuropathic origin. Fam. Pract. 2007, 24, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilron, I.; Dickenson, A.H. Emerging drugs for neuropathic pain. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2014, 19, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yekkirala, A.S.; Roberson, D.P.; Bean, B.P.; Woolf, C.J. Breaking barriers to novel analgesic drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 545–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, A.B.; Dworkin, R.H. Treatment of neuropathic pain: An overview of recent guidelines. Am. J. Med. 2009, 122, S22–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picolo, G.; Giorgi, R.; Cury, Y. delta-opioid receptors and nitric oxide mediate the analgesic effect of Crotalus durissus terrificus snake venom. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 391, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigatte, P.; Hoffmann, F.A.; Bernardi, M.M.; Giorgi, R.; Fernandes, I.; Takehara, H.A.; Barros, S.B.; Almeida, M.G.; Cury, Y. Tolerance to the antinociceptive effect of Crotalus durissus terrificus snake venom in mice is mediated by pharmacodynamic mechanisms. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1399–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, F.P.B.; Zychar, B.C.; Della-Casa, M.S.; Sampaio, S.C.; Gonçalves, L.R.C.; Cirillo, M.C. Crotoxin is responsible for the long-lasting anti-inflammatory effect of Crotalus durissus terrificus snake venom: Involvement of formyl peptide receptors. Toxicon 2010, 55, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazil, V. Do emprego da peçonha em terapêutica. Biol. Méd. 1934, 1, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio, S.C.; Hyslop, S.; Fontes, M.R.M.; Prado-Franceschi, J.; Zambelli, V.O.; Magro, A.J.; Brigatte, P.; Gutierrez, V.P.; Cury, Y. Crotoxin: Novel activities for a classic beta-neurotoxin. Toxicon 2010, 55, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira-Neto, F.D.S.; Amorim, R.L.; Brigatte, P.; Picolo, G.; Ferreira, W.; Gutierrez, V.P.; Conceição, I.M.; Della-Casa, M.S.; Takahira, R.K.; Nicoletti, J.L.M.; et al. The analgesic effect of crotoxin on neuropathic pain is mediated by central muscarinic receptors and 5-lipoxygenase-derived mediators. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2008, 91, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cura, J.E.; Blanzaco, D.P.; Brisson, C.; Cura, M.A.; Cabrol, R.; Larrateguy, L.; Mendez, C.; Sechi, J.C.; Silveira, J.S.; Theiller, E.; et al. Phase I and pharmacokinetics study of crotoxin (cytotoxic PLA(2), NSC-624244) in patients with advanced cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, F.R.; Farias, A.S.; Proença, P.L.F.; de La Hoz, C.; Langone, F.; Oliveira, E.C.; Toyama, M.H.; Marangoni, S.; Santos, L.M.B. The effect of treatment with crotapotin on the evolution of experimental autoimmune neuritis induced in Lewis rats. Toxicon 2007, 49, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Wu, D.-C.; Zhou, X.-P.; Gong, S.; Cheng, B.-C.; Qin, Z.-H.; Reid, P.F.; Yin, Q.-Z.; Jiang, X.-H. Inhibitory effect of crotoxin on the pain-evoked discharge of neurons in thalamic parafascicular nucleus in rats. Toxicon 2008, 51, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-L.; Han, R.; Chen, Z.-X.; Chen, B.-W.; Gu, Z.-L.; Reid, P.F.; Raymond, L.N.; Qin, Z.-H. Opiate and acetylcholine-independent analgesic actions of crotoxin isolated from crotalus durissus terrificus venom. Toxicon 2006, 48, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambelli, V.O.; Sampaio, S.C.; Sudo-Hayashi, L.S.; Greco, K.; Britto, L.R.G.; Alves, A.S.; Zychar, B.C.; Gonçalves, L.R.C.; Spadacci-Morena, D.D.; Otton, R.; et al. Crotoxin alters lymphocyte distribution in rats: Involvement of adhesion molecules and lipoxygenase-derived mediators. Toxicon 2008, 51, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, L.V.; Ruiz, R.D.C.; Scaramuzzi, K.; Marengo, E.B.; Matos, J.R.; Tambourgi, D.V.; Fantini, M.C.; Sant’Anna, O. Immunological parameters related to the adjuvant effect of the ordered mesoporous silica SBA-15. Vaccine 2010, 28, 7829–7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, S.; Zou, M.; Cheng, G. Enhanced mucosal and systemic immune responses obtained by porous silica nanoparticles used as an oral vaccine adjuvant: Effect of silica architecture on immunological properties. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 436, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayan, R.; Nayak, U.Y.; Raichur, A.M.; Garg, S. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: A comprehensive review on synthesis and recent advances. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Liong, M. Biocompatibility, biodistribution, and drug delivery efficiency of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cancer therapy in animals. Small 2011, 6, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenholm, J.M.; Sahlgren, C.; Lindén, M. Towards multifunctional, targeted drug delivery systems using mesoporous silica nanoparticles—Opportunities & challenges. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 1870–1883. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giorgi, R.; Bernardi, M.M.; Cury, Y. Analgesic effect evoked by low molecular weight substances extracted from Crotalus durissus terrificus venom. Toxicon 1993, 31, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moalem, G.; Tracey, D.J. Immune and inflammatory mechanisms in neuropathic pain. Brain Res. Rev. 2006, 51, 240–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primon-Barros, M.; José Macedo, A. Animal venom peptides: Potential for new antimicrobial agents. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1119–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cury, Y.; Picolo, G. Animal toxins as analgesics—An overview. Drug News Perspect. 2006, 19, 381–392. [Google Scholar]
- Zambelli, V.O.; Pasqualoto, K.F.M.; Picolo, G.; Chudzinski-Tavassi, A.M.; Cury, Y. Harnessing the knowledge of animal toxins to generate drugs. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 112, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, D.F.; Lopes-Ferreira, M.; Faquim-Mauro, E.L.; Macedo, M.S.; Farsky, S.H. Role of crotoxin, a phospholipase A2 isolated from Crotalus durissus terrificus snake venom, on inflammatory and immune reactions. Mediators Inflamm. 2001, 10, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel-Santos, A.; Lima, C.; Lopes-Ferreira, M.; Cardoso, D.F. Immunosuppresive role of principal toxin (crotoxin) of Crotalus durissus terrificus venom. Toxicon 2004, 44, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercuri, L.P.; Carvalho, L.V.; Lima, F.; Quayle, C.; Fantini, M.C.; Tanaka, G.S.; Cabrera, W.H.; Furtado, M.F.D.; Tambourgi, D.V.; Matos, J.D.R.; et al. Ordered mesoporous silica SBA-15: A new effective adjuvant to induce antibody response. Small 2006, 2, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaramuzzi, K.; Tanaka, G.D.; Neto, F.M.; Garcia, P.R.A.F.; Gabrili, J.J.M.; Oliveira, D.C.A.; Tambourgi, D.V.; Mussalem, J.S.; Paixão-Cavalcante, D.; D’Azeredo Orlando, M.T.; et al. Nanostructured SBA-15 silica: An effective protective vehicle to oral hepatitis B vaccine immunization. Nanomed. Nanotech. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 2241–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, I.; Guerrero, B.; Maria Salazar, A.; Girón, M.E.; Pérez, J.C.; Sánchez, E.E.; Rodríguez-Acosta, A. Individual venom variability in the South American rattlesnake Crotalus durissus cumanensis. Toxicon 2007, 50, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chippaux, J.P.; Williams, V.; White, J. Snake venom variability: Methods of study, results and interpretation. Toxicon 1991, 29, 1279–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francischetti, I.M.; Gombarovits, M.E.; Valenzuela, J.G.; Carlini, C.R.; Guimarães, J. Intraspecific variation in the venoms of the South American rattlesnake (Crotalus durissus terrificus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2000, 127, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolz-Richter, S.; Esser, K.-H.; Hess, A. Antinociceptive activity of crotoxin in the central nervous system: A functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging study. Toxicon 2013, 74, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmberg, A.B.; Basbaum, I. Partial sciatic nerve injury in the mouse as a model of neuropathic pain: Behavioral and neuroanatomical correlates. Pain 1998, 76, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, C.J.; Mannion, R.J. Neuropathic pain: Aetiology, symptoms, mechanisms, and management. Lancet 1999, 353, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.-W.; Hidajat, K.; Kawi, S. Functionalized SBA-15 materials as carriers for controlled drug delivery: Influence of surface properties on matrix-drug interactions. Langmuir 2005, 21, 9568–9575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, M. Ordered mesoporous materials for bioadsorption and biocatalysis. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 4577–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, A.P.; Favoretto, B.C.; Clissa, P.B.; Sampaio, S.C.; Faquim-Mauro, E.L. Crotoxin isolated from crotalus durissus terrificus venom modulates the functional activity of dendritic cells via formyl peptide receptors. J. Immunol. Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svensson, C.I.; Zattoni, M.; Serhan, C.N. Lipoxins and aspirin-triggered lipoxin inhibit inflammatory pain processing. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaramuzzi, K.; Oliveira, D.C.A.; Carvalho, L.V.; Tambourgi, D.V.; Tenório, E.C.N.; Rizzi, M.; Mussalem, J.; de Abreu Fantini, M.C.; Botosso, V.F.; Sant Anna, O.A. Nanostructured SBA-15 silica as an adjuvant in immunizations with hepatitis B vaccine. Einstein 2011, 9, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippart, M.; Schmidt, J.; Bittner, B. Oral delivery of therapeutic proteins and peptides: An overview of current technologies and recommendations for bridging from approved intravenous or subcutaneous administration to novel oral regimens. Drug Res. 2015, 66, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Kiguchi, N.; Maeda, T.; Ozaki, M.; Kishioka, S. The critical role of spinal ceramide in the development of partial sciatic nerve ligation-induced neuropathic pain in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 421, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, F.; Dong, R.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Xue, Q.; Yu, B.; Xu, J. Intrathecal administration of clonidine attenuates spinal neuroimmune activation in a rat model of neuropathic pain with existing hyperalgesia. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 614, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeber, M.B.; Christie, M.J. Multiple mechanisms of microglia: A gatekeeper’s contribution to pain states. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 234, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, M.K.; Jeon, S.; Suk, K. Glia as a link between neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain. Immune Netw. 2012, 12, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.K.; Old, E.A.; Malcangio, M. Neuropathic pain and cytokines: Current perspectives. J. Pain Res. 2013, 6, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Xia, T.; Xu, F.; Ma, Z.; Gu, X. Identification of the key genes associated with neuropathic pain. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 6371–6378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guptarak, J.; Wanchoo, S.; Durham-Lee, J.; Wu, Y.; Zivadinovic, D.; Paulucci-Holthauzen, A.; Nesic, O. Inhibition of IL-6 signaling: A novel therapeutic approach to treating spinal cord injury pain. Pain 2013, 154, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.H.; Chen, S.P.; Li, M.; Shahveranov, A.; Ye, D.W.; Tian, Y.K. Interleukin-6: An emerging regulator of pathological pain. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, W.; Quirion, R. Up-regulation of interleukin-6 induced by prostaglandin E from invading macrophages following nerve injury: An in vivo and in vitro study. J. Neurochem. 2005, 93, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melemedjian, O.K.; Asiedu, M.N.; Tillu, D.V.; Peebles, K.A.; Yan, J.; Ertz, N.; Dussor, G.O.; Price, T.J. IL-6- and NGF-induced rapid control of protein synthesis and nociceptive plasticity via convergent signaling to the eIF4F complex. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 15113–15123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melemedjian, O.K.; Tillu, D.V.; Moy, J.K.; Asiedu, M.N.; Mandell, E.K.; Ghosh, S.; Dussor, G.; Price, T.J. Local translation and retrograde axonal transport of CREB regulates IL-6-induced nociceptive plasticity. Mol. Pain 2014, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebisawa, S.; Andoh, T.; Shimada, Y.; Kuraishi, Y. Yokukansan improves mechanical allodynia through the regulation of interleukin-6 expression in the spinal cord in mice with neuropathic pain. Evid. Based. Complement. Alternat. Med. 2015, 2015, 870687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohtori, S.; Miyagi, M.; Eguchi, Y.; Inoue, G.; Orita, S.; Ochiai, N.; Kishida, S.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Nakamura, J.; Aoki, Y.; et al. Efficacy of epidural administration of anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody onto spinal nerve for treatment of sciatica. Eur. Spine J. 2012, 21, 2079–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milligan, E.D.; Soderquist, R.G.; Malone, S.M.; Mahoney, J.H.; Hughes, T.S.; Langer, S.J.; Sloane, E.M.; Maier, S.F.; Leinwand, L.A.; Watkins, L.R.; et al. Intrathecal polymer-based interleukin-10 gene delivery for neuropathic pain. Neuron Glia Biol. 2006, 2, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ledeboer, A.; Jekich, B.M.; Sloane, E.M.; Mahoney, J.H.; Langer, S.J.; Milligan, E.D.; Martin, D.; Maier, S.F.; Johnson, K.W.; Leinwand, L.A.; et al. Intrathecal interleukin-10 gene therapy attenuates paclitaxel-induced mechanical allodynia and proinflammatory cytokine expression in dorsal root ganglia in rats. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2007, 21, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, D.; Hu, X.; Zhang, H.; Lu, C.; Cui, G.; Luo, X. Orientin and neuropathic pain in rats with spinal nerve ligation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 58, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, C.D.S.; Andrade-Oliveira, V.; Câmara, N.O.S.; Jacysyn, J.F.; Faquim-Mauro, E.L. Crotoxin from Crotalus durissus terrificus is able to down-modulate the acute intestinal inflammation in mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gennari, M.; Bouthillier, Y.; Ibanez, O.M.; Ferreira, V.C.; Mevel, J.C.; Reis, M.H.; Piatti, R.M.; Ribeiro, O.G.; Biozzi, G. Effect of silica on the genetic regulation of antibody responsiveness. Ann. Inst. Pasteur. Immunol. 1987, 138, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, W.H.; Ibanez, O.M.; Oliveira, S.L.; Sant’Anna, O.A.; Siqueira, M.; Mouton, D.; Biozzi, G. Evidence for distinct polygenic regulation of antibody responses to some unrelated antigens in lines of mice selected for high or low antibody responses to somatic antigen of Salmonella. Immunogenetics 1982, 16, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M. Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain 1983, 16, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, G.; Bon, C. Several isoforms of crotoxin are present in individual venoms from the South American rattlesnake Crotalus durissus terrificus. Toxicon 1987, 25, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, J.R.; Mercuri, L.P.; Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M. Toward the synthesis of extra-large-pore MCM-41 analogues. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 1726–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, M.; Viskatis, L.J.; de la Roza, G.; Vidal, J.C. Induction of tolerance to crotoxin in mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1993, 265, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Finney, D.J.; Tattersfield, F. Probit Analysis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Mouton, D.; Siqueira, M.; Sant’Anna, O.A.; Bouthiuier, Y.; Ibanez, O.; Ferreira, V.C.A.; Mevel, J.-C.; Reis, M.H.; Piatti, R.M.; Stiffel, C.; et al. Genetic regulation of multispecific antibody responsiveness: Improvement of “high” and “low” characters. Eur. J. Immunol. 1988, 18, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, V.; Gennari, M.; Reis, M.H.; Siqueira, M.; Stiffel, C.; Mouton, D.; Biozzi, G. Potentialities of immunocompetent cells in high and low antibody-producing lines of mice obtained by selective breedings for responsiveness to flagellar or somatic antigens of Salmonellae. J. Immunogenet. 1985, 12, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Decosterd, I.; Woolf, C.J. Spared nerve injury: An animal model of persistent peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain 2000, 87, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hains, L.E.; Loram, L.C.; Weiseler, J.L.; Frank, M.G.; Bloss, E.B.; Sholar, P.; Taylor, F.R.; Harrison, J.A.; Martin, T.J.; Eisenach, J.C.; et al. Pain intensity and duration can be enhanced by prior challenge: Initial evidence suggestive of a role of microglial priming. J. Pain 2010, 11, 1004–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simonian, M.H.; Smith, J.A. Spectrophotometric and colorimetric determination of protein concentration. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2006, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravia, P.; Rojas, E.; Arce, V.; Guevara, C.; López, J.C.; Chaves, E.; Velásquez, R.; Rojas, G.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Geographic and ontogenic variability in the venom of the neotropical rattlesnake Crotalus durissus: Pathophysiological and therapeutic implications. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2002, 50, 337–346. [Google Scholar]



| Titration of Antibodies | ||
|---|---|---|
| Groups | 15 days after first dose | 20 days after second dose |
| Naive | 256 | 256 |
| SBA-15 | 256 | 128 |
| CTX | 256 | 1024 |
| CTX:SBA-15 | 256 | 4096 |
| CTX:Al(OH)3 | 256 | 32,768 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sant’Anna, M.B.; Lopes, F.S.R.; Kimura, L.F.; Giardini, A.C.; Sant’Anna, O.A.; Picolo, G. Crotoxin Conjugated to SBA-15 Nanostructured Mesoporous Silica Induces Long-Last Analgesic Effect in the Neuropathic Pain Model in Mice. Toxins 2019, 11, 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120679
Sant’Anna MB, Lopes FSR, Kimura LF, Giardini AC, Sant’Anna OA, Picolo G. Crotoxin Conjugated to SBA-15 Nanostructured Mesoporous Silica Induces Long-Last Analgesic Effect in the Neuropathic Pain Model in Mice. Toxins. 2019; 11(12):679. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120679
Chicago/Turabian StyleSant’Anna, Morena Brazil, Flavia Souza Ribeiro Lopes, Louise Faggionato Kimura, Aline Carolina Giardini, Osvaldo Augusto Sant’Anna, and Gisele Picolo. 2019. "Crotoxin Conjugated to SBA-15 Nanostructured Mesoporous Silica Induces Long-Last Analgesic Effect in the Neuropathic Pain Model in Mice" Toxins 11, no. 12: 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120679
APA StyleSant’Anna, M. B., Lopes, F. S. R., Kimura, L. F., Giardini, A. C., Sant’Anna, O. A., & Picolo, G. (2019). Crotoxin Conjugated to SBA-15 Nanostructured Mesoporous Silica Induces Long-Last Analgesic Effect in the Neuropathic Pain Model in Mice. Toxins, 11(12), 679. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120679





