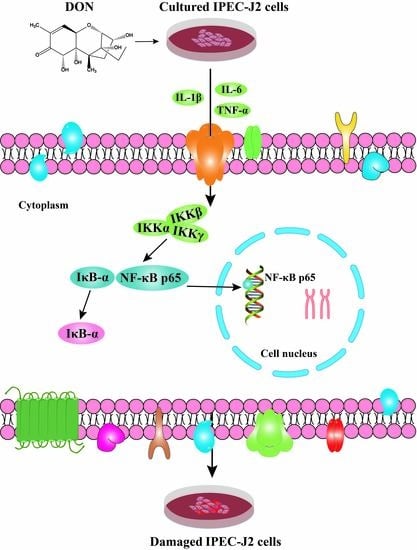
Deoxynivalenol Induces Inflammatory Injury in IPEC-J2 Cells via NF-κB Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of DON on Cell Viability Rate
2.2. Effects of DON on Morphological Changes in Intestinal Epithelial Cells
2.3. Effect of DON on the Submicroscopic Structure of Cells
2.4. Effect of DON on DAO Activity in Cell Culture Supernatant
2.5. Effect of DON on the Activity of Inflammatory Factors in Cells
2.6. DON Effect on the mRNA Expression of Inflammation-Related Genes in Cells
2.7. Effect of DON on the Expression of NF-κB p65 Protein in the Nucleus
2.8. Effect of DON on the Expression and Distribution of NF-κB p65 Protein in Cells
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Chemical and Reagents
5.2. Cell Culture and Treatments
5.3. IPEC-J2 Cell Morphology by Optical Microscope
5.4. IPEC-J2 Cell Morphology by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
5.5. Detection of Cell Viability
5.6. Detection of Inflammatory Mediators and Intestinal Permeability Indicators
5.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
5.8. Immunofluorescence
5.9. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assays (EMSAs)
5.10. Statistics Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berthiller, F.; Crews, C.; Dall’Asta, C.; Saeger, S.D.; Haesaert, G.; Karlovsky, P.; Oswald, I.P.; Seefelder, W.; Speijers, G.; Stroka, J. Masked mycotoxins: A review. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 165–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestka, J. Deoxynivalenol: Toxicity, mechanisms and animal health risks. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2007, 137, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesterházy, Á.; Bartók, T.; Mirocha, C.G.; Komoroczy, R. Nature of wheat resistance to fusarium head blight and the role of deoxynivalenol for breeding. Plant Breed. 2010, 118, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, L.I.; Wang, X.U.; Zhou, T.; Yang, D.; Wang, Q.I.; Zhou, Y.U. Occurrence of four mycotoxins in cereal and oil products in Yangtze Delta region of China and their food safety risks. Food Control 2014, 35, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, R.; Zhang, L.; Liu, M.; Su, Y.T.; Xie, W.M.; Zhang, N.Y.; Dai, J.F.; Wang, Y.; Rajput, S.A.; Qi, D.S. Individual and combined occurrence of mycotoxins in feed ingredients and complete feeds in China. Toxins 2018, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Liao, P.; He, L.; Ren, W.; Yin, J.; Duan, J.; Li, T. Growth performance, serum biochemical profile, jejunal morphology, and the expression of nutrients transporter genes in deoxynivalenol (DON)- challenged growing pigs. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, A.C.; Todd, S.M.; Hansen, J.A.; Kim, Y.B.; De, S.A.L.P.; Middleton, T.F.; Woo, K.S. The use of feed additives to reduce the effects of aflatoxin and deoxynivalenol on pig growth, organ health and immune status during chronic exposure. Toxins 2013, 5, 1261–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Srivastava, S.; Dewangan, J.; Divakar, A.; Rath, S.K. Global occurrence of deoxynivalenol in food commodities and exposure risk assessment in humans in the last decade: A survey. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 14, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Fan, M.; Chu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Rahman, S.U.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, D.; Feng, S.; Li, Y. Deoxynivalenol induces toxicity and apoptosis in piglet hippocampal nerve cells via the MAPK signaling pathway. Toxicon 2018, 155, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manda, G.; Neagu, M.; Constantin, C.; Neagoe, I.; Marin, D.; Taranu, I. Immunotoxicology of mycotoxins produced by fusarium fungi—low concentrations of deoxynivalenol interfere with nucleotide metabolism. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 172, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maresca, M. From the Gut to the Brain: Journey and pathophysiological effects of the Food-Associated trichothecene mycotoxin deoxynivalenol. Toxins 2013, 5, 784–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotter, B.A.; Thompson, B.K.; Lessard, M.; Trenholm, H.L.; Tryphonas, H. Influence of low-level exposure to fusarium mycotoxins on selected immunological and hematological parameters in young swine. fundamental & applied toxicology official. Soc. Toxicol. 1994, 23, 117. [Google Scholar]
- Bouhet, S.; Oswald, I.P. The effects of mycotoxins, fungal food contaminants, on the intestinal epithelial cell-derived innate immune response. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2005, 108, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Wang, S.B.; Wang, R.G.; Zhang, W.; Wang, P.L.; Su, X.O. Phosphoproteome analysis reveals the molecular mechanisms underlying deoxynivalenol-induced intestinal toxicity in IPEC-J2 cells. Toxins 2016, 8, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallès, J.P.; Boudry, G.; Favier, C.; Floc’H, N.L.; Huêrou-Luron, I.L.; Montagne, L.; Oswald, I.P.; Pié, S.; Piel, C.; Sève, B. Gut function and dysfunction in young pigs: Physiology. Physiology 2002, 53, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schierack, P.; Nordhoff, M.; Pollmann, M.; Weyrauch, K.D.; Amasheh, S.; Lodemann, U.; Jores, J.; Tachu, B.; Kleta, S.; Blikslager, A. Characterization of a porcine intestinal epithelial cell line for in vitro studies of microbial pathogenesis in swine. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 125, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diesing, A.K.; Nossol, C.; Panther, P.; Walk, N.; Post, A.; Kluess, J.; Kreutzmann, P.; Dänicke, S.; Rothkötter, H.J.; Kahlert, S. Mycotoxin deoxynivalenol (DON) mediates biphasic cellular response in intestinal porcine epithelial cell lines IPEC-1 and IPEC-J2. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 200, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, R.; Takeda, K. Roles of intestinal epithelial cells in the maintenance of gut homeostasis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, I. Mucosal immune system: The second way of the host defense. Nihon Rinsho 2007, 65 Pt 1 (Suppl. 2), 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Welsh, D.A.; Mason, C.M. Host defense in respiratory infections. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2001, 85, 1329–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitman, R.S.; Blumberg, R.S. First line of defense: The role of the intestinal epithelium as an active component of the mucosal immune system. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 35, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosnahan, A.J.; Brown, D.R. Porcine IPEC-J2 intestinal epithelial cells in microbiological investigations. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 156, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.J.; Li, H.P.; Zhu, H.S.; Sui, S.P.; Chen, P.G.; Deng, Y.; Sui, T.M.; Wang, Y.Y. NF-κB is involved in the LPS-mediated proliferation and apoptosis of MAC-T epithelial cells as part of the subacute ruminal acidosis response in cows. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 1839–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Gaynor, R.B. Therapeutic potential of inhibition of the NF-κB pathway in the treatment of inflammation and cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Ge, Y.; Yang, M.U.; Wei, Z.; Jian-Ping, L.I.; An-Shan, S. Effect of ZEN on mRNA expression and activity of inflammation related factors in IPEC-J2 cells. Chin. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 53, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Awad, W.A.; Aschenbach, J.R.; Zentek, J. Cytotoxicity and metabolic stress induced by deoxynivalenol in the porcine intestinal IPEC-J2 cell line. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2012, 96, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, G.M.; Kwang, S.S.; Sung Moo, P.; In Kyu, L.; Cheol-Heui, Y. Bacillus subtilis protects porcine intestinal barrier from deoxynivalenol via improved zonula occludens-1 expression. Asian-Australas. Anim. Sci. 2014, 27, 580–586. [Google Scholar]
- Namikawa, T.; Fukudome, I.; Kitagawa, H.; Okabayashi, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Hanazaki, K. Plasma diamine oxidase activity is a useful biomarker for evaluating gastrointestinal tract toxicities during chemotherapy with oral fluorouracil anti-cancer drugs in patients with gastric cancer. Oncology 2012, 82, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Zhang, Y.F.; Cao, L.; Zhu, L.; Huang, Y.Y.; Chen, X.F.; Chu, X.Y.; Zhu, D.F.; Sajid, U.R.; Feng, S.B.; et al. Deoxynivalenol induces intestinal damage and inflammatory response through the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway in piglets. Toxins 2019, 11, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbroucke, V.; Croubels, S.; An, M.; Verbrugghe, E.; Goossens, J.; Deun, K.V.; Boyen, F.; Thompson, A.; Shearer, N.; Backer, P.D. The mycotoxin deoxynivalenol potentiates intestinal inflammation by salmonella typhimurium in porcine ileal loops. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, W.; Ghareeb, K.; Böhm, J.; Zentek, J. The toxicological impacts of the fusarium mycotoxin, deoxynivalenol, in poultry flocks with special reference to immunotoxicity. Toxins 2013, 5, 912–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giridharan, S.; Srinivasan, M. Mechanisms of NF-κB p65 and strategies for therapeutic manipulation. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van De Walle, J.; Romier, B.; Larondelle, Y.; Schneider, Y.J. Influence of deoxynivalenol on NF-κB activation and IL-8 secretion in human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 177, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benitash, S.A.; Valeròn, P.F.; Lacal, J.C. ROCK and nuclear factor-kappa B-dependent activation of cyclooxygenase-2 by Rho GTPases: Effects on tumor growth and therapeutic cinsequences. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 3041–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.; Li, G.; Cai, M.; Qian, Y.Y.; Wang, L.Q. Prostate cancer downregulated SIRP-alpha modulates apoptosis and proliferation through p38-MAPK/NF-kappa B/COX-2 signaling. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 4995–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adesso, S.; Autore, G.; Quaroni, A.; Popolo, A.; Severino, L.; Marzocco, S. The food contaminants nivalenol and deoxynivalenol induce inflammation in intestinal epithelial cells by regulating reactive oxygen species release. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.C.; Xu, W.; Fan, M.X.; Meng, T.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Hu, W.; Gong, J.; Feng, S.; et al. Deoxynivalenol induces apoptosis in PC12 cells via the mitochondrial pathway. Environ. Toxicol. Pharm. 2016, 43, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, D.; Wu, Q.H.; Qu, W.; Liu, G.; Wang, X. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC) inhibits DON-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis via the NF-κB/iNOS pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1324173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Genes | Accession Number | Primers | Sequences (5′–3′) | Production Size/bp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-actin | AY_550069.1 | Forward | AGATCAAGATCATCGCGCCT | 170 |
| Reverse | ATGCAACTAACAGTCCGCCT | |||
| IL-1β | NW_018085011.1 | Forward | TCAGCACCTCTCAAGCAGAA | 120 |
| Reverse | GACCCTCTGGGTATGGCTTT | |||
| IL-6 | NC_010451.4 | Forward | CTGCAGTCACAGAACGAGTG | 131 |
| Reverse | GACGGCATCAATCTCAGGTG | |||
| NF-κB p65 | NM_001114281.1 | Forward | GGGGCGATGAGATCTTCCTG | 110 |
| Reverse | CACGTCGGCTTGTGAAAAGG | |||
| IκB-α | NC_010449.5 | Forward | GGAGTACGAGCAGATGGTGA | 157 |
| Reverse | TTCCATGGTCAGTGCCTTCT | |||
| iNOS | NC_010454.4 | Forward | GGGTCAGAGCTACCATCCTC | 114 |
| Reverse | CGTCCATGCAGAGAACCTTG | |||
| IKKα | NC_010456.5 | Forward | CACTCTTACAGCGACAGCAC | 145 |
| Reverse | CCACCTTGGGCAGTAGATCA | |||
| IKKβ | NT_176339.1 | Forward | ACCTGGCTCCCAACGACTT | 184 |
| Reverse | AGATCCCGATGGATGATTCTG | |||
| COX-2 | NC_010451.4 | Forward | TGCGGGAACATAATAGAG | 90 |
| Reverse | GTATCAGCCTGCTCGTCT |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Cao, L.; Zhu, L.; Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Rahman, S.U.; Feng, S.; Li, Y.; et al. Deoxynivalenol Induces Inflammatory Injury in IPEC-J2 Cells via NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Toxins 2019, 11, 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120733
Wang X, Zhang Y, Zhao J, Cao L, Zhu L, Huang Y, Chen X, Rahman SU, Feng S, Li Y, et al. Deoxynivalenol Induces Inflammatory Injury in IPEC-J2 Cells via NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Toxins. 2019; 11(12):733. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120733
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xichun, Yafei Zhang, Jie Zhao, Li Cao, Lei Zhu, Yingying Huang, Xiaofang Chen, Sajid Ur Rahman, Shibin Feng, Yu Li, and et al. 2019. "Deoxynivalenol Induces Inflammatory Injury in IPEC-J2 Cells via NF-κB Signaling Pathway" Toxins 11, no. 12: 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120733
APA StyleWang, X., Zhang, Y., Zhao, J., Cao, L., Zhu, L., Huang, Y., Chen, X., Rahman, S. U., Feng, S., Li, Y., & Wu, J. (2019). Deoxynivalenol Induces Inflammatory Injury in IPEC-J2 Cells via NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Toxins, 11(12), 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120733