FGF23, Biomarker or Target?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
3. FGF23 Origin and Structure
4. Mechanisms of Action of FGF23
5. Regulation of FGF23 Production
5.1. Vitamin D
5.2. Phosphate
5.3. Calcium and PTH
5.4. Inflammation and Iron Deficiency
5.5. Erythropoietin
5.6. Others
5.6.1. Adiponectin
5.6.2. Insulin
5.6.3. Aldosterone
5.6.4. Regulation of FGF23 Production by Bone Cell Factors
6. Effect on Different Organs
6.1. The Heart
6.2. Liver
6.3. Immune System
6.4. Skeleton
6.5. Bone Marrow and Anemia
6.6. Other Organs
7. Clinical Impact of FGF23
8. Targeting FGF23
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gorostidi, M.; Santamaria, R.; Alcazar, R.; Fernandez-Fresnedo, G.; Galceran, J.M.; Goicoechea, M.; Oliveras, A.; Portoles, J.; Rubio, E.; Segura, J.; et al. Spanish Society of Nephrology document on KDIGO guidelines for the assessment and treatment of chronic kidney disease. Nefrologia 2014, 34, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD-MBD Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD). Kidney. Int. Suppl. 2009, 113, S1–S130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.A.; Larsson, A.; Lind, L.; Larsson, T.E. Circulating fibroblast growth factor-23 is associated with vascular dysfunction in the community. Atherosclerosis 2009, 205, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernheim, J.; Benchetrit, S. The potential roles of FGF23 and Klotho in the prognosis of renal and cardiovascular diseases. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 2433–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isakova, T.; Xie, H.; Yang, W.; Xie, D.; Anderson, A.H.; Scialla, J.; Wahl, P.; Gutierrez, O.M.; Steigerwalt, S.; He, J.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and Risks of Mortality and End-Stage Renal Disease in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. JAMA 2011, 305, 2432–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketteler, M.; Block, G.A.; Evenepoel, P.; Fukagawa, M.; Herzog, C.A.; McCann, L.; Moe, S.M.; Shroff, R.; Tonelli, M.A.; Toussaint, N.D.; et al. Executive summary of the 2017 KDIGO Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD) Guideline Update: Whats changed and why it matters. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evenepoel, P.; Rodriguez, M.; Ketteler, M. Laboratory abnormalities in CKD-MBD: Markers, predictors, or mediators of disease? Semin. Nephrol. 2014, 34, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenfeld, A.J.; Levine, B.S.; Rodriguez, M. Pathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphorus, and Magnesium Dysregulation in Chronic Kidney Disease. Semin. Dial. 2015, 28, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.; Lopez, I.; Munoz, J.; Aguilera-Tejero, E.; Almaden, Y. FGF23 and mineral metabolism, implications in CKD-MBD. Nefrologia 2012, 32, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mirza, M.A.; Larsson, A.; Melhus, H.; Lind, L.; Larsson, T.E. Serum intact FGF23 associate with left ventricular mass, hypertrophy and geometry in an elderly population. Atherosclerosis 2009, 207, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, N.R.; Fatoba, S.T.; Oke, J.L.; Hirst, J.A.; O’Callaghan, C.A.; Lasserson, D.S.; Hobbs, F.D.R. Global Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, V.; Vilme, H.; Maciejewski, M.L.; Boulware, L.E. The Economic Burden of Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Renal Disease. Semin. Nephrol. 2016, 36, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, R.M.; Dalboni, M.A.; Coelho, A.C.E.; Moysés, R.M.A. CKD-MBD: From the Pathogenesis to the Identification and Development of Potential Novel Therapeutic Targets. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2018, 16, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, C.A.; Asinger, R.W.; Berger, A.K.; Charytan, D.M.; Díez, J.; Hart, R.G.; Eckardt, K.-U.; Kasiske, B.L.; McCullough, P.A.; Passman, R.S.; et al. Cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease. A clinical update from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 572–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bover, J.; Ureña-Torres, P.; Górriz, J.L.; Lloret, M.J.; da Silva, I.; Ruiz-García, C.; Chang, P.; Rodríguez, M.; Ballarín, J. Cardiovascular calcifications in chronic kidney disease: Potential therapeutic implications. Nefrologia 2016, 36, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, C.; Krane, V.; März, W.; Olschewski, M.; Mann, J.F.E.; Ruf, G.; Ritz, E.; German Diabetes and Dialysis Study Investigators. Atorvastatin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus undergoing hemodialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isakova, T.; Ix, J.H.; Sprague, S.M.; Raphael, K.L.; Fried, L.; Gassman, J.J.; Raj, D.; Cheung, A.K.; Kusek, J.W.; Flessner, M.F.; et al. Rationale and Approaches to Phosphate and Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 Reduction in CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2328–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chonchol, M.; Greene, T.; Zhang, Y.; Hoofnagle, A.N.; Cheung, A.K. Low Vitamin D and High Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 Serum Levels Associate with Infectious and Cardiac Deaths in the HEMO Study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, G.A.; Klassen, P.S.; Lazarus, J.M.; Ofsthun, N.; Lowrie, E.G.; Chertow, G.M. Mineral metabolism, mortality, and morbidity in maintenance hemodialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 2208–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marthi, A.; Donovan, K.; Haynes, R.; Wheeler, D.C.; Baigent, C.; Rooney, C.M.; Landray, M.J.; Moe, S.M.; Yang, J.; Holland, L.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 and Risks of Cardiovascular and Noncardiovascular Diseases: A Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 2015–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodelo-Haad, C.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, M.E.; Martin-Malo, A.; Pendon-Ruiz de Mier, M.V.; Agüera, M.L.; Muñoz-Castañeda, J.R.; Soriano, S.; Caravaca, F.; Alvarez-Lara, M.A.; Felsenfeld, A.; et al. Phosphate control in reducing FGF23 levels in hemodialysis patients. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallas, S.L.; Prideaux, M.; Bonewald, L.F. The osteocyte: An endocrine cell… and more. Endocr. Rev. 2013, 34, 658–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.C.; Shiizaki, K.; Kuro-o, M.; Moe, O.W. Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and Klotho: Physiology and Pathophysiology of an Endocrine Network of Mineral Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 503–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, N.; Wijenayaka, A.R.; Prideaux, M.; Kogawa, M.; Ormsby, R.T.; Evdokiou, A.; Bonewald, L.F.; Findlay, D.M.; Atkins, G.J. Regulation of FGF23 expression in IDG-SW3 osteocytes and human bone by pro-inflammatory stimuli. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 399, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mace, M.L.; Gravesen, E.; Hofman-Bang, J.; Olgaard, K.; Lewin, E. Key role of the kidney in the regulation of fibroblast growth factor 23. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuro-O, M.; Kuro, O.M. A phosphate-centric paradigm for pathophysiology and therapy of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2013, 3, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hruska, K.A.; Seifert, M.; Sugatani, T.; Canalejo, R.; Canalejo, A.; Martinez-Moreno, J.M.; Rodriguez-Ortiz, M.E.; Estepa, J.C.; Mendoza, F.J.; Munoz-Castaneda, J.R.; et al. Forging forward with 10 burning questions on FGF23 in kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar]
- Imanishi, Y.; Inaba, M.; Nakatsuka, K.; Nagasue, K.; Okuno, S.; Yoshihara, A.; Miura, M.; Miyauchi, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Miki, T.; et al. FGF-23 in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1943–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, J.; Rodriguez, M.; Slatopolsky, E. FGF23 and PTH—Double agents at the heart of CKD. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vervloet, M. Renal and extrarenal effects of fibroblast growth factor 23. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, C.; Amaral, A.P.; Oskouei, B.; Hu, M.C.; Sloan, A.; Isakova, T.; Gutierrez, O.M.; Aguillon-Prada, R.; Lincoln, J.; Hare, J.M.; et al. FGF23 induces left ventricular hypertrophy. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4393–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murali, S.K.; Roschger, P.; Zeitz, U.; Klaushofer, K.; Andrukhova, O.; Erben, R.G. FGF23 Regulates Bone Mineralization in a 1,25(OH)2D3 and Klotho-Independent Manner. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2016, 31, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portillo, M.R.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, M.E. Secondary Hyperparthyroidism: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, Preventive and Therapeutic Strategies. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2017, 18, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, M.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, M.E. Advances in pharmacotherapy for secondary hyperparathyroidism. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2015, 16, 1703–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenfeld, A.; Rodriguez, M.; Levine, B. New insights in regulation of calcium homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2013, 22, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenfeld, A.J.; Levine, B.S.; Kleeman, C.R. Fuller Albright and our current understanding of calcium and phosphorus regulation and primary hyperparathyroidism. Nefrologia 2011, 31, 346–357. [Google Scholar]
- de Francisco, A.L.; Cobo, M.A.; Setien, M.A.; Rodrigo, E.; Fresnedo, G.F.; Unzueta, M.T.; Amado, J.A.; Ruiz, J.C.; Arias, M.; Rodriguez, M. Effect of serum phosphate on parathyroid hormone secretion during hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 1998, 54, 2140–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaden, Y.; Felsenfeld, A.J.; Rodriguez, M.; Cañadillas, S.; Luque, F.; Bas, A.; Bravo, J.; Torregrosa, V.; Palma, A.; Ramos, B.; et al. Proliferation in hyperplastic human and normal rat parathyroid glands: Role of phosphate, calcitriol, and gender. Kidney Int. 2003, 64, 2311–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.; Felsenfeld, A.J.; Llach, F. Calcemic response to parathyroid hormone in renal failure: Role of calcitriol and the effect of parathyroidectomy. Kidney Int. 1991, 40, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuro, O.M. Phosphate and Klotho. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, S20–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujikawa, H.; Kurotaki, Y.; Fujimori, T.; Fukuda, K.; Nabeshima, Y.-I. Klotho, a gene related to a syndrome resembling human premature aging, functions in a negative regulatory circuit of vitamin D endocrine system. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 17, 2393–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isakova, T.; Gutierrez, O.; Shah, A.; Castaldo, L.; Holmes, J.; Lee, H.; Wolf, M. Postprandial mineral metabolism and secondary hyperparathyroidism in early CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, J.; Locatelli, F.; Rodriguez, M. Secondary Hyperparathyroidism: Pathogenesis, Disease Progression, and Therapeutic Options. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, N.; Ohta, H.; Konishi, M. Endocrine FGFs: Evolution, Physiology, Pathophysiology, and Pharmacotherapy. Front. Endocrinol. 2015, 6, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornitz, D.M.; Itoh, N. The Fibroblast Growth Factor signaling pathway. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2015, 4, 215–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.; David, V.; Quarles, L.D. Regulation and function of the FGF23/klotho endocrine pathways. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 131–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, N.; Ornitz, D.M. Evolution of the Fgf and Fgfr gene families. Trends Genet. 2004, 20, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, T.J.; Craig, T.A.; McCormick, D.J.; Lanske, B.; Sitara, D.; Razzaque, M.S.; Pragnell, M.; Bowe, A.E.; O’Brien, S.P.; Schiavi, S.C.; et al. Biological activity of FGF-23 fragments. Pflugers Arch. 2007, 454, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.; Levine, K.; Sergi, J.; Chamoun, J.; Roach, R.; Vekich, J.; Favis, M.; Horn, M.; Cao, X.; Miller, B.; et al. Therapeutic Effects of FGF23 c-tail Fc in a Murine Preclinical Model of X-Linked Hypophosphatemia Via the Selective Modulation of Phosphate Reabsorption. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2017, 32, 2062–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, M.; White, K.E. Coupling fibroblast growth factor 23 production and cleavage: Iron deficiency, rickets, and kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2014, 23, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T.; Hasegawa, H.; Yamazaki, Y.; Muto, T.; Hino, R.; Takeuchi, Y.; Fujita, T.; Nakahara, K.; Fukumoto, S.; Yamashita, T. FGF-23 is a potent regulator of vitamin D metabolism and phosphate homeostasis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2004, 19, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Quarles, L.D. How fibroblast growth factor 23 works. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquillet, G.; Unwin, R.J. Physiological regulation of phosphate by vitamin D, parathyroid hormone (PTH) and phosphate (Pi). Pflugers Arch. 2019, 471, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-A.; Watanabe, M.; Yamada, H.; Nagai, A.; Kinuta, M.; Takei, K. Immunohistochemical localization of Klotho protein in brain, kidney, and reproductive organs of mice. Cell Struct. Funct. 2004, 29, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuro-o, M.; Matsumura, Y.; Aizawa, H.; Kawaguchi, H.; Suga, T.; Utsugi, T.; Ohyama, Y.; Kurabayashi, M.; Kaname, T.; Kume, E.; et al. Mutation of the mouse klotho gene leads to a syndrome resembling ageing. Nature 1997, 390, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Castañeda, J.R.; Herencia, C.; Pendón-Ruiz de Mier, M.V.; Rodriguez-Ortiz, M.E.; Diaz-Tocados, J.M.; Vergara, N.; Martínez-Moreno, J.M.; Salmerón, M.D.; Richards, W.G.; Felsenfeld, A.; et al. Differential regulation of renal Klotho and FGFR1 in normal and uremic rats. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 3858–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.; Faul, C. FGF23 Actions on Target Tissues-With and Without Klotho. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dov, I.Z.; Galitzer, H.; Lavi-Moshayoff, V.; Goetz, R.; Kuro-o, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Sirkis, R.; Naveh-Many, T.; Silver, J. The parathyroid is a target organ for FGF23 in rats. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 4003–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, I.; Rodriguez-Ortiz, M.E.; Almaden, Y.; Guerrero, F.; de Oca, A.M.; Pineda, C.; Shalhoub, V.; Rodriguez, M.; Aguilera-Tejero, E. Direct and indirect effects of parathyroid hormone on circulating levels of fibroblast growth factor 23 in vivo. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canalejo, R.; Canalejo, A.; Martinez-Moreno, J.M.; Rodriguez-Ortiz, M.E.; Estepa, J.C.; Mendoza, F.J.; Munoz-Castaneda, J.R.; Shalhoub, V.; Almaden, Y.; Rodriguez, M. FGF23 fails to inhibit uremic parathyroid glands. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, S.; Kazama, J.J.; Nii-Kono, T.; Omori, K.; Yamashita, T.; Fukumoto, S.; Gejyo, F.; Shigematsu, T.; Fukagawa, M. Serum fibroblast growth factor-23 levels predict the future refractory hyperparathyroidism in dialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, N.; Fujimori, T.; Nishiguchi, S.; Tamori, A.; Shiomi, S.; Nakatani, T.; Sugimura, K.; Kishimoto, T.; Kinoshita, S.; Kuroki, T.; et al. Severely reduced production of klotho in human chronic renal failure kidney. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 280, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.C.; Shi, M.; Zhang, J.; Quinones, H.; Griffith, C.; Kuro-o, M.; Moe, O.W. Klotho deficiency causes vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, R.; Ohnishi, M.; Kir, S.; Kurosu, H.; Wang, L.; Pastor, J.; Ma, J.; Gai, W.; Kuro-o, M.; Razzaque, M.S.; et al. Conversion of a paracrine fibroblast growth factor into an endocrine fibroblast growth factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 29134–29146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Liu, Y.; Goetz, R.; Fu, L.; Jayaraman, S.; Hu, M.-C.; Moe, O.W.; Liang, G.; Li, X.; Mohammadi, M. α-Klotho is a non-enzymatic molecular scaffold for FGF23 hormone signalling. Nature 2018, 553, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuro-O, M. The Klotho proteins in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Yoon, J.; An, S.-W.; Kuro-o, M.; Huang, C.-L. Soluble Klotho Protects against Uremic Cardiomyopathy Independently of Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and Phosphate. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Cha, S.-K.; An, S.-W.; Kuro-o, M.; Birnbaumer, L.; Huang, C.-L. Cardioprotection by Klotho through downregulation of TRPC6 channels in the mouse heart. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.M.; Chirinos, J.A.; Litt, H.; Yang, W.; Rosas, S.E. FGF-23 and the progression of coronary arterial calcification in patients new to dialysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 2017–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saji, F.; Shigematsu, T.; Sakaguchi, T.; Ohya, M.; Orita, H.; Maeda, Y.; Ooura, M.; Mima, T.; Negi, S. Fibroblast growth factor 23 production in bone is directly regulated by 1{alpha},25-dihydroxyvitamin D, but not PTH. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2010, 299, F1212–F1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprague, S.M.; Wetmore, J.B.; Gurevich, K.; Da Roza, G.; Buerkert, J.; Reiner, M.; Goodman, W.; Cooper, K. Effect of Cinacalcet and Vitamin D Analogs on Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 during the Treatment of Secondary Hyperparathyroidism. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen-Yamamoto, L.; Karaplis, A.C.; St-Arnaud, R.; Goltzman, D. Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 Regulation by Systemic and Local Osteoblast-Synthesized 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chande, S.; Bergwitz, C. Role of phosphate sensing in bone and mineral metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 637–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perwad, F.; Azam, N.; Zhang, M.Y.H.; Yamashita, T.; Tenenhouse, H.S.; Portale, A.A. Dietary and serum phosphorus regulate fibroblast growth factor 23 expression and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D metabolism in mice. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 5358–5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.; Felsenfeld, A.J. PTH, FGF-23 and early CKD. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 3391–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano, S.; Ojeda, R.; Rodriguez, M.; Almaden, Y.; Rodriguez, M.; Martin-Malo, A.; Aljama, P. The effect of phosphate binders, calcium and lanthanum carbonate on FGF23 levels in chronic kidney disease patients. Clin. Nephrol. 2013, 80, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavi-Moshayoff, V.; Wasserman, G.; Meir, T.; Silver, J.; Naveh-Many, T. PTH increases FGF23 gene expression and mediates the high-FGF23 levels of experimental kidney failure: A bone parathyroid feedback loop. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2010, 299, F882–F889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meir, T.; Durlacher, K.; Pan, Z.; Amir, G.; Richards, W.G.; Silver, J.; Naveh-Many, T. Parathyroid hormone activates the orphan nuclear receptor Nurr1 to induce FGF23 transcription. Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urena Torres, P.; Friedlander, G.; de Vernejoul, M.C.; Silve, C.; Prie, D. Bone mass does not correlate with the serum fibroblast growth factor 23 in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Ortiz, M.E.; Lopez, I.; Munoz-Castaneda, J.R.; Martinez-Moreno, J.M.; Ramirez, A.P.; Pineda, C.; Canalejo, A.; Jaeger, P.; Aguilera-Tejero, E.; Rodriguez, M.; et al. Calcium Deficiency Reduces Circulating Levels of FGF23. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, T.; Yamazaki, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Urakawa, I.; Oshima, T.; Ono, K.; Kakitani, M.; Tomizuka, K.; Fujita, T.; et al. Vitamin D receptor-independent FGF23 actions in regulating phosphate and vitamin D metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2005, 289, F1088–F1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervloet, M.G.; van Ittersum, F.J.; Büttler, R.M.; Heijboer, A.C.; Blankenstein, M.A.; ter Wee, P.M. Effects of dietary phosphate and calcium intake on fibroblast growth factor-23. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, S.J.; Thomsen, A.R.; Pang, J.L.; Kantham, L.; Brauner-Osborne, H.; Pollak, M.; Goltzman, D.; Brown, E.M. Interactions between calcium and phosphorus in the regulation of the production of fibroblast growth factor 23 in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 304, E310–E320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, S.M.; Chertow, G.M.; Parfrey, P.S.; Kubo, Y.; Block, G.A.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Drueke, T.B.; Herzog, C.A.; London, G.M.; Mahaffey, K.W.; et al. Cinacalcet, Fibroblast Growth Factor-23, and Cardiovascular Disease in Hemodialysis: The Evaluation of Cinacalcet HCl Therapy to Lower Cardiovascular Events (EVOLVE) Trial. Circulation 2015, 132, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Grabner, A.; Yanucil, C.; Schramm, K.; Czaya, B.; Krick, S.; Czaja, M.J.; Bartz, R.; Abraham, R.; Di Marco, G.S.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 directly targets hepatocytes to promote inflammation in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 985–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz Mendoza, J.; Isakova, T.; Cai, X.; Bayes, L.Y.; Faul, C.; Scialla, J.J.; Lash, J.P.; Chen, J.; He, J.; Navaneethan, S.; et al. Inflammation and elevated levels of fibroblast growth factor 23 are independent risk factors for death in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, J.; Herrlinger, S.; Pruy, A.; Metzger, T.; Wanner, C. Inflammation enhances cardiovascular risk and mortality in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 1999, 55, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, O.M.; Mannstadt, M.; Isakova, T.; Rauh-Hain, J.A.; Tamez, H.; Shah, A.; Smith, K.; Lee, H.; Thadhani, R.; Juppner, H.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 and mortality among patients undergoing hemodialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, V.; Martin, A.; Isakova, T.; Spaulding, C.; Qi, L.; Ramirez, V.; Zumbrennen-Bullough, K.B.; Sun, C.C.; Lin, H.Y.; Babitt, J.L.; et al. Inflammation and functional iron deficiency regulate fibroblast growth factor 23 production. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.; Koch, T.A.; Bregman, D.B. Effects of iron deficiency anemia and its treatment on fibroblast growth factor 23 and phosphate homeostasis in women. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2013, 28, 1793–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz Mendoza, J.; Isakova, T.; Ricardo, A.C.; Xie, H.; Navaneethan, S.D.; Anderson, A.H.; Bazzano, L.A.; Xie, D.; Kretzler, M.; Nessel, L.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 and Inflammation in CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agoro, R.; Montagna, A.; Goetz, R.; Aligbe, O.; Singh, G.; Coe, L.M.; Mohammadi, M.; Rivella, S.; Sitara, D. Inhibition of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) signaling rescues renal anemia. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 3752–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabadi, S.; Udo, I.; Leaf, D.E.; Waikar, S.S.; Christov, M. Acute blood loss stimulates fibroblast growth factor 23 production. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2018, 314, F132–F139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toro, L.; Barrientos, V.; León, P.; Rojas, M.; Gonzalez, M.; González-Ibáñez, A.; Illanes, S.; Sugikawa, K.; Abarzúa, N.; Bascuñán, C.; et al. Erythropoietin induces bone marrow and plasma fibroblast growth factor 23 during acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanudel, M.R.; Eisenga, M.F.; Rappaport, M.; Chua, K.; Qiao, B.; Jung, G.; Gabayan, V.; Gales, B.; Ramos, G.; de Jong, M.A.; et al. Effects of erythropoietin on fibroblast growth factor 23 in mice and humans. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, gfy189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, J.M.; Wang, Z.V.; Park, A.S.D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Hu, M.C.; Moe, O.W.; Susztak, K.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin promotes functional recovery after podocyte ablation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cammisotto, P.G.; Londono, I.; Gingras, D.; Bendayan, M. Control of glycogen synthase through ADIPOR1-AMPK pathway in renal distal tubules of normal and diabetic rats. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2008, 294, F881–F889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajimura, D.; Lee, H.W.; Riley, K.J.; Arteaga-Solis, E.; Ferron, M.; Zhou, B.; Clarke, C.J.; Hannun, Y.A.; DePinho, R.A.; Guo, X.E.; et al. Adiponectin regulates bone mass via opposite central and peripheral mechanisms through FoxO1. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 901–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkowski, J.M.; Pastor, J.; Sun, K.; Park, S.K.; Bobulescu, I.A.; Chen, C.T.; Moe, O.W.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin alters renal calcium and phosphate excretion through regulation of klotho expression. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Garcia, R.; Garcia-Martín, A.; García-Fontana, B.; Morales-Santana, S.; Rozas-Moreno, P.; Muñoz-Torres, M. FGF23 in type 2 diabetic patients: Relationship with bone metabolism and vascular disease. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, e89–e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanks, L.J.; Casazza, K.; Judd, S.E.; Jenny, N.S.; Gutiérrez, O.M. Associations of Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 with Markers of Inflammation, Insulin Resistance and Obesity in Adults. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bär, L.; Feger, M.; Fajol, A.; Klotz, L.-O.; Zeng, S.; Lang, F.; Hocher, B.; Föller, M. Insulin suppresses the production of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5804–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrukhova, O.; Slavic, S.; Smorodchenko, A.; Zeitz, U.; Shalhoub, V.; Lanske, B.; Pohl, E.E.; Erben, R.G. FGF23 regulates renal sodium handling and blood pressure. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 744–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Umbach, A.T.; Chen, H.; Yan, J.; Fakhri, H.; Fajol, A.; Salker, M.S.; Spichtig, D.; Daryadel, A.; Wagner, C.A.; et al. Up-regulation of FGF23 release by aldosterone. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 470, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humalda, J.K.; Riphagen, I.J.; Assa, S.; Hummel, Y.M.; Westerhuis, R.; Vervloet, M.G.; Voors, A.A.; Navis, G.; Franssen, C.F.M.M.; De Borst, M.H.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 correlates with volume status in haemodialysis patients and is not reduced by haemodialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Liu, S.; Spurney, R.F.; Quarles, L.D. Analysis of recombinant Phex: An endopeptidase in search of a substrate. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 281, E837–E847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greaves, S.C.; Gamble, G.D.; Collins, J.F.; Whalley, G.A.; Sharpe, D.N. Determinants of left ventricular hypertrophy and systolic dysfunction in chronic renal failure. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1994, 24, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, C. FGF23 effects on the heart-levels, time, source, and context matter. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabner, A.; Amaral, A.P.; Schramm, K.; Singh, S.; Sloan, A.; Yanucil, C.; Li, J.; Shehadeh, L.A.; Hare, J.M.; David, V.; et al. Activation of Cardiac Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 4 Causes Left Ventricular Hypertrophy. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.C.; Shi, M.; Cho, H.J.; Adams-Huet, B.; Paek, J.; Hill, K.; Shelton, J.; Amaral, A.P.; Faul, C.; Taniguchi, M.; et al. Klotho and phosphate are modulators of pathologic uremic cardiac remodeling. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1290–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaría, R.; Díaz-Tocados, J.M.; Pendón-Ruiz de Mier, M.V.; Robles, A.; Salmerón-Rodríguez, M.D.; Ruiz, E.; Vergara, N.; Aguilera-Tejero, E.; Raya, A.; Ortega, R.; et al. Increased Phosphaturia Accelerates the Decline in Renal Function: A Search for Mechanisms. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leifheit-Nestler, M.; Grosse Siemer, R.; Flasbart, K.; Richter, B.; Kirchhoff, F.; Ziegler, W.H.; Klintschar, M.; Becker, J.U.; Erbersdobler, A.; Aufricht, C.; et al. Induction of cardiac FGF23/FGFR4 expression is associated with left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 1088–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuburg, S.; Dussold, C.; Gerber, C.; Wang, X.; Francis, C.; Qi, L.; David, V.; Wolf, M.; Martin, A. Genetic background influences cardiac phenotype in murine chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, H.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Lin, H.; Chen, Z.; Xie, J.; Xuan, W.; Liao, W.; Bin, J.; Huang, X.; et al. FGF23 promotes myocardial fibrosis in mice through activation of β-catenin. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 64649–64664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavic, S.; Ford, K.; Modert, M.; Becirovic, A.; Handschuh, S.; Baierl, A.; Katica, N.; Zeitz, U.; Erben, R.G.; Andrukhova, O. Genetic Ablation of Fgf23 or Klotho Does not Modulate Experimental Heart Hypertrophy Induced by Pressure Overload. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leifheit-Nestler, M.; Kirchhoff, F.; Nespor, J.; Richter, B.; Soetje, B.; Klintschar, M.; Heineke, J.; Haffner, D. Fibroblast growth factor 23 is induced by an activated renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in cardiac myocytes and promotes the pro-fibrotic crosstalk between cardiac myocytes and fibroblasts. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 1722–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touchberry, C.D.; Green, T.M.; Tchikrizov, V.; Mannix, J.E.; Mao, T.F.; Carney, B.W.; Girgis, M.; Vincent, R.J.; Wetmore, L.A.; Dawn, B.; et al. FGF23 is a novel regulator of intracellular calcium and cardiac contractility in addition to cardiac hypertrophy. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 304, E863–E873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leifheit-Nestler, M.; Haffner, D. Paracrine Effects of FGF23 on the Heart. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fon Tacer, K.; Bookout, A.L.; Ding, X.; Kurosu, H.; John, G.B.; Wang, L.; Goetz, R.; Mohammadi, M.; Kuro-o, M.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; et al. Research resource: Comprehensive expression atlas of the fibroblast growth factor system in adult mouse. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 2050–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Li, L.; Yang, J.; King, G.; Xiao, Z.; Quarles, L.D. Counter-regulatory paracrine actions of FGF-23 and 1,25(OH)2 D in macrophages. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Shen, Y.; Ma, X.; Ying, L.; Peng, J.; Pan, X.; Bao, Y.; Zhou, J. The association of serum FGF23 and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is independent of vitamin D in type 2 diabetes patients. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2018, 45, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenvinkel, P. Interactions between inflammation, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction in end-stage renal disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2003, 13, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M. Update on fibroblast growth factor 23 in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabner, A.; Schramm, K.; Silswal, N.; Hendrix, M.; Yanucil, C.; Czaya, B.; Singh, S.; Wolf, M.; Hermann, S.; Stypmann, J.; et al. FGF23/FGFR4-mediated left ventricular hypertrophy is reversible. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossaint, J.; Oehmichen, J.; Van Aken, H.; Reuter, S.; Pavenstädt, H.J.; Meersch, M.; Unruh, M.; Zarbock, A. FGF23 signaling impairs neutrophil recruitment and host defense during CKD. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 962–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossaint, J.; Spelten, O.; Kässens, N.; Mueller, H.; Van Aken, H.K.; Singbartl, K.; Zarbock, A. Acute loss of renal function attenuates slow leukocyte rolling and transmigration by interfering with intracellular signaling. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalhoub, V.; Ward, S.C.; Sun, B.; Stevens, J.; Renshaw, L.; Hawkins, N.; Richards, W.G. Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) and alpha-klotho stimulate osteoblastic MC3T3.E1 cell proliferation and inhibit mineralization. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2011, 89, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komaba, H.; Kaludjerovic, J.; Hu, D.Z.; Nagano, K.; Amano, K.; Ide, N.; Sato, T.; Densmore, M.J.; Hanai, J.-I.; Olauson, H.; et al. Klotho expression in osteocytes regulates bone metabolism and controls bone formation. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coe, L.M.; Madathil, S.V.; Casu, C.; Lanske, B.; Rivella, S.; Sitara, D. FGF-23 is a negative regulator of prenatal and postnatal erythropoiesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 9795–9810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalrymple, L.S.; Go, A.S. Epidemiology of acute infections among patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3, 1487–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, L.E.; Khzam, L.B.; Hajjar, F.; Merhi, Y.; Sirois, M.G. Characterization of FGF receptor expression in human neutrophils and their contribution to chemotaxis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 301, C1036–C1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Peretz-Soroka, H.; Wu, J.; Zhu, L.; Cui, X.; Zhang, M.; Rigatto, C.; Liu, Y.; Lin, F. Fibroblast growth factor 23 weakens chemotaxis of human blood neutrophils in microfluidic devices. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacchetta, J.; Sea, J.L.; Chun, R.F.; Lisse, T.S.; Wesseling-Perry, K.; Gales, B.; Adams, J.S.; Salusky, I.B.; Hewison, M. Fibroblast growth factor 23 inhibits extrarenal synthesis of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D in human monocytes. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2013, 28, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.; Cai, X.; Hodakowski, A.; Lee, J.; Leonard, M.; Ricardo, A.; Chen, J.; Hamm, L.; Sondheimer, J.; Dobre, M.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and Anemia in the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort Study. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensel, N.; Schön, A.; Konen, T.; Lübben, V.; Förthmann, B.; Baron, O.; Grothe, C.; Leifheit-Nestler, M.; Claus, P.; Haffner, D. Fibroblast growth factor 23 signaling in hippocampal cells: Impact on neuronal morphology and synaptic density. J. Neurochem. 2016, 137, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Chen, L.; Bai, X.; Karaplis, A.; Miao, D.; Gu, N. Impairment of spatial learning and memory in transgenic mice overexpressing human fibroblast growth factor-23. Brain Res. 2011, 1412, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Mitch, W.E. Mechanisms of muscle wasting in chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aono, Y.; Hasegawa, H.; Yamazaki, Y.; Shimada, T.; Fujita, T.; Yamashita, T.; Fukumoto, S. Anti-FGF-23 neutralizing antibodies ameliorate muscle weakness and decreased spontaneous movement of Hyp mice. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2011, 26, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Caretti, G.; Mitchell, S.; McKeehan, W.L.; Boskey, A.L.; Pachman, L.M.; Sartorelli, V.; Hoffman, E.P. Fgfr4 is required for effective muscle regeneration in vivo. Delineation of a MyoD-Tead2-Fgfr4 transcriptional pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krick, S.; Baumlin, N.; Aller, S.P.; Aguiar, C.; Grabner, A.; Sailland, J.; Mendes, E.; Schmid, A.; Qi, L.; David, N.V.; et al. Klotho Inhibits Interleukin-8 Secretion from Cystic Fibrosis Airway Epithelia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suga, T.; Kurabayashi, M.; Sando, Y.; Ohyama, Y.; Maeno, T.; Maeno, Y.; Aizawa, H.; Matsumura, Y.; Kuwaki, T.; Kuro-O, M.; et al. Disruption of the klotho gene causes pulmonary emphysema in mice. Defect in maintenance of pulmonary integrity during postnatal life. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2000, 22, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buendía, P.; Carracedo, J.; Soriano, S.; Madueño, J.A.; Ortiz, A.; Martín-Malo, A.; Aljama, P.; Ramírez, R. Klotho Prevents NFκB Translocation and Protects Endothelial Cell from Senescence Induced by Uremia. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2015, 70, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, B.; Haller, J.; Haffner, D.; Leifheit-Nestler, M. Klotho modulates FGF23-mediated NO synthesis and oxidative stress in human coronary artery endothelial cells. Pflugers Arch. 2016, 468, 1621–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scialla, J.J.; Lau, W.L.; Reilly, M.P.; Isakova, T.; Yang, H.-Y.; Crouthamel, M.H.; Chavkin, N.W.; Rahman, M.; Wahl, P.; Amaral, A.P.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 is not associated with and does not induce arterial calcification. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Arroyo, E.-M.; Gehring, N.; Krudewig, C.; Costantino, S.; Bettoni, C.; Knöpfel, T.; Sabrautzki, S.; Lorenz-Depiereux, B.; Pastor, J.; Strom, T.M.; et al. The elevation of circulating fibroblast growth factor 23 without kidney disease does not increase cardiovascular disease risk. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baia, L.C.; Heilberg, I.P.; Navis, G.; de Borst, M.H.; NIGRAM Investigators. Phosphate and FGF-23 homeostasis after kidney transplantation. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baia, L.C.; Humalda, J.K.; Vervloet, M.G.; Navis, G.; Bakker, S.J.L.; de Borst, M.H.; NIGRAM Consortium. Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and Cardiovascular Mortality after Kidney Transplantation. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 1968–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestenbaum, B.; Sampson, J.N.; Rudser, K.D.; Patterson, D.J.; Seliger, S.L.; Young, B.; Sherrard, D.J.; Andress, D.L. Serum phosphate levels and mortality risk among people with chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, M.; Sacks, F.; Pfeffer, M.; Gao, Z.; Curhan, G.; Cholesterol and Recurrent Events Trial Investigators. Relation between serum phosphate level and cardiovascular event rate in people with coronary disease. Circulation 2005, 112, 2627–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olauson, H.; Qureshi, A.R.; Miyamoto, T.; Barany, P.; Heimburger, O.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P.; Larsson, T.E. Relation between serum fibroblast growth factor-23 level and mortality in incident dialysis patients: Are gender and cardiovascular disease confounding the relationship? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 3033–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Niizuma, S.; Yoshihara, F.; Horio, T.; Kawano, Y. Coronary calcification in patients with chronic kidney disease and coronary artery disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1892–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, C.B.; Dong, C.; Stark, M.; Silverberg, S.; Rundek, T.; Elkind, M.S.V.; Sacco, R.L.; Mendez, A.; Wolf, M. Plasma FGF23 and the risk of stroke: The Northern Manhattan Study (NOMAS). Neurology 2014, 82, 1700–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuczera, P.; Adamczak, M.; Wiecek, A. Fibroblast Growth Factor-23-A Potential Uremic Toxin. Toxins 2016, 8, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isakova, T.; Cai, X.; Lee, J.; Xie, D.; Wang, X.; Mehta, R.; Allen, N.B.; Scialla, J.J.; Pencina, M.J.; Anderson, A.H.; et al. Longitudinal FGF23 Trajectories and Mortality in Patients with CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Mei, C.; Dai, B.; Xue, C. Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 May Follow Cardiovascular Disease Rather than Causing It in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.-C.; Wu, H.-Y.; Peng, Y.-S.; Hsu, S.-P.; Chiu, Y.-L.; Chen, H.-Y.; Yang, J.-Y.; Ko, M.-J.; Pai, M.-F.; Tu, Y.-K.; et al. Effects of lower versus higher phosphate diets on fibroblast growth factor-23 levels in patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 1977–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.; Block, G.A.; Rosenbaum, D.P.; Yan, A.; Chertow, G.M.; Greasley, P.J. The effects of tenapanor on serum fibroblast growth factor 23 in patients receiving hemodialysis with hyperphosphatemia. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 34, 339–346. [Google Scholar]
- Sprague, S.M.; Ketteler, M.; Rastogi, A.; Walpen, S.; Spinowitz, B.; Rakov, V.; Covic, A.C.; Floege, J. Effects of sucroferric oxyhydroxide and sevelamer carbonate on chronic kidney disease–mineral bone disorder parameters in dialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancela, A.L.; Oliveira, R.B.; Graciolli, F.G.; dos Reis, L.M.; Barreto, F.; Barreto, D.V.; Cuppari, L.; Jorgetti, V.; Carvalho, A.B.; Canziani, M.E.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 in hemodialysis patients: Effects of phosphate binder, calcitriol and calcium concentration in the dialysate. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2011, 117, c74–c82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, T.O.; Whyte, M.P.; Imel, E.A.; Boot, A.M.; Högler, W.; Linglart, A.; Padidela, R.; Van’t Hoff, W.; Mao, M.; Chen, C.-Y.; et al. Burosumab Therapy in Children with X-Linked Hypophosphatemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1987–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalhoub, V.; Shatzen, E.M.; Ward, S.C.; Davis, J.; Stevens, J.; Bi, V.; Renshaw, L.; Hawkins, N.; Wang, W.; Chen, C.; et al. FGF23 neutralization improves chronic kidney disease-associated hyperparathyroidism yet increases mortality. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2543–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
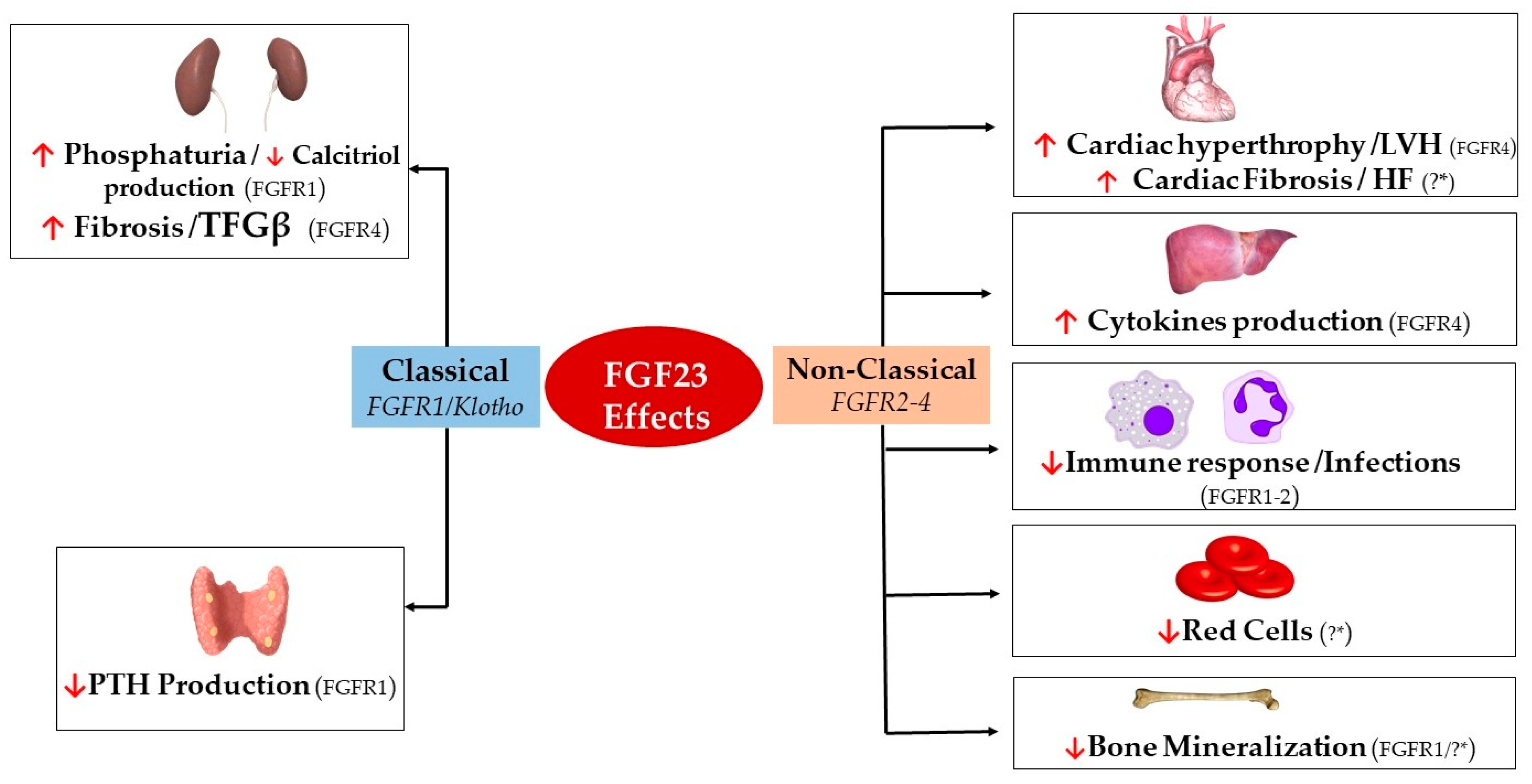
| Effect | Organ Target | Cell Type | FGFR Isoform | Organ Effect | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGF23 | Classical (FGFR1/Klotho) | Kidneys [25,123] | Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells | FGFR1 | ↑ Phosphate Excretion ↓ Calcitriol production |
| Renal Fibroblasts | FGFR4 | ↑ TFGβ/Fibrosis | |||
| Parathyroid Glands [58,59,77] | Parathyroid Chief Cells | FGFR1 | ↓ PTH Excretion | ||
| Non-classical (FGFR2-4) | Heart [31,109,112,114,124] | Cardiac Myocytes | FGFR4 | Hypertrophy/LVH | |
| Cardiac Fibroblasts | ?* | Cardiac Fibrosis/HF | |||
| Liver [85] | Hepatocytes | FGFR4 | ↑ IL-6/CRP Secretion | ||
| Immune System [120,125,126] | Neutrophils | FGFR2 | ↓ β-2 Integrin Activation | ||
| Macrophages | FGFR1 | ↑ TNFα Production | |||
| Skeleton [32,127,128] | Osteocytes/Osteoblasts | FGFR1/?* | ↓ TNAP Transcription | ||
| Bone Marrow [92,129] | Early Erythroid Progenitors/BFU-E Colonies | ?* | ↓ Red Cells |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodelo-Haad, C.; Santamaria, R.; Muñoz-Castañeda, J.R.; Pendón-Ruiz de Mier, M.V.; Martin-Malo, A.; Rodriguez, M. FGF23, Biomarker or Target? Toxins 2019, 11, 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030175
Rodelo-Haad C, Santamaria R, Muñoz-Castañeda JR, Pendón-Ruiz de Mier MV, Martin-Malo A, Rodriguez M. FGF23, Biomarker or Target? Toxins. 2019; 11(3):175. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030175
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodelo-Haad, Cristian, Rafael Santamaria, Juan R. Muñoz-Castañeda, M. Victoria Pendón-Ruiz de Mier, Alejandro Martin-Malo, and Mariano Rodriguez. 2019. "FGF23, Biomarker or Target?" Toxins 11, no. 3: 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030175
APA StyleRodelo-Haad, C., Santamaria, R., Muñoz-Castañeda, J. R., Pendón-Ruiz de Mier, M. V., Martin-Malo, A., & Rodriguez, M. (2019). FGF23, Biomarker or Target? Toxins, 11(3), 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030175






