Discovery of a Potential Human Serum Biomarker for Chronic Seafood Toxin Exposure Using an SPR Biosensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The DA Antibody Biomarker Was Detected in Some Chronic Shellfish Consumers via ELISA
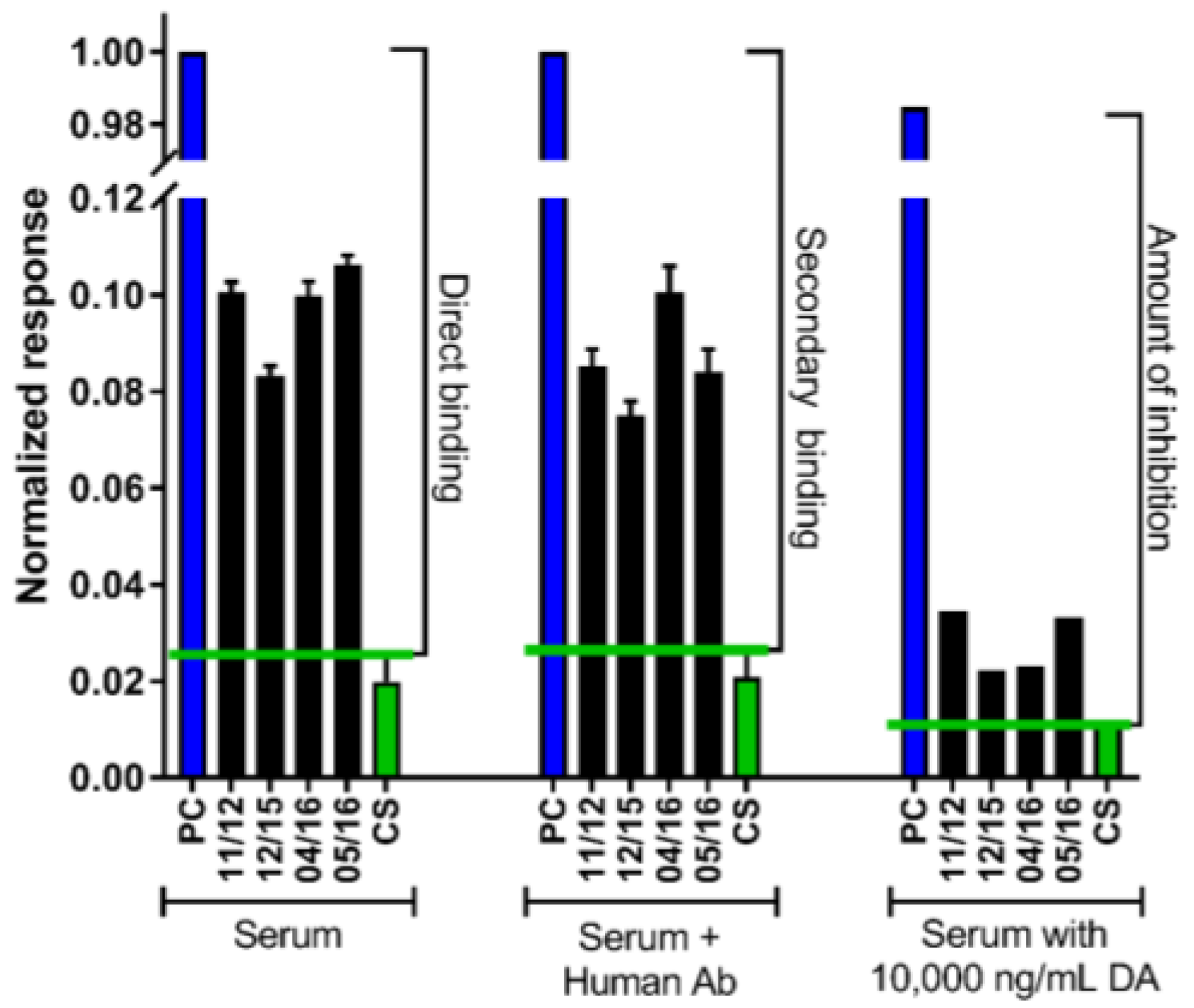
2.2. The DA Antibody Biomarker Was Detected in a Majority of Chronic Shellfish Consumers via an SPR Biosensor
2.3. Recent RC Consumption and Detection of DA in Urine Confirms Systemic Exposure
3. Discussion
3.1. Detection of a DA-Specific Antibody in Serum Indicates Chronic Exposure
3.2. Uses for a Biomarker of Chronic DA Exposure
3.3. Detection of DA in Urine Confirms Systemic Exposure and Recent Consumption
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Quantification of Long-Term RC Consumption and Chronic Exposure
5.2. Blood Collection for Biomarkers of Long-Term Chronic DA Exposure
5.3. Domoic Acid-Specific Antibody Presence via ELISA
5.4. Domoic Acid-Specific Antibody Presence via an SPR Biosensor
5.5. Quantification of Recent RC Consumption and DA Exposure
5.6. Quantification of DA in Urine as an Indicator of Systemic Exposure and Recent Consumption
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trainer, V.L.; Hickey, B.M.; Bates, S.S. Toxic diatoms. In Oceans and Human Health: Risks and Remedies from the Sea; Walsh, P.J., Smith, S.L., Fleming, L.E., Solo-Gabriele, H., Gerwick, W.H., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 219–238. [Google Scholar]
- Scholin, C.A.; Gulland, F.; Doucette, G.J.; Benson, S.; Busman, M.; Chavez, F.P.; Cordaro, J.; DeLong, R.; De Vogelaere, A.; Harvey, J.; et al. Mortality of sea lions along the central california coast linked to a toxic diatom bloom. Nature 2000, 403, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Work, T.M.; Barr, B.; Beale, A.M.; Fritz, L.; Quilliam, M.A.; Wright, J.L.C. Epidemiology of domoic acid poisoning in brown pelicans (Pelicanus occidentalis) and brandt’s cormorants (Phalacrocorax penicillatus) in california. J. Zoo Wild. Med. 1993, 24, 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Perl, T.M.; Bedard, L.; Kosatsky, T.; Hockin, J.C.; Todd, E.C.; Remis, R.S. An outbreak of toxic encephalopathy caused by eating mussels contaminated with domoic acid. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 1775–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Powell, C.L.; Busman, M.; Doucette, C.J.; Moeller, P.D.R.; Sliver, J.B.; Miller, P.E.; Hughes, M.P.; Singaram, S.; Silver, M.W.; et al. Detection of domoic acid in northern anchovies and california sea lions associated with an unusual mortality event. Nat. Toxins 1999, 7, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, E.C.D. Domoic acid and amnesic shellfish poisoning: A review. J. Food Prot. 1993, 56, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, E. Amnesic shellfish poisoning—A new seafood toxin syndrome. In Toxic Marine Phytoplankton; Graneli, E., Sundstrom, B., Edler, L., Anderson, D.M., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 504–508. [Google Scholar]
- Wekell, J.C.; Hurst, J.; Lefebvre, K.A. The origin of the regulatory limits for PSP and ASP toxins in shellfish. J. Shellfish Res. 2004, 23, 927–930. [Google Scholar]
- Marien, K. Establishing tolerable dungeness crab (Cancer magister) and razor clam (Siliqua patula) domoic acid contaminant levels. Environ. Health Perspect. 1996, 104, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Ferriss, B.E.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Ayres, D.; Borchert, J.; Marcinek, D.J. Acute and chronic dietary exposure to domoic acid in recreational harvesters: A survey of shellfish consumption behavior. Environ. Int. 2017, 101, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Kendrick, P.S.; Ladiges, W.C.; Hiolski, E.M.; Ferriss, B.E.; Smith, D.R.; Marcinek, D.J. Chronic low-level exposure to the common seafood toxin domoic acid causes cognitive deficits in mice. Harmful Algae 2017, 64, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiotani, M.; Cole, T.B.; Hong, S.; Park, J.J.Y.; Griffith, W.C.; Burbacher, T.M.; Workman, T.; Costa, L.G.; Faustman, E.M. Neurobehavioral assessment of mice following repeated oral exposures to domoic acid during prenatal development. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2017, 64, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbacher, T.M.; Grant, K.S.; Petroff, R.; Shum, S.; Crouthamel, B.; Stanley, C.; McKain, N.; Jing, J.; Isoherranen, N. Effects of oral domoic acid exposure on maternal reproduction and infant birth characteristics in a preclinical nonhuman primate model. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2018, 72, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroff, R.; Richards, T.; Crouthamel, B.; McKain, N.; Stanley, C.; Grant, K.S.; Burbacher, T.M. Chronic, low-level oral exposure to marine toxin, domoic acid, alters whole brain morphometry in nonhuman primates. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2018, 72, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boushey, C.J.; Delp, E.J.; Ahmad, Z.; Wang, Y.; Roberts, S.M.; Grattan, L.M. Dietary assessment of domoic acid exposure: What can be learned from traditional methods and new applications for a technology assisted device. Harmful Algae 2016, 57, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grattan, L.M.; Boushey, C.; Tracy, K.; Trainer, V.L.; Roberts, S.M.; Schluterman, N.; Morris, J.G., Jr. The association between razor clam consumption and memory in the coastal cohort. Harmful Algae 2016, 57, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattan, L.; Boushey, C.; Liang, Y.; Lefebvre, K.; Castellon, L.; Roberts, K.; Toben, A.; Morris, J. Repeated dietary exposure to low levels of domoic acid and problems with everyday memory: Research to public health outreach. Toxins 2018, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, R.M.; Hickey, B.M.; Kudela, R.M.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Adams, N.G.; Bill, B.D.; Gulland, F.D.M.; Thomson, R.E.; Cochlan, W.P.; Trainer, V.L. An unprecedented coastwide toxic algal bloom linked to anomalous ocean conditions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.K.; Trainer, V.L.; Mantua, N.J.; Parker, M.S.; Laws, E.A.; Backer, L.C.; Fleming, L.E. Impacts of climate variability and future climate change on harmful algal blooms and human health. Environ. Health 2008, 7 (Suppl. 2), S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dolah, F.M. Marine algal toxins: Origins, health effects, and their increased occurrence. Environm. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wekell, J.C.; Gauglitz, E.J., Jr.; Barnett, H.J.; Hatfield, C.L.; Simons, D.; Ayres, D. Occurrence of domoic acid in washington state razor clams (siliqua patula) during 1991–1993. Nat. Toxins 1994, 2, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Frame, E.R.; Gulland, F.; Hansen, J.D.; Kendrick, P.S.; Beyer, R.P.; Bammler, T.K.; Farin, F.M.; Hiolski, E.M.; Smith, D.R.; et al. A novel antibody-based biomarker for chronic algal toxin exposure and sub-acute neurotoxicity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvagni, P.A.; Lowenstine, L.J.; Spraker, T.; Lipscomb, T.P.; Gulland, F. Pathology of domoic acid toxicity in california sea lions (Zalophus californianus). Vet. Pathol. 2005, 42, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scallet, A.C.; Binienda, Z.; Caputo, F.A.; Hall, S.; Paule, M.G.; Rountree, R.L.; Schmued, L.; Sobotka, T.; Slikker, W., Jr. Domoic acid-treated cynomolgus monkeys (M. Fascicularis): Effects of dose on hippocampal neuronal and terminal degeneration. Brain Res. 1993, 627, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strain, S.M.; Tasker, R.A. Hippocampal damage produced by systemic injections of domoic acid in mice. Neuroscience 1991, 44, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, C.E.; Hiolski, E.M.; Marcinek, D.J.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Smith, D.R. Repeated low level domoic acid exposure increases ca1 vglut1 levels, but not bouton density, vglut2 or vgat levels in the hippocampus of adult mice. Harmful Algae. in press. [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, C.A.; Hierlihy, S.L. Renal clearance of domoic acid in the rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1993, 31, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulland, F.M.; Haulena, M.; Fauquier, D.; Langlois, G.; Lander, M.E.; Zabka, T.; Duerr, R. Domoic acid toxicity in californian sea lions (Zalophus californianus): Clinical signs, treatment and survival. Vet. Rec. 2002, 150, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabka, T.S.; Goldstein, T.; Cross, C.; Mueller, R.W.; Kreuder-Johnson, C.; Gill, S.; Gulland, F.M.D. Characterization of a degenerative cardiomyopathy associated with domoic acid toxicity in california sea lions (Zalophus californianus). Vet. Pathol. 2009, 46, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialkowski, M.K.; McCrory, M.A.; Roberts, S.M.; Tracy, J.K.; Grattan, L.M.; Boushey, C.J. Evaluation of dietary assessment tools used to assess the diet of adults participating in the communities advancing the studies of tribal nations across the lifespan cohort. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2010, 110, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, K.; Boushey, C.J.; Roberts, S.M.; Morris, J.G.; Grattan, L.M. Communities advancing the studies of tribal nations across their lifespan: Design, methods, and baseline of the coastal cohort. Harmful Algae 2016, 57, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakes, B.J.; Buijs, C.T.; Elliott, C.T.; Campbell, K. Surface plasmon resonance biosensing: Approaches for screening and characterising antibodies for food diagnostics. Talanta 2016, 156, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Robertson, A.; Frame, E.R.; Colegrove, C.M.; Nance, S.; Baugh, K.A.; Wiedenhoft, A.; Gulland, F.M.D. Clinical signs and histopathology associated with domoic acid poisoning in northern fur seals (Callorhinus ursinus) and comparison of toxin detection methods. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.L.C.; Quilliam, M.A. Methods for domoic acid, the amnesic shellfish poisons. In Manual on Harmful Marine Microalgae; Hallegraeff, G., Anderson, D.M., Cembella, A.D., Eds.; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission Manuals and Guides No. 33; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1995; pp. 113–133. [Google Scholar]
- Shum, S.; Kirkwood, J.S.; Jing, J.; Petroff, R.; Crouthamel, B.; Grant, K.S.; Burbacher, T.M.; Nelson, W.L.; Isoherranen, N. Validated hplc-ms/ms method to quantify low levels of domoic acid in plasma and urine after subacute exposure. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 12079–12088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample ID | Average Monthly Consumption | Antibody Presence (Nov 2012) | Antibody Presence (Dec 2015) | Antibody Presence (April 2016) | Antibody Presence (May 2016) | Years of SASs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | High | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9 |
| 2 | High | Yes | Yes | Yes | ns | 10 |
| 3 | High | Yes | No | **+ | **+ | 6 |
| 4 | High | Yes | No | ns | ns | 10 |
| 5 | High | ns | Yes | Yes | Yes | 2 |
| 6 | High | ns | Yes+ | Yes+ | Yes+ | 1 |
| 7 | High | ns | Yes+ | Yes | ns | 3 |
| 8 | High | ns | No | Yes | No | 2 |
| 9 | High | ns | No | No | No | 9 |
| 10 | High | ns | No | No | ns | 1 |
| 11 | Moderate | Yes | Yes | ns | Yes+ | 8 |
| 12 | Moderate | Yes | Yes | Yes+ | ns | 8 |
| 13 | Moderate | Yes | Yes | No | ns | 10 |
| 14 | Moderate | Yes | No | ns | ns | 6 |
| 15 | Moderate | No | No | No | ns | 7 |
| 16 | Moderate | ns | No | No | No | 1 |
| 17 | Moderate | ns | No | No | No | 1 |
| 18 | Moderate | ns | No | ns | No | 9 |
| 19 | Moderate | ns | No | No | ns | 2 |
| 20 | Moderate | ns | No | No | ns | 10 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lefebvre, K.A.; Yakes, B.J.; Frame, E.; Kendrick, P.; Shum, S.; Isoherranen, N.; Ferriss, B.E.; Robertson, A.; Hendrix, A.; Marcinek, D.J.; et al. Discovery of a Potential Human Serum Biomarker for Chronic Seafood Toxin Exposure Using an SPR Biosensor. Toxins 2019, 11, 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11050293
Lefebvre KA, Yakes BJ, Frame E, Kendrick P, Shum S, Isoherranen N, Ferriss BE, Robertson A, Hendrix A, Marcinek DJ, et al. Discovery of a Potential Human Serum Biomarker for Chronic Seafood Toxin Exposure Using an SPR Biosensor. Toxins. 2019; 11(5):293. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11050293
Chicago/Turabian StyleLefebvre, Kathi A., Betsy Jean Yakes, Elizabeth Frame, Preston Kendrick, Sara Shum, Nina Isoherranen, Bridget E. Ferriss, Alison Robertson, Alicia Hendrix, David J. Marcinek, and et al. 2019. "Discovery of a Potential Human Serum Biomarker for Chronic Seafood Toxin Exposure Using an SPR Biosensor" Toxins 11, no. 5: 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11050293
APA StyleLefebvre, K. A., Yakes, B. J., Frame, E., Kendrick, P., Shum, S., Isoherranen, N., Ferriss, B. E., Robertson, A., Hendrix, A., Marcinek, D. J., & Grattan, L. (2019). Discovery of a Potential Human Serum Biomarker for Chronic Seafood Toxin Exposure Using an SPR Biosensor. Toxins, 11(5), 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11050293








