A Novel αIIbβ3 Antagonist from Snake Venom Prevents Thrombosis without Causing Bleeding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Purification and Characterization of TFV1 and TFV3
2.2. Aggregation Studies of the RGD-Containing Disintegrins, TFV-1 and TFV-3
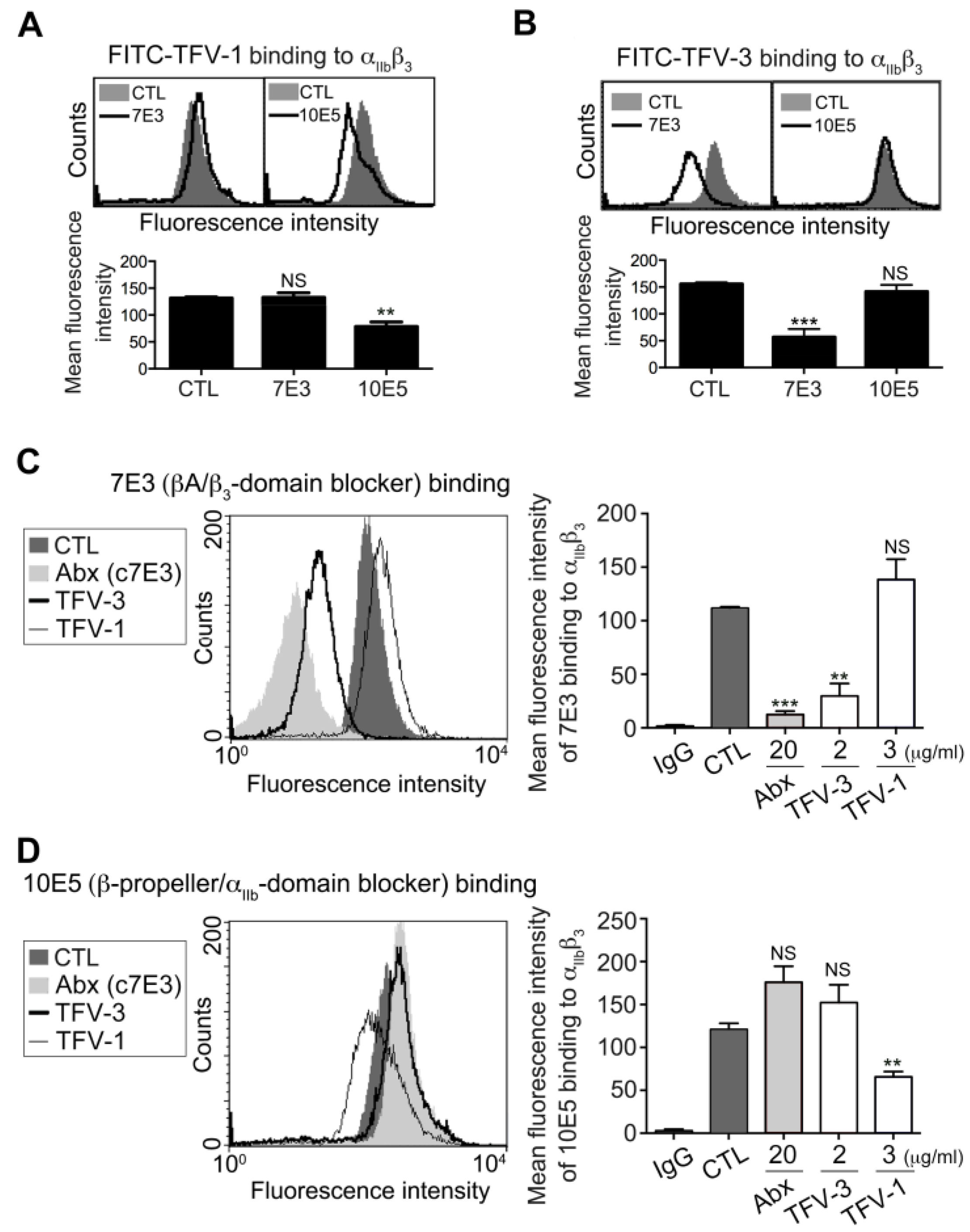
2.3. TFV-1 Binds to an Epitope of Integrin αIIbβ3, Different from Those Bound by TFV-3 and Abciximab
2.4. TFV-1 Binding to Integrin αIIbβ3 Does Not Prime the Resting αIIbβ3 to Bind Ligand
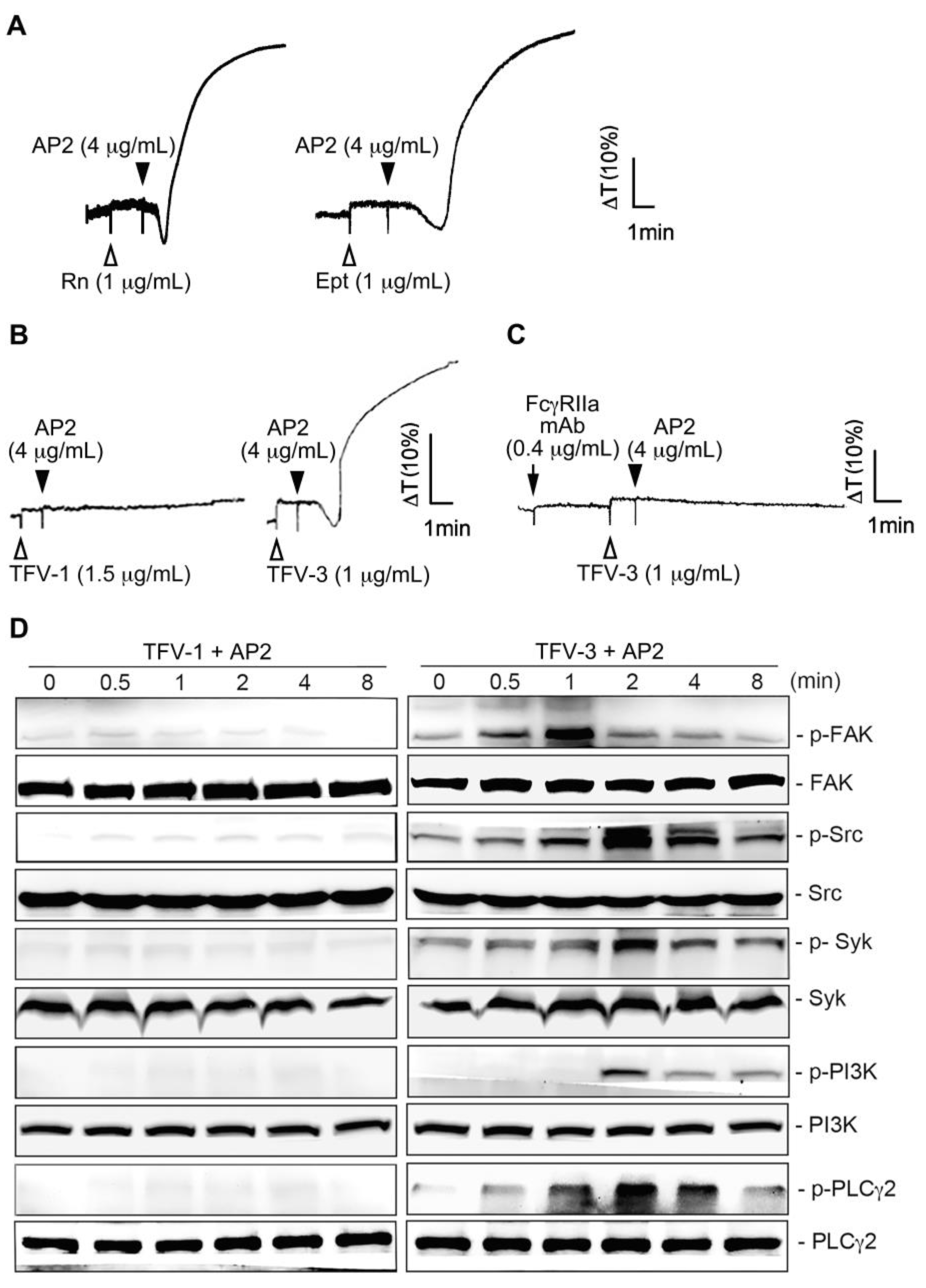
2.5. TFV-1 Does Not Cause a Conformational Change of αIIbβ3 Identified by LIBS Antibody AP5 or mAb AP2
2.6. Combination of TFV-1 with AP2 Does Not Induce FcγRIIa-Mediated Activation of the Downstream ITAM/Syk/PLCγ2 Pathway and Platelet Aggregation
2.7. Combination of TFV-1 with AP2 Does Not Increase Intracellular Ca2+ Mobilization and P-selectin Expression in Human Platelets
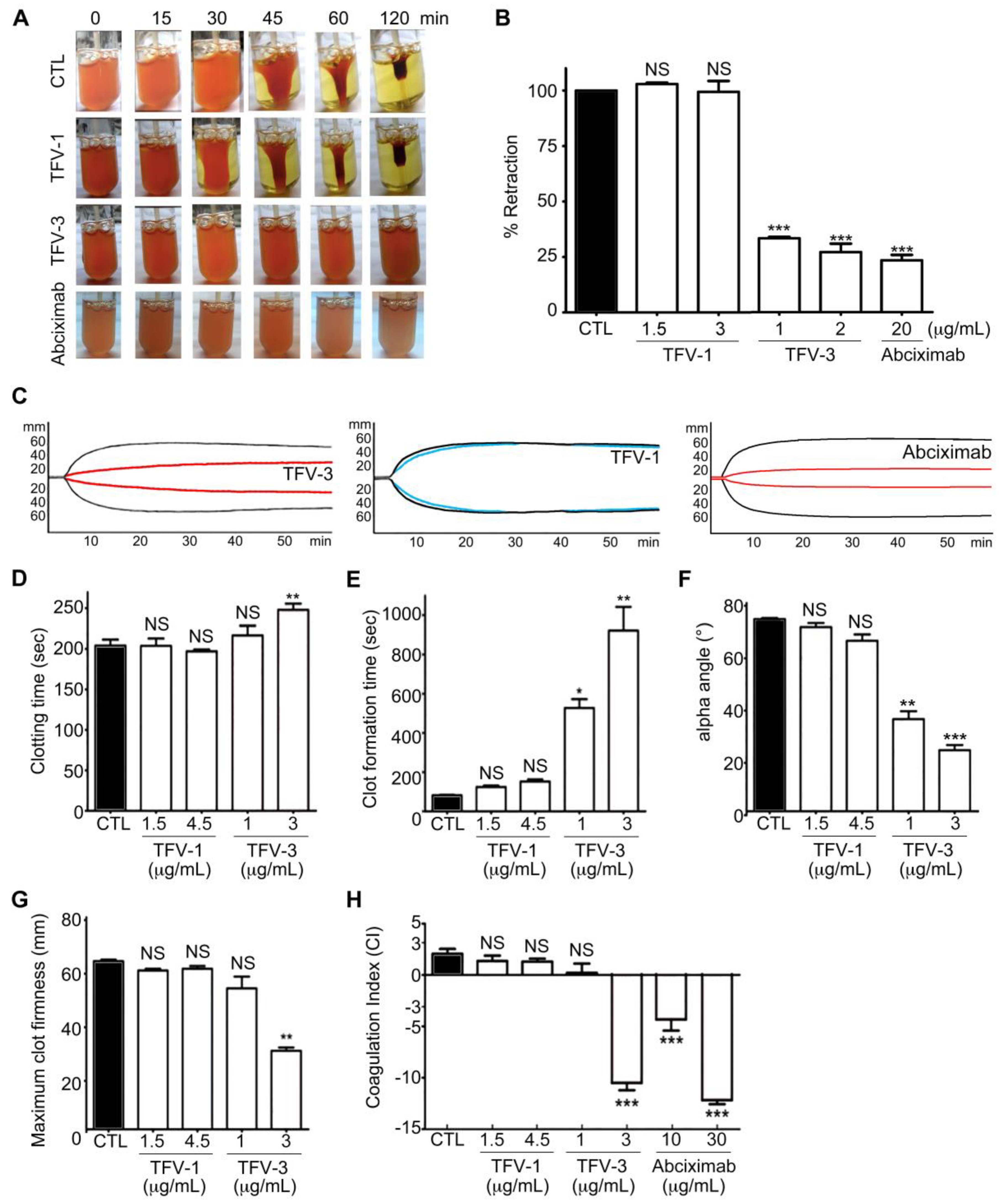
2.8. TFV-1 Exhibits Anti-Thrombotic Activity, but Reduced Tendencies to Cause FcγRIIa-Mediated Immune Clearance and Hemorrhage In Vivo
2.9. TFV-1 Does Not Affect the Interaction between Integrin αIIbβ3 and Its Mediator Talin Responsible for the Hemostatic Process
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Materials
5.2. Top-Down Analysis
5.3. Endoproteinase Asp-N or Glu-C Digestion and LC-MS/MS Analysis
5.4. Preparation of Human Platelets and Aggregation Assay
5.5. Western Blotting and Immunoprecipitation
5.6. Binding Study
5.7. Priming Assay
5.8. Definition of Safety Index
5.9. Clot Retraction
5.10. Rotational Thromboelastometry (ROTEM)
5.11. Animal Preparation
5.12. FeCl3-Induced Arterial Thrombosis Model
5.13. Tail-Bleeding Time
5.14. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADP | Adenosine 5′-diphosphate |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| FACS | Fluorescence activator cell sorter |
| FITC | Fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| FPLC | Fast protein liquid chromatography |
| GP | Glycoprotein |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| IV | Intravenous |
| mAb | Monoclonal antibody |
| MALDI-TOF | Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight |
| LIBS | Ligand-induced binding site |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PRP | Platelet-rich plasma |
| PS | Platelet suspension |
| RGD | Arg-Gly-Asp |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| TFV | Trimeresurus flavoviridis venom |
References
- Bledzka, K.; Smyth, S.S.; Plow, E.F. Integrin alphaiibbeta3: From discovery to efficacious therapeutic target. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pytela, R.; Pierschbacher, M.D.; Ginsberg, M.H.; Plow, E.F.; Ruoslahti, E. Platelet membrane glycoprotein iib/iiia: Member of a family of arg-gly-asp—Specific adhesion receptors. Science 1986, 231, 1559–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.F.; Holt, J.C.; Lukasiewicz, H.; Niewiarowski, S. Trigramin. A low molecular weight peptide inhibiting fibrinogen interaction with platelet receptors expressed on glycoprotein iib-iiia complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 16157–16163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.F.; Holt, J.C.; Kirby, E.P.; Niewiarowski, S. Trigramin—Primary structure and its inhibition of vonwillebrand-factor binding to glycoprotein-iib/iiia complex on human-platelets. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.F.; Sheu, J.R.; Teng, C.M.; Chen, S.W.; Liu, C.S. Triflavin, an antiplatelet arg-gly-asp-containing peptide, is a specific antagonist of platelet membrane glycoprotein iib-iiia complex. J. Biochem. 1991, 109, 328–334. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, Y.J.; Chung, C.H.; Huang, T.F. From discovery of snake venom disintegrins to a safer therapeutic antithrombotic agent. Toxins 2019, 11, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassand, J.P. Current antithrombotic agents for acute coronary syndromes: Focus on bleeding risk. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 163, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swieringa, F.; Kuijpers, M.J.; Heemskerk, J.W.; van der Meijden, P.E. Targeting platelet receptor function in thrombus formation: The risk of bleeding. Blood Rev. 2014, 28, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkowitz, S.D.; Harrington, R.A.; Rund, M.M.; Tcheng, J.E. Acute profound thrombocytopenia after c7e3 fab (abciximab) therapy. Circulation 1997, 95, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Boylan, B.; Bougie, D.; Gill, J.C.; Birenbaum, J.; Newman, D.K.; Aster, R.H.; Newman, P.J. Eptifibatide-induced thrombocytopenia and thrombosis in humans require fcgammariia and the integrin beta3 cytoplasmic domain. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, B.H. Drug-induced thrombocytopenia: Mibs trumps libs. Blood 2012, 119, 6177–6178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougie, D.W.; Rasmussen, M.; Zhu, J.; Aster, R.H. Antibodies causing thrombocytopenia in patients treated with rgd-mimetic platelet inhibitors recognize ligand-specific conformers of alphaiib/beta3 integrin. Blood 2012, 119, 6317–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmanabhan, A.; Jones, C.G.; Bougie, D.W.; Curtis, B.R.; McFarland, J.G.; Wang, D.; Aster, R.H. Heparin-independent, pf4-dependent binding of hit antibodies to platelets: Implications for hit pathogenesis. Blood 2015, 125, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, O.; Jesel, L.; Chauvin, M.; Freyssinet, J.M.; Toti, F. Eptifibatide-induced thrombocytopenia and circulating procoagulant platelet-derived microparticles in a patient with acute coronary syndrome. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2003, 1, 2685–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pedicord, D.L.; Dicker, I.; O’Neil, K.; Breth, L.; Wynn, R.; Hollis, G.F.; Billheimer, J.T.; Stern, A.M.; Seiffert, D. Cd32-dependent platelet activation by a drug-dependent antibody to glycoprotein iib/iiia antagonists. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 89, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, H.; Rauova, L.; Hayes, V.; Gao, C.; Boylan, B.; Newman, D.K.; McKenzie, S.E.; Cooley, B.C.; Poncz, M.; Newman, P.J. Cooperative integrin/itam signaling in platelets enhances thrombus formation in vitro and in vivo. Blood 2013, 121, 1858–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boylan, B.; Gao, C.; Rathore, V.; Gill, J.C.; Newman, D.K.; Newman, P.J. Identification of fcgammariia as the itam-bearing receptor mediating alphaiibbeta3 outside-in integrin signaling in human platelets. Blood 2008, 112, 2780–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, P.C.; Peter, K. Gpiib/iiia inhibitors: From bench to bedside and back to bench again. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 107, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.J.; Chen, Y.R.; Hsu, C.C.; Peng, H.C.; Huang, T.F. An alphaiib beta3 antagonist prevents thrombosis without causing fc receptor gamma-chain iia-mediated thrombocytopenia. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2017, 15, 2230–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Sakai, Y.; Taniuchi, Y.; Sato, K.; Maruyama, K.; Shimizu, M.; Kaku, S.; Yano, S.; Inagaki, O.; Tomioka, K.; et al. Biochemical characterization of a new disintegrin, flavostatin, isolated from trimeresurus flavoviridis venom. Biochimie 1996, 78, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Okuda, D.; Fujimoto, Z.; Horii, K.; Morita, T.; Mizuno, H. Crystal structure of trimestatin, a disintegrin containing a cell adhesion recognition motif rgd. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 332, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byron, A.; Humphries, J.D.; Askari, J.A.; Craig, S.E.; Mould, A.P.; Humphries, M.J. Anti-integrin monoclonal antibodies. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 4009–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.F.; Liu, C.Z.; Ouyang, C.H.; Teng, C.M. Halysin, an antiplatelet arg-gly-asp-containing snake venom peptide, as fibrinogen receptor antagonist. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1991, 42, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Artoni, A.; Li, J.; Mitchell, B.; Ruan, J.; Takagi, J.; Springer, T.A.; French, D.L.; Coller, B.S. Integrin beta3 regions controlling binding of murine mab 7e3: Implications for the mechanism of integrin alphaiibbeta3 activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13114–13120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, A.; Li, J.; Naini, S.; Coller, B.S.; Filizola, M. Structure-based virtual screening of small-molecule antagonists of platelet integrin alphaiibbeta3 that do not prime the receptor to bind ligand. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2012, 26, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalescot, G. Platelet biology and implications for antiplatelet therapy in atherothrombotic disease. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2011, 17, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullard, J.F. The role of the platelet glycoprotein iib/iiia in thrombosis and haemostasis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidard, D.; Montgomery, R.R.; Bennett, J.S.; Kunicki, T.J. Interaction of ap-2, a monoclonal antibody specific for the human platelet glycoprotein iib-iiia complex, with intact platelets. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 12582–12586. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.F.; Chang, C.H.; Ho, P.L.; Chung, C.H. Fcgammarii mediates platelet aggregation caused by disintegrins and gpiib/iiia monoclonal antibody, ap2. Exp. Hematol. 2008, 36, 1704–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Mkaddem, S.; Hayem, G.; Jonsson, F.; Rossato, E.; Boedec, E.; Boussetta, T.; El Benna, J.; Launay, P.; Goujon, J.M.; Benhamou, M.; et al. Shifting fcgammariia-itam from activation to inhibitory configuration ameliorates arthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3945–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenette, P.S.; Johnson, R.C.; Hynes, R.O.; Wagner, D.D. Platelets roll on stimulated endothelium in vivo: An interaction mediated by endothelial p-selectin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7450–7454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merten, M.; Thiagarajan, P. P-selectin expression on platelets determines size and stability of platelet aggregates. Circulation 2000, 102, 1931–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leytin, V.; Mody, M.; Semple, J.W.; Garvey, B.; Freedman, J. Quantification of platelet activation status by analyzing p-selectin expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 273, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, K.L.; Sage, T.; Gibbins, J.M. Clot retraction. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 788, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Haling, J.R.; Monkley, S.J.; Critchley, D.R.; Petrich, B.G. Talin-dependent integrin activation is required for fibrin clot retraction by platelets. Blood 2011, 117, 1719–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flevaris, P.; Li, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Du, X. Two distinct roles of mitogen-activated protein kinases in platelets and a novel rac1-mapk-dependent integrin outside-in retractile signaling pathway. Blood 2009, 113, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganter, M.T.; Hofer, C.K. Coagulation monitoring: Current techniques and clinical use of viscoelastic point-of-care coagulation devices. Anesth. Analg. 2008, 106, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lance, M.D. A general review of major global coagulation assays: Thrombelastography, thrombin generation test and clot waveform analysis. Thromb. J. 2015, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worth, R.G.; Chien, C.D.; Chien, P.; Reilly, M.P.; McKenzie, S.E.; Schreiber, A.D. Platelet fcgammariia binds and internalizes igg-containing complexes. Exp. Hematol. 2006, 34, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, S.E.; Taylor, S.M.; Malladi, P.; Yuhan, H.; Cassel, D.L.; Chien, P.; Schwartz, E.; Schreiber, A.D.; Surrey, S.; Reilly, M.P. The role of the human fc receptor fc gamma riia in the immune clearance of platelets: A transgenic mouse model. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 4311–4318. [Google Scholar]
- Petrich, B.G.; Marchese, P.; Ruggeri, Z.M.; Spiess, S.; Weichert, R.A.; Ye, F.; Tiedt, R.; Skoda, R.C.; Monkley, S.J.; Critchley, D.R.; et al. Talin is required for integrin-mediated platelet function in hemostasis and thrombosis. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 3103–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Zhao, X.; O’Brien, K.A.; Stojanovic-Terpo, A.; Delaney, M.K.; Kim, K.; Cho, J.; Lam, S.C.; Du, X. A directional switch of integrin signalling and a new anti-thrombotic strategy. Nature 2013, 503, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhu, J.; Negri, A.; Provasi, D.; Filizola, M.; Coller, B.S.; Springer, T.A. Closed headpiece of integrin alphaiibbeta3 and its complex with an alphaiibbeta3-specific antagonist that does not induce opening. Blood 2010, 116, 5050–5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estevez, B.; Shen, B.; Du, X. Targeting integrin and integrin signaling in treating thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougie, D.W.; Wilker, P.R.; Wuitschick, E.D.; Curtis, B.R.; Malik, M.; Levine, S.; Lind, R.N.; Pereira, J.; Aster, R.H. Acute thrombocytopenia after treatment with tirofiban or eptifibatide is associated with antibodies specific for ligand-occupied gpiib/iiia. Blood 2002, 100, 2071–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billheimer, J.T.; Dicker, I.B.; Wynn, R.; Bradley, J.D.; Cromley, D.A.; Godonis, H.E.; Grimminger, L.C.; He, B.; Kieras, C.J.; Pedicord, D.L.; et al. Evidence that thrombocytopenia observed in humans treated with orally bioavailable glycoprotein iib/iiia antagonists is immune mediated. Blood 2002, 99, 3540–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aster, R.H. Immune thrombocytopenia caused by glycoprotein iib/iiia inhibitors. Chest 2005, 127, 53S–59S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Z.; Wang, Y.W.; Shen, M.C.; Huang, T.F. Analysis of human platelet glycoprotein iib-iiia by fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated disintegrins with flow-cytometry. Thromb. Haemost. 1994, 72, 919–925. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.P.; Plow, E.F.; Frelinger, A.L., 3rd; O’Toole, T.E.; Loftus, J.C.; Ginsberg, M.H. Ligands “activate” integrin alpha iib beta 3 (platelet gpiib-iiia). Cell 1991, 65, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Chung, C.H.; Kuo, H.L.; Hsu, C.C.; Huang, T.F. The highly specific platelet glycoprotein (gp) vi agonist trowaglerix impaired collagen-induced platelet aggregation ex vivo through matrix metalloproteinase-dependent gpvi shedding. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2008, 6, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Antithrombotic Agents | TFV-1 (μg/mL) | TFV-3 (μg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inducer | PRP | PS | PRP | PS |
| ADP (20 μM) | 0.720 ± 0.025 | 0.133 ± 0.003 | ||
| Collagen (10 μg/mL) | 1.090 ± 0.148 | 0.530 ± 0.03 | 0.323 ± 0.124 | 0.217 ± 0.007 |
| Thrombin (0.1 U/mL) | 0.467 ± 0.02 | 0.301 ± 0.014 | ||
| Antithrombotic Agents | TFV-1 | TFV-3 | Abciximab | Eptifibatide | Control | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Dose of Agents (Fold of IC50) | 2× | 6× | 2× | 6× | 2× | 6× | 2× | 6× | - |
| IC50 (μg/mL) | 0.74 | 0.45 | 5 | 0.52 | - | ||||
| Safety index | 20.27 | 2.22 | 2.00 | 1.92 | - | ||||
| Clot formation time (s) | 135 (NS) | 172 (NS) | 540 (*) | 967 (**) | 569 (***) | 1355 (***) | 518 (**) | 622 (**) | 105 |
| Inhibition of Clot retraction (%) | 0 | 0 | 77.3 | 86.1 | 54.7 | 92.5 | 63.2 | 89.4 | - |
| Tail-bleeding time (s) | 66.8 (NS) | 102.5 (NS) | 233.3 (**) | 574.0 (***) | 373.4 (***) | 580.8 (***) | 538.6 (***) | 1341.2 (***) | 68.7 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuo, Y.-J.; Chung, C.-H.; Pan, T.-Y.; Chuang, W.-J.; Huang, T.-F. A Novel αIIbβ3 Antagonist from Snake Venom Prevents Thrombosis without Causing Bleeding. Toxins 2020, 12, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010011
Kuo Y-J, Chung C-H, Pan T-Y, Chuang W-J, Huang T-F. A Novel αIIbβ3 Antagonist from Snake Venom Prevents Thrombosis without Causing Bleeding. Toxins. 2020; 12(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuo, Yu-Ju, Ching-Hu Chung, Tzu-Yu Pan, Woei-Jer Chuang, and Tur-Fu Huang. 2020. "A Novel αIIbβ3 Antagonist from Snake Venom Prevents Thrombosis without Causing Bleeding" Toxins 12, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010011
APA StyleKuo, Y.-J., Chung, C.-H., Pan, T.-Y., Chuang, W.-J., & Huang, T.-F. (2020). A Novel αIIbβ3 Antagonist from Snake Venom Prevents Thrombosis without Causing Bleeding. Toxins, 12(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010011






