Bee Venom Phospholipase A2 Ameliorates Atherosclerosis by Modulating Regulatory T Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
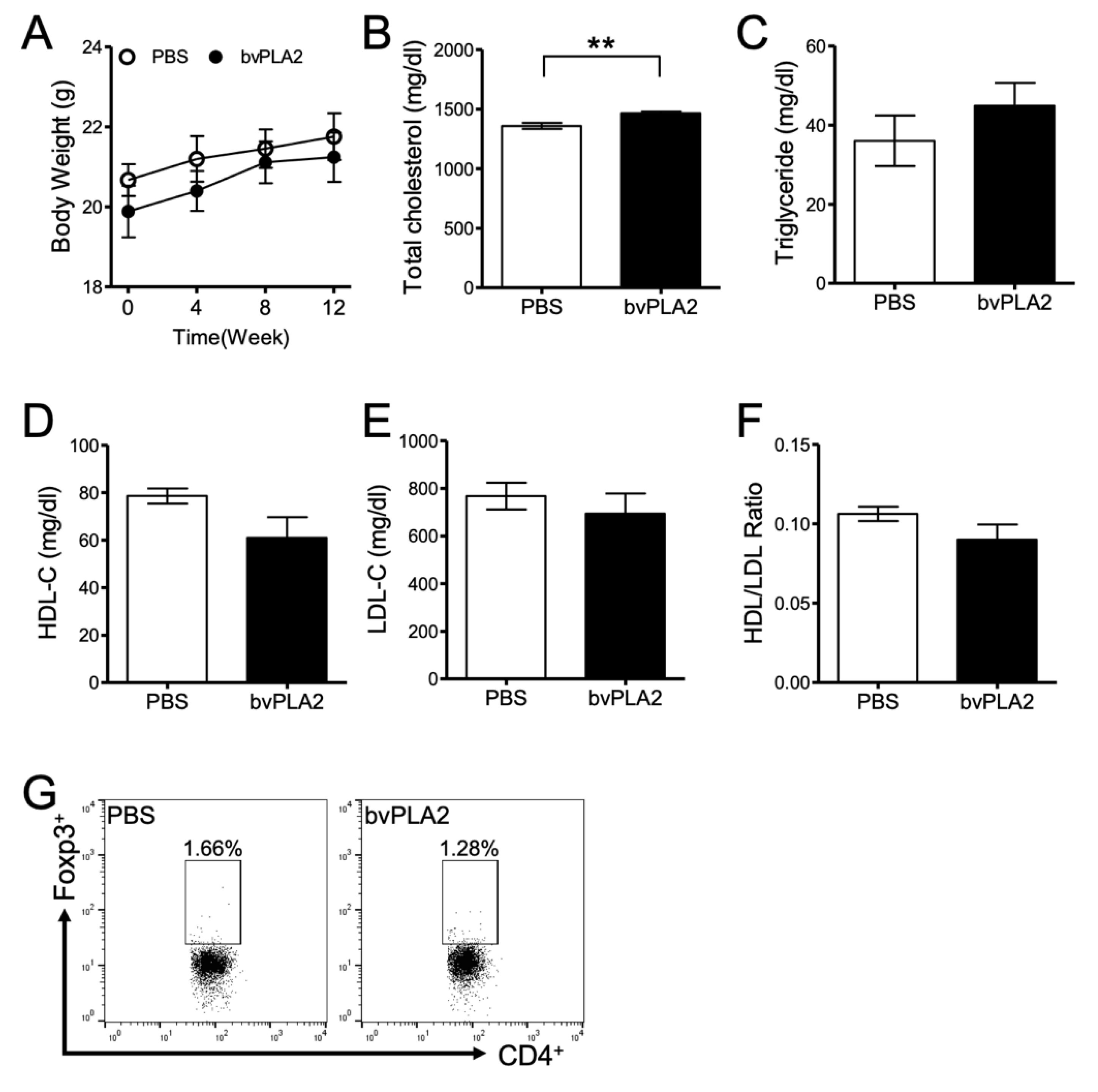
2.1. Effect of bvPLA2 Treatment on Atherosclerotic Mice
2.2. bvPLA2 Treatment Increases Regulatory T Cells in Lymph Nodes
2.3. bvPLA2 Treatment Reduces the Inflammatory Cytokines
2.4. bvPLA2 Treatment Reduces Atherosclerotic Lesions and Foam Cell Formation
2.5. Effect of bvPLA2 Treatment on ApoE-/-/Foxp3DTR Mice
2.6. Effects of Treg Deletion on the Treatment of Arteriosclerosis with bvPLA2
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Mice
4.2. Body Weight and Lipid Profile
4.3. Flow Cytometric Analysis
4.4. ELISA and Inflammatory Cytokines Analysis
4.5. Measurement of Atherosclerotic Lesions in the Aorta
4.6. Histological Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Binder, C.J.; Chang, M.K.; Shaw, P.X.; Miller, Y.I.; Hartvigsen, K.; Dewan, A.; Witztum, J.L. Innate and acquired immunity in atherogenesis. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 2002, 420, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, G.K. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hansson, G.K.; Hermansson, A. The immune system in atherosclerosis. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, J.E.; Dennis, E.A. Phospholipase A2 structure/function, mechanism, and signaling1. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S237–S242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakashima, S.; Kitamoto, K.; Arioka, M. The catalytic activity, but not receptor binding, of sPLA2s plays a critical role for neurite outgrowth induction in PC12 cells. Brain Res. 2004, 1015, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, J.M.; Brachova, L.; Higgins, K.; Obermiller, L.; Sevanian, A.; Khandrika, S.; Reaven, P.D. Induction of monocyte differentiation and foam cell formation in vitro by 7-ketocholesterol. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 26–35. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Ma, H.; Qiu, L.; Li, L.; Cao, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhao, Y. Phenotypic and functional switch of macrophages induced by regulatory CD4+CD25+ T cells in mice. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2011, 89, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastrana, J.L.; Sha, X.; Virtue, A.; Mai, J.; Cueto, R.; Lee, I.A.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.F. Regulatory T cells and Atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Exp. Cardiolog. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Sasaki, N.; Kasahara, K.; Hirata, K. Anti-inflammatory and immune-modulatory therapies for preventing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. J. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foks, A.C.; Lichtman, A.H.; Kuiper, J. Treating atherosclerosis with regulatory T cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spitz, C.; Winkels, H.; Bürger, C.; Weber, C.; Lutgens, E.; Hansson, G.K.; Gerdes, N. Regulatory T cells in atherosclerosis: Critical immune regulatory function and therapeutic potential. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 901–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ou, H.X.; Guo, B.B.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.K.; Yang, Z.; Feng, W.J.; Mo, Z.C. Regulatory T cells as a new therapeutic target for atherosclerosis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Baek, H.; Jung, K.H.; Lee, G.; Lee, H.; Kang, G.H.; Bae, H. Bee venom phospholipase A2 suppresses allergic airway inflammation in an ovalbumin-induced asthma model through the induction of regulatory T cells. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2015, 3, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Lee, H.; Lee, G.; Jang, H.; Kim, S.S.; Yoon, H.; Kang, G.H.; Hwang, D.S.; Kim, S.K.; Chung, H.S.; et al. Phospholipase A2 inhibits cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by modulating regulatory T cells by the CD206 mannose receptor. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, K.H.; Baek, H.; Kang, M.; Kim, N.; Lee, S.Y.; Bae, H. Bee Venom Phospholipase A2 Ameliorates House Dust Mite Extract Induced Atopic Dermatitis Like Skin Lesions in Mice. Toxins 2017, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, H.; Lee, C.J.; Choi, D.B.; Kim, N.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Ye, Y.J.; Kim, J.S.; Shim, I.; Bae, H. Bee venom phospholipase A2 ameliorates Alzheimer′s disease pathology in Aβ vaccination treatment without inducing neuro-inflammation in a 3xTg-AD mouse model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, H.; Yang, H.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, N.H.; Lee, J.; Bae, H.; Hwang, D.S. Prophylactic Effects of Bee Venom Phospholipase A2 in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Pregnancy Loss. Toxins 2019, 11, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, G.; Bae, H. Bee Venom Phospholipase A2: Yesterday’s Enemy Becomes Today’s Friend. Toxins 2016, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, E.S.; Lee, G.; Lee, C.; Ye, M.; Chung, H.S.; Kim, H.; Bae, S.J.; Hwang, D.S.; Bae, H. Bee Venom Phospholipase A2, a Novel Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cell Inducer, Protects Dopaminergic Neurons by Modulating Neuroinflammatory Responses in a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 4853–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milanez-Almeida, P.; Meyer-Hermann, M.; Toker, A.; Khailaie, S.; Huehn, J. Foxp3+ regulatory T-cell homeostasis quantitatively differs in murine peripheral lymph nodes and spleen. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.; He, S.; Ma, X.; Li, D. The role of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in macrophage-derived foam-cell formation. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kita, T.; Yamashita, T.; Sasaki, N.; Kasahara, K.; Sasaki, Y.; Yodoi, K.; Takeda, M.; Nakajima, K.; Hirata, K. Regression of atherosclerosis with anti-CD3 antibody via augmenting a regulatory T-cell response in mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 102, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingenberg, R.; Gerdes, N.; Badeau, R.M.; Gisterå, A.; Strodthoff, D.; Ketelhuth, D.F.; Lundberg, A.M.; Rudling, M.; Nilsson, S.K.; Olivecrona, G.; et al. Depletion of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells promotes hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landucci, E.C.; Toyama, M.; Marangoni, S.; Oliveira, B.; Cirino, G.; Antunes, E.; de Nucci, G. Effect of crotapotin and heparin on the rat paw oedema induced by different secretory phospholipases A2. Toxicon 2000, 38, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.K.; Zhang, Y.P.; Titsworth, W.L.; Jiang, X.; Han, S.; Lu, P.H.; Shields, C.B.; Xu, X.M. A novel role of phospholipase A2 in mediating spinal cord secondary injury. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 59, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titsworth, W.L.; Onifer, S.M.; Liu, N.K.; Xu, X.M. Focal phospholipases A2 group III injections induce cervical white matter injury and functional deficits with delayed recovery concomitant with Schwann cell remyelination. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 207, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Keum, D.J.; Kwak, J.; Chung, H.S.; Bae, H. Bee venom phospholipase A2 protects against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury by modulating regulatory T cells and IL-10 in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Lee, Y.; Kim, W.; Lee, K.; Bae, H.; Kim, S.K. Analgesic Effects of Bee Venom Derived Phospholipase A (2) in a Mouse Model of Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathic Pain. Toxins 2015, 7, 2422–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Mao, S.; Zhan, Z.; Yu, K.; He, C.; Wang, C. Effect of hyperlipidemia on Foxp3 expression in apolipoprotein E-knockout mice. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2014, 15, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-M.; Chen, J.; Dai, X.; Liao, X.-X.; Hu, C.-L.; Li, Y.-J. Changes in CD4. Exp. Biol. Med. Maywood 2017, 242, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, P.W. High-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein and coronary artery disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 1990, 66, 7A–10A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, C.M.; Rodríguez-Perea, A.L.; Moreno-Fernandez, M.; Jackson, C.M.; Melchior, J.T.; Davidson, W.S.; Chougnet, C.A. High density lipoproteins selectively promote the survival of human regulatory T cells. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1514–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raffai, R.L.; Weisgraber, K.H. Hypomorphic apolipoprotein E mice: A new model of conditional gene repair to examine apolipoprotein E-mediated metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 11064–11068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, G.-H.; Lee, S.; Choi, D.B.; Shin, D.; Kim, J.; Yang, H.; Bae, H. Bee Venom Phospholipase A2 Ameliorates Atherosclerosis by Modulating Regulatory T Cells. Toxins 2020, 12, 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12100609
Kang G-H, Lee S, Choi DB, Shin D, Kim J, Yang H, Bae H. Bee Venom Phospholipase A2 Ameliorates Atherosclerosis by Modulating Regulatory T Cells. Toxins. 2020; 12(10):609. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12100609
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Geun-Hyung, Sujin Lee, Da Bin Choi, Dasom Shin, Jahee Kim, HyeJin Yang, and Hyunsu Bae. 2020. "Bee Venom Phospholipase A2 Ameliorates Atherosclerosis by Modulating Regulatory T Cells" Toxins 12, no. 10: 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12100609
APA StyleKang, G.-H., Lee, S., Choi, D. B., Shin, D., Kim, J., Yang, H., & Bae, H. (2020). Bee Venom Phospholipase A2 Ameliorates Atherosclerosis by Modulating Regulatory T Cells. Toxins, 12(10), 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12100609




