Fumonisin B1 Epigenetically Regulates PTEN Expression and Modulates DNA Damage Checkpoint Regulation in HepG2 Liver Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. FB1 Induces DNA Damage in HepG2 Cells
2.2. FB1 Increases miR-30c Expression in HepG2 Cells
2.3. FB1 Induces H3K4me3 by Downregulating KDM5B in HepG2 Cells
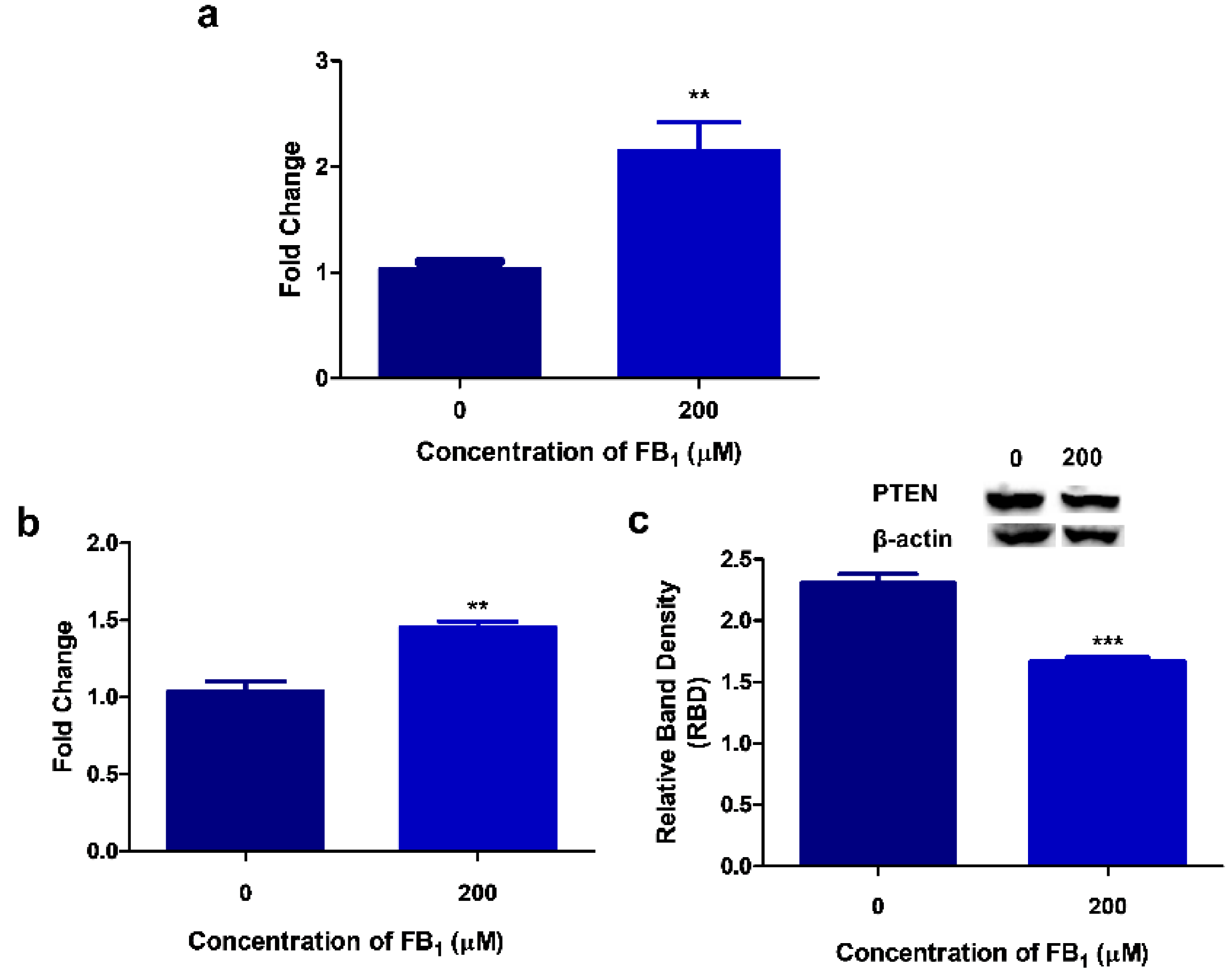
2.4. FB1 Alters PTEN Expression in HepG2 Cells
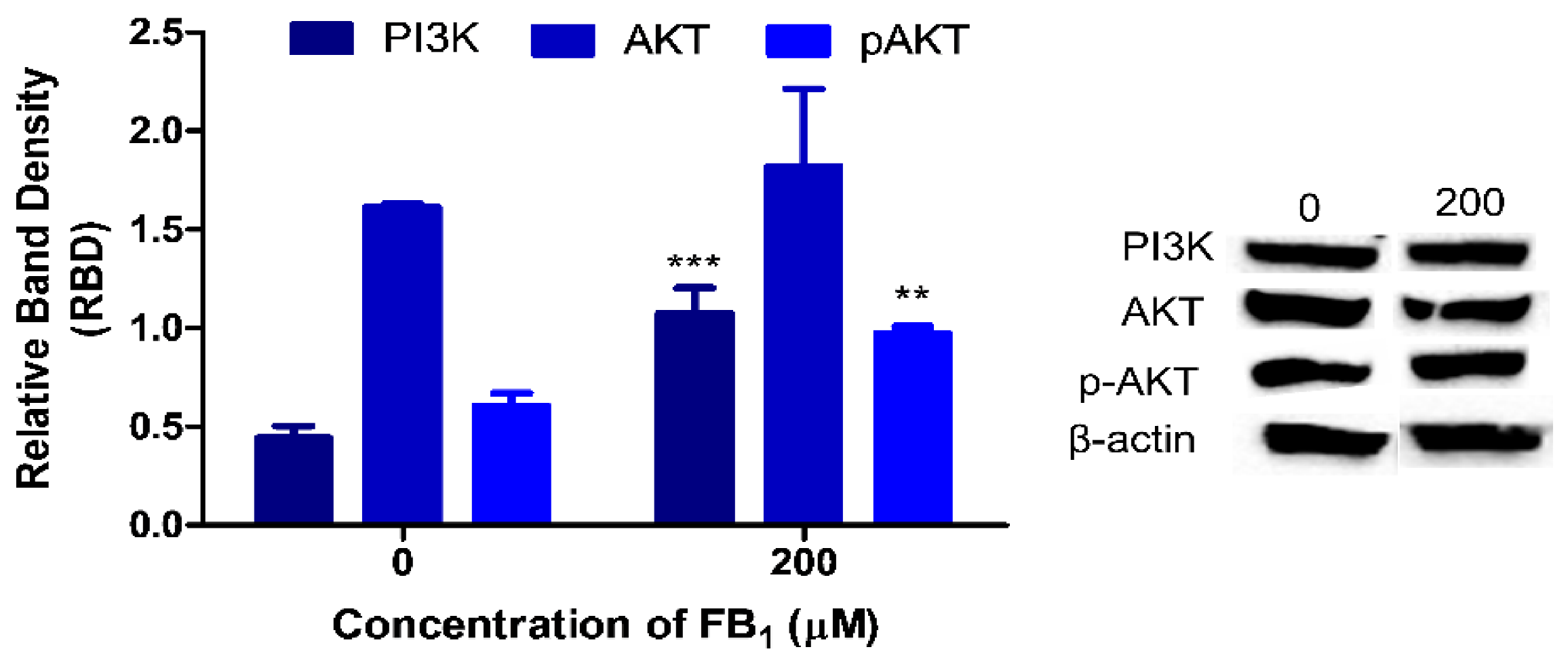
2.5. FB1 Affects PI3K/AKT Signaling in HepG2 Cells
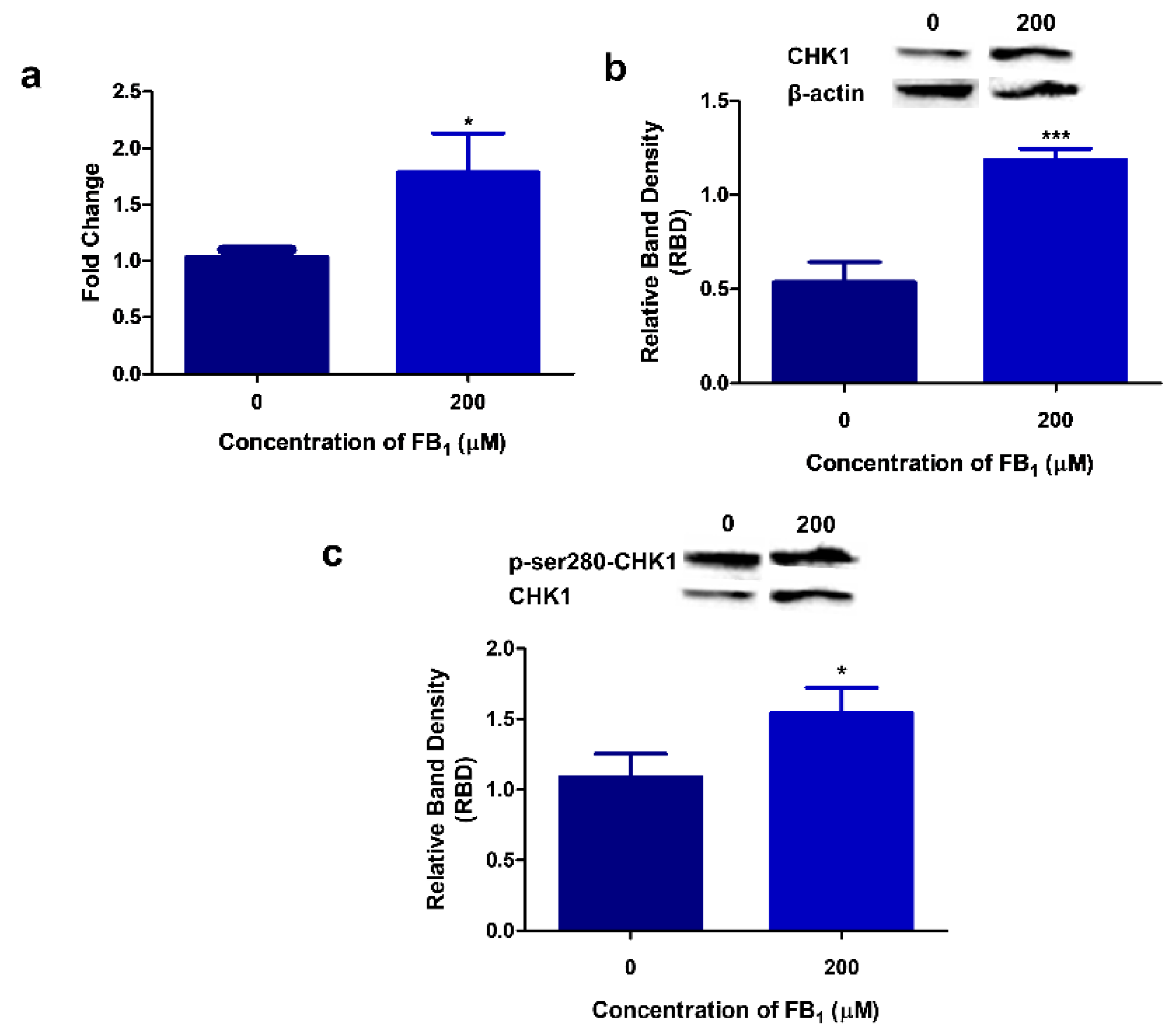
2.6. FB1 Modulates CHK1 Expression and Activity in HepG2 Cells
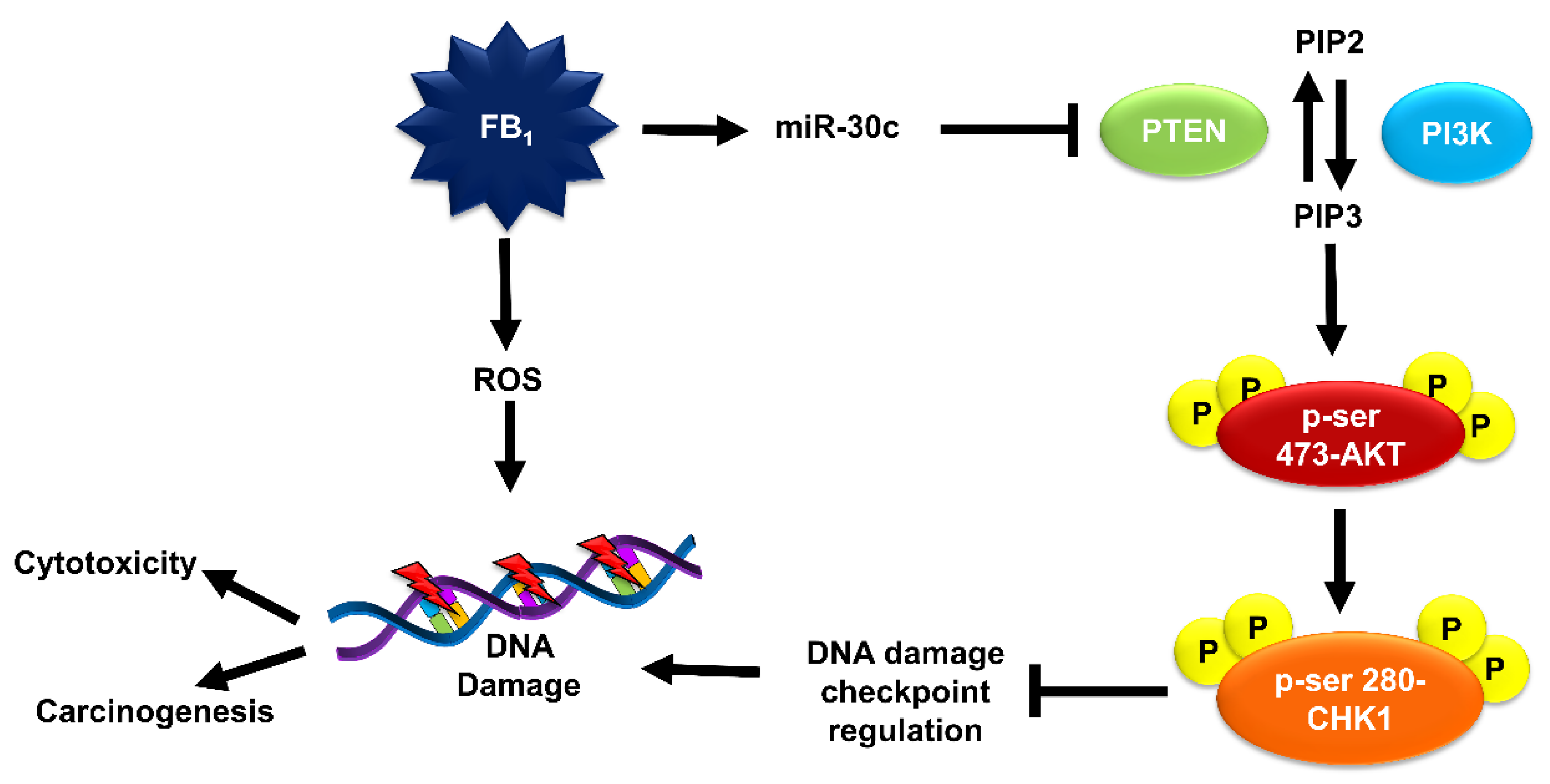
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Method and Materials
5.1. Materials
5.2. Cell Culture and Treatments
5.3. DNA Damage
5.4. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
5.5. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assay
5.6. Protein Isolation and Western Blotting
5.7. Statistical Analysis
5.8. Ethics Approval
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gelderblom, W.C.; Jaskiewicz, K.; Marasas, W.F.; Thiel, P.G.; Horak, R.M.; Vleggaar, R.; Kriek, N.P. Fumonisins—Novel mycotoxins with cancer-promoting activity produced by Fusarium moniliforme. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1988, 54, 1806–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rheeder, J.P.; Marasas, W.F.; Vismer, H.F. Production of fumonisin analogs by Fusarium species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 2101–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, F.A.; Ferreira, F.M.D.; Ferreira, F.D.; Bando, É.; Nerilo, S.B.; Hirooka, E.Y.; Machinski, M., Jr. Daily intake estimates of fumonisins in corn-based food products in the population of Parana, Brazil. Food Control 2012, 26, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamle, M.; Mahato, D.K.; Devi, S.; Lee, K.E.; Kang, S.G.; Kumar, P. Fumonisins: Impact on Agriculture, Food, and Human Health and their Management Strategies. Toxins 2019, 11, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, S.; Ramos, A.J.; Cano-Sancho, G.; Sanchis, V. Mycotoxins: Occurrence, toxicology, and exposure assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 60, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, N.; He, Q.; Sharma, R.P. Gender-related differences in subacute fumonisin B1 hepatotoxicity in BALB/c mice. Toxicology 2001, 165, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, D.E.; Taranu, L.; Pascale, F.; Lionide, A.; Burlacu, R.; Bailly, J.D.; Oswalt, I.P. Sex-related differences in the immune response of weanling piglets exposed to low doses of fumonisin extract. Br. J. Nutr. 2006, 95, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domijan, A.-M. Fumonisin B1: A neurotoxic mycotoxin. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2012, 63, 531–544. [Google Scholar]
- Mathur, S.; Constable, P.D.; Eppley, R.M.; Waggoner, A.L.; Tumbleson, M.E.; Haschek, W.M. Fumonisin B1 is hepatotoxic and nephrotoxic in milk-fed calves. Toxicol. Sci. 2001, 60, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Dekant, W.; Mally, A. Fumonisin B1 and the kidney: Modes of action for renal tumor formation by fumonisin B1 in rodents. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3833–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Rocha, M.E.B.; Freire, F.C.O.; Maia, F.E.F.; Guedes, M.I.F.; Rondina, D. Mycotoxins and their effects on human and animal health. Food Control 2014, 36, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Some traditional herbal medicines, some mycotoxins, naphthalene and styrene. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2002, 82, 1–556. [Google Scholar]
- Gelderblom, W.; Abel, S.; Smuts, C.M.; Marnewick, J.; Marasas, W.F.; Lemmer, E.R.; Ramlijak, D. Fumonisin-induced hepatocarcinogenesis: Mechanisms related to cancer initiation and promotion. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109 (Suppl. 2), 291–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Wang, S.; Hu, X.; Su, J.; Huang, T.; Yu, J.; Tang, L.; Gao, W.; Wang, J.S. Fumonisin B1 contamination of home-grown corn in high-risk areas for esophageal and liver cancer in China. Food Addit. Contam. 2007, 24, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, A.M.; Roshandel, G.; Roudbarmohammadi, S.; Roudbary, M.; Sohanaki, H.; Ghiasian, S.A.; Taherkhani, A.; Semenani, S.; Aghasi, M. Fumonisin B1 contamination of cereals and risk of esophageal cancer in a high risk area in northeastern Iran. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 2625–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knasmüller, S.; Bresgen, N.; Kassie, F.; Volker, M.S.; Gelderblom, W.; Zöhrer, E.; Eckl, P.M. Genotoxic effects of three Fusarium mycotoxins, fumonisin B1, moniliformin and vomitoxin in bacteria and in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagenesis 1997, 391, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norred, W.P.; Plattner, W.P.; Vesonder, R.F.; Bacon, C.W.; Voss, K.A. Effects of selected secondary metabolites of Fusarium moniliforme on unscheduled synthesis of DNA by rat primary hepatocytes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1992, 30, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelderblom, W.C.A.; Semple, E.; Marasas, W.F.O.; Farber, E. The cancer-initiating potential of the fumonisin B mycotoxins. Carcinogenesis 1992, 13, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theumer, M.G.; Cánepa, M.C.; López, A.G.; Mary, V.S.; Dambolena, J.S.; Rubinstein, H.R. Subchronic mycotoxicoses in Wistar rats: Assessment of the in vivo and in vitro genotoxicity induced by fumonisins and aflatoxin B, and oxidative stress biomarkers status. Toxicology 2010, 268, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.M.; Abdel-Aziem, S.H.; El-Nekeety, A.A.; Abdel-Wahhab, M.A. Panaxginseng extract modulates oxidative stress, DNA fragmentation and up-regulate gene expression in rats sub chronically treated with aflatoxin B 1 and fumonisin B 1. Cytotechnology 2015, 67, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuturgoon, A.; Phulukdaree, A.; Moodley, D. Fumonisin B1 induces global DNA hypomethylation in HepG2 cells—An alternative mechanism of action. Toxicology 2014, 315, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.P.; Bartek, J. The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature 2009, 461, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.X.; Cao, L.L.; Chen, X.; Xiao, J.; Zou, Y.; Chen, Q. PTEN Inhibits Cell Proliferation, Promotes Cell Apoptosis, and Induces Cell Cycle Arrest via Downregulating the PI3K/AKT/hTERT Pathway in Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2476842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otaegi, G.; Yusta-Boyo, M.J.; Vergaño-Vera, E.; Méndez-Gómez, H.R.; Carrera, A.C.; Abad, J.L.; González, M.; Enrique, J.; Vicario-Abejón, C.; de Pablo, F. Modulation of the PI 3-kinase—Akt signalling pathway by IGF-I and PTEN regulates the differentiation of neural stem/precursor cells. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 2739–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassi, C.; Ho, J.; Srikumar, T.; Dowling, R.J.O.; Gorrini, C.; Miller, S.J.; Mak, T.W.; Neel, B.G.; Raught, B.; Stambolic, V. Nuclear PTEN controls DNA repair and sensitivity to genotoxic stress. Science 2013, 341, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, M.; He, Y.-Y. PTEN in DNA damage repair. Cancer Lett. 2012, 319, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puc, J.; Parsons, R. PTEN loss inhibits CHK1 to cause double stranded-DNA breaks in cells. Cell Cycle 2005, 4, 927–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puc, J.; Keniry, M.; Li, H.S.; Pandita, T.J.; Choudhury, A.D.; Memeo, L.; Mansukhani, M.; Murty, V.V.V.S.; Gaciong, Z.; Meek, S.E.M. Lack of PTEN sequesters CHK1 and initiates genetic instability. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 193–204. [Google Scholar]
- Peyrou, M.; Bourgoin, L.; Foti, M. PTEN in liver diseases and cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 4627–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinciguerra, M.; Foti, M. PTEN at the crossroad of metabolic diseases and cancer in the liver. Ann. Hepatol. 2008, 7, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, W.L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, S.P.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.L. Epigenetic and genetic alterations of PTEN in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2007, 37, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.M.; Yu, X.N.; Liu, T.T.; Zhu, H.R.; Shi, X.; Bilegsaikhan, E.; Guo, H.Y.; Song, G.Q.; Weng, S.Q.; Huang, X.X.; et al. microRNA-19a-3p promotes tumor metastasis and chemoresistance through the PTEN/Akt pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed. Pharm. 2018, 105, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Henson, R.; Wehbe-Janek, H.; Ghoshal, K.; Jacob, S.T.; Patel, T. MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Cheng, G.; Xu, L.; Wu, W.; Chen, Z.; Du, P. Jumonji AT-rich interactive domain 1B promotes the growth of pancreatic tumors via the phosphatase and tensin homolog/protein kinase B signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 267–275. [Google Scholar]
- Chuturgoon, A.A.; Phulukdaree, A.; Moodley, D. Fumonisin B1 modulates expression of human cytochrome P450 1b1 in human hepatoma (Hepg2) cells by repressing Mir-27b. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 227, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, R.J.; Kallin, E.M.; Zhang, Y. JmjC-domain-containing proteins and histone demethylation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidder, B.L.; Hu, G.; Zhao, K. KDM5B focuses H3K4 methylation near promoters and enhancers during embryonic stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Hong, L.; Xu, X.; Huang, S.; Herpai, D.; Li, L.; Xu, Y.; Truong, L.; Hu, W.Y.; Wu, X.; et al. miR-30 disrupts senescence and promotes cancer by targeting both p16 (INK4A) and DNA damage pathways. Oncogene 2018, 37, 5618–5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvano, F.; Russo, A.; Cardile, V.; Galvano, G.; Vanella, A.; Renis, M. DNA damage in human fibroblasts exposed to fumonisin B1. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2002, 40, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockmann-Juvala, H.; Mikkola, J.; Naarala, J.; Loikkanen, J.; Elovaara, E.; Saolainen, K. Fumonisin B1-induced toxicity and oxidative damage in U-118MG glioblastoma cells. Toxicology 2004, 202, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domijan, A.M.; Abramov, A.Y. Fumonisin B1 inhibits mitochondrial respiration and deregulates calcium homeostasis--implication to mechanism of cell toxicity. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mary, V.S.; Theumer, M.G.; Arias, S.L.; Rubinstein, H.R. Reactive oxygen species sources and biomolecular oxidative damage induced by aflatoxin B1 and fumonisin B1 in rat spleen mononuclear cells. Toxicology 2012, 302, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, T.; Pillay, Y.; Ghazi, T.; Nagiah, S.; Abdul, N.S.; Chuturgoon, A.A. Fumonisin B 1-induced oxidative stress triggers Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cells. Mycotoxin Res. 2019, 35, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.; Rinker, L.; Peng, J.; Chilian, W. Reactive Oxygen Species: The Good and the Bad. React. Oxyg. Species Living Cells 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, V.; Darroudi, F.; Uhl, M.; Steinkellner, H.; Zsivkovits, M.; Knasmueller, S. Fumonisin B1 is genotoxic in human derived hepatoma (HepG2) cells. Mutagenesis 2002, 17, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domijan, A.-M.; Želježić, D.; Milić, M.; Peraica, M. Fumonisin B1: Oxidative status and DNA damage in rats. Toxicology 2007, 232, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Larranaga, M.R.; Anadon, A.; Anadon, A.; Diaz, M.J.; Fernandez-Cruz, M.L.; Martinez, M.A.; Frejo, M.T.; Martinez, M.; Fernandez, R.; Anton, R.M.; et al. Toxicokinetics and oral bioavailability of fumonisin B1. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 1999, 41, 357–362. [Google Scholar]
- Kammerer, S.; Küpper, J.-H. Human hepatocyte systems for in vitro toxicology analysis. J. Cell Biotechnol. 2018, 3, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Braver-Sewradj, S.P.; den Braver, M.W.; Vermeulen, N.P.; Commandeur, J.N.; Richert, L.; Vos, J.C. Inter-donor variability of phase I/phase II metabolism of three reference drugs in cryopreserved primary human hepatocytes in suspension and monolayer. Toxicol. Vitr. 2016, 33, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Seo, J.E.; Li, X.; Mei, N. Genetic toxicity assessment using liver cell models: Past, present, and future. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2020, 23, 27–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearfield, K.L.; Jacobson-Kram, D.; Brown, N.A.; Williams, J.R. Evaluation of a human hepatoma cell line as a target cell in genetic toxicology. Mutat. Res. 1983, 108, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knasmüller, S.; Mersch-Sundermann, V.; Kevekordes, S.; Darroudi, F.; Huber, W.W.; Hoelzl, C.; Bichler, J.; Majer, B.J. Use of human-derived liver cell lines for the detection of environmental and dietary genotoxicants; current state of knowledge. Toxicology 2004, 198, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.-Z.; Xu, Z.; Liang, Y.L.; Su, J.M.; Li, Z.X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.Y.; Zha, X.L. Down-regulation of PTEN expression due to loss of promoter activity in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feoktistova, M.; Geserick, P.; Leverkus, M. Crystal violet assay for determining viability of cultured cells. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2016, 2016, pdb-prot087379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Loon, B.; Markkanen, E.; Hubscher, U. Oxygen as a friend and enemy: How to combat the mutational potential of 8-oxo-guanine. DNA Repair 2010, 9, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.C.; Cahill, D.S.; Kasai, H.; Nishimura, S.; Loeb, L.A. 8-Hydroxyguanine, an abundant form of oxidative DNA damage, causes G----T and A----C substitutions. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Irani, S.; Hussain, M.M. Role of microRNA-30c in lipid metabolism, adipogenesis, cardiac remodeling and cancer. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2015, 26, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, K.; Sharma, A.K.; Ward, A.; Will, R.; Hielscher, T.; Balwierz, A.; Breuing, C.; Munstermann, E.; Konig, R.; Keklikoglou, L.; et al. MicroRNA-30c-2-3p negatively regulates NF-kappaB signaling and cell cycle progression through downregulation of TRADD and CCNE1 in breast cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 1106–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, M.; Peng, Y.; Hu, X.; Xu, J.; Zhu, S.; Yu, Z.; Han, S. miR-30c regulates proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation via the Shh signaling pathway in P19 cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yekta, S.; Shih, I.-h.; Bartel, D.P. MicroRNA-Directed Cleavage of HOXB8 mRNA. Science 2004, 304, 594–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathonnet, G.; Fabian, M.R.; Svitkin, Y.V.; Parsyan, A.; Huck, L.; Murata, T.; Biffo, S.; Merrick, W.C.; Darzynkiewicz, E.; Pillai, R.S. MicroRNA Inhibition of Translation Initiation in Vitro by Targeting the Cap-Binding Complex eIF4F. Science 2007, 317, 1764–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia-Sanchez, M.A.; Liu, J.; Hannon, G.J.; Parker, R. Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and siRNAs. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellanda, H.; Forges, T.; Bressenot, A.; Chango, A.; Bronowicki, J.P.; Guéant, J.L.; Namour, F. Fumonisin FB 1 treatment acts synergistically with methyl donor deficiency during rat pregnancy to produce alterations of H 3-and H 4-histone methylation patterns in fetuses. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancak, D.; Ozden, S. Global histone modifications in fumonisin B1 exposure in rat kidney epithelial cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2015, 29, 1809–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, N.M.; Riley, R.T.; Showker, J.L.; Voss, K.A.; Sachs, A.J.; Maddox, J.R.; Gelineau-van Waes, J.B. Elevated nuclear sphingoid base-1-phosphates and decreased histone deacetylase activity after fumonisin B1 treatment in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2016, 298, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, M.G.; Levine, S.S.; Boyer, L.A.; Jaenisch, R.; Young, R.A. A chromatin landmark and transcription initiation at most promoters in human cells. Cell 2007, 130, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barski, A.; Cuddapah, S.; Cui, K.; Roh, T.Y.; Schones, D.E.; Wang, Z.; Wei, G.; Chepelev, I.; Zhao, K. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell 2007, 129, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantley, L.C.; Neel, B.G. New insights into tumor suppression: PTEN suppresses tumor formation by restraining the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 4240–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, F.W.; Skeen, J.; Hay, N.; Shtivelman, E. Inhibition of Chk1 by activated PKB/Akt. Cell Cycle 2004, 3, 632–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, E.S.; Skeen, J.; Majewski, N.; Di Cristofano, A.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Feliciano, C.S.; Gartel, A.; Hay, N. Activation of Akt/protein kinase B overcomes a G2/M cell cycle checkpoint induced by DNA damage. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 22, 7831–7841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonic, I.; Yu, W.N.; Park, Y.; Chen, C.C.; Hay, N. Akt activation emulates Chk1 inhibition and Bcl2 overexpression and abrogates G2 cell cycle checkpoint by inhibiting BRCA1 foci. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 23790–23798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shtivelman, E.; Sussman, J.; Stokoe, D. A role for PI3K and PKB activity in the G2/M phase of the cell cycle. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Norred, W.P.; Bacon, C.W.; Riley, R.T.; Merrill, A.H. Inhibition of sphingolipid biosynthesis by fumonisins. Implications for diseases associated with Fusarium moniliforme. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 14486–14490. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, K.M.; Scheid, M.P.; Duronio, V. Ceramide Inhibits Protein Kinase B/Akt by Promoting Dephosphorylation of Serine 473. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 13330–13335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zundel, W.; Giaccia, A. Inhibition of the anti-apoptotic PI K/Akt/Bad pathway by stress. Genes Devel. 1998, 12, 1941–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Ruiz, M.; Lee, M.J.; Zöllner, S.; Gratton, J.P.; Scotland, R.; Shiojima, I.; Walsh, K.; Hla, T.; Sessa, W.C. Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Activates Akt, Nitric Oxide Production, and Chemotaxis through a GiProtein/Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Pathway in Endothelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 19672–19677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Gunasekera, A.H.; Sowin, T.J.; Rosenberg, S.H.; Fesik, S.; Zhang, H. Chk1 mediates S and G2 arrests through Cdc25A degradation in response to DNA-damaging agents. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 21767–21773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uto, K.; Inoue, D.; Shimauta, K.; Nakajo, N.; Sagata, N. Chk1, but not Chk2, inhibits Cdc25 phosphatases by a novel common mechanism. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 3386–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobio, T.A.; Anane, R.; Baudrimont, I.; Carratú, M.R.; Shier, T.W.; Dano, S.D.; Ueno, Y.; Creppy, E.E. Epigenetic properties of fumonisin B1: Cell cycle arrest and DNA base modification in C6 glioma cells. Toxicol. App. Pharmacol. 2000, 164, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramljak, D.; Calvert, R.; Wiesenfeld, P.; Diwan, B.; Catipovic, B.; Marasas, W.; Victor, T.; Anderson, L.; Gelderblom, W. A potential mechanism for fumonisin B1-mediated hepatocarcinogenesis: Cyclin D1 stabilization associated with activation of Akt and inhibition of GSK-3β activity. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 1537–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, S.-K.; Liu, S.; Yang, L.G.; Shi, R.F.; Sun, G.J. Effect of fumonisin B1 on the cell cycle of normal human liver cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 1970–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattson, M.P. Hormesis defined. Ageing Res. Rev. 2008, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazi, T.; Nagiah, S.; Naidoo, P.; Chuturgoon, A.A. Fusaric acid-induced promoter methylation of DNA methyltransferases triggers DNA hypomethylation in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cells. Epigenetics 2019, 14, 804–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| KDM5B | 55 | Sense | 5′-CGA CAA AGC CAA GAG TCT CC-3′ |
| Anti-sense | 5′-CTG CCG TAG CAA GGC TATTC-3 | ||
| PTEN | 56.6 | Sense | 5′-TTT GAA GAC CAT AAC CCA CCA C-3′ |
| Anti-sense | 5′-ATT ACA CCA GTT CGT CCC TTT C-3′ | ||
| AKT1 | 55 | Sense | 5′-GCC TGG GTC AAA GAA GTC AA-3′ |
| Anti-sense | 5′-CAT CCC TCC AAG CTA TCG TC-3′ | ||
| CHK1 | 59.1 | Sense | 5′-CCA GAT GCT CAG AGA TTC TTC CA-3′ |
| Anti-sense | 5′-TGT TCAACA AAC GCT CAC GAT TA-3′ | ||
| GAPDH | Same as gene of interest | Sense | 5′-TCCACCACCCTGTTGCTGTA-3′ |
| Anti-sense | 5′-ACCACAGTCCATGCCATCAC-3′ |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arumugam, T.; Ghazi, T.; Chuturgoon, A. Fumonisin B1 Epigenetically Regulates PTEN Expression and Modulates DNA Damage Checkpoint Regulation in HepG2 Liver Cells. Toxins 2020, 12, 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12100625
Arumugam T, Ghazi T, Chuturgoon A. Fumonisin B1 Epigenetically Regulates PTEN Expression and Modulates DNA Damage Checkpoint Regulation in HepG2 Liver Cells. Toxins. 2020; 12(10):625. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12100625
Chicago/Turabian StyleArumugam, Thilona, Terisha Ghazi, and Anil Chuturgoon. 2020. "Fumonisin B1 Epigenetically Regulates PTEN Expression and Modulates DNA Damage Checkpoint Regulation in HepG2 Liver Cells" Toxins 12, no. 10: 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12100625
APA StyleArumugam, T., Ghazi, T., & Chuturgoon, A. (2020). Fumonisin B1 Epigenetically Regulates PTEN Expression and Modulates DNA Damage Checkpoint Regulation in HepG2 Liver Cells. Toxins, 12(10), 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12100625





