Effect of Zinc on Microcystis aeruginosa UTEX LB 2385 and Its Toxin Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
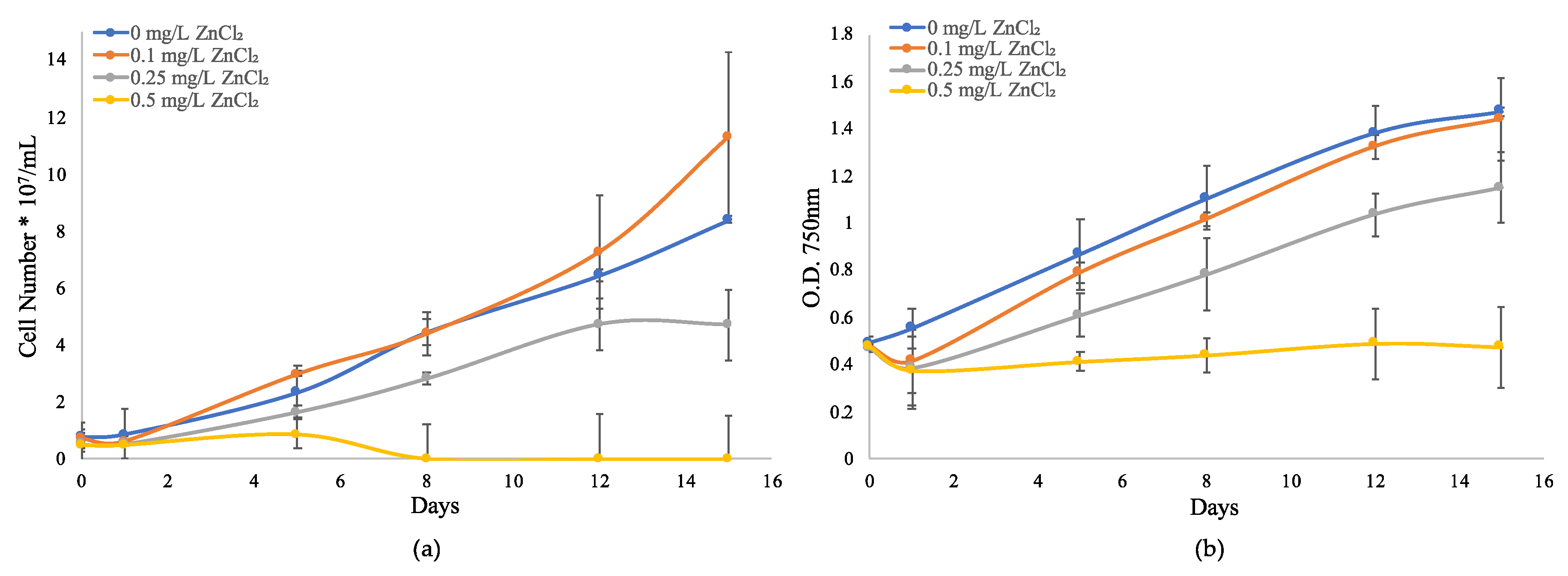
2.1. Growth Response to ZnCl2 in M. Aeruginosa UTEX LB 2385
2.2. Phase Contrast Microscopy Imaging in ZnCl2 Exposed Cells
2.3. Flow Cytometry
2.4. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) Analysis of M. Aeruginosa UTEX LB 2385
2.5. ELISA Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Growth Monitoring
5.2. Experimental Design
5.3. Phase Contrast Microscopy
5.4. Flow Cytometry
5.5. Total RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
5.6. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
5.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
5.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cassier-Chauvat, C.; Chauvat, F. Responses to Oxidative and Heavy Metal Stresses in Cyanobacteria: Recent Advances. IJMS 2014, 16, 871–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Neil, J.M.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Gobler, C.J. The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: The potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Fulton, R.S.; Moisander, P.H.; Dyble, J. Harmful Freshwater Algal Blooms, With an Emphasis on Cyanobacteria. Sci. World J. 2001, 1, 76–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Hall, N.S.; Calandrino, E.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a world experiencing anthropogenic and climatic-induced change. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patidar, S.K.; Chokshi, K.; George, B.; Bhattacharya, S.; Mishra, S. Dominance of cyanobacterial and cryptophytic assemblage correlated to CDOM at heavy metal contamination sites of Gujarat, India. Environ. Monit. Assess 2015, 187, 4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, P.M.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Sandrini, G.; Stal, L.J.; Matthijs, H.C.P.; Davis, T.W.; Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. How rising CO2 and global warming may stimulate harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, Y.; Chen, W.; Zuo, Y.; Lin, L.; Song, L. Heavy metal migration and risk transference associated with cyanobacterial blooms in eutrophic freshwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 1324–1330. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969717325317?via%3Dihub (accessed on 20 December 2019). [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, M.; Chua, T.T.; Chew, C.Y.; Bryant, D.A. Fur-type transcriptional repressors and metal homeostasis in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Ruiz, E.B.; Martínez-Jerónimo, F. How do toxic metals affect harmful cyanobacteria? An integrative study with a toxigenic strain of Microcystis aeruginosa exposed to nickel stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 133, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyak, Y.; Zaytseva, T.; Medvedeva, N. Response of Toxic Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa to Environmental Pollution. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Xuan, Y.; Hu, T. Effects and control of metal nutrients and species on Microcystis aeruginosa growth and bloom. Water Environ. Res. 2019, 91, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, M.Y.; Liang, S.; Lee, J. Toxin-producing cyanobacteria in freshwater: A review of the problems, impact on drinking water safety, and efforts for protecting public health. J. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Rodas, V.; Maneiro, E.; Lanzarot, M.P.; Perdigones, N.; Costas, E. Mass wildlife mortality due to cyanobacteria in the Donana National Park, Spain. Vet Rec. 2008, 162, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codd, G.; Bell, S.; Kaya, K.; Ward, C.; Beattie, K.; Metcalf, J. Cyanobacterial toxins, exposure routes and human health. Eur. J. Phycol. 1999, 34, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitzfeld, B.C.; Hoger, S.J.; Dietrich, D.R. Cyanobacterial toxins: Removal during drinking water treatment, and human risk assessment. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Otten, T.G.; Paerl, H.W. Health Effects of Toxic Cyanobacteria in U.S. Drinking and Recreational Waters: Our Current Understanding and Proposed Direction. Curr. Envir. Health Rpt. 2015, 2, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carmichael, W.W. Cyanobacteria secondary metabolites-the cyanotoxins. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1992, 72, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmann, E.; Fewer, D.P.; Neilan, B.A. Cyanobacterial toxins: biosynthetic routes and evolutionary roots. Fems. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, W.W.; Azevedo, S.M.; An, J.S.; Molica, R.J.; Jochimsen, E.M.; Lau, S.; Rinehart, K.L.; Shaw, G.R.; Eaglesham, G.K. Human fatalities from cyanobacteria: chemical and biological evidence for cyanotoxins. Envrion. Health Perspect 2001, 109, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanseverino, I.; Conduto, D.; Pozzoli, L.; Dobricic, S.; Lettieri, T.; European, C.; Joint Research, C. Algal Bloom and Its Economic Impact; JRC Science Hub: Ispra, Italy, 2016; Volume 52, Available online: https://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/bitstream/JRC101253/lbna27905enn.pdf. (accessed on 20 December 2019).
- Dodds, W.K.; Bouska, W.W.; Eitzmann, J.L.; Pilger, T.J.; Pitts, K.L.; Riley, A.J.; Schloesser, J.T.; Thornbrugh, D.J. Eutrophication of U.S. Freshwaters: Analysis of Potential Economic Damages. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chorus, I.; Falconer, I.R.; Salas, H.J.; Bartram, J. Health risks caused by freshwater cyanobacteria in recreational waters. J. Toxicol Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2000, 3, 323–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Anglada, L.V. Editorial on the special issue “harmful algal blooms (HABs) and public health: progress and current challenges”. Toxins (Basel) 2015, 7, 4437–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, T.W.; Berry, D.L.; Boyer, G.L.; Gobler, C.J. The effects of temperature and nutrients on the growth and dynamics of toxic and non-toxic strains of Microcystis during cyanobacteria blooms. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziallas, C.; Grossart, H.P. Increasing oxygen radicals and water temperature select for toxic Microcystis sp. PloS ONE 2011, 6, e25569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Gremberghe, I.; Leliaert, F.; Mergeay, J.; Vanormelingen, P.; Van der Gucht, K.; Debeer, A.E.; Lacerot, G.; De Meester, L.; Vyverman, W. Lack of phylogeographic structure in the freshwater cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa suggests global dispersal. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mlouka, A.; Comte, K.; Castets, A.M.; Bouchier, C.; Tandeau de Marsac, N. The gas vesicle gene cluster from Microcystis aeruginosa and DNA rearrangements that lead to loss of cell buoyancy. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 2355–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mlouka, A.; Comte, K.; Tandeau de Marsac, N. Mobile DNA elements in the gas vesicle gene cluster of the planktonic cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa. Fems. Microbiol Lett. 2004, 237, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-X.; Gan, N.-Q.; Huang, Q.; Song, L.-R. Response of Microcystis to copper stress – Do phenotypes of Microcystis make a difference in stress tolerance? Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Rzymski, P. Programmed Cell Death-Like and Accompanying Release of Microcystin in Freshwater Bloom-Forming Cyanobacterium Microcystis: From Identification to Ecological Relevance. Toxins (Basel) 2019, 11, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oksanen, I.; Lohtander, K.; Sivonen, K.; Rikkinen, J. Repeat-type distribution in trnL intron does not correspond with species phylogeny: comparison of the genetic markers 16S rRNA and trnL intron in heterocystous cyanobacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atencio, L.; Moreno, I.; Jos, A.; Prieto, A.I.; Moyano, R.; Blanco, A.; Camean, A.M. Effects of dietary selenium on the oxidative stress and pathological changes in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to a microcystin-producing cyanobacterial water bloom. Toxicon 2009, 53, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidi, A.; Esterhuizen-Londt, M.; Pflugmacher, S. Still challenging: the ecological function of the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin – What we know so far. Toxin Rev. 2018, 37, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeung, A.C.Y.; D’Agostino, P.M.; Poljak, A.; McDonald, J.; Bligh, M.W.; Waite, T.D.; Neilan, B.A. Physiological and Proteomic Responses of Continuous Cultures of Microcystis aeruginosa PCC 7806 to Changes in Iron Bioavailability and Growth Rate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5918–5929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gasperi, J.; Garnaud, S.; Rocher, V.; Moilleron, R. Priority pollutants in wastewater and combined sewer overflow. Sci. Total Enviorn. 2008, 407, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakson, G.; Brzezinska, A.; Zawilski, M. Emission of heavy metals from an urban catchment into receiving water and possibility of its limitation on the example of Lodz city. Enviorn. Monit. Assess 2018, 190, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandstead, H.H.; Au, W. Zinc. In Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals; Nordberg, G.F., Fowler, B.A., Nordberg, M., Friberg, L.T., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 925–947. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/book/9780444594532/handbook-on-the-toxicology-of-metals (accessed on 20 December 2019).
- Martin, G.D.; George, R.; Shaiju, P.; Muraleedharan, K.R.; Nair, S.M.; Chandramohanakumar, N. Toxic Metals Enrichment in the Surficial Sediments of a Eutrophic Tropical Estuary (Cochin Backwaters, Southwest Coast of India). Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- USEPA; USACE; USDOE-BNL. Fast Track Dredged Material Decontamination Demonstration for the Port of New York and New Jersey; USEPA: Springfield, VA, USA, 1999; Volume 65. Available online: https://www.nj.gov/dep/passaicdocs/docs/NJDOTSupportingCosts/DECON-REPORT-EPA-FastTrkDredgedMatDeconDemoPortNYNJ1999.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2019).
- Hemalatha, S.; Banerjee, T.K. Histopathological analysis of sublethal toxicity of zinc chloride to the respiratory organs of the airbreathing catfish Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch). Biol. Res. 1997, 30, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Salvaggio, A.; Marino, F.; Albano, M.; Pecoraro, R.; Camiolo, G.; Tibullo, D.; Bramanti, V.; Lombardo, B.M.; Saccone, S.; Mazzei, V.; et al. Toxic Effects of Zinc Chloride on the Bone Development in Danio rerio (Hamilton, 1822). Front Physiol. 2016, 7, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roney, N.; Smith, C.V.; Williams, M.; Osier, M.; Paikoff, S.J. Toxicological Profile for Zinc. ATSDR, 2005; p. 352. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp60.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2019).
- Chu, T.-C.; Murray, S.R.; Todd, J.; Perez, W.; Yarborough, J.R.; Okafor, C.; Lee, L.H. Adaption of Synechococcus sp. IU 625 to growth in the presence of mercuric chloride. Acta Histochem. 2012, 114, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dudkowiak, A.; Olejarz, B.; Łukasiewicz, J.; Banaszek, J.; Sikora, J.; Wiktorowicz, K. Heavy Metals Effect on Cyanobacteria Synechocystis aquatilis Study Using Absorption, Fluorescence, Flow Cytometry, and Photothermal Measurements. Int. J. Thermophys 2011, 32, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morby, A.P.; Turner, J.S.; Huckle, J.W.; Robinson, N.J. SmtB is a metal-dependent repressor of the cyanobacterial metallothionein gene smtA: identification of a Zn inhibited DNA-protein complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pochodylo, A.L.; Klein, A.R.; Aristilde, L. Metal-binding selectivity and coordination dynamics for cyanobacterial microcystins with Zn, Cu, Fe, Mg, and Ca. Environ. Chem Lett. 2017, 15, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capdevila, M.; Atrian, S. Metallothionein protein evolution: A miniassay. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 16, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.-C.; de Francisco, P.; Amaro, F.; Díaz, S.; Martín-González, A. Structural and Functional Diversity of Microbial Metallothionein Genes. In Microbial Diversity in the Genomic Era; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 387–407. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128148495000228?via%3Dihub (accessed on 20 December 2019).
- Liu, T.; Nakashima, S.; Hirose, K.; Uemura, Y.; Shibasaka, M.; Katsuhara, M.; Kasamo, K. A metallothionein and CPx-ATPase handle heavy-metal tolerance in the filamentous cyanobacterium Oscillatoria brevis. Febs. Lett. 2003, 542, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newby, R.; Lee, L.H.; Perez, J.L.; Tao, X.; Chu, T. Characterization of zinc stress response in Cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. IU 625. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 186, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikalsen, B.; Boison, G.; Skulberg, O.M.; Fastner, J.; Davies, W.; Gabrielsen, T.M.; Rudi, K.; Jakobsen, K.S. Natural Variation in the Microcystin Synthetase Operon mcyABC and Impact on Microcystin Production in Microcystis Strains. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 2774–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pacheco, A.; Guedes, I.; Azevedo, S. Is qPCR a Reliable Indicator of Cyanotoxin Risk in Freshwater? Toxins 2016, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiu, Y.-T.; Chen, Y.-H.; Wang, T.-S.; Yen, H.-K.; Lin, T.-F. A qPCR-Based Tool to Diagnose the Presence of Harmful Cyanobacteria and Cyanotoxins in Drinking Water Sources. Ijerph 2017, 14, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallinder, I.O.; Leygraf, C. A Critical Review on Corrosion and Runoff from Zinc and Zinc-Based Alloys in Atmospheric Environments. Corrosion 2017, 73, 1060–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, R.; Guerrero, F.; Delgado, D.; Araya, R. Atmospheric Corrosion of Galvanized Steel and Precipitation Runoff from Zinc in a Marine Environment. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2013, ,24, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Luo, G.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Gao, B.; He, X. Integrated Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination in Sediments from a Coastal Industrial Basin, NE China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surosz, W.; Palinska, K.A. Effects of Heavy-Metal Stress on Cyanobacterium Anabaena flos-aquae. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol 2004, 48, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Juneau, P.; Qiu, B. Growth and photosynthetic responses of the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa to elevated levels of cadmium. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 1738–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, W.X. Cadmium and zinc uptake and toxicity in two strains of Microcystis aeruginosa predicted by metal free ion activity and intracellular concentration. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 91, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouvêa, S.P.; Boyer, G.L.; Twiss, M.R. Influence of ultraviolet radiation, copper, and zinc on microcystin content in Microcystis aeruginosa (Cyanobacteria). Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzymski, P.; Poniedzialek, B.; Niedzielski, P.; Tabaczewski, P.; Wiktorowicz, K. Cadmium and lead toxicity and bioaccumulation in Microcystis aeruginosa. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2014, 8, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, D.; Pan, X. Effects of arsenic on growth and photosystem II (PSII) activity of Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 84, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Li, M.; Reynolds, C.S. Colony formation in the cyanobacterium Microcystis. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2018, 93, 1399–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ybarra, G.R.; Webb, R. Effects of Divalent Metal Cations and Resistance Mechanisms of the Cyanobacterium Synechococcus SP. Strain PCC 7942. J. Hazard. Subst. Res. 1999, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tillett, D.; Dittmann, E.; Erhard, M.; von Döhren, H.; Börner, T.; Neilan, B.A. Structural organization of microcystin biosynthesis in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806: an integrated peptide–polyketide synthetase system. Chem. Biol. 2000, 7, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaebernick, M.; Neilan, B.A. Ecological and molecular investigations of cyanotoxin production. Fems Microbiol. Ecol. 2001, 35, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Kong, F.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Z.; Shi, X.; Du, M. The Dynamics of Microcystis Genotypes and Microcystin Production and Associations with Environmental Factors during Blooms in Lake Chaohu, China. Toxins 2014, 6, 3238–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Lin, L.; Shen, G.; Li, M. Heavy-metal pollution alters dissolved organic matter released by bloom-forming Microcystis aeruginosa. Rsc. Adv. 2017, 7, 18421–18427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gan, N.; Xiao, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wu, Z.; Liu, J.; Hu, C.; Song, L. The role of microcystins in maintaining colonies of bloom-forming Microcystis spp.: Microcystis colony maintenance by microcystins. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 730–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohomovich, B.; Nguyen, B.T.; Quintanilla, M.; Lee, L.H.; Murray, S.R.; Chu, T.-C. Physiological effects of nickel chloride on the freshwater cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. IU 625. ABB 2013, 04, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babu, N.G.; Sarma, P.A.; Attitalla, I.H.; Murthy, S.D.S. Effect of Selected Heavy Metal Ions on the Photosynthetic Electron Transport and Energy Transfer in the Thylakoid Membrane of the Cyanobacterium, Spirulina platensis. Acad. J. Plant. Sci 2010, 3, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Khattar, J.I.S.; Sarma, T.A.; Sharma, A. Effect of Cr6+ Stress on Photosynthetic Pigments and Certain Physiological Processes in the Cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans and Its Chromium Resistant Strain. J. Microbiol Biotech. 2004, 14, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar]
- Spoof, L.; Vesterkvist, P.; Lindholm, T.; Meriluoto, J. Screening for cyanobacterial hepatotoxins, microcystins and nodularin in environmental water samples by reversed-phase liquid chromatography-electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr A 2003, 1020, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perez, J.L.; Chu, T. Effect of Zinc on Microcystis aeruginosa UTEX LB 2385 and Its Toxin Production. Toxins 2020, 12, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020092
Perez JL, Chu T. Effect of Zinc on Microcystis aeruginosa UTEX LB 2385 and Its Toxin Production. Toxins. 2020; 12(2):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020092
Chicago/Turabian StylePerez, Jose L., and Tinchun Chu. 2020. "Effect of Zinc on Microcystis aeruginosa UTEX LB 2385 and Its Toxin Production" Toxins 12, no. 2: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020092
APA StylePerez, J. L., & Chu, T. (2020). Effect of Zinc on Microcystis aeruginosa UTEX LB 2385 and Its Toxin Production. Toxins, 12(2), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020092




