Individual and Combined Effect of Zearalenone Derivates and Beauvericin Mycotoxins on SH-SY5Y Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
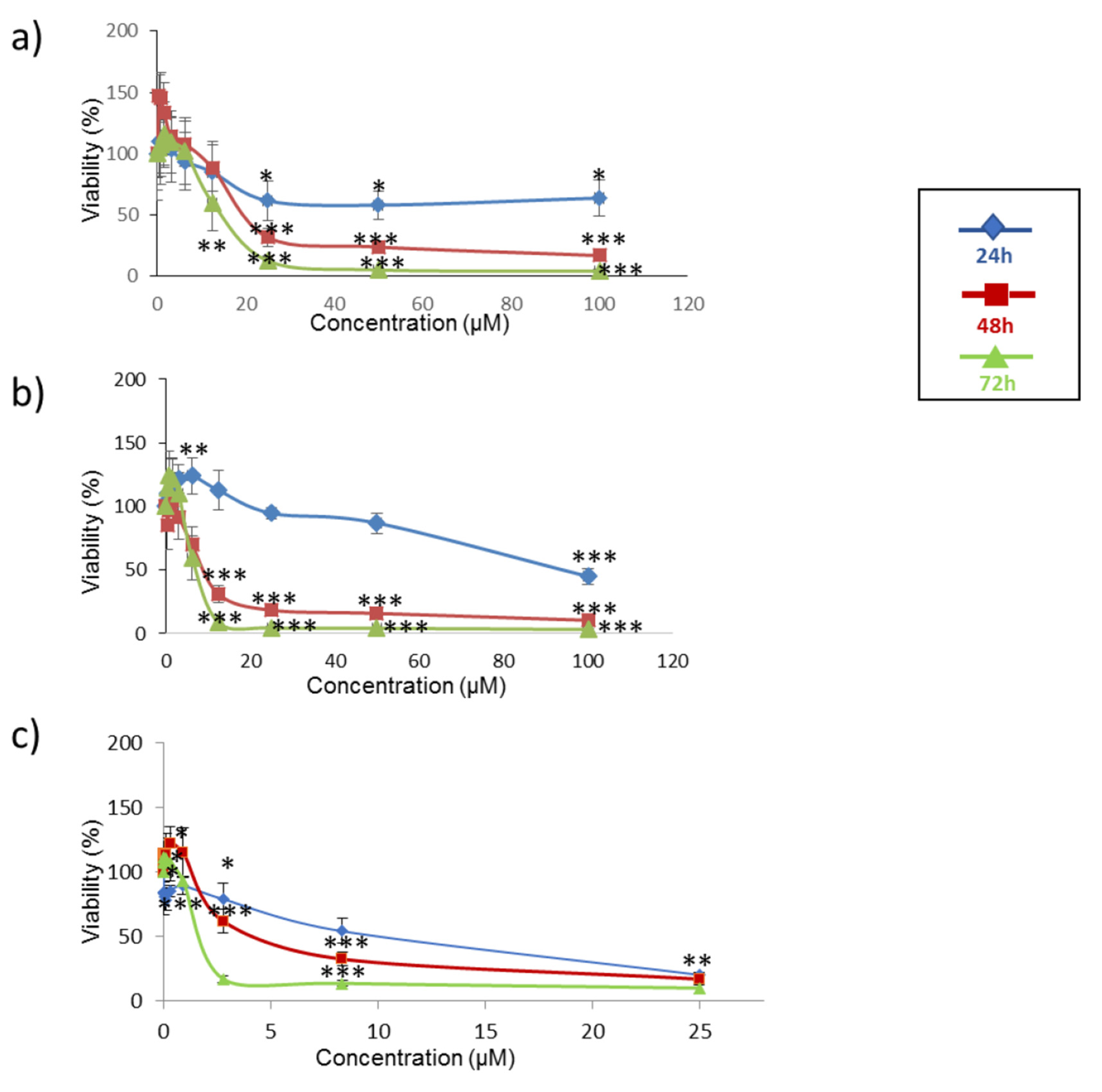
2.1. Cytotoxicity Assay of Individual and Combined Mycotoxins
2.2. α-ZEL, β-ZEL, and BEA Present in Cell Medium after Treatment in Binary and Tertiary Combination
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Reagents
5.2. Cell Culture
5.3. Mycotoxin Exposure
5.4. MTT Assay
5.5. Experimental Design and Combination Index
5.6. Extraction of α-ZEL, β-ZEL, and BEA from the Culture Media
5.7. Determination of BEA, β-ZEL, and α-ZEL by LC–ESI–qTOF-MS
5.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zain, M.E. Impact of mycotoxins on humans and animals. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2011, 15, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mally, A.; Solfrizzo, M.; Degen, G.H. Volume Biomonitoring of the mycotoxin Zearalenone: Current state-of-the art and application to human exposure assessment. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 1281–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, J.L. Some major mycotoxins and their mycotoxicoses—An overview. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 119, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hueza, I.M.; Raspantini, P.C.; Raspantini, L.E.; Latorre, A.O.; Górniak, S.L. Zearalenone, an estrogenic mycotoxin, is an immunotoxic compound. Toxins 2014, 6, 1080–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, M.; Tulayakul, P.; Li, J.-Y.; Dong, K.-S.; Manabe, N.; Kumagai, S. Metabolic Conversion of Zearalenone to α-Zearalenol by Goat Tissues. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2010, 72, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venkataramana, M.; Chandra Nayaka, S.; Anand, T.; Rajesh, R.; Aiyaz, M.; Divakara, S.T.; Murali, H.S.; Prakash, H.S.; Lakshmana Rao, P.V. Zearalenone induced toxicity in SHSY-5Y cells: The role of oxidative stress evidenced by N-acetyl cysteine. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 65, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajecka, M.; Zielonka, L.; Gajecki, M. The effect of low monotonic doses of zearalenone on selected reproductive tissues in pre-pubertal female dogs-a review. Molecules 2015, 20, 20669–20687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EFSA CONTAM Panel (EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain). Scientific opinion on the appropriateness to set a group health-based guidance value for zearalenone and its modified forms. EFSA J. 2016, 14, 4425. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.J.; Wei, Z.K.; Han, Z.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhu, X.Y.; Li, X.W.; Wang, K.; Yang, Z.T. Zearalenone Induces Estrogen-Receptor-Independent Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Release in Vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4588–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Makawy, A.; Hassanane, M.S.; Abd Alla, E.S.A.M. Genotoxic evaluation for the estrogenic mycotoxin zearalenone. Reprod. Nutr. Dev 2001, 41, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid-Essefi, S.; Baudrimont, I.; Hassen, W.; Ouanes, Z.; Mobio, T.A.; Anane, R.; Creppy, E.E.; Bacha, H. DNA fragmentation, apoptosis and cell cycle arrest induced by zearalenone in cultured DOK, Vero and Caco-2 cells: Prevention by Vitamin E. Toxicology 2003, 192, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Pan, S.; Feng, N.; Zou, H.; Gu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Bian, J. Zearalenone inhibits T cell chemotaxis by inhibiting cell adhesion and migration related proteins. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2019, 175, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassen, W.; El Golli, E.; Baudrimont, I.; Mobio, A.T.; Ladjimi, M.M.; Creppy, E.E.; Bacha, H. Cytotoxicity and Hsp70 induction in HepG2 cells in response to zearalenone and cytoprotection by sub-lethal heat shock. Toxicology 2005, 207, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosperini, A.; Juan-García, A.; Font, G.; Ruiz, M.J. Beauvericin induced cytotoxicity via ROS production and mitochondrial damage in Caco-2 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 222, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Tan, X.; Li, Y.; Liang, G.; Ning, Z.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y. Transcriptional profiling analysis of Zearalenone-induced inhibition proliferation on mouse thymic epithelial cell line 1. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2018, 153, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouaoui, N.; Mallebrera, B.; Berrada, H.; Abid-Essefi, S.; Bacha, H.; Ruiz, M.J. Cytotoxic effects induced by patulin, sterigmatocystin and beauvericin on CHO–K1 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 89, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan-García, A.; Tolosa, J.; Juan, C.; Ruiz, M.J. Cytotoxicity, Genotoxicity and Disturbance of Cell Cycle in HepG2 Cells Exposed to OTA and BEA: Single and Combined Actions. Toxins 2019, 11, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrer, E.; Juan-García, A.; Font, G.; Ruiz, M.J. Reactive oxygen species induced by beauvericin, patulin and zearalenone in CHO-K1 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2009, 23, 1504–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallebrera, B.; Font, G.; Ruiz, M.J. Disturbance of antioxidant capacity produced by beauvericin in CHO-K1 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 226, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockmann-Juvala, H.; Mikkola, J.; Naarala, J.; Loikkanen, J.; Elovaara, E.; Savolainen, K. Oxidative stress induced by fumonisin B1 in continuous human and rodent neural cell cultures. Free Radic. Res. 2004, 38, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Boesch-Saadatmandi, C.; Lou, Y.; Wolffram, S.; Huebbe, P.; Rimbach, G. Ochratoxin A induces apoptosis in neuronal cells. Genes Nutr. 2009, 4, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zingales, V.; Fernández-Franzón, M.; Ruiz, M.J. Sterigmatocystin-induced cytotoxicity via oxidative stress induction in human neuroblastoma cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 110956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanciu, O.; Juan, C.; Miere, D.; Loghin, F.; Mañes, J. Occurrence and co-occurrence of Fusarium mycotoxins in wheat grains and wheat flour from Romania. Food Control. 2017, 73, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.; Berrada, H.; Mañes, J.; Oueslati, S. Multi-mycotoxin determination in barley and derived products from Tunisia and estimation of their dietary intake. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 103, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oueslati, S.; Berrada, H.; Mañes, J.; Juan, C. Presence of mycotoxins in Tunisian infant foods samples and subsequent risk assessment. Food Control. 2017, 84, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Guidance on harmonised methodologies for human health, animal health and ecological risk assessment of combined exposure to multiple chemicals. EFSA J. 2019, 17, 5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz, M.J.; Franzova, P.; Juan-García, A.; Font, G. Toxicological interactions between the mycotoxins beauvericin, deoxynivalenol and T-2 toxin in CHO-K1 cells in vitro. Toxicon 2011, 58, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan-García, A.; Juan, C.; König, S.; Ruiz, M.J. Cytotoxic effects and degradation products of three mycotoxins: Alternariol, 3-acetyl-deoxynivalenol and 15-acetyl-deoxynivalenol in liver hepatocelular carcinoma cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 235, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan-García, A.; Juan, C.; Manyes, L.; Ruiz, M.J. Binary and tertiary combination of alternariol, 3-acetyl-deoxynivalenol and 15-acetyl-deoxynivalenol on HepG2 cells: Toxic effects and evaluation of degradation products. Toxicol. In Vitro 2016, 34, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C.; Talalay, P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv. Enzyme Regul. 1984, 22, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C. Theoretical basis, experimental design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in drug combination studies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 621–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatay, E.; Meca, G.; Font, G.; Ruiz, M.J. Interactive effects of zearalenone and its metabolites on cytotoxicity and metabolization in ovarian CHO-K1 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2014, 28, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, D.E.; Pistol, G.C.; Bulgaru, C.V.; Taranu, I. Cytotoxic and inflammatory effects of individual and combined exposure of HepG2 cells to zearalenone and its metabolites. N-S. Arch. Pharmacol. 2019, 392, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, N.; Gao, Y.N.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.W.; Wang, J.Q. Individual and combined cytotoxicity assessment of zearalenone with ochratoxin A or α-zearalenol by full factorial design. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Wang, Q.; Wud, H.; Xiaa, S.; Guoa, H.; Blaženovićc, I.; Zhanga, Y.; Suna, X. Insights into cellular metabolic pathways of the combined toxicity responses of Caco-2 cells exposed to deoxynivalenol, zearalenone and Aflatoxin B1. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 126, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abid, S.; Bouaziz, C.E.; Golli-Bennour, E.; Ouanes Ben Othmen, Z.; Bacha, H. Comparative study of toxic effects of zearalenone and its two major metabolites α-zearalenol and β-zearalenol on cultured human Caco-2 cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxic. 2009, 23, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, M.J.; Festila, L.E.; Fernandez, M. Comparison of basal cytotoxicity of seven carbamates in CHO-K1 cells. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 88, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Mycotoxin | IC50 (µM) ± SD | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |
| α-ZEL | n.a | 20.8 ± 0.5 | 14.0 ± 1.8 |
| β-ZEL | 94.3 ± 2.0 | 9.1 ± 1.8 | 7.5 ± 1.2 |
| BEA | n.a | n.a | 2.5 ± 0.2 |
| Mycotoxin | Time (h) | Dm (µM) | m | r | IC Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | IC75 | CI90 | ||||||||
| α-ZEL | 24 | 66.10 | 1.36 | 0.9679 | ||||||
| 48 | 31.59 | 1.82 | 0.9726 | |||||||
| 72 | 15.24 | 2.02 | 0.9873 | |||||||
| β-ZEL | 24 | 171.33 | 1.28 | 0.9709 | ||||||
| 48 | 12.46 | 1.26 | 0.9715 | |||||||
| 72 | 11.65 | 2.28 | 0.9464 | |||||||
| BEA | 24 | 21.65 | 0.98 | 0.9763 | ||||||
| 48 | 3.68 | 1.24 | 0.9945 | |||||||
| 72 | 2.59 | 1.40 | 0.9805 | |||||||
| α-ZEL+BEA | 24 | 3.05 | 1.36 | 0.9736 | 0.37 ± 0.33 | Syn | 0.34 ± 0.35 | Syn | 0.31 ± 0.38 | Syn |
| 48 | 1.16 | 1.56 | 0.9933 | 0.50 ± 0.24 | Syn | 0.47 ± 0.26 | Syn | 0.44 ± 0.29 | Syn | |
| 72 | 1.34 | 1.54 | 0.94708 | 0.96 ± 0.86 | Add | 1.00 ± 0.51 | Add | 1.20 ± 1.30 | Ant | |
| β-ZEL+BEA | 24 | 3.78 | 1.20 | 0.9698 | 0.29 ± 0.19 | Syn | 0.26 ± 0.21 | Syn | 0.24 ± 0.24 | Syn |
| 48 | 4.81 | 3.04 | 0.7744 | 3.24 ± 0.42 | Ant | 1.94 ± 0.32 | Ant | 1.00 ± 0.14 | Add | |
| 72 | 1.89 | 3.14 | 0.7585 | 1.35 ± 0.51 | Ant | 1.00 ± 0.12 | Add | 0.60 ± 0.52 | Syn | |
| α-ZEL+β-ZEL | 24 | 133.46 | 1.73 | 0.7782 | 2.80 ± 1.01 | Ant | 2.32 ± 0.51 | Ant | 1.92 ± 0.62 | Ant |
| 48 | 19.12 | 3.40 | 0.7782 | 2.14 ± 0.23 | Ant | 1.35 ± 0.18 | Ant | 0.30 ± 0.14 | Syn | |
| 72 | 7.89 | 5.01 | 0.9409 | 2.60 ± 0.90 | Ant | 1.42 ± 0.63 | Ant | 0.45 ± 0.42 | Syn | |
| α-ZEL+β-ZEL+BEA | 24 | 3.74 | 3.14 | 0.9478 | 0.57 ± 0.30 | Syn | 0.32 ± 0.20 | Syn | 0.19 ± 0.14 | Syn |
| 48 | 0.01 | 0.43 | 0.7465 | 0.23 ± 0.06 | Syn | 0.15 ± 0.07 | Syn | 0.18 ± 0.10 | Syn | |
| 72 | 7.47 | 2.30 | 0.8966 | 8.54 ± 0.77 | Ant | 7.60 ± 0.85 | Ant | 6.88 ± 0.95 | Ant | |
| Combination Tested | Concentration Range (μM) |
|---|---|
| α-ZEL | (0.39–00) |
| β-ZEL | (0.39–100) |
| BEA | (0.009–25) |
| α-ZEL + BEA | (1.56–2.5) + (0.31–2.5) |
| β-ZEL + BEA | (1.56–2.5) + (0.31–2.5) |
| α-ZEL + β-ZEL | (1.56–12.5) + (1.56–12.5) |
| α-ZEL + β-ZEL + BEA | (1.56–12.5) + (1.56–12.5) + (0.31–2.5) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agahi, F.; Font, G.; Juan, C.; Juan-García, A. Individual and Combined Effect of Zearalenone Derivates and Beauvericin Mycotoxins on SH-SY5Y Cells. Toxins 2020, 12, 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12040212
Agahi F, Font G, Juan C, Juan-García A. Individual and Combined Effect of Zearalenone Derivates and Beauvericin Mycotoxins on SH-SY5Y Cells. Toxins. 2020; 12(4):212. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12040212
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgahi, Fojan, Guillermina Font, Cristina Juan, and Ana Juan-García. 2020. "Individual and Combined Effect of Zearalenone Derivates and Beauvericin Mycotoxins on SH-SY5Y Cells" Toxins 12, no. 4: 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12040212
APA StyleAgahi, F., Font, G., Juan, C., & Juan-García, A. (2020). Individual and Combined Effect of Zearalenone Derivates and Beauvericin Mycotoxins on SH-SY5Y Cells. Toxins, 12(4), 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12040212







