Shiga Toxin Selectively Upregulates Expression of Syndecan-4 and Adhesion Molecule ICAM-1 in Human Glomerular Microvascular Endothelium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
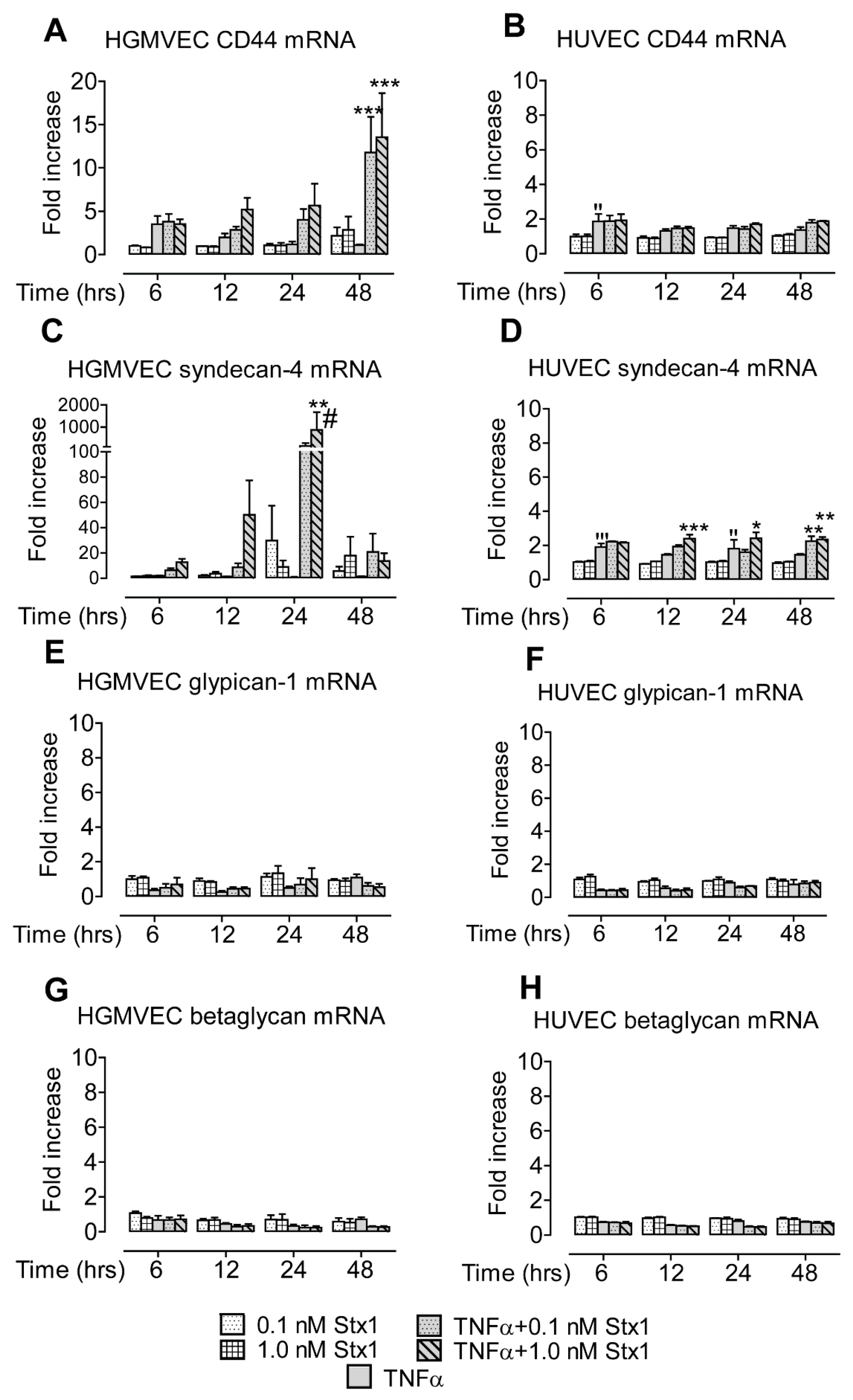
2.1. Stx1 Upregulates Syndecan-4 mRNA and Protein Expression in HGMVECs
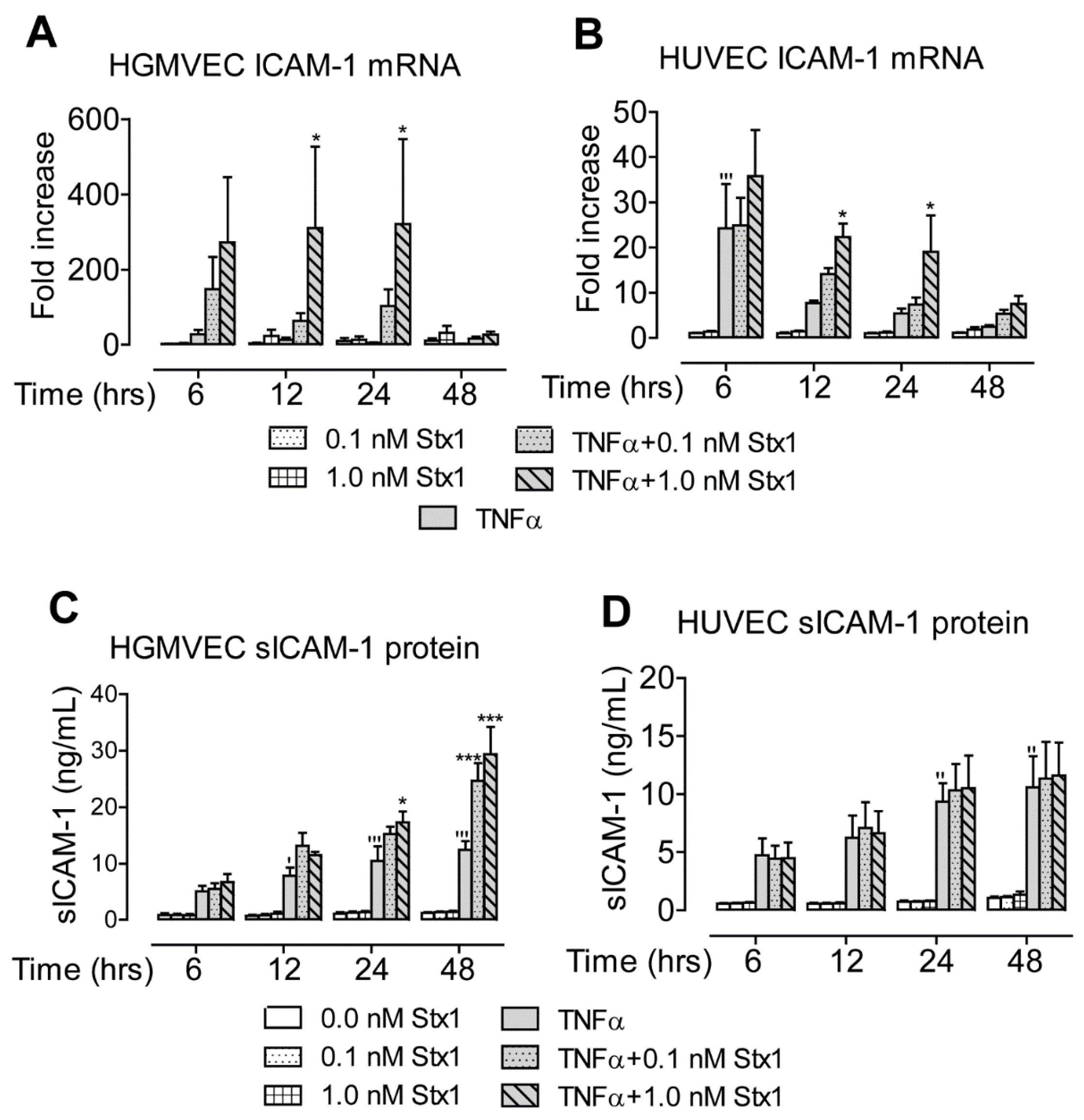
2.2. Stx1 Increases ICAM-1 mRNA Expression and Secretion in Primary HGMVECs
2.3. Stx1 Increases mRNA, but Not Protein Expression of Complement Component C3
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
4.3. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.4. Protein Analyses
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karpman, D.; Loos, S.; Tati, R.; Arvidsson, I. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 281, 123–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, C.; Remuzzi, G.; Noris, M. Hemolytic uremic syndrome. Semin. Immunopathol. 2014, 36, 399–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarr, P.I.; A Gordon, C.A.; Chandler, W.L. Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli and haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Lancet 2005, 365, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.P.; Neill, R.J.; O’Brien, A.D.; Holmes, R.K.; Newland, J.W. Nucleotide sequence analysis and comparison of the structural genes for Shiga-like toxin I and Shiga-like toxin II encoded by bacteriophages from Escherichia coli 933. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1987, 44, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, A.A.; Brown, J.E.; Strömberg, N.; Westling-Ryd, M.; Schultz, J.E.; Karlsson, K.A. Identification of the carbohydrate receptor for Shiga toxin produced by Shigella dysenteriae type 1. J. Boil. Chem. 1987, 262, 1779–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Melton-Celsa, A.R. Shiga Toxin (Stx) Classification, Structure, and Function. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Kar, N.C.; Monnens, L.A.; Karmali, M.A.; van Hinsbergh, V.W. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 induce expression of the verocytotoxin receptor globotriaosylceramide on human endothelial cells: Implications for the pathogenesis of the hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood 1992, 80, 2755–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannes, L.; Römer, W. Shiga toxins—From cell biology to biomedical applications. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 8, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauwens, A.; Betz, J.; Meisen, I.; Kemper, B.; Karch, H.; Müthing, J. Facing glycosphingolipid–Shiga toxin interaction: Dire straits for endothelial cells of the human vasculature. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 70, 425–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Setten, P.A.; van Hinsbergh, V.W.M.; van den Heuvel, L.P.; Preyers, F.; Dïjkman, H.B.; Assmann, K.J.; Van Der Velden, T.J.A.; Monnens, L.A.H. Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 and Interleukin-8 Levels in Urine and Serum of Patents with Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Pediatr. Res. 1998, 43, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inward, C.D.; Howie, A.J.; Fitzpatrick, M.M.; Rafaat, F.; Milford, D.V.; Taylor, C.M. Renal histopathology in fatal cases of diarrhoea-associated haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 1997, 11, 556–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, S.E.; Karmali, M.; Becker, L.E.; Smith, C.R. The histopathology of the hemolytic uremic syndrome associated with verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli infections. Hum. Pathol. 1988, 19, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milford, D.V.; Staten, J.; MacGreggor, I.; Dawes, J.; Taylor, C.M.; Hill, F.G. Prognostic Markers in Diarrhoea-Associated Haemolytic-Uraemic Syndrome: Initial Neutrophil Count, Human Neutrophil Elastase and Von Willebrand Factor Antigen. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 1991, 6, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geelen, J.M.; Valsecchi, F.; van der Velden, T.; Heuvel, L.V.D.; Monnens, L.; Morigi, M. Shiga-toxin-induced firm adhesion of human leukocytes to endothelium is in part mediated by heparan sulfate. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2008, 23, 3091–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rops, A.L.; van der Vlag, J.; Lensen, J.F.; Wijnhoven, T.J.; Heuvel, L.P.V.D.; van Kuppevelt, T.H.; Berden, J.H. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans in glomerular inflammation. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 768–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monnens, L.; Molenaar, J.; Lambert, P.H.; Proesmans, W.; van Munster, P. The complement system in hemolytic-uremic syndrome in childhood. Clin. Nephrol. 1980, 13, 168–171. [Google Scholar]
- Thurman, J.M.; Marians, R.; Emlen, W.; Wood, S.; Smith, C.; Akana, H.; Holers, V.M.; Lesser, M.; Kline, M.; Hoffman, C.; et al. Alternative pathway of complement in children with diarrhea-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1920–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth-Höller, D.; Khan, A.B.; Naim, A.; Grif, K.; Brockmeyer, J.; Karch, H.; Joannidis, M.; Clark, S.J.; Day, A.J.; Fidanzi, S.; et al. Shiga Toxin Activates Complement and Binds Factor H: Evidence for an Active Role of Complement in Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 6394–6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morigi, M.; Galbusera, M.; Gastoldi, S.; Locatelli, M.; Buelli, S.; Pezzotta, A.; Pagani, C.; Noris, M.; Gobbi, M.; Stravalaci, M.; et al. Alternative Pathway Activation of Complement by Shiga Toxin Promotes Exuberant C3a Formation That Triggers Microvascular Thrombosis. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, A.; Cointe, A.; Kurkdjian, P.M.; Rafat, C.; Hertig, A. Shiga Toxin-Associated Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: A Narrative Review. Toxins 2020, 12, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, P.; Johnson, S. Eculizumab in the treatment of Shiga toxin haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 34, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigotti, M.; Alfieri, R.; Sestili, P.; Bonelli, M.; Petronini, P.G.; Guidarelli, A.; Barbieri, L.; Stirpe, F.; Sperti, S. Damage to nuclear DNA induced by Shiga toxin 1 and ricin in human endothelial cells 1. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesh, V.L. Induction of apoptosis by Shiga toxins. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 431–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherla, R.P.; Lee, S.-Y.; Tesh, V.L. Shiga toxins and apoptosis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 228, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruzziello-Pellegrini, T.N.; Moslemi-Naeini, M.; Marsden, P.A. New insights into Shiga toxin-mediated endothelial dysfunction in hemolytic uremic syndrome. Virulence 2013, 4, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Fuster, M.; Sriramarao, P.; Esko, J.D. Endothelial heparan sulfate deficiency impairs L-selectin- and chemokine-mediated neutrophil trafficking during inflammatory responses. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfenbein, A.; Simons, M. Syndecan-4 signaling at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126 Pt 17, 3799–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannaway, M.; Yang, X.; Meegan, J.E.; Coleman, D.C.; Yuan, S.Y. Thrombin-cleaved syndecan-3/-4 ectodomain fragments mediate endothelial barrier dysfunction. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, T.T.; Reine, T.M.; Sudworth, A.; Jenssen, T.G.; Kolset, S.O. Syndecan-4 Is a Major Syndecan in Primary Human Endothelial Cells In Vitro, Modulated by Inflammatory Stimuli and Involved in Wound Healing. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2015, 63, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morigi, M.; Micheletti, G.; Figliuzzi, M.; Imberti, B.; Karmali, M.; Remuzzi, A.; Remuzzi, G.; Zoja, C. Verotoxin-1 promotes leukocyte adhesion to cultured endothelial cells under physiologic flow conditions. Blood 1995, 86, 4553–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacewicz, M.S.; Acheson, D.W.K.; Binion, D.G.; West, G.A.; Lincicome, L.L.; Fiocchi, C.; Keusch, G.T. Responses of Human Intestinal Microvascular Endothelial Cells to Shiga Toxins 1 and 2 and Pathogenesis of Hemorrhagic Colitis. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 1439–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Froio, R.M.; Sciuto, T.E.; Dvorak, A.M.; Alon, R.; Luscinskas, F.W. ICAM-1 regulates neutrophil adhesion and transcellular migration of TNF-α-activated vascular endothelium under flow. Blood 2005, 106, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowkes, R.C.; Wolf, S. ICAM-1 signaling in endothelial cells. Pharmacol. Rep. 2009, 61, 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Legendre, C.; Licht, C.; Muus, P.; Greenbaum, L.; Babu, S.; Bedrosian, C.; Bingham, C.; Cohen, D.; Delmas, Y.; Douglas, K.; et al. Terminal Complement Inhibitor Eculizumab in Atypical Hemolytic–Uremic Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2169–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenbaum, L.A.; Fila, M.; Ardissino, G.; Al-Akash, S.I.; Evans, J.; Henning, P.; Lieberman, K.V.; Maringhini, S.; Pape, L.; Rees, L.; et al. Eculizumab is a safe and effective treatment in pediatric patients with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayle, C.; Milinkevitch, S.; Favreau, F.; Doucet, C.; Richer, J.; Deretz, S.; Mauco, G.; Rabb, H.; Hauet, T. Protective role of selectin ligand inhibition in a large animal model of kidney ischemia–reperfusion injury. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, D.; Brennan, M.; Moran, N. Integrins as therapeutic targets: Lessons and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 804–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Setten, P.A.; van Hinsbergh, V.W.; van der Velden, T.J.; van de Kar, N.C.; Vermeer, M.; Mahan, J.D.; Assmann, K.J.; van den Heuvel, L.P.W.J.; Monnens, L.A. Effects of TNFα on verocytotoxin cytotoxicity in purified human glomerular microvascular endothelial cells. Kidney Int. 1997, 51, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, E.A.; Nachman, R.L.; Becker, C.G.; Minick, C.R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J. Clin. Investig. 1973, 52, 2745–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Volokhina, E.B.; Feitz, W.J.C.; Elders, L.M.; van der Velden, T.J.A.M.; van de Kar, N.C.A.J.; van den Heuvel, L.P.W.J. Shiga Toxin Selectively Upregulates Expression of Syndecan-4 and Adhesion Molecule ICAM-1 in Human Glomerular Microvascular Endothelium. Toxins 2020, 12, 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12070435
Volokhina EB, Feitz WJC, Elders LM, van der Velden TJAM, van de Kar NCAJ, van den Heuvel LPWJ. Shiga Toxin Selectively Upregulates Expression of Syndecan-4 and Adhesion Molecule ICAM-1 in Human Glomerular Microvascular Endothelium. Toxins. 2020; 12(7):435. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12070435
Chicago/Turabian StyleVolokhina, Elena B., Wouter J. C. Feitz, Lonneke M. Elders, Thea J. A. M. van der Velden, Nicole C. A. J. van de Kar, and Lambertus P. W. J. van den Heuvel. 2020. "Shiga Toxin Selectively Upregulates Expression of Syndecan-4 and Adhesion Molecule ICAM-1 in Human Glomerular Microvascular Endothelium" Toxins 12, no. 7: 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12070435
APA StyleVolokhina, E. B., Feitz, W. J. C., Elders, L. M., van der Velden, T. J. A. M., van de Kar, N. C. A. J., & van den Heuvel, L. P. W. J. (2020). Shiga Toxin Selectively Upregulates Expression of Syndecan-4 and Adhesion Molecule ICAM-1 in Human Glomerular Microvascular Endothelium. Toxins, 12(7), 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12070435




