Scavenging Intracellular ROS Attenuates p-Cresyl Sulfate-Triggered Osteogenesis through MAPK Signaling Pathway and NF-?B Activation in Human Arterial Smooth Muscle Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Circulating Levels of PCS/ IS were CKD Severity-Dependent and Positively Correlated with Ca-P Product and Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP), Suggesting that PCS is a Long-Neglected Mineralization Inducer in UVC
2.2. Effects of CKD Severity-Dependent Vascular Oxidative Injury on HASMC Osteogenesis in Human Arteries
2.3. PCS Inhibits Cell Viability of HASMC in a Time- and Dose-Dependent Manner
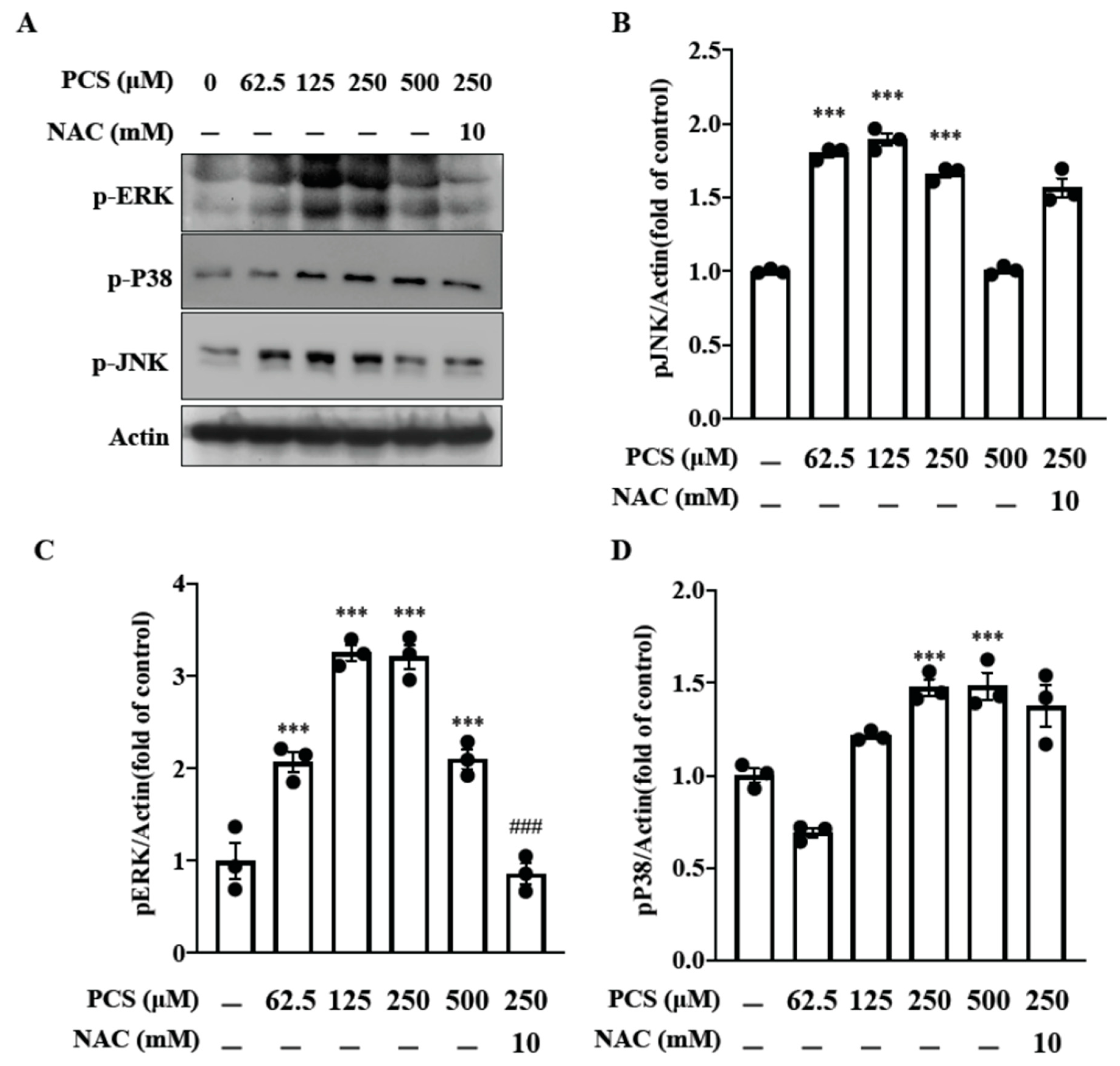
2.4. PCS Triggers Phosphorylation of the MAPK Family Members (JNK, ERK and P38) in HASMC: Intracellular ROS Scavenger Inhibits PCS-Induced pERK MAPK Pathway
2.5. PCS Triggers Translocation of NF-κB From the Cytoplasm to the Nucleus in HASMC
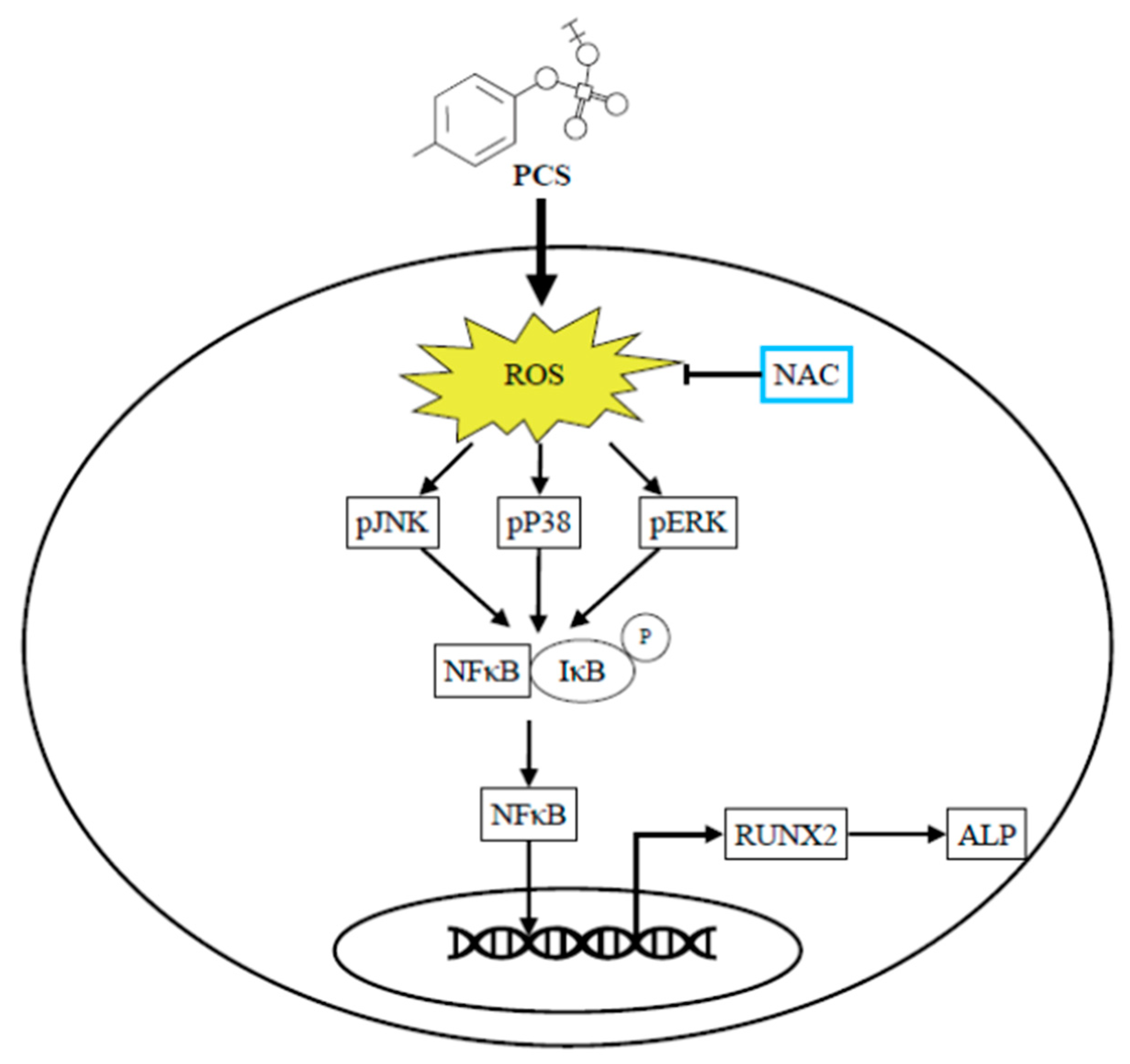
2.6. PCS-Induced Intracellular ROS Triggers Osteogenic Conversion of HASMC, and ROS Scavenger NAC Inhibits PCS-Induced Osteogenic Transcription Factor Runx2 and Osteoblast-Specific Protein ALP
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. IHC Staining and Image Analyses
5.2. Reagents and Chemicals
5.3. Cell and Treatments
5.4. Cell Viability Assay
5.5. Sequential Fractionation and Isolation of Subcellar Proteins
5.6. Detection of Intracellular ROS Production
5.7. Measurement of Circulating PCS and IS Levels
5.8. Statistics
6. Patients and Bio-Clinical Data
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liabeuf, S.; Desjardins, L.; Diouf, M.; Temmar, M.; Renard, C.; Choukroun, G.; Massy, Z.A. The Addition of Vascular Calcification Scores to Traditional Risk Factors Improves Cardiovascular Risk Assessment in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, W.-C.; Choy, C.-S.; Lin, W.-N.; Chang, S.-W.; Liou, J.-C.; Tung, T.-H.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Chang, J.-F. Galectin-3 Interacts with Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 to Increase Cardiovascular Mortality in Hemodialysis Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, J.-F.; Liu, S.-H.; Lu, K.-C.; Ka, S.-M.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Ho, C.-T.; Lin, W.-N.; Wen, L.-L.; Liou, J.-C.; Chang, S.-W.; et al. Uremic Vascular Calcification Is Correlated with Oxidative Elastic Lamina Injury, Contractile Smooth Muscle Cell Loss, Osteogenesis, and Apoptosis: The Human Pathobiological Evidence. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2020, 7, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shroff, R.C.; Donald, A.E.; Hiorns, M.P.; Watson, A.; Feather, S.; Milford, D.; Ellins, E.A.; Storry, C.; Ridout, D.; Deanfield, J.; et al. Mineral metabolism and vascular damage in children on dialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 2996–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, R.N.; Parfrey, P.S.; Sarnak, M.J. Clinical epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1998, 32, S112–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Albuquerque Suassuna, P.G.; Sanders-Pinheiro, H.; De Paula, R.B. Uremic Cardiomyopathy: A New Piece in the Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder Puzzle. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cozzolino, M.; Ciceri, P.; Galassi, A.; Mangano, M.; Carugo, S.; Capelli, I.; Cianciolo, G. The Key Role of Phosphate on Vascular Calcification. Toxins 2019, 11, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, J.-F.; Liang, S.-S.; Thanasekaran, P.; Chang, H.-W.; Wen, L.-L.; Chen, C.-H.; Liou, J.-C.; Yeh, J.-C.; Liu, S.-H.; Dai, H.-M.; et al. Translational Medicine in Pulmonary-Renal Crosstalk: Therapeutic Targeting of p-Cresyl Sulfate Triggered Nonspecific ROS and Chemoattractants in Dyspneic Patients with Uremic Lung Injury. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muteliefu, G.; Enomoto, A.; Jiang, P.; Takahashi, M.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl sulphate induces oxidative stress and the expression of osteoblast-specific proteins in vascular smooth muscle cells. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vanholder, R.; Schepers, E.; Pletinck, A.; Nagler, E.V.; Glorieux, G. The uremic toxicity of indoxyl sulfate and p-cresyl sulfate: A systematic review. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2014, 25, 1897–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hénaut, L.; Mary, A.; Chillon, J.-M.; Kamel, S.; Massy, Z.A. The Impact of Uremic Toxins on Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Function. Toxins 2018, 10, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hénaut, L.; Mentaverri, R.; Liabeuf, S.; Bargnoux, A.S.; Delanaye, P.; Cavalier, É.; Cristol, J.P.; Massy, Z.; Kamel, S. Pathophysiological mechanisms of vascular calcification. Ann. Biol. Clin. 2015, 73, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proudfoot, D.; Skepper, J.N.; Hegyi, L.; Bennett, M.R.; Shanahan, C.M.; Weissberg, P.L. Apoptosis regulates human vascular calcification in vitro: Evidence for initiation of vascular calcification by apoptotic bodies. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, H.; Iwasaki, Y.; Yamato, H.; Mori, Y.; Komaba, H.; Watanabe, H.; Maruyama, T.; Fukagawa, M. p-Cresyl sulfate induces osteoblast dysfunction through activating JNK and p38 MAPK pathways. Bone 2013, 56, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakamatsu, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Ito, T.; Sato, Y.; Matsuo, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Kaneko, Y.; Goto, S.; Kazama, J.J.; Gejyo, F.; et al. Indoxyl Sulfate Promotes Macrophage IL-1β Production by Activating Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor/NF-κ/MAPK Cascades, but the NLRP3 inflammasome Was Not Activated. Toxins 2018, 10, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shimizu, H.; Bolati, D.; Higashiyama, Y.; Nishijima, F.; Shimizu, K.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl sulfate upregulates renal expression of MCP-1 via production of ROS and activation of NF-κB, p53, ERK, and JNK in proximal tubular cells. Life Sci. 2012, 90, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, L.; Diao, Z.; Liu, W. Indoxyl sulfate promotes vascular smooth muscle cell calcification via the JNK/Pit-1 pathway. Ren. Fail. 2016, 38, 1702–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barreto, F.C.; Barreto, D.V.; Liabeuf, S.; Meert, N.; Glorieux, G.; Temmar, M.; Choukroun, G.; Vanholder, R.; Massy, Z.A.; European Uremic Toxin Work Group. Serum indoxyl sulfate is associated with vascular disease and mortality in chronic kidney disease patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adijiang, A.; Goto, S.; Uramoto, S.; Nishijima, F.; Niwa, T. Indoxyl sulphate promotes aortic calcification with expression of osteoblast-specific proteins in hypertensive rats. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 1892–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durham, A.L.; Speer, M.Y.; Scatena, M.; Giachelli, C.M.; Shanahan, C.M. Role of smooth muscle cells in vascular calcification: Implications in atherosclerosis and arterial stiffness. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shroff, R.C.; McNair, R.; Skepper, J.N.; Figg, N.; Schurgers, L.J.; Deanfield, J.; Rees, L.; Shanahan, C.M. Chronic mineral dysregulation promotes vascular smooth muscle cell adaptation and extracellular matrix calcification. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2010, 21, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berti, D.A.; Seger, R. The Nuclear Translocation of ERK. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1487, 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opdebeeck, B.; Maudsley, S.; Azmi, A.; De Maré, A.; De Leger, W.; Meijers, B.; Verhulst, A.; Evenepoel, P.; D’Haese, P.C.; Neven, E. Indoxyl Sulfate and p-Cresyl Sulfate Promote Vascular Calcification and Associate with Glucose Intolerance. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2019, 30, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Li, L.H.; Rao, Y.K.; Ju, T.C.; Nai, Y.S.; Chen, Y.W.; Hua, K.F. Mechanistic insight into the attenuation of gouty inflammation by Taiwanese green propolis via inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, K.F.; Chou, J.C.; Ka, S.M.; Tasi, Y.L.; Chen, A.; Wu, S.H.; Chiu, H.W.; Wong, W.T.; Wang, Y.F.; Tsai, C.L.; et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 regulates NLRP3 inflammasome-derived IL-1beta production. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, J.C.; Wu, C.C.; Choy, C.S.; Chang, S.W.; Liou, J.C.; Chen, K.S.; Tung, T.H.; Lin, W.N.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Ho, C.T.; et al. Non-Hepatic Alkaline Phosphatase, hs-CRP and Progression of Vertebral Fracture in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Population-Based Longitudinal Study. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, J.F.; Feng, Y.F.; Peng, Y.S.; Hsu, S.P.; Pai, M.F.; Chen, H.Y.; Wu, H.Y.; Yang, J.Y. Combined alkaline phosphatase and phosphorus levels as a predictor of mortality in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Medicine 2014, 93, e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.F.; Chou, Y.S.; Wu, C.C.; Chen, P.C.; Ko, W.C.; Liou, J.C.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Lin, W.N.; Wen, L.L.; Chang, S.W.; et al. A Joint Evaluation of Neurohormone Vasopressin-Neurophysin II-Copeptin and Aortic Arch Calcification on Mortality Risks in Hemodialysis Patients. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Variables | Controls (n = 9) | Mild-to-Moderate CKD (n = 9) | Severe CKD (n = 9) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 67.1 ± 17.0 | 70.4 ± 10.3 | 61.3 ± 13.9 | 0.39 |
| Male, n (%) | 7 (77.8) | 6 (66.7) | 7 (77.8) | 0.84 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 131.7 ± 31.3 | 132.0 ± 24.4 | 130.0 ± 27.9 | 0.98 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 75.2 ± 14.1 | 76.2 ± 15.0 | 75.1 ± 13.9 | 0.98 |
| Blood urea nitrogen (mg/dL) | 17.7 ± 7.0 | 46.1 ± 24.0 | 48.2 ± 25.0 | <0.01 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 2.2 ± 0.6 | 5.6 ± 2.4 | <0.01 |
| eGFR (mL/min) | 88.5 ± 20.8 | 32.9 ± 15.8 | 12.3 ± 4.5 | <0.01 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 136.2 ± 6.1 | 136.2 ± 5.4 | 134.0 ± 2.5 | 0.55 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 3.8 ± 5.6 | 4.0 ± 0.7 | 4.4 ± 0.7 | 0.16 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 146.0 ± 43.6 | 238.8 ± 92.7 | 249.1 ± 136.3 | 0.07 |
| Alanine aminotransferase (IU/L) | 33.2 ± 22.8 | 20.7 ± 10.8 | 16.8 ± 12.6 | 0.12 |
| Alkaline phosphatase (IU/L) | 128.6 ± 40.8 | 147.5 ± 12.9 | 202.5 ± 75.5 | 0.02 |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 8.9 ± 0.4 | 8.8 ± 0.7 | 8.8 ± 1.0 | 0.95 |
| Phosphate (mg/dL) | 3.0 ± 0.4 | 4.3 ± 0.7 | 5.6 ± 1.2 | <0.01 |
| Calcium-phosphate product b | 26.8 ± 2.8 | 37.9 ± 7.0 | 48.9 ± 9.2 | <0.01 |
| AAC grade score | 2.0 ± 1.0 | 2.3 ± 0.9 | 3.1 ± 0.6 | <0.05 |
| PCS (μM) | 6.9 ± 4.8 | 52.7 ± 20.7 | 109.0 ± 42.0 | <0.01 |
| IS (μM) | 5.2 ± 2.8 | 50.2 ± 35.2 | 108.5 ± 31.0 | <0.01 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, J.-F.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Liou, J.-C.; Liu, S.-H.; Hung, C.-F.; Lu, K.-C.; Lin, C.-C.; Wu, C.-C.; Ka, S.-M.; Wen, L.-L.; et al. Scavenging Intracellular ROS Attenuates p-Cresyl Sulfate-Triggered Osteogenesis through MAPK Signaling Pathway and NF-?B Activation in Human Arterial Smooth Muscle Cells. Toxins 2020, 12, 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12080472
Chang J-F, Hsieh C-Y, Liou J-C, Liu S-H, Hung C-F, Lu K-C, Lin C-C, Wu C-C, Ka S-M, Wen L-L, et al. Scavenging Intracellular ROS Attenuates p-Cresyl Sulfate-Triggered Osteogenesis through MAPK Signaling Pathway and NF-?B Activation in Human Arterial Smooth Muscle Cells. Toxins. 2020; 12(8):472. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12080472
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Jia-Feng, Chih-Yu Hsieh, Jian-Chiun Liou, Shih-Hao Liu, Chi-Feng Hung, Kuo-Cheng Lu, Chih-Cheng Lin, Chang-Chin Wu, Shuk-Man Ka, Li-Li Wen, and et al. 2020. "Scavenging Intracellular ROS Attenuates p-Cresyl Sulfate-Triggered Osteogenesis through MAPK Signaling Pathway and NF-?B Activation in Human Arterial Smooth Muscle Cells" Toxins 12, no. 8: 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12080472
APA StyleChang, J.-F., Hsieh, C.-Y., Liou, J.-C., Liu, S.-H., Hung, C.-F., Lu, K.-C., Lin, C.-C., Wu, C.-C., Ka, S.-M., Wen, L.-L., Wu, M.-S., Zheng, C.-M., & Ko, W.-C. (2020). Scavenging Intracellular ROS Attenuates p-Cresyl Sulfate-Triggered Osteogenesis through MAPK Signaling Pathway and NF-?B Activation in Human Arterial Smooth Muscle Cells. Toxins, 12(8), 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12080472








