Clostridial C3 Toxins Enter and Intoxicate Human Dendritic Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
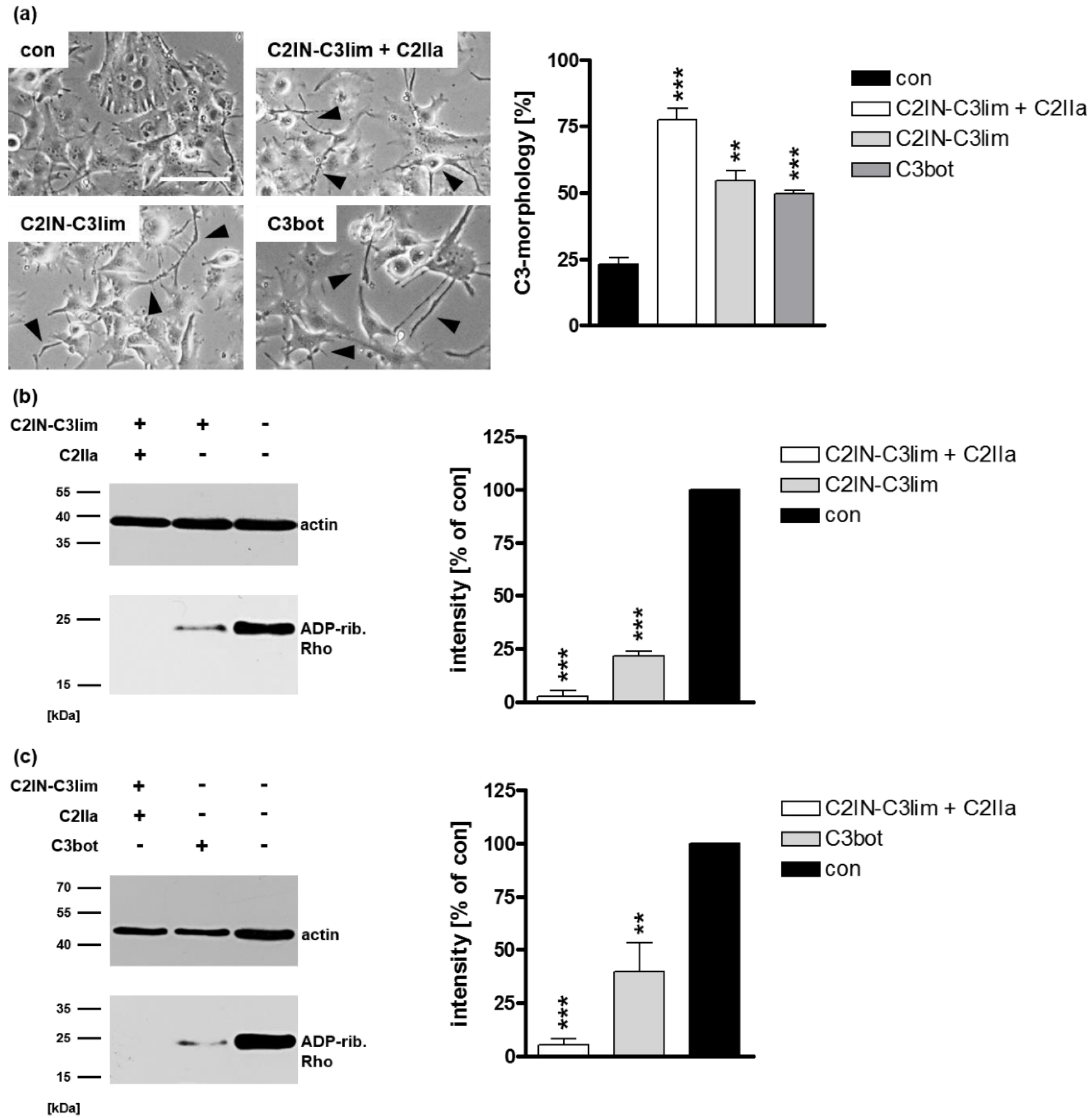
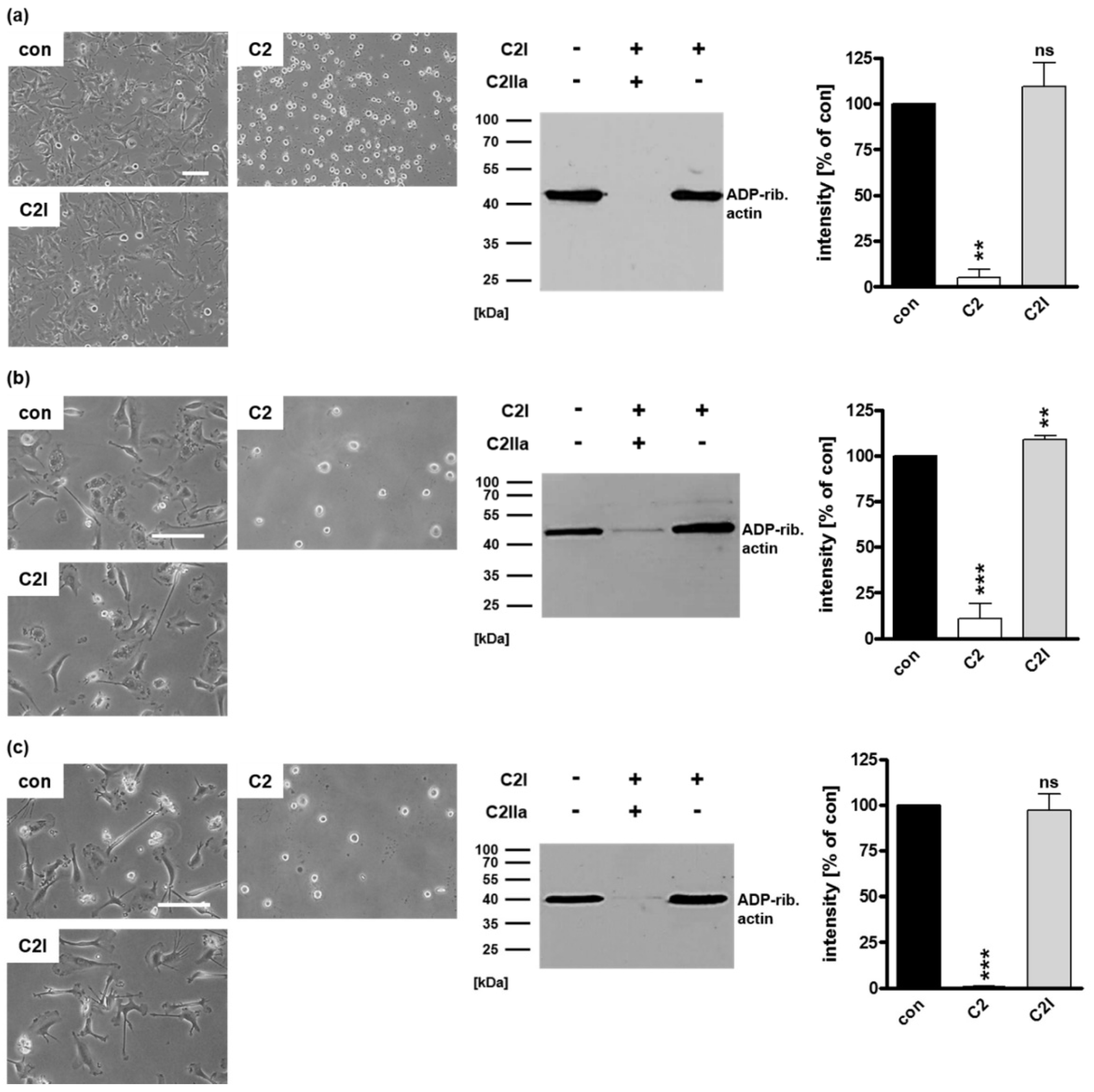
2.1. Selective Internalization of Clostridial C3 Toxins into the Cytosol of an Immortalized Human U-DCS Cell Line
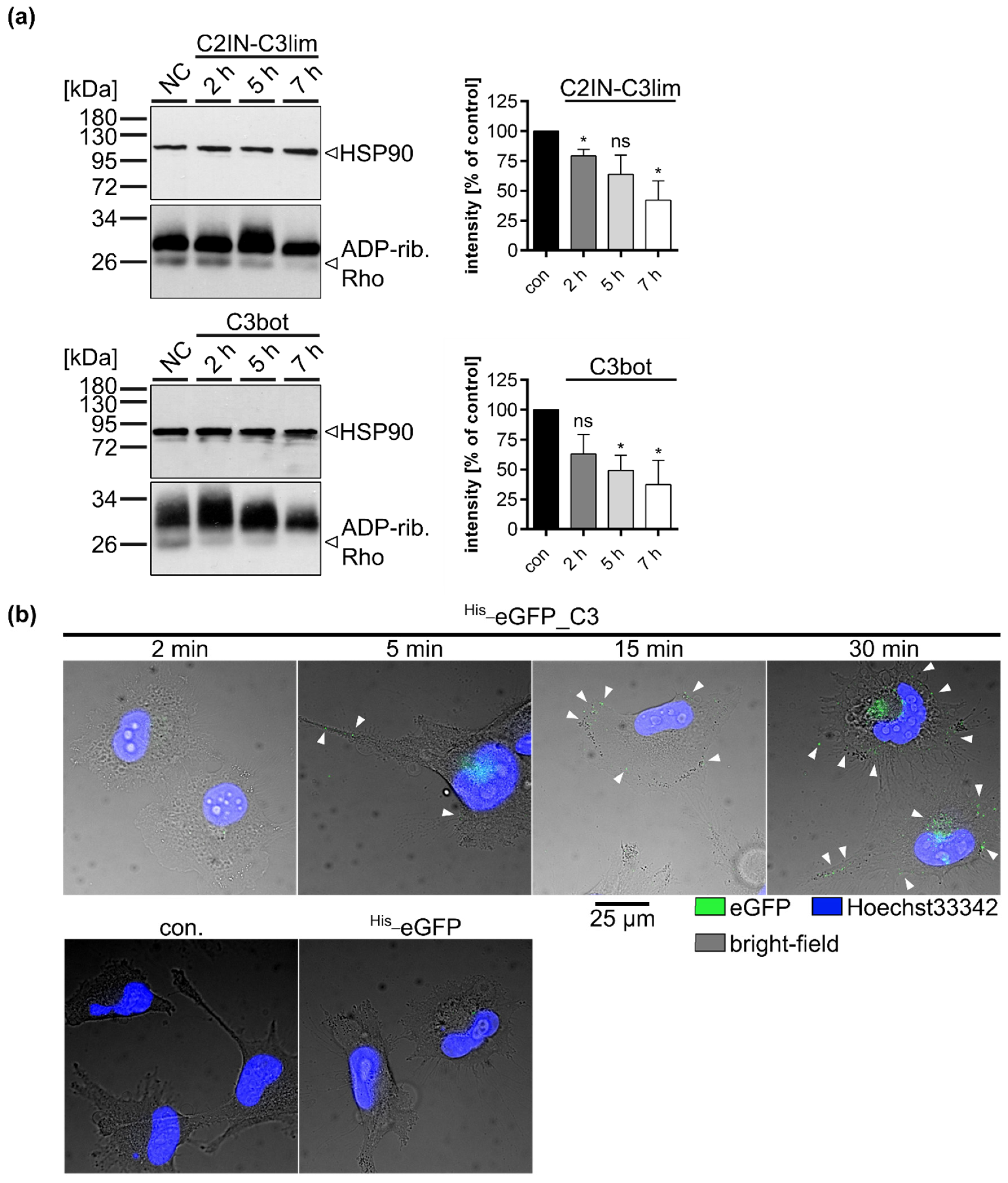
2.2. Clostridial C3 Toxins Are Internalized into the Cytosol of Immature and Mature Human Monocyte-Derived DCs
2.3. Confirming the Selectivity and Specificity of the Uptake of C3 Toxins into DCs
2.4. Specific Internalization of C3bot into Early Endosomes of Mature and Immature DCs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Generation of Mature and Immature DCs Based on Isolated Human Monocytes
4.3. Cloning of His_eGFP-Labeled C3bot and C3botE174Q
4.4. Protein Expression and Cell Lysis
4.5. Purification of GST-Tagged Proteins
4.6. Purification of 6xHis-Tagged Proteins
4.7. Phase Contrast Microscopy
4.8. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
4.9. Sequential ADP-Ribosylation of Rho
4.10. Immunofluorescence Staining with Following Confocal and Epifluorescence Microscopy
4.11. STED Super-Resolution Microscopy
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vogelsgesang, M.; Pautsch, A.; Aktories, K. C3 exoenzymes, novel insights into structure and action of Rho-ADP-ribosylating toxins. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2007, 374, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrbeck, A.; Höltje, M.; Adolf, A.; Oms, E.; Hagemann, S.; Ahnert-Hilger, G.; Just, I. The Rho ADP-ribosylating C3 exoenzyme binds cells via an Arg–Gly–Asp motif. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 17668–17680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktories, K. Bacterial protein toxins that modify host regulatory GTPases. Nat. Publ. Group 2011, 9, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktories, K.; Weller, U.; Chhatwal, G.S. Clostridium botulinum type C produces a novel ADP-ribosyltransferase distinct from botulinum C2 toxin. FEBS Lett. 1987, 212, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just, I.; Mohr, C.; Schallehn, G.; Menard, L.; Didsbury, J.R.; Vandekerckhove, J.; Van Damme, J.; Aktories, K. Purification and characterization of an ADP-ribosyltransferase produced by Clostridium limosum. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 10274–10280. [Google Scholar]
- Barth, H.; Fischer, S.; Möglich, A.; Förtsch, C. Clostridial C3 toxins target monocytes/macrophages and modulate their functions. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krska, D.; Ravulapalli, R.; Fieldhouse, R.J.; Lugo, M.R.; Merrill, A.R. C3larvin Toxin, an ADP-ribosyltransferase from Paenibacillus larvae. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 1639–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fünfhaus, A.; Poppinga, L.; Genersch, E. Identification and characterization of two novel toxins expressed by the lethal honey bee pathogen Paenibacillus larvae, the causative agent of American foulbrood. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 2951–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeling, J.; Knispel, H.; Fünfhaus, A.; Genersch, E. The biological role of the enigmatic C3larvinAB toxin of the honey bee pathogenic bacterium Paenibacillus larvae. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 3091–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktories, K.; Wilde, C.; Vogelsgesang, M. Rho-modifying C3-like ADP-ribosyltransferases. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 152, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrer, J.; Kuban, J.; Heine, K.; Rupps, G.; Kaiser, E.; Felder, E.; Benz, R.; Barth, H. Selective and specific internalization of clostridial C3 ADP-ribosyltransferases into macrophages and monocytes. Cell. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotsch, J.; Rohrbeck, A.; May, M.; Kolbe, T.; Hagemann, S.; Schelle, I.; Just, I.; Genth, H.; Huelsenbeck, S.C. Inhibition of macrophage migration by C. botulinum exoenzyme C3. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2012, 385, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrbeck, A.; Schröder, A.; Hagemann, S.; Pich, A.; Höltje, M.; Ahnert-Hilger, G.; Just, I. Vimentin Mediates Uptake of C3 Exoenzyme. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adolf, A.; Leondaritis, G.; Rohrbeck, A.; Eickholt, B.J.; Just, I.; Ahnert-Hilger, G.; Höltje, M. The intermediate filament protein vimentin is essential for axonotrophic effects of Clostridium botulinum C3 exoenzyme. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, M.F.; Ashworth, A.; Hall, A. An essential role for Rho, Rac, and Cdc42 GTPases in cell cycle progression through G1. Science 1995, 269, 1270–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kippert, A.; Trajkovic, K.; Rajendran, L.; Ries, J.; Simons, M. Rho regulates membrane transport in the endocytic pathway to control plasma membrane specialization in oligodendroglial cells. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 3560–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.C.; Price, L.S.; Ridley, A.J.; Koffer, A. The small GTP-binding proteins, Rac and Rho, regulate cytoskeletal organization and exocytosis in mast cells by parallel pathways. Mol. Biol. Cell 1996, 7, 1429–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chardin, P.; Boquet, P.; Madaule, P.; Popoff, M.R.; Rubin, E.J.; Gill, D.M. The mammalian G protein rhoC is ADP-ribosylated by Clostridium botulinum exoenzyme C3 and affects actin microfilaments in Vero cells. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, H.; Hofmann, F.; Olenik, C.; Just, I.; Aktories, K. The N-Terminal Part of the Enzyme Component (C2I) of the Binary Clostridium botulinum C2 Toxin Interacts with the Binding Component C2II and Functions as a Carrier System for a Rho ADP-Ribosylating C3-Like Fusion Toxin. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 1364–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, H.F.; Self, A.J.; Garrett, M.D.; Just, I.; Aktories, K.; Hall, A. Microinjection of recombinant p21(rho) induces rapid changes in cell morphology. J. Cell Biol. 1990, 111, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, N.; Madaule, P.; Reid, T.; Ishizaki, T.; Watanabe, G.; Kakizuka, A.; Saito, Y.; Nakao, K.; Jockusch, B.M.; Narumiya, S. p140mDia, a mammalian homolog of Drosophila diaphanous, is a target protein for Rho small GTPase and is a ligand for profilin. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 3044–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Kim, J.-S.; Jung, K.-C.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, J.-I.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Park, J.-B.; Choi, S.Y. Exoenzyme Tat-C3 inhibits association of zymosan particles, phagocytosis, adhesion, and complement binding in macrophage cells. Mol. Cells 2003, 16, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Winton, M.J.; Dubreuil, C.I.; Lasko, D.; Leclerc, N.; McKerracher, L. Characterization of new cell permeable C3-like proteins that inactivate Rho and stimulate neurite outgrowth on inhibitory substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 32820–32829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauzeau, V.; Le Mellionnec, E.; Bertoglio, J.; Scalbert, E.; Pacaud, P.; Loirand, G. Human Urotensin II–Induced Contraction and Arterial Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation Are Mediated by RhoA and Rho-Kinase. Circ. Res. 2001, 88, 1102–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aullo, P.; Giry, M.; Olsnes, S.; Popoff, M.R.; Kocks, C.; Boquet, P. A chimeric toxin to study the role of the 21 kDa GTP binding protein rho in the control of actin microfilament assembly. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktories, K.; Barth, H. The actin-ADP-ribosylating Clostridium botulinum C2 toxin. Anaerobe 2004, 10, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.; Möglich, A.; Felix, I.; Förtsch, C.; Rittlinger, A.; Palmer, A.; Denk, S.; Schneider, J.; Notbohm, L.; Vogel, M.; et al. Rho-inhibiting C2IN-C3 fusion toxin inhibits chemotactic recruitment of human monocytes ex vivo and in mice in vivo. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tautzenberger, A.; Förtsch, C.; Zwerger, C.; Dmochewitz, L.; Kreja, L.; Ignatius, A.; Barth, H. C3 Rho-inhibitor for targeted pharmacological manipulation of osteoclast-like cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e85695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aepfelbacher, M.; Essler, M.; Huber, E.; Sugai, M.; Weber, P.C. Bacterial toxins block endothelial wound repair. Evidence that Rho GTPases control cytoskeletal rearrangements in migrating endothelial cells. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1997, 17, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipscomb, M.F.; Masten, B.J. Dendritic Cells: Immune Regulators in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 97–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worbs, T.; Hammerschmidt, S.I.; Förster, R. Dendritic cell migration in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banchereau, J.; Briere, F.; Caux, C.; Davoust, J.; Lebecque, S.; Liu, Y.-J.; Pulendran, B.; Palucka, K. Immunobiology of Dendritic Cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 767–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirazzini, M.; Rossetto, O.; Eleopra, R.; Montecucco, C. Botulinum Neurotoxins: Biology, Pharmacology, and Toxicology. Pharm. Rev. 2017, 69, 200–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinefield, H.R. Overview of the development and current use of CRM197 conjugate vaccines for pediatric use. Vaccine 2010, 28, 4335–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichichero, M.E. Protein carriers of conjugate vaccines. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2013, 9, 2505–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.P.; Parker, K.; Bacha, P.; Bishai, W.; Borowski, M.; Genbauffe, F.; Strom, T.B.; Murphy, J.R. Diphtheria toxin receptor binding domain substitution with interleukin-2: Genetic construction and properties of a diphtheria toxin-related interleukin-2 fusion protein. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1987, 1, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.P.; Snider, C.E.; Strom, T.B.; Murphy, J.R. Structure/function analysis of interleukin-2-toxin (DAB486-IL-2). Fragment B sequences required for the delivery of fragment A to the cytosol of target cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 11885–11889. [Google Scholar]
- Frankel, A.E.; Fleming, D.R.; Powell, B.L.; Gartenhaus, R. DAB 389 IL2 (ONTAK ®) fusion protein therapy of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2003, 3, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, H.; Olenik, C.; Sehr, P.; Schmidt, G.; Aktories, K.; Meyer, D.K. Neosynthesis and activation of Rho by Escherichia coli cytotoxic necrotizing factor (CNF1) reverse cytopathic effects of ADP-ribosylated Rho. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 27407–27414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiering, D.; Hodgson, L. Dynamics of the Rho-family small GTPases in actin regulation and motility. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2011, 5, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, B.R.M.; Swanson, J. Commentary The Endoeytie Activity of Dendritic Cells By Ralph, M. Steinman* and Joel Swanson. Commentary 1995, 182. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, C.D.; Ma, J.K.; Chalouni, C.; Ebersold, M.; Bou-Reslan, H.; Carano, R.A.D.; Mellman, I.; Delamarre, L. Mature dendritic cells use endocytic receptors to capture and present antigens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4287–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktories, K.; Bärmann, M.; Ohishi, I.; Tsuyama, S.; Jakobs, K.H.; Habermann, E. Botulinum C2 toxin ADP-ribosylates actin. Nature 1986, 322, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohishi, I.; Miyake, M.; Ogura, H.; Nakamura, S. Cytopathic effect of botulinum C 2 toxin on tissue-culture cells. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1984, 23, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, H.; Stiles, B.G. Protein Toxins from Bacteria. In Comprehensive Natural Products II; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 149–173. ISBN 9780080453828. [Google Scholar]
- Swetman, C.A.; Leverrier, Y.; Garg, R.; Gan, C.H.V.; Ridley, A.J.; Katz, D.R.; Chain, B.M. Extension, retraction and contraction in the formation of a dendritic cell dendrite: Distinct roles for Rho GTPases. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Azuma, E.; Ido, M.; Hirayama, M.; Jiang, Q.; Iwamoto, S.; Kumamoto, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Sakurai, M.; Komada, Y. A Pivotal Role of Rho GTPase in the Regulation of Morphology and Function of Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 3585–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, S.; Thrasher, A.J.; Blundell, M.P.; Machesky, L.; Jones, G.E. Configuration of human dendritic cell cytoskeleton by Rho GTPases, the WAS protein, and differentiation. Blood 2001, 98, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocana-Morgner, C.; Wahren, C.; Jessberger, R. SWAP-70 regulates RhoA/RhoB-dependent MHCII surface localization in dendritic cells. Blood 2009, 113, 1474–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neefjes, J.J.; Stollorz, V.; Peters, P.J.; Geuze, H.J.; Ploegh, H.L. The biosynthetic pathway of MHC class II but not class I molecules intersects the endocytic route. Cell 1990, 61, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, C.P.; Giltiay, N.V.; Dresch, C.; Clark, E.A. Controlling immune responses by targeting antigens to dendritic cell subsets and B cells. Int. Immunol. 2014, 26, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bros, M.; Haas, K.; Moll, L.; Grabbe, S. RhoA as a Key Regulator of Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Cells 2019, 8, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shlomchik, W.D.; Couzens, M.S.; Tang, C.B.; McNiff, J.; Robert, M.E.; Liu, J.; Shlomchik, M.J.; Emerson, S.G. Prevention of graft versus host disease by inactivation of host antigen-presenting cells. Science 1999, 285, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorvel, L.; Textoris, J.; Banchereau, R.; Ben Amara, A.; Tantibhedhyangkul, W.; von Bargen, K.; Ka, M.B.; Capo, C.; Ghigo, E.; Gorvel, J.-P.; et al. Intracellular bacteria interfere with dendritic cell functions: Role of the type I interferon pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillich, M.; Chen, X.; Weil, T.; Barth, H.; Fahrer, J. Streptavidin-conjugated C3 protein mediates the delivery of mono-biotinylated RNAse A into macrophages. Bioconjugate Chem. 2012, 23, 1426–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmochewitz, L.; Förtsch, C.; Zwerger, C.; Vaeth, M.; Felder, E.; Huber-Lang, M.; Barth, H. A Recombinant Fusion Toxin Based on Enzymatic Inactive C3bot1 Selectively Targets Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christow, H.; Lillich, M.; Sold, A.; Fahrer, J.; Barth, H. Recombinant streptavidin-C3bot for delivery of proteins into macrophages. Toxicon 2013, 75, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buettner, M.; Meinken, C.; Bastian, M.; Bhat, R.; Stössel, E.; Faller, G.; Cianciolo, G.; Ficker, J.; Wagner, M.; Röllinghoff, M.; et al. Inverse Correlation of Maturity and Antibacterial Activity in Human Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 4203–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osseforth, C.; Moffitt, J.R.; Schermelleh, L.; Michaelis, J. Simultaneous dual-color 3D STED microscopy. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 7028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fellermann, M.; Huchler, C.; Fechter, L.; Kolb, T.; Wondany, F.; Mayer, D.; Michaelis, J.; Stenger, S.; Mellert, K.; Möller, P.; et al. Clostridial C3 Toxins Enter and Intoxicate Human Dendritic Cells. Toxins 2020, 12, 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12090563
Fellermann M, Huchler C, Fechter L, Kolb T, Wondany F, Mayer D, Michaelis J, Stenger S, Mellert K, Möller P, et al. Clostridial C3 Toxins Enter and Intoxicate Human Dendritic Cells. Toxins. 2020; 12(9):563. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12090563
Chicago/Turabian StyleFellermann, Maximilian, Christina Huchler, Lea Fechter, Tobias Kolb, Fanny Wondany, Daniel Mayer, Jens Michaelis, Steffen Stenger, Kevin Mellert, Peter Möller, and et al. 2020. "Clostridial C3 Toxins Enter and Intoxicate Human Dendritic Cells" Toxins 12, no. 9: 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12090563
APA StyleFellermann, M., Huchler, C., Fechter, L., Kolb, T., Wondany, F., Mayer, D., Michaelis, J., Stenger, S., Mellert, K., Möller, P., Barth, T. F. E., Fischer, S., & Barth, H. (2020). Clostridial C3 Toxins Enter and Intoxicate Human Dendritic Cells. Toxins, 12(9), 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12090563





