Enhanced Photocatalytic Removal of Cyanotoxins by Al-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles with Visible-LED Irradiation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
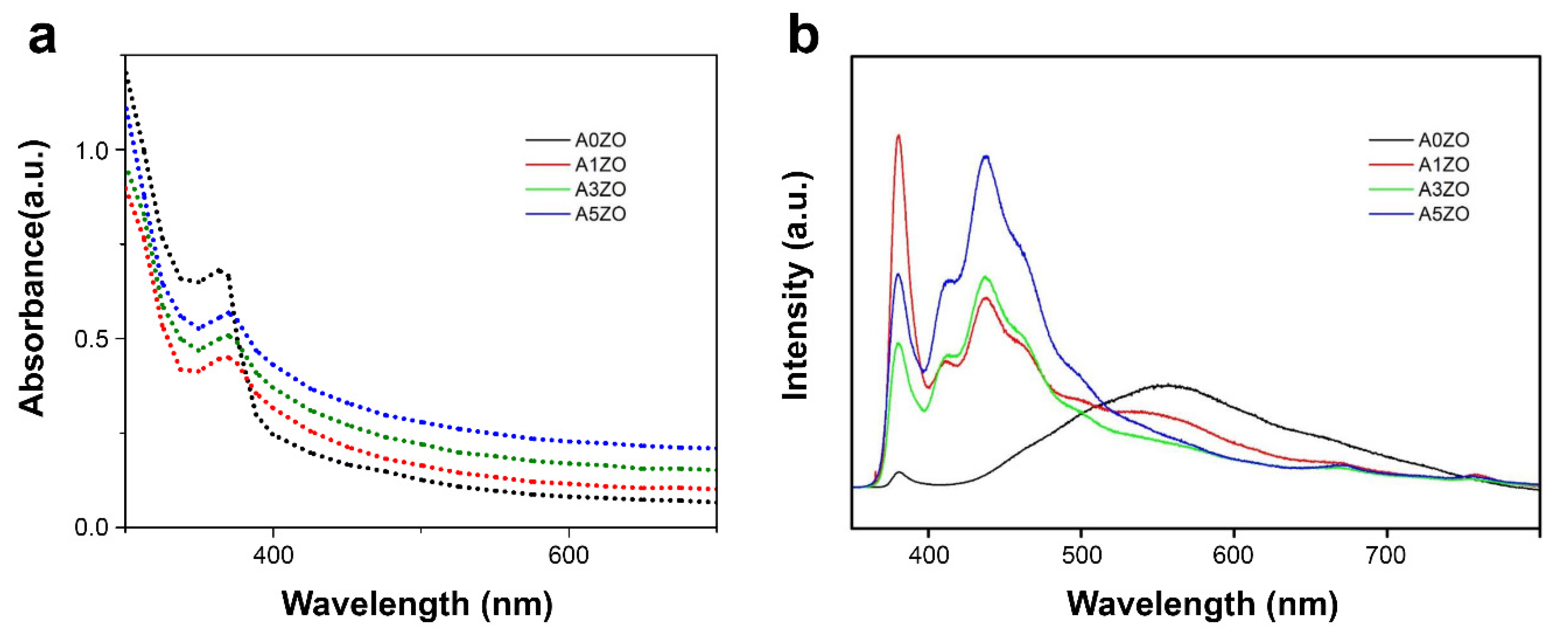
2.1. Characterization of Photocatalysts
2.1.1. Microstructural and Morphological Characterization
2.1.2. Optoelectronic Characterization
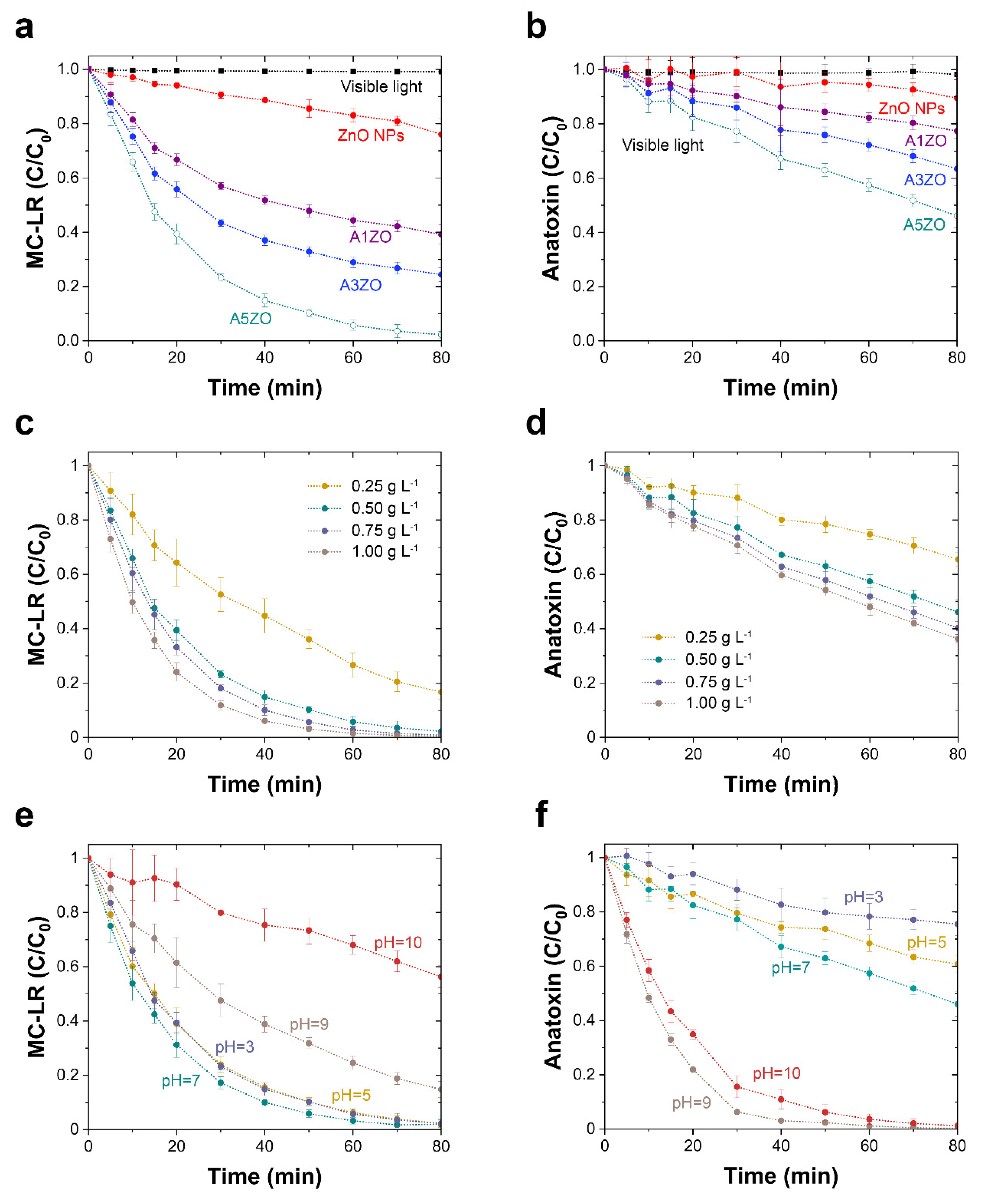
2.2. Photocatalytic Degradation of Cyanotoxins
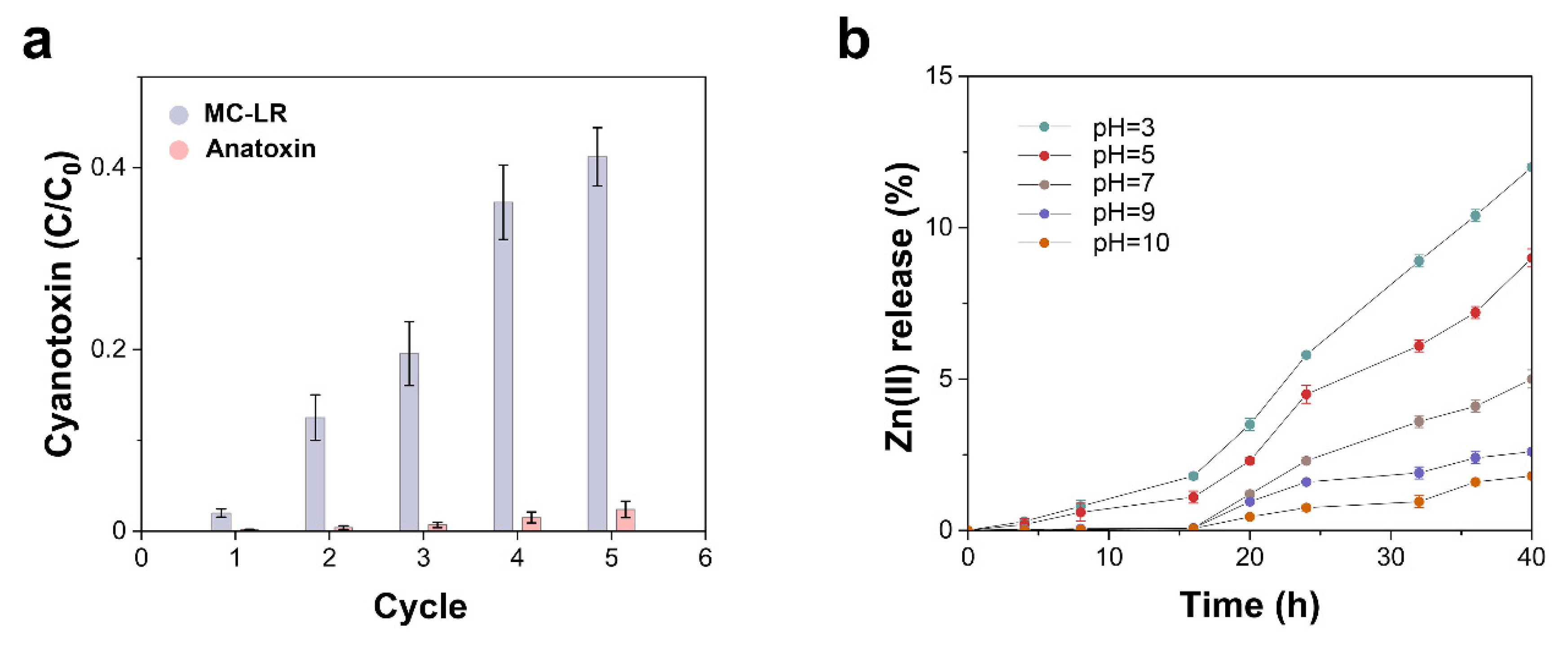
2.3. Photocatalyst Reusability
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of Nanoparticles
4.2. Materials Characterization
4.3. Photocatalytic Activity
4.4. Photocatalyst Reusability
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buratti, F.M.; Manganelli, M.; Vichi, S.; Stefanelli, M.; Scardala, S.; Testai, E.; Funari, E. Cyanotoxins: Producing organisms, occurrence, toxicity, mechanism of action and human health toxicological risk evaluation. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 1049–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmann, E.; Wiegand, C. Cyanobacterial toxins—Occurrence, biosynthesis and impact on human affairs. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meriluoto, J.; Blaha, L.; Bojadzija, G.; Bormans, M.; Brient, L.; Codd, G.A.; Drobac, D.; Faassen, E.J.; Fastner, J.; Hiskia, A.; et al. Toxic cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins in European waters—Recent progress achieved through the CYANOCOST action and challenges for further research. Adv. Oceanogr. Limnol. 2017, 8, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, D.; Huang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Liu, Y. Cyanobacteria-/cyanotoxin-contaminations and eutrophication status before Wuxi Drinking Water Crisis in Lake Taihu, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkelis, S.; Zaoutsos, N. Cyanotoxin occurrence and potentially toxin producing cyanobacteria in freshwaters of Greece: A multi-disciplinary approach. Toxicon 2014, 78, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Backer, L.C.; Kardinaal, W.E.A.; Chorus, I. Current approaches to cyanotoxin risk assessment and risk management around the globe. Harmful Algae 2014, 40, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, X.; Liu, H.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, R.; Chen, X.; Losiewicz, M.D.; Guo, H.; Zhang, H. The diversity of cyanobacterial toxins on structural characterization, distribution and identification: A systematic review. Toxins 2019, 11, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serrà, A.; Philippe, L.; Perreault, F.; Garcia-Segura, S. Photocatalytic treatment of natural waters. Reality or hype? The case of cyanotoxins remediation. Water Res. 2020, 188, 116543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoffersen, K.; Kaas, H. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water. A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring, and Management; CRC Press: London, UK, 2000; Volume 45, ISBN 0419239308. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, M.A.; Davis, T.W.; Cory, R.M.; Duhaime, M.B.; Johengen, T.H.; Kling, G.W.; Marino, J.A.; Den Uyl, P.A.; Gossiaux, D.; Dick, G.J.; et al. Cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms are a biological disturbance to Western Lake Erie bacterial communities. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1149–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrà, A.; Pip, P.; Gómez, E.; Philippe, L. Efficient magnetic hybrid ZnO-based photocatalysts for visible-light-driven removal of toxic cyanobacteria blooms and cyanotoxins. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 268, 118745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Bláha, L. Advanced oxidation processes for the removal of cyanobacterial toxins from drinking water. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Nadagouda, M.N.; O’Shea, K.; El-Sheikh, S.M.; Ismail, A.A.; Likodimos, V.; Falaras, P.; Dionysiou, D.D. Degradation of cylindrospermopsin by using polymorphic titanium dioxide under UV-Vis irradiation. Catal. Today 2014, 224, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, M.G.; Zhao, C.; O’Shea, K.E.; Zhang, G.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Zhao, C.; Han, C.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Choi, H.; Fotiou, T.; et al. Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Contaminants in Water: Process Optimization and Degradation Pathways; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2016; Volume 2016, ISBN 9781782620419. [Google Scholar]
- Mauter, M.S.; Zucker, I.; Perreault, F.; Werber, J.R.; Kim, J.H.; Elimelech, M. The role of nanotechnology in tackling global water challenges. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, M.G.; Shoemaker, J.A.; de la Cruz, A.A.; Dionysiou, D.D. LC/MS/MS structure elucidation of reaction intermediates formed during the TiO2 photocatalysis of microcystin-LR. Toxicon 2008, 51, 1103–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, L.A.; Robertson, P.K.J.; Cornish, B.J.P.A.; Marr, I.L.; Jaspars, M. Processes influencing surface interaction and photocatalytic destruction of microcystins on titanium dioxide photocatalysts. J. Catal. 2003, 213, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeb, S.K.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Brame, J.A.; Cates, E.L.; Choi, W.; Crittenden, J.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Li, Q.; Li-Puma, G.; Quan, X.; et al. The Technology Horizon for Photocatalytic Water Treatment: Sunrise or Sunset? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2937–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrà, A.; Philippe, L. Simple and scalable fabrication of hairy ZnO@ZnS core@shell Cu cables for continuous sunlight-driven photocatalytic water remediation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 126164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirhashemi, M.; Habibi-Yangjeh, A.; Rahim Pouran, S. Review on the criteria anticipated for the fabrication of highly efficient ZnO-based visible-light-driven photocatalysts. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 62, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrà, A.; Zhang, Y.; Sepúlveda, B.; Gómez, E.; Nogués, J.; Michler, J.; Philippe, L. Highly reduced ecotoxicity of ZnO-based micro/nanostructures on aquatic biota: Influence of architecture, chemical composition, fixation, and photocatalytic efficiency. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthika, K.; Ravichandran, K. Tuning the Microstructural and Magnetic Properties of ZnO Nanopowders through the Simultaneous Doping of Mn and Ni for Biomedical Applications. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahouli, M.; Barhoumi, A.; Bouzid, A.; Al-Hajry, A.; Guermazi, S. Structural and optical properties of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by direct precipitation method. Superlattices Microstruct. 2015, 85, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.J.; Kokila, M.K.; Nagabhushana, H.; Chakradhar, R.P.S.; Shivakumara, C.; Rao, J.L.; Nagabhushana, B.M. Structural, optical and EPR studies on ZnO:Cu nanopowders prepared via low temperature solution combustion synthesis. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 5349–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, S.; Çetinkara, H.A.; Bayansal, F.; Çakmak, H.M.; Güder, H.S. Characterisation of ZnO nanorod arrays grown by a low temperature hydrothermal method. Philos. Mag. 2012, 92, 2150–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjiri, M.; El Mir, L.; Leonardi, S.G.; Pistone, A.; Mavilia, L.; Neri, G. Al-doped ZnO for highly sensitive CO gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 196, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Chai, L.; Wang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Deng, P.; Chen, Y. Evaluating the doping effect of Fe, Ti and Sn on gas sensing property of ZnO. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 147, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Hu, P.; Zuo, A.; Zhang, D.; Tian, Y.; Chen, Y. Photoluminescence investigation on the gas sensing property of ZnO nanorods prepared by plasma-enhanced CVD method. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 145, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.J.; Chen, H.X.; Ma, S.Y. Structural and photoluminescence properties of Al-doped ZnO films deposited on Si substrate. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2010, 42, 1861–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, L.X. Photocatalytic Degradation of Cyanobacteria and Cyanotoxins Using Suspended and Immobilized TiO2. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Porto, Porto, Portugal, 2014; p. 168. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Hu, X.; Tang, C.; Wen, S.; Wu, X.; Long, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, L. Mechanisms underlying degradation pathways of microcystin-LR with doped TiO2 photocatalysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.; Han, C.; O’Shea, K.; Dionysiou, D.D. Revealing the degradation intermediates and pathways of visible light-induced NF-TiO2 photocatalysis of microcystin-LR. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 154–155, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, M.G.; de la Cruz, A.A.; Dionysiou, D.D. Degradation of microcystin-LR using sulfate radicals generated through photolysis, thermolysis and e- transfer mechanisms. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 96, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likodimos, V.; Han, C.; Pelaez, M.; Kontos, A.G.; Liu, G.; Zhu, D.; Liao, S.; De La Cruz, A.A.; O’Shea, K.; Dunlop, P.S.M.; et al. Anion-doped TiO2 nanocatalysts for water purification under visible light. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 13957–13964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, M.G.; Boraei, I.; Solakidou, M.; Deligiannakis, Y.; Abhishek, M.; Lawton, L.A.; Edwards, C. Enhancing photocatalytic degradation of the cyanotoxin microcystin-LR with the addition of sulfate-radical generating oxidants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 360, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Feng, C.; Zhang, Z.; Sugiura, N.; Yang, Y. Photocatalytic removal of microcystin-LR by advanced WO3-based nanoparticles under simulated solar light. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brillas, E.; Serrà, A.; Garcia-Segura, S. Biomimicry designs for photoelectrochemical systems: Strategies to improve light delivery efficiency. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 26, 100660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrà, A.; Gómez, E.; Philippe, L. Bioinspired ZnO-based solar photocatalysts for the efficient decontamination of persistent organic pollutants and hexavalent chromium in wastewater. Catalysts 2019, 9, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.C.; Nadagouda, M.; Han, C.; O’Shea, K.; El-Sheikh, S.M.; Ismail, A.A.; Dionysiou, D.D. Visible light-sensitized S, N and C co-doped polymorphic TiO2 for photocatalytic destruction of microcystin-LR. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 144, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrà, A.; Gómez, E.; Michler, J.; Philippe, L. Facile cost-effective fabrication of Cu@Cu2O@CuO-microalgae photocatalyst with enhanced visible light degradation of tetracycline. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 127477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Säbel, C.E.; Neureuther, J.M.; Siemann, S. A spectrophotometric method for the determination of zinc, copper, and cobalt ions in metalloproteins using Zincon. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 397, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrà, A.; Artal, R.; García-Amorós, J.; Sepúlveda, B.; Gómez, E.; Nogués, J.; Philippe, L. Hybrid Ni@ZnO@ZnS-Microalgae for Circular Economy: A Smart Route to the Efficient Integration of Solar Photocatalytic Water Decontamination and Bioethanol Production. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
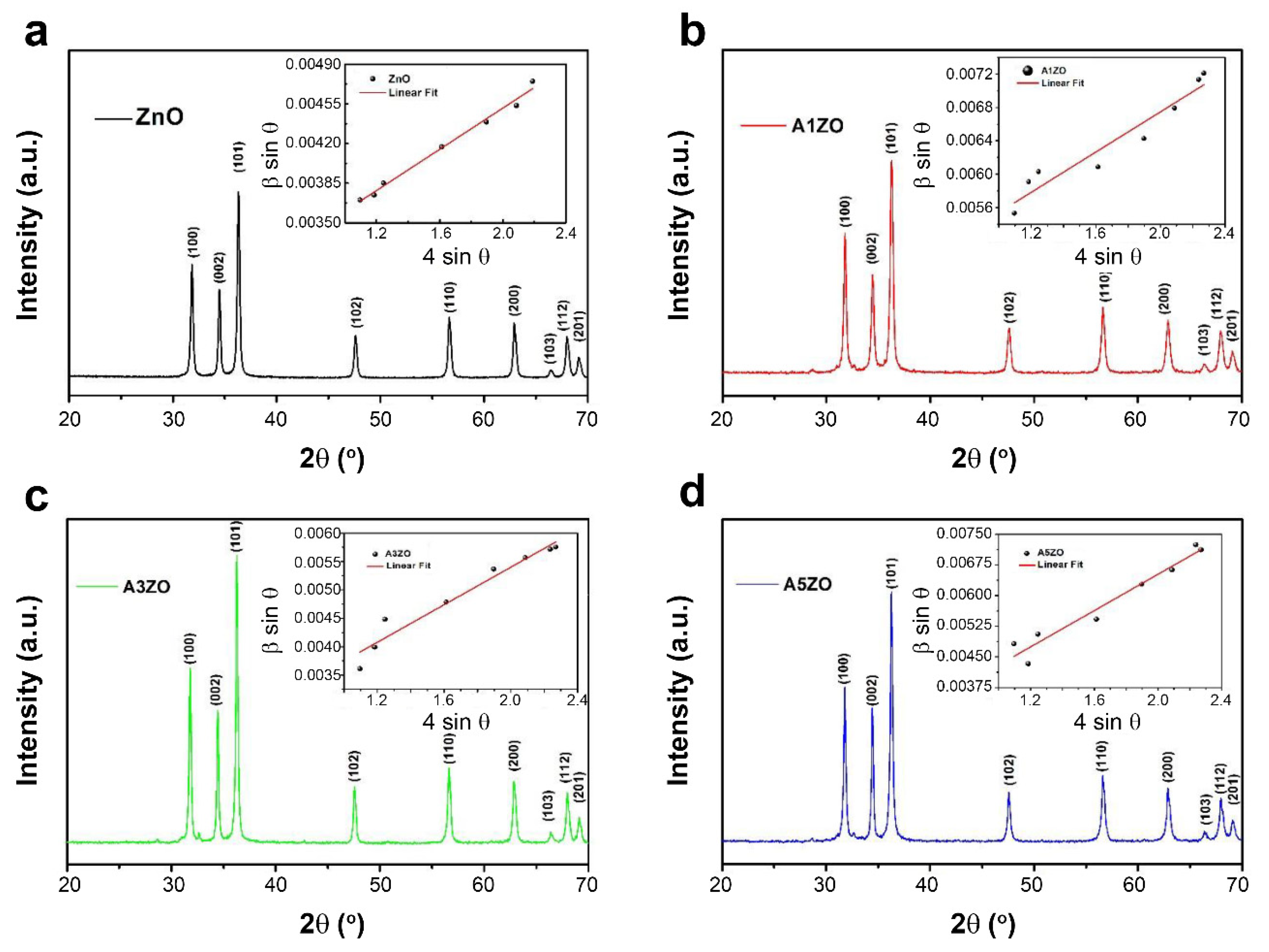
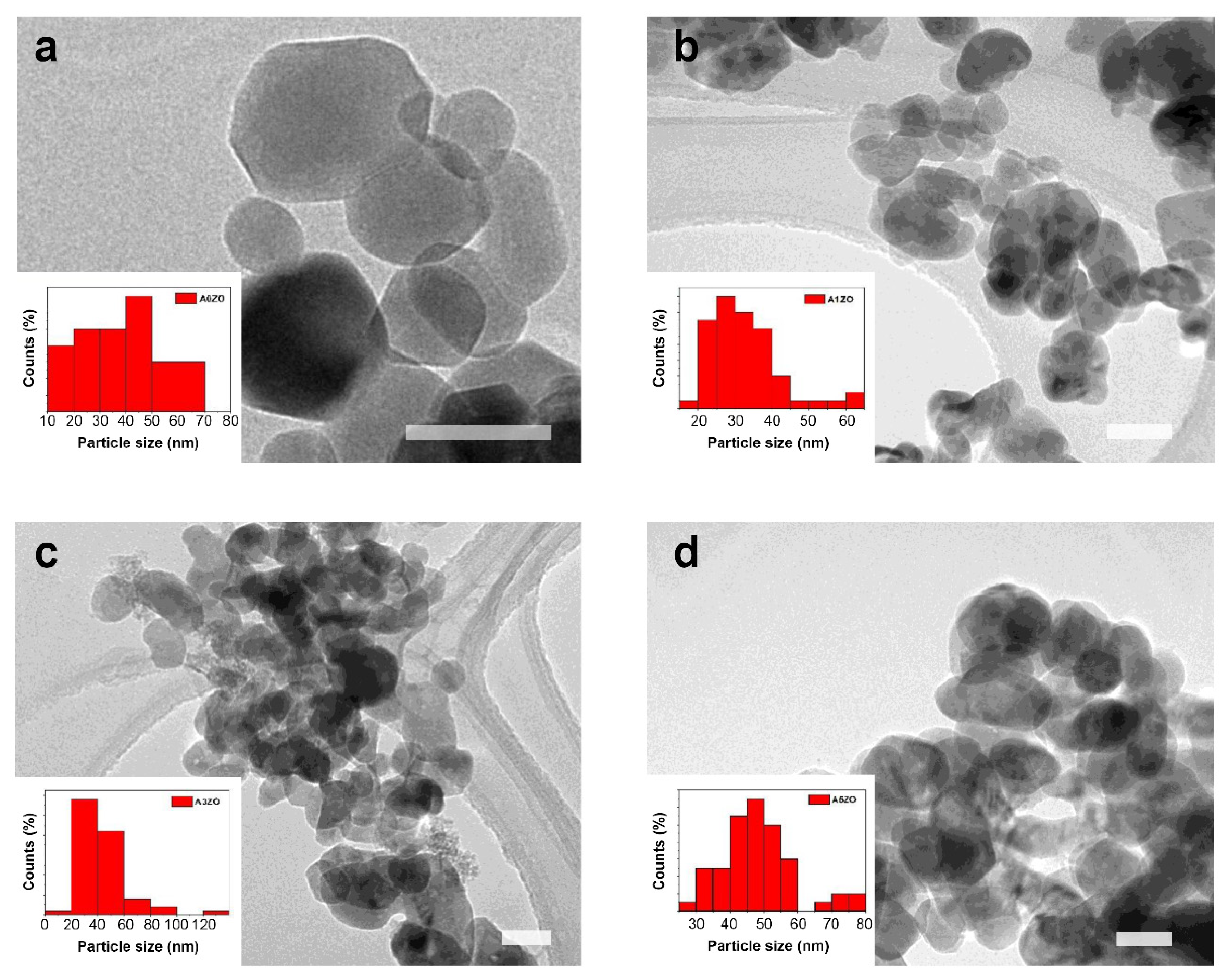


| a (Å) | c (Å) | V (Å3) | DW-H (nm) | DTEM (nm) | ε (10−4) | δ (10−3 Line × nm−2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0ZO | 3.244 | 5.195 | 47.338 | 52 | 39 | 9.1 | 81 |
| A1ZO | 3.246 | 5.201 | 47.465 | 32 | 33 | 12.0 | 174 |
| A3ZO | 3.245 | 5.200 | 47.431 | 66 | 43 | 16.5 | 116 |
| A5ZO | 3.245 | 5.199 | 47.423 | 69 | 48 | 22.2 | 148 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benamara, M.; Gómez, E.; Dhahri, R.; Serrà, A. Enhanced Photocatalytic Removal of Cyanotoxins by Al-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles with Visible-LED Irradiation. Toxins 2021, 13, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010066
Benamara M, Gómez E, Dhahri R, Serrà A. Enhanced Photocatalytic Removal of Cyanotoxins by Al-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles with Visible-LED Irradiation. Toxins. 2021; 13(1):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010066
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenamara, Majdi, Elvira Gómez, Ramzi Dhahri, and Albert Serrà. 2021. "Enhanced Photocatalytic Removal of Cyanotoxins by Al-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles with Visible-LED Irradiation" Toxins 13, no. 1: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010066
APA StyleBenamara, M., Gómez, E., Dhahri, R., & Serrà, A. (2021). Enhanced Photocatalytic Removal of Cyanotoxins by Al-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles with Visible-LED Irradiation. Toxins, 13(1), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13010066








