Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning (PSP) in Mussels from the Eastern Cantabrian Sea: Toxicity, Toxin Profile, and Co-Occurrence with Cyclic Imines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
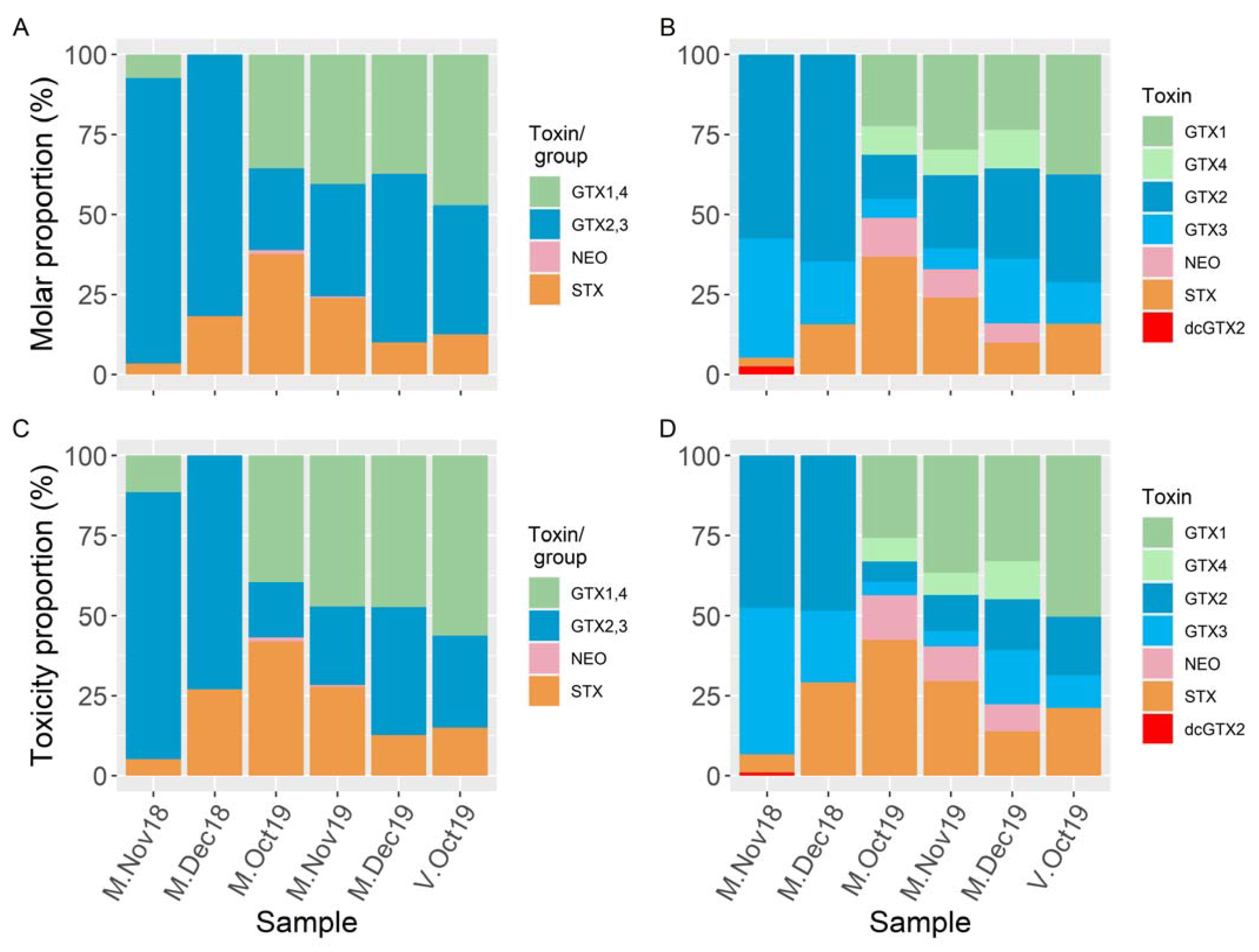
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Standards, Solvents, and Reagents
4.2. Shellfish Sampling and Tissue Preparation
4.3. Sample Extraction and Preparation
4.3.1. LC–FLD
4.3.2. LC–MS/MS
4.3.3. Cyclic Imines
4.4. LC–FLD Conditions
4.5. LC–MS Conditions
4.5.1. PSP Toxins
4.5.2. Cyclic Imines
4.6. Toxicity Computation
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deeds, J.R.; Landsberg, J.H.; Etheridge, S.M.; Pitcher, G.C.; Longan, S.W. Non-traditional vectors for paralytic shellfish poi-soning. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 308–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schantz, E.J. Chemistry and Biology of Saxitoxin and Related Toxins. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1986, 479, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, L.E. Saxitoxin, a toxic marine natural product that targets a multitude of receptors. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 200–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, M.; D’Agostino, P.M.; Mihali, T.K.; Moffitt, M.C.; Neilan, B.A. Neurotoxic Alkaloids: Saxitoxin and Its Analogs. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2185–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oshima, Y. Post-column Derivatization HPLC Methods for Paralytic Shellfish Poisons. In Manual on Harmful Marine Microalgae; Hallegraeff, G.M., Anderson, D.M., Cembella, A.D., Eds.; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1995; pp. 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain on a request from the European Commission on Marine Biotoxins in Shellfish—Saxitoxin Group. EFSA J. 2009, 1019, 1–76. [Google Scholar]
- Bricelj, V.M.; Connell, L.; Konoki, K.; MacQuarrie, S.P.; Scheuer, T.; Catterall, W.A.; Trainer, V.L. Sodium channel mutation leading to saxitoxin resistance in clams increases risk of PSP. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 434, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bricelj, V.M.; Shumway, S.E. Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Bivalve Molluscs: Occurrence, Transfer Kinetics, and Biotransformation. Rev. Fish. Sci. 1998, 6, 315–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberkorn, H.; Lambert, C.; Le Goïc, N.; Quéré, C.; Bruneau, A.; Riso, R.; Auffret, M.; Soudant, P. Cellular and biochemical responses of the oyster Crassostrea gigas to controlled exposures to metals and Alexandrium minutum. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 147, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ben-Gigirey, B.; Rossignoli, A.E.; Riobó, P.; Rodríguez, F. First Report of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Marine Invertebrates and Fish in Spain. Toxins 2020, 12, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EC. Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 laying down specific hygiene rules for food of animal origin. Off. J. Eur. Union 2004, L139. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32004R0853 (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- EC. Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2021/1374 of 12 April 2021 Amending Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council on Specific Hygiene Requirements for Food of Animal Origin (Text with EEA Rele-Vance). Off. J. Eur. Union 2021, L297. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg_del/2021/1374/oj (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- EC. COMMISSION IMPLEMENTING REGULATION (EU) 2019/627 of 15 March 2019 laying down uniform practical arrangements for the performance of official controls on products of animal origin intended for human consumption in accordance with Regulation (EU) 2017/625 of the European Parliament and of the Council and amending Commission Regulation (EC) No 2074/2005 as regards official controls. Off. J. Eur. Union 2019, L131. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/en/ALL/?uri=CELEX:32019R0627 (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- Lawrence, J.F.; Menard, C.; Charbonneauc, C.F. A study of ten toxins associated whit paralytic shellfish poison using pre-chromatographic oxidation and liquid chromatography whit fluorescence detection. J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 1991, 74, 404–409. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, J.F.; Niedzwiadek, B.; Menard, C. Quantitative Determination of Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning Toxins in Shellfish Using Prechromatographic Oxidation and Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection: Collaborative Study. J. AOAC Int. 2005, 88, 1714–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turner, A.D.; Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; Fong, S.Y.T.; Hungerford, J.; McNabb, P.S.; Boundy, M.J.; Harwood, D.T.; Aanrud, S.; Alfonso, C.; Alvarez, M.; et al. Ultrahigh-Performance Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Determination of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins and Tetrodotoxin in Mussels, Oysters, Clams, Cockles, and Scallops: Collaborative Study. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 103, 533–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresnan, E.; Arévalo, F.; Belin, C.; Branco, M.A.C.; Cembella, A.D.; Clarke, D.; Correa, J.; Davidson, K.; Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; Lozano, R.F.; et al. Diversity and regional distribution of harmful algal events along the Atlantic margin of Europe. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Sullivan, J.J.; Reguera, B. Paralytic shellfish poisoning in northwest Spain: The toxicity of the dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum. Toxicon 1989, 27, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamán, L.; Fernández, R.; Jaén, D.; Mata, A.J.; Morales, J.; Jiménez, C.; Márquez, I. Estudio de las proliferaciones del dino-flagelado Gymnodinium catenatum (Graham) en la costa de Andalucía (Sur Península Ibérica). In VIII Reunión Ibérica sobre Fi-toplacton Tóxico y Biotoxinas; Norte, M., Fernández, J.J., Eds.; Instituto de Bio-orgánica, Universidad de La Laguna: La Laguna, Spain, 2004; pp. 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Ordas, M.C.; Fraga, S.; Franco, J.M.; Ordas, A.; Figueras, A. Toxin and molecular analysis of Gymnodinium catenatum (Di-nophyceae) strains from Galicia (NW Spain) and Andalucia (S Spain). J. Plankton Res. 2004, 26, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, S.M.; de Carvalho, M.; Mestre, T.; Ferreira, J.J.; Coelho, M.; Peralta, R.; Vale, P. Paralytic shellfish poisoning due to ingestion of Gymnodinium catenatum contaminated cockles—Application of the AOAC HPLC Official Method. Toxicon 2012, 59, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, I.; Fraga, S.; Figueroa, R.I.; Pazos, Y.; Massanet, A.; Ramilo, I. Bloom dynamics and life cycle strategies of two toxic dinoflagellates in a coastal upwelling system (NW Iberian Peninsula). Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2010, 57, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzet, N.; Franco, J.M.; Raine, R. Characterization of nontoxic and toxin-producing strains of Alexandrium minutum (Di-nophyceae) in Irish coastal waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3333–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Touzet, N.; Farrell, H.; Rathaille, A.N.; Rodriguez, P.; Alfonso, A.; Botana, L.M.; Raine, R. Dynamics of co-occurring Alexandrium minutum (Global Clade) and A. tamarense (West European) (Dinophyceae) during a summer bloom in Cork Harbour, Ireland (2006). Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2010, 57, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, P.; Botelho, M.J.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Gomes, S.S.; Sampayo, M.A.d.M. Two decades of marine biotoxin monitoring in bi-valves from Portugal (1986–2006): A review of exposure assessment. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, S.M.; Purdie, D.A.; Lilly, E.L.; Larsen, J.; Morris, S. Toxin Profile, Pigment Composition, and Large Subunit rDNA Phylogenetic Analysis of an Alexandrium minutum (Dinophyceae) Strain Isolated from the Fleet Lagoon, United Kingdom. J. Phycol. 2005, 41, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, G.; Daugbjerg, N.; Franco, J.M. Morphology, toxin composition and LSU rDNA phylogeny of Alexandrium minutum (Dinophyceae) from Denmark, with some morphological observations on other European strains. Harmful Algae 2003, 2, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrell, S.; Gunnarsson, T.; Gunnarsson, K.; Clarke, D.; Turner, A.D. First detection of paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) toxins in Icelandic mussels (Mytilus edulis): Links to causative phytoplankton species. Food Control. 2013, 31, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlson, B.; Andersen, P.; Arneborg, L.; Cembella, A.; Eikrem, W.; John, U.; West, J.J.; Klemm, K.; Kobos, J.; Lehtinen, S.; et al. Harmful algal blooms and their effects in coastal seas of Northern Europe. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassus, P.; Baron, R.; Garen, P.; Truquet, P.; Masselin, P.; Bardouil, M.; Leguay, D.; Amzil, Z. Paralytic shellfish poison outbreaks in the Penzé estuary: Environmental factors affecting toxin uptake in the oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Aquat. Living Resour. 2004, 17, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrer, L.; Revilla, M.; Laza-Martínez, A.; Sagarminaga, Y.; Fontán, A.; Larreta, J.; Zorita, I.; Solaun, O.; Rodríguez, J.G.; Arantzamendi, L.; et al. Occurrence of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii in the coastal waters of the southeastern Bay of Biscay. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembella, A.D.; Lewis, N.I.; Quilliam, M.A. Spirolide composition of micro-extracted pooled cells isolated from natural plankton assemblages and from cultures of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii. Nat. Toxins 1999, 7, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wagoner, R.M.; Misner, I.; Tomas, C.R.; Wright, J.L.C. Occurrence of 12-methylgymnodimine in a spirolide-producing dinoflagellate Alexandrium peruvianum and the biogenetic implications. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 4243–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, U.; Krock, B.; Wietkamp, S.; Beran, A. A Mediterranean Alexandrium taylorii (Dinophyceae) Strain Produces Goniodomin A and Lytic Compounds but Not Paralytic Shellfish Toxins. Toxins 2020, 12, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, C.M.; Reece, K.S.; Harris, T.M. Revisiting the toxin profile of Alexandrium pseudogonyaulax; Formation of a desmethyl congener of goniodomin A. Toxicon 2020, 188, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsia, M.H.; Morton, S.L.; Smith, L.L.; Beauchesne, K.R.; Huncik, K.M.; Moeller, P.D.R. Production of goniodomin A by the planktonic, chain-forming dinoflagellate Alexandrium monilatum (Howell) Balech isolated from the Gulf Coast of the United States. Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Wen, Y.Y.; Hansen, P.J.; Larsen, T.O.; Andersen, A.J.C. Development of a LC-MS/MS method for the quantification of goniodomins A and B and its application to Alexandrium pseudogonyaulax strains and plankton field samples of Danish coastal waters. Toxicon 2018, 155, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salgado, P.; Riobo, P.; Rodríguez, F.; Franco, J.M.; Bravo, I. Differences in the toxin profiles of Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Di-nophyceae) strains isolated from different geographic origins: Evidence of paralytic toxin, spirolide, and gymnodimine. Toxicon 2015, 103, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zurhelle, C.; Nieva, J.; Tillmann, U.; Harder, T.; Krock, B.; Tebben, J. Identification of Novel Gymnodimines and Spirolides from the Marine Dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cembella, A.D.; Lewis, N.I.; Quilliam, M. The marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) as the causative organism of spirolide shellfish toxins. Phycologia 2000, 39, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belin, C.; Soudant, D. Trente Années d’Observation des Micro-Algues et des Toxines d’Algues sur le Littoral; Editions Quae: Versailles, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Riobó, P.; Rodriguez, F.; Garrido, J.L.; Franco, J.M. Toxin profiles of A. ostenfeldii and A. peruvianum. Comparison of two clonal strains with different light tolerance. Marine and Freshwater Toxins Analysis. In Proceedings of the Fourth Joint Symposium and AOAC Task Force Meeting, Baiona-Pontevedra, Spain, 5–9 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanen, P.; Suikkanen, S.; Franzén, J.; Franzén, H.; Kankaanpää, H.; Kremp, A. Bloom and toxin dynamics of Alexandrium ostenfeldii in a shallow embayment at the SW coast of Finland, northern Baltic Sea. Harmful Algae 2012, 15, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremp, A.; Lindholm, T.; Dreßler, N.; Erler, K.; Gerdts, G.; Eirtovaara, S.; Leskinen, E. Bloom forming Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) in shallow waters of the Åland Archipelago, Northern Baltic Sea. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamas, J.; Arévalo, F.; Moroño, Á.; Correa, J.; Rossignoli, A.E.; Blanco, J. Gymnodimine A in mollusks from the north Atlantic Coast of Spain: Prevalence, concentration, and relationship with spirolides. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 279, 116919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, J.M.; Fernandez, P.; Reguera, B. Toxin profiles of natural populations and cultures of Alexandrium minutum Halim from Galician (Spain) coastal waters. Environ. Boil. Fishes 1994, 6, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembella, A.D.; Sullivan, J.J.; Boyer, G.L.; Taylor, F.J.R.; Andersen, R.J. Variation in paralytic shellfish toxin composition within the Protogonyaulax tamarensis/catenella species complex; red tide dinoflagellates. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1987, 15, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, M.; Giacobbe, M.G.; Masó, M.; Gangemi, E.; Penna, A.; Sampedro, N.; Azzaro, F.; Camp, J.; Galluzzi, L. A comparative study on recurrent blooms of Alexandrium minutum in two Mediterranean coastal areas. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 673–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatiades, L.; Gotsisskretas, O.; Metaxatos, A. Field and culture studies on the ecophysiology of the toxic dinoflagellate Alex-andrium minutum (Halim) present in Greek coastal waters. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, I.; Beszteri, S.; Tillmann, U.; Cembella, A.; John, U. Growth- and nutrient-dependent gene expression in the toxigenic marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum. Harmful Algae 2011, 12, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimizu, Y.; Yoshioka, M. Transformation of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins as Demonstrated in Scallop Homogenates. Science 1981, 212, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotaki, Y. Screening of Bacteria which Convert Gonyautoxin 2, 3 to Saxitoxin. Nippon. Suisan Gakkaishi 1989, 55, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotaki, Y.; Oshima, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Bacterial transformation of paralytic shellfish toxins in coral reef crabs and a marine snail. Nippon. Suisan Gakkaishi 1985, 51, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amzil, Z.; Quilliam, M.A.; Hu, T.; Wright, J.L.C. Winter accumulation of paralytic shellfish toxins in digestive glands of mussels from Arcachon and Toulon (France) without detectable toxic plankton species revealed by interference in the mouse bioassay for lipophilic toxins. Nat. Toxins 1999, 7, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.R.; Robertson, A.; Quilliam, M.A. Toxin Profile of Gymnodinium catenatum (Dinophyceae) from the Portuguese Coast, as Determined by Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2046–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guallar, C.; Bacher, C.; Chapelle, A. Global and local factors driving the phenology of Alexandrium minutum (Halim) blooms and its toxicity. Harmful Algae 2017, 67, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neaud-Masson, N.; Gautier, E. Lieux et Périodes à Risque Pour les Toxines Paralysantes dans les Coquillages des Côtes Françaises; Note d’Information—Données REPHYTOX-Ifremer, Banque Quadrige. 2021, p. 6. Available online: https://archimer.ifremer.fr/doc/00692/80445/83582.pdf (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- Muñiz, O.; Revilla, M.; Rodríguez, M.I.R.; Laza-Martínez, A.; Seoane, S.; Franco, J.; Orive, E. Evaluation of phytoplankton quality and toxicity risk based on a long-term time series previous to the implementation of a bivalve farm (Basque coast as a case study). Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2017, 10, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilbao, J.; Muñiz, O.; Revilla, M.; Rodríguez, J.G.; Laza-Martínez, A.; Seoane, S. Suitability of two areas of the Basque coast to sustain shellfish aquaculture according to both the presence of potentially toxic phytoplankton and the biotoxins regulated by the European Union. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 36, 101279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EURLMB. EU-Harmonised Standard Operating Procedure for Determination of Lipophilic Marine Biotoxins in Molluscs by LC-MS/MS.Version 5. 2014. Available online: https://www.aesan.gob.es/AECOSAN/docs/documentos/laboratorios/LNRBM/ARCHIVO2EU-Harmonised-SOP-LIPO-LCMSMS_Version5.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2021).
- Boundy, M.J.; Selwood, A.I.; Harwood, D.T.; McNabb, P.S.; Turner, A.D. Development of a sensitive and selective liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry method for high throughput analysis of paralytic shellfish toxins using graphitised carbon solid phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1387, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Warton, D.I.; Duursma, R.A.; Falster, D.S.; Taskinen, S. smatr 3—An R package for estimation and inference about allometric lines: The smatr 3—An R package. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2012, 3, 257–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; p. 260. [Google Scholar]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Cabo, T.; Moroño, Á.; Arévalo, F.; Correa, J.; Lamas, J.P.; Rossignoli, A.E.; Blanco, J. Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning (PSP) in Mussels from the Eastern Cantabrian Sea: Toxicity, Toxin Profile, and Co-Occurrence with Cyclic Imines. Toxins 2021, 13, 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13110761
Rodríguez-Cabo T, Moroño Á, Arévalo F, Correa J, Lamas JP, Rossignoli AE, Blanco J. Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning (PSP) in Mussels from the Eastern Cantabrian Sea: Toxicity, Toxin Profile, and Co-Occurrence with Cyclic Imines. Toxins. 2021; 13(11):761. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13110761
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Cabo, Tamara, Ángeles Moroño, Fabiola Arévalo, Jorge Correa, Juan Pablo Lamas, Araceli E. Rossignoli, and Juan Blanco. 2021. "Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning (PSP) in Mussels from the Eastern Cantabrian Sea: Toxicity, Toxin Profile, and Co-Occurrence with Cyclic Imines" Toxins 13, no. 11: 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13110761
APA StyleRodríguez-Cabo, T., Moroño, Á., Arévalo, F., Correa, J., Lamas, J. P., Rossignoli, A. E., & Blanco, J. (2021). Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning (PSP) in Mussels from the Eastern Cantabrian Sea: Toxicity, Toxin Profile, and Co-Occurrence with Cyclic Imines. Toxins, 13(11), 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13110761





