Temporal Patterns of Bacterial and Viral Communities during Algae Blooms of a Reservoir in Macau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
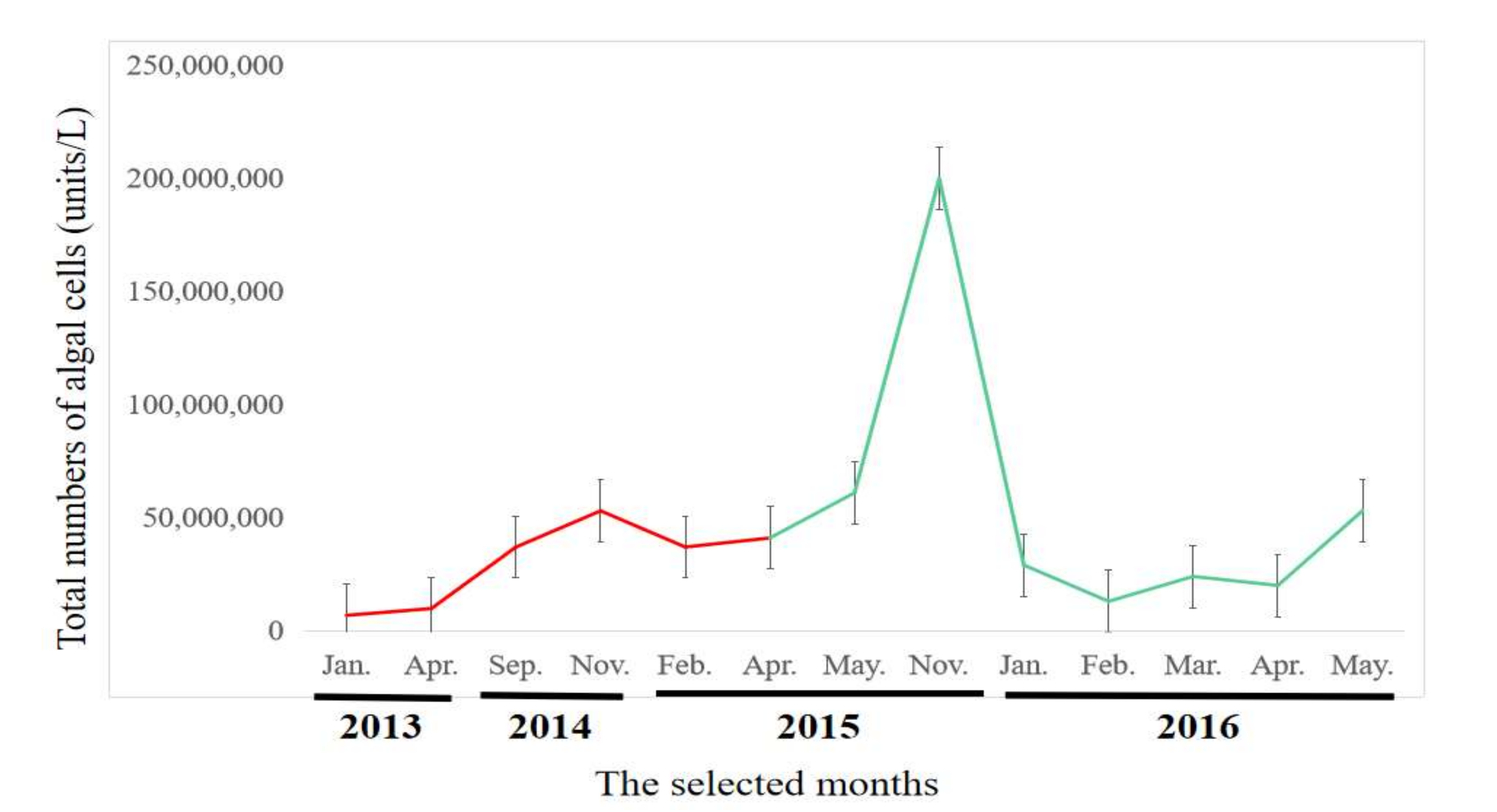
2.1. Algal Biomass and Temporal Changes
2.2. 16S rRNA Sequencing Results and Diversity Analysis
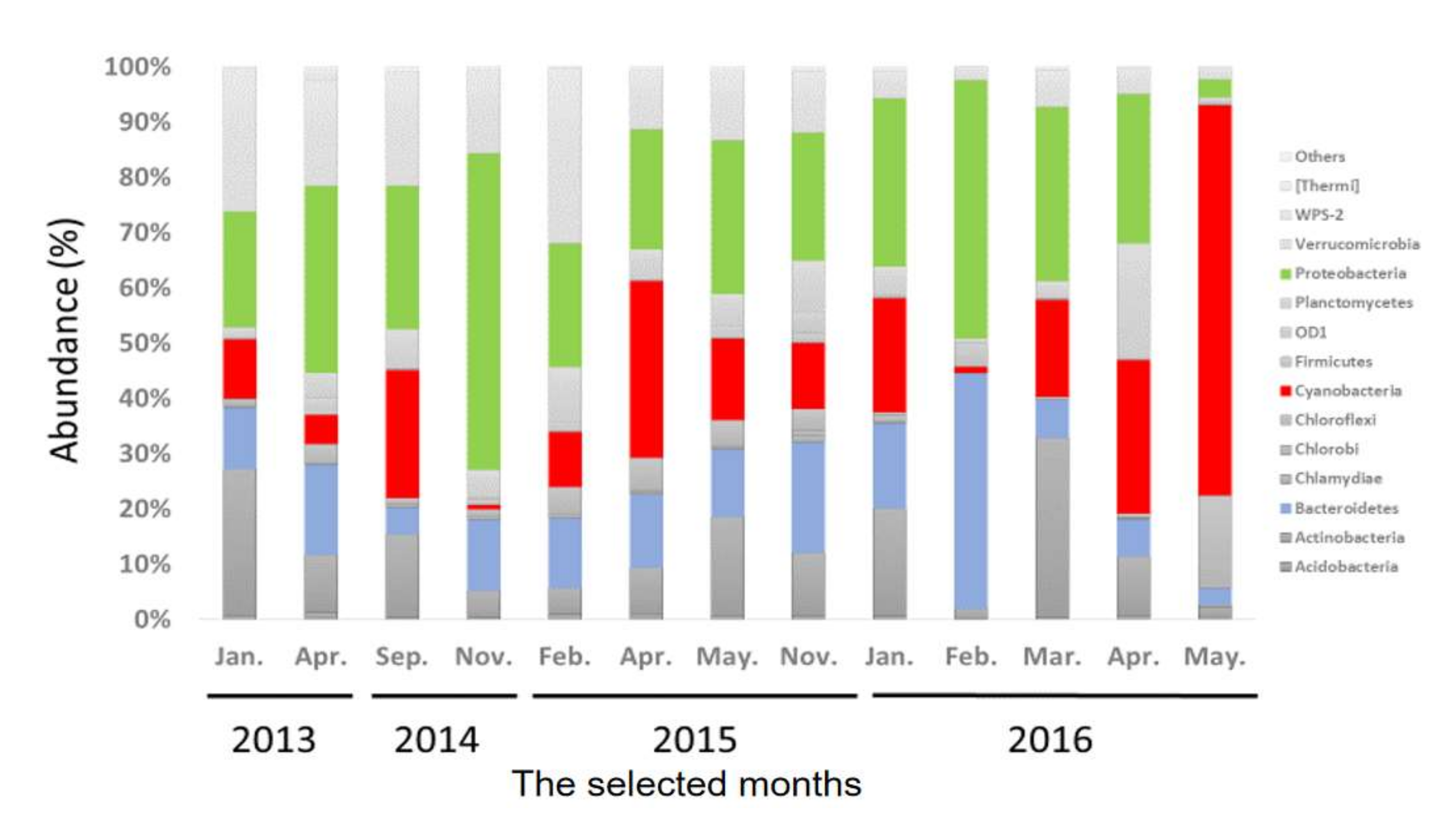
2.3. Taxonomic Compositions of Bacterial Communities
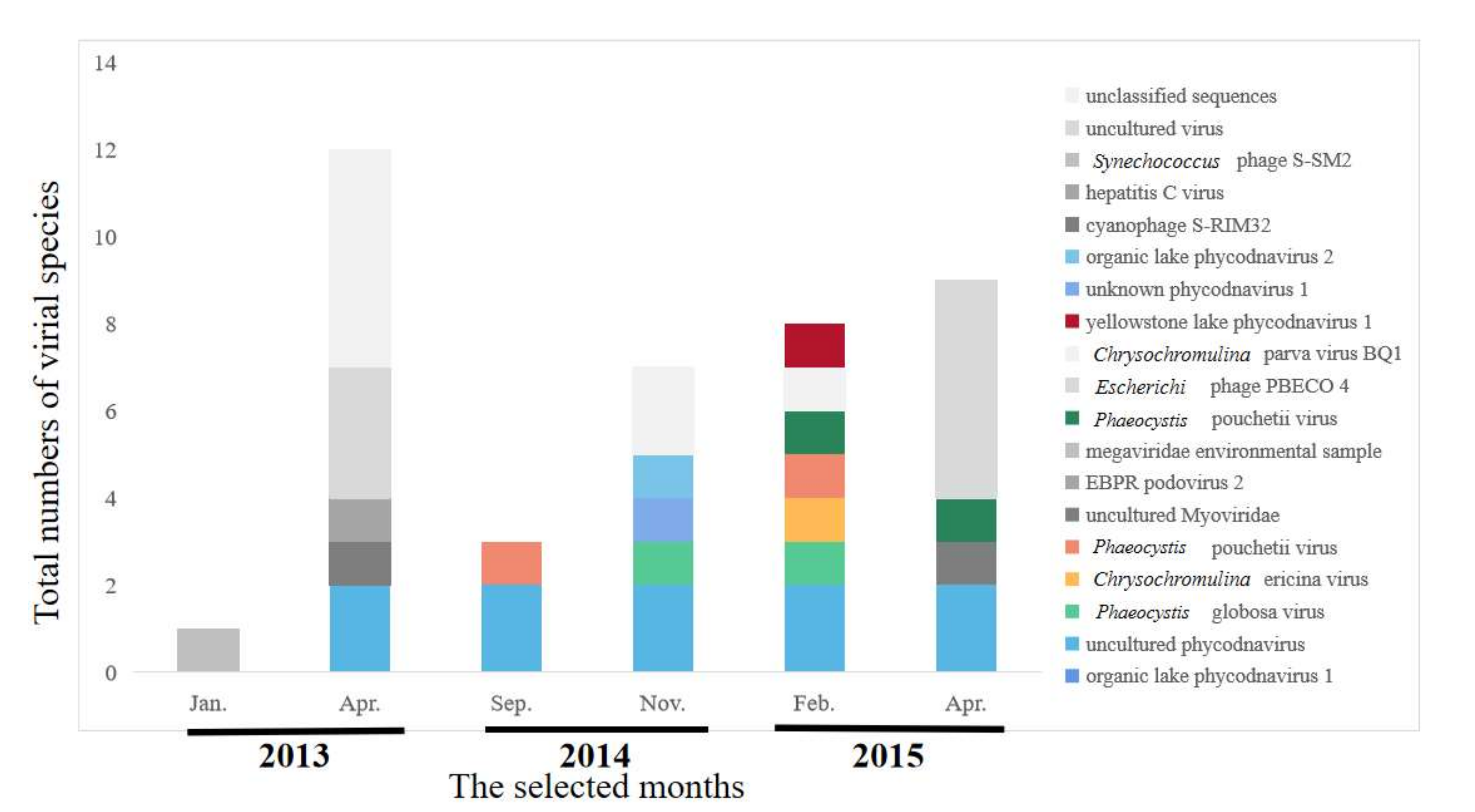
2.4. Composition of Viral Communities Based on Metagenomic Sequences
2.5. Relationships between Phycodnavirus and Communities of Algae and Bacteria
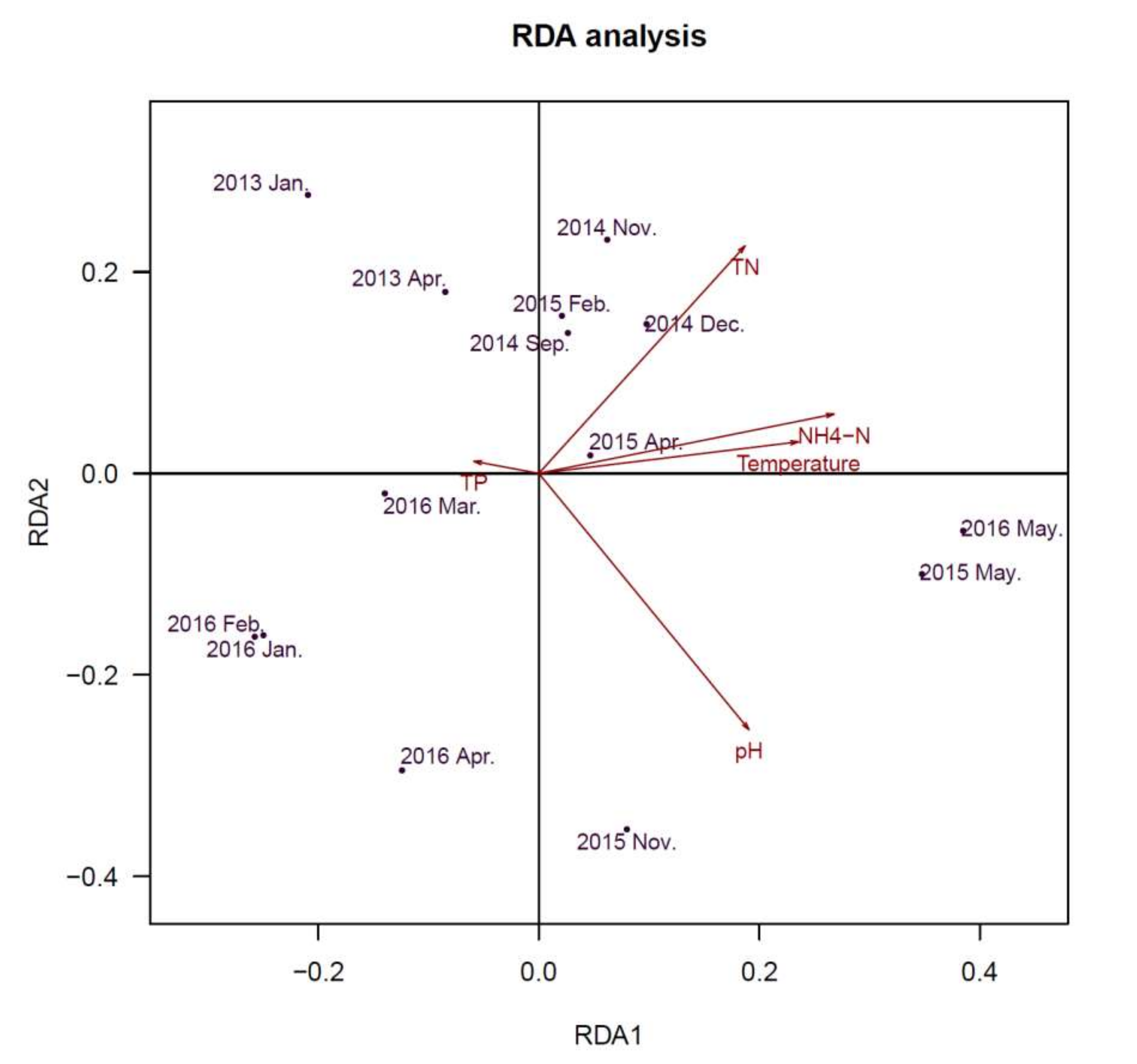
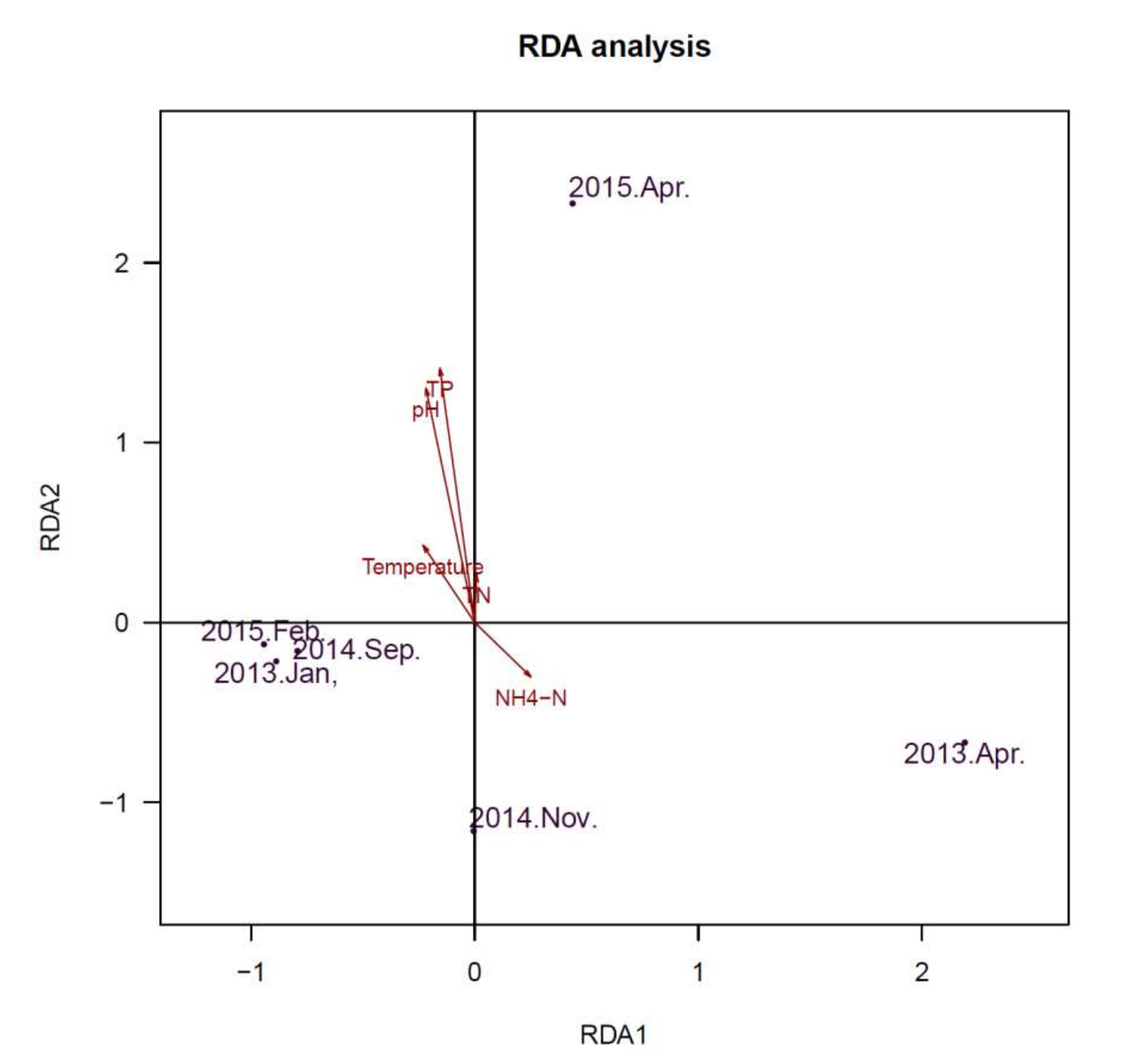
2.6. Comparison of Microbial Community Composition with Water Parameters
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling Sites and Collection
4.2. Water Parameters
4.3. Extraction and Sequencing of DNA
4.4. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paerl, H.W.; Paul, V.J. Climate change: Links to global expansion of harmful cyanobacteria. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1349–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, W.W.; Boyer, G.L. Health impacts from cyanobacteria harmful algae blooms: Implications for the North American Great Lakes. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 194–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavicchioli, R. Microbial ecology of Antarctic aquatic systems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masoud, A.A.; Koike, K.; Mashaly, H.A.; Gergis, F. Spatio-temporal trends and change factors of groundwater quality in an arid area with peat rich aquifers: Emergence of water environmental problems in Tanta District, Egypt. J. Arid Environ. 2016, 124, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Stanley, E.H.; Vander Zanden, M.J. State of the world's freshwater ecosystems: Physical, chemical, and biological changes. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2011, 36, 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Neil, J.M.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Gobler, C.J. The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: The potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Hall, N.S.; Calandrino, E.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a world experiencing anthropogenic and climatic-induced change. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payet, J.P.; McMinds, R.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L. Unprecedented evidence for high viral abundance and lytic activity in coral reef waters of the South Pacific Ocean. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhauser, S.; Kirchmair, M.; Gleason, F.H. Ecological roles of the parasitic phytomyxids (plasmodiophorids) in marine ecosystems—A review. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johannessen, T.V.; Bratbak, G.; Larsen, A.; Ogata, H.; Egge, E.S.; Edvardsen, B.; Eikrem, W.; Sandaa, R.A. Characterisation of three novel giant viruses reveals huge diversity among viruses infecting Prymnesiales (Haptophyta). Virology 2015, 476, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, B.; Dai, M.; Zhai, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, K.; Chen, J.; Lin, J.; Han, A.; Xu, Y. Distribution, degradation and dynamics of dissolved organic carbon and its major compound classes in the Pearl River estuary, China. Mar. Chem. 2010, 119, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, A.Y.T.; Xu, J.; Yin, K.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Lei, H.; Anderson, D.M.; Lee, J.H.W.; Harrison, P.J. Phytoplankton biomass and production in subtropical Hong Kong waters: Influence of the Pearl River Outflow. Estuaries Coasts 2010, 33, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Z.M.; Gan, J.P. Controls of seasonal variability of phytoplankton blooms in the Pearl River Estuary. Deep-Sea Res. Part II-Trop. Stud. Oceanogr. 2015, 117, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, L.; Zhang, B.; Gitelson, A.A. Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in estuarine waters: Case study of the Pearl River estuary, South China Sea. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 024016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Lou, I.; Ung, W.K.; Kong, Y.J.; Mok, K.M. Spatio-temporal variations of phytoplankton structure and water quality in the eutrophic freshwater reservoir of Macau. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 55, 2237–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Lou, I.; Ung, W.K.; Kong, Y.J.; Mok, K.M. Analysis of cylindrospermopsin- and microcystin-producing genotypes and cyanotoxin concentrations in the Macau storage reservoir. Hydrobiologia 2014, 741, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.W.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Howard, M.D.; Johnson, M.V.; Morton, S.L.; Perkins, D.A.; Reavie, E.D.; Scott, G.I.; Smith, S.A.; Steevens, J.A. Are harmful algal blooms becoming the greatest inland water quality threat to public health and aquatic ecosystems? Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessi, I.S.; Maalouf, P.D.C.; Laughinghouse, H.D.; Baurain, D.; Wilmotte, A.; Post, A. On the use of high-throughput sequencing for the study of cyanobacterial diversity in Antarctic aquatic mats. J. Phycol. 2016, 52, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Xu, J.; Lavoie, M.; Fan, X.; Liu, G.; Sun, L.; Fu, Z.; Qian, H. Biological and chemical factors driving the temporal distribution of cyanobacteria and heterotrophic bacteria in a eutrophic lake (West Lake, China). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 1685–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.M.; Barry, K.; Hu, G.D.; Meng, S.l.; Song, C.; Wu, W.; Chen, J.Z.; Xu, P. Bacterioplankton community analysis in tilapia ponds by Illumina high-throughput sequencing. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, A.; Hulax, M.; Sylvester, F.; Huang, X.; Adebayo, A.; Abbott, C.L.; Adamowicz, S.J.; Heath, D.D.; Cristescu, M.E.; Maclsaac, H.J. High sensitivity of 454 pyrosequencing for detection of rare species in aquatic communities. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2013, 4, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westram, A.M.; Jokela, J.; Baumgartner, C.; Keller, I. Spatial distribution of cryptic species diversity in European freshwater Amphipods (Gammarus fossarum) as revealed by pyrosequencing. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Labonte, J.M.; Swan, B.K.; Poulos, B.; Luo, H.; Koren, S.; Hallam, S.J.; Sullivan, M.B.; Woyke, T.; Wommack, K.E.; Stepanauskas, R. Single-cell genomics-based analysis of virus-host interactions in marine surface bacterioplankton. ISME J. 2015, 9, 2386–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Pei, H.; Jin, Y.; Ma, C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, H. High-throughput sequencing reveals microbial communities in drinking water treatment sludge from six geographically distributed plants, including potentially toxic cyanobacteria and pathogens. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 1, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Deng, L.; Lou, K.; Zhang, T.; Yang, H.; Shi, Y.; Lin, Q. Molecular characterization of the planktonic microorganisms in water of two mountain brackish lakes. J. Basic Microbiol. 2014, 54, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.J.; Schroeder, J.; Lunn, M.; Sloan, W.; Raskin, L. Spatial-temporal survey and occupancy-abundance modeling to predict bacterial community dynamics in the drinking water microbiome. Mbio 2014, 5, e01135-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lacativa, B.I.; Alexander, E.; Stefan, B.; Dag, K.; Piton, T.L.; Henriques, V.A.A.; Ban, S. Host-specificity and dynamics in bacterial communities associated with bloom-forming freshwater phytoplankton. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85950. [Google Scholar]
- Eiler, A.; Bertilsson, S. Composition of freshwater bacterial communities associated with cyanobacterial blooms in four Swedish lakes. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 1228–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, R.J.; Jones, S.E.; Helmus, M.R.; McMahon, K.D. Phylogenetic ecology of the freshwater Actinobacteria acI lineage. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7169–7176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eigemann, F.; Hilt, S.; Salka, I.; Grossart, H.P. Bacterial community composition associated with freshwater algae: Species specificity vs. dependency on environmental conditions and source community. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 83, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossart, H.P.; Levold, F.; Allgaier, M.; Simon, M.; Brinkhoff, T. Marine diatom species harbour distinct bacterial communities. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 860–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staley, C.; Unno, T.; Gould, T.J.; Jarvis, B.; Phillips, J.; Cotner, J.B.; Sadowsky, M.J. Application of Illumina next-generation sequencing to characterize the bacterial community of the Upper Mississippi River. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 115, 1147–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salis, R.K.; Bruder, A.; Piggott, J.J.; Summerfield, T.C.; Matthaei, C.D. High-throughput amplicon sequencing and stream benthic bacteria: Identifying the best taxonomic level for multiple-stressor research. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guemes, A.G.C.; Youle, M.; Cantu, V.A.; Felts, B.; Nulton, J.; Rohwer, F. Viruses as winners in the game of life. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2016, 3, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portillo, M.C.; Anderson, S.P.; Fierer, N. Temporal variability in the diversity and composition of stream bacterioplankton communities. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 2417–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logue, J.B.; Langenheder, S.; Andersson, A.F.; Bertilsson, S.; Drakare, S.; Lanzen, A.; Lindstrm, E.S. Freshwater bacterioplankton richness in oligotrophic lakes depends on nutrient availability rather than on species-area relationships. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Yang, D.; Yong, Z.; Ji, S.; Gast, C.V.D.; Hahn, M.W.; Wu, Q. Do patterns of bacterial diversity along salinity gradients differ from those observed for macroorganisms? PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allison, S.D.; Lu, Y.; Weihe, C.; Goulden, M.L.; Martiny, A.C.; Treseder, K.K.; Martiny, J.B.H. Microbial abundance and composition influence litter decomposition response to environmental change. Ecology 2013, 94, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sapp, M.; Wichels, A.; Wiltshire, K.H.; Gerdts, G. Bacterial community dynamics during the winter-spring transition in the North Sea. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 59, 622–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, L.; Jeppesen, E.; He, D.; Wang, J.; Liboriussen, L.; Xing, P.; Wu, Q. pH influences the importance of niche-related and neutral processes in lacustrine bacterioplankton assembly. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 3104–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dziallas, C.; Grossart, H.P. Temperature and biotic factors influence bacterial communities associated with the cyanobacterium Microcystis sp. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1632–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, A.M.; Frederico, M.P.; Vidal, L.O.; Hugo, S.; Suhett, A.L.; Farjalla, V.F.; Cotner, J.B.; Fabio, R. Tropical freshwater ecosystems have lower bacterial growth efficiency than temperate ones. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kujawinski, E.B. The impact of microbial metabolism on marine dissolved organic matter. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2011, 3, 567–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Lou, I.; Ung, W.K.; Kong, Y.; Mok, K.M. Application of PCR and real-time PCR for monitoring cyanobacteria, Microcystis spp. and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskiiin Macau freshwater reservoir. Front. Earth Sci. 2014, 8, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lou, I.; Kong, Y.; Ung, W.K.; Mok, K.M. Eutrophication analyses and principle component regression for two subtropical storage reservoirs in Macau. Desalination Water Treat. 2013, 51, 7331–7340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.X.; Duan, Y.S.; Yi, X.S.; Wang, S.; Ma, C. Biological removal of nitrogen by a membrane bioreactor-attapulgite clay system in treating polluted water. Desalination 2013, 317, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, C.; Lungu, L.; Savoiu, M.; Bradu, C.; Dinoiu, V.; Danet, A.F. Total antioxidant activity and phenols and flavonoids content of several plant extracts. Int. J. Food Prop. 2012, 15, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebina, J.; Tsutsui, T.; Shirai, T. Simultaneous determination of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in water using peroxodisulfate oxidation. Water Res. 1983, 17, 1721–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, J.W.G. Citation classic—The inverted microscope method of estimating algal numbers and the statistical basis of estimations by counting. Agric. Biol. Environ. 1981, 11, 143–170. [Google Scholar]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, D.; Giesy, J.P.; Guo, M.; Ung, W.K.; Kong, Y.; Mok, K.M.; Lee, S.M.-Y. Temporal Patterns of Bacterial and Viral Communities during Algae Blooms of a Reservoir in Macau. Toxins 2021, 13, 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13120894
Hu D, Giesy JP, Guo M, Ung WK, Kong Y, Mok KM, Lee SM-Y. Temporal Patterns of Bacterial and Viral Communities during Algae Blooms of a Reservoir in Macau. Toxins. 2021; 13(12):894. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13120894
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Dini, John P. Giesy, Min Guo, Wai Kin Ung, Yijun Kong, Kai Meng Mok, and Simon Ming-Yuen Lee. 2021. "Temporal Patterns of Bacterial and Viral Communities during Algae Blooms of a Reservoir in Macau" Toxins 13, no. 12: 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13120894





