The Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factors (CNFs)—A Family of Rho GTPase-Activating Bacterial Exotoxins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Regulation of cnf Gene Expression
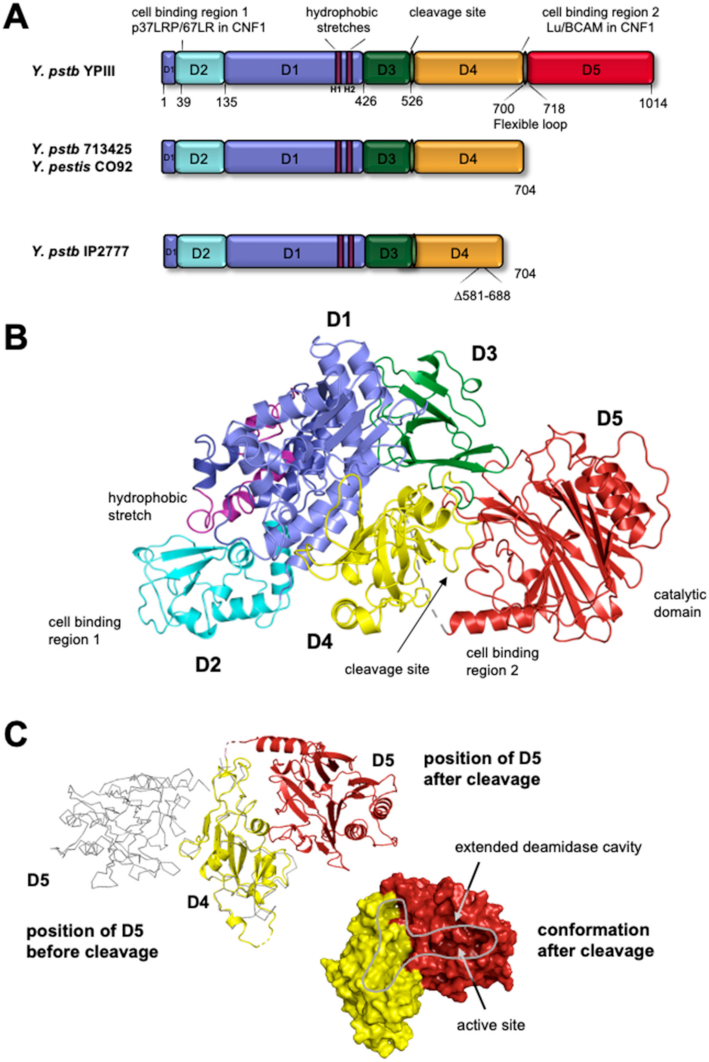
3. Structure and Domain Organization of CNFs
4. Export of CNFs
5. Receptor Binding of CNF Toxins
6. The Intracellular Uptake and Trafficking
7. Release of Activated CNFs into the Host Cell Cytoplasm
8. Mode of Action and Pathogenesis
8.1. CNF-Mediated Activation of Rho GTPases
8.2. CNF-Induced Signaling Pathways
8.3. CNF-Mediated Influence on Tissue Integrity, Cell Barriers, and Cell Death
8.4. Influence of CNFs on Bacterial Virulence and Host Immune Responses
9. Potential Therapeutic Applications
10. Conclusions and Perspectives
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aili, M.; Isaksson, E.L.; Carlsson, S.E.; Wolf-Watz, H.; Rosqvist, R.; Francis, M.S. Regulation of Yersinia Yop-Effector Delivery by Translocated YopE. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 298, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andor, A.; Trülzsch, K.; Essler, M.; Roggenkamp, A.; Wiedemann, A.; Heesemann, J.; Aepfelbacher, M. YopE of Yersinia, a GAP for Rho GTPases, Selectively Modulates Rac-dependent Actin Structures in Endothelial Cells. Cell. Microbiol. 2001, 3, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalonga, P.; Ridley, A.J. Rho GTPases and Cell Cycle Control. Growth Factors 2006, 24, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Pawel-Rammingen, U.; Telepnev, M.V.; Schmidt, G.; Aktories, K.; Wolf-Watz, H.; Rosqvist, R. GAP Activity of the Yersinia YopE Cytotoxin Specifically Targets the Rho Pathway: A Mechanism for Disruption of Actin Microfilament Structure. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 36, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktories, K. Bacterial Toxins That Target Rho Proteins. J. Clin. Invest. 1997, 99, 827–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falbo, V.; Pace, T.; Picci, L.; Pizzi, E.; Caprioli, A. Isolation and Nucleotide Sequence of the Gene Encoding Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 of Escherichia Coli. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 4909–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caprioli, A.; Falbo, V.; Roda, L.; Ruggeri, F.; Zona, C. Partial Purification and Characterization of an Escherichia Coli Toxic Factor That Induces Morphological Cell Alterations. Infect. Immun. 1983, 39, 1300–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiorentini, C.; Arancia, G.; Caprioli, A.; Falbo, V.; Ruggeri, F.; Donelli, G. Cytoskeletal Changes Induced in HEp-2 Cells by the Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor of Escherichia Coli. Toxicon 1988, 26, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smati, M.; Clermont, O.; Bleibtreu, A.; Fourreau, F.; David, A.; Daubié, A.; Hignard, C.; Loison, O.; Picard, B.; Denamur, E. Quantitative Analysis of Commensal Escherichia Coli Populations Reveals Host-specific Enterotypes at the Intra-species Level. Microbiologyopen 2015, 4, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsumori, K.; Terai, A.; Yamamoto, S.; Ishitoya, S.; Yoshida, O. Virulence Characteristics of Eschevichia Coli in Acute Bacterial Prostatitis. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 180, 1378–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blum, G.; Falbo, V.; Caprioli, A.; Hacker, J. Gene Clusters Encoding the Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor Type 1, Prs-Fimbriae and α-Hemolysin Form the Pathogenicity Island II of the Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli Strain J96. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1995, 126, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, D.L.; Bukanov, N.O.; Berg, D.E.; Welch, R.A. Two Pathogenicity Islands in Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli J96: Cosmid Cloning and Sample Sequencing. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 3736–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Rycke, J.; Gonzalez, E.; Blanco, J.; Oswald, E.; Blanco, M.; Boivin, R. Evidence for Two Types of Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor in Human and Animal Clinical Isolates of Escherichia Coli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lockman, H.A.; Gillespie, R.A.; Baker, B.D.; Shakhnovich, E. Yersinia Pseudotuberculosis Produces a Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 2708–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oswald, E.; De Rycke, J.; Guillot, J.F.; Boivin, R. Cytotoxic Effect of Multinucleation in HeLa Cell Cultures Associated with the Presence of Vir Plasmid in Escherichia Coli Strains. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1989, 58, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péres, S.Y.; Marchès, O.; Daigle, F.; Nougayrède, J.; Hérault, F.; Tasca, C.; De Rycke, J.; Oswald, E. A New Cytolethal Distending Toxin (CDT) from Escherichia Coli Producing CNF2 Blocks HeLa Cell Division in G2/M Phase. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 24, 1095–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oswald, E.; Sugai, M.; Labigne, A.; Wu, H.C.; Fiorentini, C.; Boquet, P.; O’Brien, A.D. Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor Type 2 Produced by Virulent Escherichia Coli Modifies the Small GTP-Binding Proteins Rho Involved in Assembly of Actin Stress Fibers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3814–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flatau, G.; Lemichez, E.; Gauthier, M.; Chardin, P.; Paris, S.; Fiorentini, C.; Boquet, P. Toxin-Induced Activation of the G Protein P21 Rho by Deamidation of Glutamine. Nature 1997, 387, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, G.; Sehr, P.; Wilm, M.; Selzer, J.; Mann, M.; Aktories, K. Gin 63 of Rho Is Deamidated by Escherichia Coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor-1. Nature 1997, 387, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orden, J.A.; Domínguez-Bernal, G.; Martínez-Pulgarín, S.; Blanco, M.; Blanco, J.E.; Mora, A.; Blanco, J.; de la Fuente, R. Necrotoxigenic Escherichia Coli from Sheep and Goats Produce a New Type of Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor (CNF3) Associated with the Eae and EhxA Genes. Int. Microbiol. 2007, 10, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Stoll, T.; Markwirth, G.; Reipschläger, S.; Schmidt, G. A New Member of a Growing Toxin Family—Escherichia Coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 3 (CNF3). Toxicon 2009, 54, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reipschläger, S.; Kubatzky, K.; Taromi, S.; Burger, M.; Orth, J.; Aktories, K.; Schmidt, G. Toxin-Induced RhoA Activity Mediates CCL1-Triggered Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription Protein Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 11183–11194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, C.; Pop, M.; Leemhuis, J.; Schirmer, J.; Aktories, K.; Schmidt, G. The Yersinia Pseudotuberculosis Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor (CNF y) Selectively Activates RhoA. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 16026–16032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, C.; Schmidt, G. CNF and DNT. In Reviews of Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 49–63. [Google Scholar]
- Schweer, J.; Kulkarni, D.; Kochut, A.; Pezoldt, J.; Pisano, F.; Pils, M.C.; Genth, H.; Huehn, J.; Dersch, P. The Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor of Yersinia Pseudotuberculosis (CNFY) Enhances Inflammation and Yop Delivery during Infection by Activation of Rho GTPases. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haywood, E.E.; Ho, M.; Wilson, B.A. Modular Domain Swapping among the Bacterial Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor (CNF) Family for Efficient Cargo Delivery into Mammalian Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 3860–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, M.; Mettouchi, A.; Wilson, B.A.; Lemichez, E. CNF1-like Deamidase Domains: Common Lego Bricks among Cancer-Promoting Immunomodulatory Bacterial Virulence Factors. Pathog. Dis. 2018, 76, fty045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemichez, E.; Flatau, G.; Bruzzone, M.; Boquet, P.; Gauthier, M. Molecular Localization of the Escherichia Coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor CNF1 Cell-Binding and Catalytic Domains. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 24, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, K.; Elling, F. The Pathogenesis of Atrophic Rhinitis in Pigs Induced by Toxigenic Pasteurella Multocida. J. Comp. Pathol. 1984, 94, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, Y.; Senda, T.; Sugimoto, N.; Katahira, J.; Matsuda, M. Bordetella Bronchiseptica Dermonecrotizing Toxin Stimulates Assembly of Actin Stress Fibers and Focal Adhesions by Modifying the Small GTP-Binding Protein Rho. J. Cell Sci. 1995, 108, 3243–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacerda, H.M.; Pullinger, G.D.; Lax, A.J.; Rozengurt, E. Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 from Escherichia Coli and Dermonecrotic Toxin from Bordetella Bronchiseptica Induce P21rho-Dependent Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Focal Adhesion Kinase and Paxillin in Swiss 3T3 Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 9587–9596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, G.; Selzer, J.; Lerm, M.; Aktories, K. The Rho-Deamidating Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 From Escherichia Coli Possesses Transglutaminase Activity CYSTEINE 866 AND HISTIDINE 881 ARE ESSENTIAL FOR ENZYME ACTIVITY. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 13669–13674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kitadokoro, K.; Kamitani, S.; Miyazawa, M.; Hanajima-Ozawa, M.; Fukui, A.; Miyake, M.; Horiguchi, Y. Crystal Structures Reveal a Thiol Protease-like Catalytic Triad in the C-Terminal Region of Pasteurella Multocida Toxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5139–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orth, J.H.C.; Aktories, K. Molecular Biology of Pasteurella Multocida Toxin. In Pasteurella Multocida; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 73–92. [Google Scholar]
- Pullinger, G.D.; Lax, A.J. Histidine Residues at the Active Site of the Pasteurella Multocida Toxin. Open Biochem. J. 2007, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ollis, D.L.; Cheah, E.; Cygler, M.; Dijkstra, B.; Frolow, F.; Franken, S.M.; Harel, M.; Remington, S.J.; Silman, I.; Schrag, J. The α/β Hydrolase Fold. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1992, 5, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kourist, R.; Jochens, H.; Bartsch, S.; Kuipers, R.; Padhi, S.K.; Gall, M.; Böttcher, D.; Joosten, H.-J.; Bornscheuer, U. The α/β-Hydrolase Fold 3DM Database (ABHDB) as a Tool for Protein Engineering. Exist. Data Nov. Hypotheses 2010, 175, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landraud, L.; Gibert, M.; Popoff, M.R.; Boquet, P.; Gauthier, M. Expression of Cnf1 by Escherichia Coli J96 Involves a Large Upstream DNA Region Including the HlyCABD Operon, and Is Regulated by the RfaH Protein. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 47, 1653–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbri, A.; Gauthier, M.; Boquet, P. The 5′ Region of Cnf1 Harbours a Translational Regulatory Mechanism for CNF1 Synthesis and Encodes the Cell-Binding Domain of the Toxin. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 33, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kouokam, J.C.; Wai, S.N. Outer Membrane Vesicle-Mediated Export of a Pore-Forming Cytotoxin from Escherichia Coli. Toxin Rev. 2006, 25, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhigetti, F.; Nuss, A.M.; Twittenhoff, C.; Beele, S.; Urban, K.; Will, S.; Bernhart, S.H.; Stadler, P.F.; Dersch, P.; Narberhaus, F. Temperature-Responsive in Vitro RNA Structurome of Yersinia Pseudotuberculosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2016, 113, 7237–7242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Twittenhoff, C.; Heroven, A.K.; Mühlen, S.; Dersch, P.; Narberhaus, F. An RNA Thermometer Dictates Production of a Secreted Bacterial Toxin. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, G.; Selzer, J.; Lerm, M.; Aktories, K. The Rho-Deamidating Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 from Escherichia Coli Possesses Transglutaminase Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 273, 13669–13674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buetow, L.; Flatau, G.; Chiu, K.; Boquet, P.; Ghosh, P. Structure of the Rho-Activating Domain of Escherichia Coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2001, 8, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buetow, L.; Ghosh, P. Structural Elements Required for Deamidation of RhoA by Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 12784–12791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaoprasid, P.; Lukat, P.; Mühlen, S.; Heidler, T.; Gazdag, E.; Dong, S.; Bi, W.; Rüter, C.; Kirchenwitz, M.; Steffen, A. Crystal Structure of Bacterial Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor CNFY Reveals Molecular Building Blocks for Intoxication. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e105202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, S.; Doye, A.; Boquet, P. Mutation of Specific Acidic Residues of the CNF1 T Domain into Lysine Alters Cell Membrane Translocation of the Toxin. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 41, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Connell, T.D.; Metzger, D.J.; Wang, M.; Jobling, M.G.; Holmes, R.K. Initial Studies of the Structural Signal for Extracellular Transport of Cholera Toxin and Other Proteins Recognized by Vibrio Cholerae. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 4091–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Findlay, G.; Yu, J.; Hirst, T.R. Analysis of Enterotoxin Synthesis in a Vibrio Cholerae Strain Lacking DsbA, a Periplasmic Enzyme Involved in Disulphide Bond Formation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1993, 21, 212S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichow, S.L.; Korotkov, K.V.; Gonen, M.; Sun, J.; Delarosa, J.R.; Hol, W.G.J.; Gonen, T. The Binding of Cholera Toxin to the Periplasmic Vestibule of the Type II Secretion Channel. Channels 2011, 5, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaudhuri, K.; Chatterjee, S.N. Cholera Toxins; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; ISBN 3540884521. [Google Scholar]
- Monnappa, A.K.; Bari, W.; Seo, J.K.; Mitchell, R.J. The Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor of Yersinia Pseudotuberculosis (CNFy) Is Carried on Extracellular Membrane Vesicles to Host Cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Kim, K.S. Ferredoxin Is Involved in Secretion of Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 across the Cytoplasmic Membrane in Escherichia Coli K1. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Kim, K.S. YgfZ Contributes to Secretion of Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 into Outer-Membrane Vesicles in Escherichia Coli. Microbiology 2012, 158, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, J.M.; Carvalho, H.M.; Rasmussen, S.B.; O’Brien, A.D. Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor Type 1 Delivered by Outer Membrane Vesicles of Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli Attenuates Polymorphonuclear Leukocyte Antimicrobial Activity and Chemotaxis. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 4401–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Falzano, L.; Fiorentini, C.; Donelli, G.; Michel, E.; Kocks, C.; Cossart, P.; Cabanié, L.; Oswald, E.; Boquet, P. Induction of Phagocytic Behaviour in Human Epithelial Cells by Escherichia Coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor Type1. Mol. Microbiol. 1993, 9, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouokam, J.C.; Wai, S.N.; Fällman, M.; Dobrindt, U.; Hacker, J.; Uhlin, B.E. Active Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 Associated with Outer Membrane Vesicles from Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 2022–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gillet, D.; Barbier, J.; Popoff, M.R.; Gillet, D.; Barbier, J. Diphtheria Toxin. In The Comprehensive Sourcebook of Bacterial Protein Toxins; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 111–132. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, B.A.; Collier, R.J. Diphtheria Toxin and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Exotoxin A: Active-Site Structure and Enzymic Mechanism. In ADP-Ribosylating Toxins; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 27–41. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, B.A.; Ho, M. Pasteurella Multocida: From Zoonosis to Cellular Microbiology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 631–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McNichol, B.A.; Rasmussen, S.B.; Carvalho, H.M.; Meysick, K.C.; O’Brien, A.D. Two Domains of Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor Type 1 Bind the Cellular Receptor, Laminin Receptor Precursor Protein. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 5095–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chung, J.W.; Hong, S.J.; Kim, K.J.; Goti, D.; Stins, M.F.; Shin, S.; Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M.; Kim, K.S. 37-KDa Laminin Receptor Precursor Modulates Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1-Mediated RhoA Activation and Bacterial Uptake. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 16857–16862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reppin, F.; Cochet, S.; El Nemer, W.; Fritz, G.; Schmidt, G. High Affinity Binding of Escherichia Coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 (CNF1) to Lu/BCAM Adhesion Glycoprotein. Toxins 2018, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blumenthal, B.; Hoffmann, C.; Aktories, K.; Backert, S.; Schmidt, G. The Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factors from Yersinia Pseudotuberculosis and from Escherichia Coli Bind to Different Cellular Receptors but Take the Same Route to the Cytosol. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 3344–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piteau, M.; Papatheodorou, P.; Schwan, C.; Schlosser, A.; Aktories, K.; Schmidt, G. Lu/BCAM Adhesion Glycoprotein Is a Receptor for Escherichia Coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 (CNF1). PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowarschik, S.; Schöllkopf, J.; Müller, T.; Tian, S.; Knerr, J.; Bakker, H.; Rein, S.; Dong, M.; Weber, S.; Grosse, R. Yersinia Pseudotuberculosis Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor Interacts with Glycosaminoglycans. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varki, A.; Cummings, R.; Esko, J.; Freeze, H.; Hart, G.; Marth, J. Proteoglycans and Glycosaminoglycans. In Essentials of Glycobiology; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Belting, M. Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan as a Plasma Membrane Carrier. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003, 28, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, G.J.; McMahon, H.T. Mechanisms of Endocytosis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 857–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eierhoff, T.; Stechmann, B.; Rmer, W. Pathogen and Toxin Entry—How Pathogens and Toxins Induce and Harness Endocytotic Mechanisms. Mol. Regul. Endocytosis 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naslavsky, N.; Caplan, S. The Enigmatic Endosome–Sorting the Ins and Outs of Endocytic Trafficking. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs216499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guillard, S.; Minter, R.R.; Jackson, R.H. Engineering Therapeutic Proteins for Cell Entry: The Natural Approach. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shete, H.K.; Prabhu, R.H.; Patravale, V.B. Endosomal Escape: A Bottleneck in Intracellular Delivery. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 460–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varkouhi, A.K.; Scholte, M.; Storm, G.; Haisma, H.J. Endosomal Escape Pathways for Delivery of Biologicals. J. Controlled Release 2011, 151, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandvig, K.; Spilsberg, B.; Lauvrak, S.U.; Torgersen, M.L.; Iversen, T.G.; Van Deurs, B. Pathways Followed by Protein Toxins into Cells. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 293, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandvig, K.; Grimmer, S.; Lauvrak, S.; Torgersen, M.; Skretting, G.; Van Deurs, B.; Iversen, T. Pathways Followed by Ricin and Shiga Toxin into Cells. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2002, 117, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandvig, K.; van Deurs, B. Entry of Ricin and Shiga Toxin into Cells: Molecular Mechanisms and Medical Perspectives. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 5943–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torgersen, M.L.; Skretting, G.; van Deurs, B.; Sandvig, K. Internalization of Cholera Toxin by Different Endocytic Mechanisms. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 3737–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contamin, S.; Galmiche, A.; Doye, A.; Flatau, G.; Benmerah, A.; Boquet, P. The P21 Rho-Activating Toxin Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 Is Endocytosed by a Clathrin-Independent Mechanism and Enters the Cytosol by an Acidic-Dependent Membrane Translocation Step. Mol. Biol. Cell 2000, 11, 1775–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Duve, C.; De Barsy, T.; Poole, B.; Tulkens, P. Lysosomotropic Agents. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1974, 23, 2495–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda, H.M. Bacterial Toxins Stimulate Rho-Dependent Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Focal Adhesion Proteins; University of London, University College London (United Kingdom): London, UK, 1997; ISBN 1-339-50393-X. [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook, J.L.; Dorland, R.B. Bacterial Toxins: Cellular Mechanisms of Action. Microbiol. Rev. 1984, 48, 199–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, D.J.; Kondow-McConaghy, H.M.; Hager, E.C.; Pellois, J.-P. Endosomal Escape and Cytosolic Penetration of Macromolecules Mediated by Synthetic Delivery Agents. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 30, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krantz, B.A.; Finkelstein, A.; Collier, R.J. Protein Translocation through the Anthrax Toxin Transmembrane Pore Is Driven by a Proton Gradient. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 355, 968–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umata, T.; Moriyama, Y.; Futai, M.; Mekada, E. The Cytotoxic Action of Diphtheria Toxin and Its Degradation in Intact Vero Cells Are Inhibited by Bafilomycin A1, a Specific Inhibitor of Vacuolar-Type H (+)-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 21940–21945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimori, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Moriyama, Y.; Futai, M.; Tashiro, Y. Bafilomycin A1, a Specific Inhibitor of Vacuolar-Type H (+)-ATPase, Inhibits Acidification and Protein Degradation in Lysosomes of Cultured Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 17707–17712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.A.; Ho, M. Pasteurella Multocida Toxin Interaction with Host Cells: Entry and Cellular Effects. In Pasteurella Multocida; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 93–111. [Google Scholar]
- Repella, T.L.; Ho, M.; Chong, T.P.M.; Bannai, Y.; Wilson, B.A. Arf6-Dependent Intracellular Trafficking of Pasteurella Multocida Toxin and PH-Dependent Translocation from Late Endosomes. Toxins 2011, 3, 218–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zuverink, M.; Chen, C.; Przedpelski, A.; Blum, F.C.; Barbieri, J.T. A Heterologous Reporter Defines the Role of the Tetanus Toxin Interchain Disulfide in Light-Chain Translocation. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 2714–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baldwin, M.R.; Lakey, J.H.; Lax, A.J. Identification and Characterization of the Pasteurella Multocida Toxin Translocation Domain. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masin, J.; Osickova, A.; Sukova, A.; Fiser, R.; Halada, P.; Bumba, L.; Linhartova, I.; Osicka, R.; Sebo, P. Negatively Charged Residues of the Segment Linking the Enzyme and Cytolysin Moieties Restrict the Membrane-Permeabilizing Capacity of Adenylate Cyclase Toxin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurnikov, I.V.; Kyrychenko, A.; Flores-Canales, J.C.; Rodnin, M.V.; Simakov, N.; Vargas-Uribe, M.; Posokhov, Y.O.; Kurnikova, M.; Ladokhin, A.S. PH-Triggered Conformational Switching of the Diphtheria Toxin T-Domain: The Roles of N-Terminal Histidines. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 2752–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knust, Z.; Blumenthal, B.; Aktories, K.; Schmidt, G. Cleavage of Escherichia Coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 Is Required for Full Biologic Activity. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 1835–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christianson, H.C.; Belting, M. Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan as a Cell-Surface Endocytosis Receptor. Matrix Biol. 2014, 35, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktories, K.; Barbieri, J.T. Bacterial Cytotoxins: Targeting Eukaryotic Switches. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiguchi, Y.; Inoue, N.; Masuda, M.; Kashimoto, T.; Katahira, J.; Sugimoto, N.; Matsuda, M. Bordetella Bronchiseptica Dermonecrotizing Toxin Induces Reorganization of Actin Stress Fibers through Deamidation of Gln-63 of the GTP-Binding Protein Rho. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 11623–11626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caprioli, A.; Donelli, G.; Falbo, V.; Possenti, R.; Roda, L.G.; Roscetti, G.; Ruggeri, F.M. A Cell Division-Active Protein from E. Coli. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1984, 118, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellenbroek, S.I.J.; Collard, J.G. Rho GTPases: Functions and Association with Cancer. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2007, 24, 657–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, M.L.; Marshall, C.J.; Olson, M.F. RAS and RHO GTPases in G1-Phase Cell-Cycle Regulation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorentini, C.; Matarrese, P.; Straface, E.; Falzano, L.; Donelli, G.; Boquet, P.; Malorni, W. Rho-Dependent Cell Spreading Activated by E.Coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 Hinders Apoptosis in Epithelial Cells. Cell Death Differ. 1998, 5, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiorentini, C.; Fabbri, A.; Flatau, G.; Donelli, G.; Matarrese, P.; Lemichez, E.; Falzano, L.; Boquet, P. Escherichia Coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 (CNF1), a Toxin That Activates the Rho GTPase. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 19532–19537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, C.; Aktories, K.; Schmidt, G. Change in Substrate Specificity of Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor Unmasks Proteasome-Independent down-Regulation of Constitutively Active RhoA. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 10826–10832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lerm, M.; Selzer, J.; Hoffmeyer, A.; Rapp, U.; Aktories, K.; Schmidt, G. Deamidation of Cdc42 and Rac by Escherichia Coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1: Activation of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase in HeLa Cells. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baumer, Y.; Burger, S.; Curry, F.; Golenhofen, N.; Drenckhahn, D.; Waschke, J. Differential Role of Rho GTPases in Endothelial Barrier Regulation Dependent on Endothelial Cell Origin. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 129, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, L.; Turchi, L.; Desnues, B.; Doye, A.; Ponzio, G.; Mege, J.-L.; Yamashita, M.; Zhang, Y.E.; Bertoglio, J.; Flatau, G. CNF1-Induced Ubiquitylation and Proteasome Destruction of Activated RhoA Is Impaired in Smurf1−/− Cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 2489–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, W.; Pullinger, G.D.; Lax, A.J.; Rozengurt, E. Escherichia Coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor and Pasteurella Multocida Toxin Induce Focal Adhesion Kinase Autophosphorylation and Src Association. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 5931–5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, W.; Ascott, Z.K.; Harmey, D.; Slice, L.W.; Rozengurt, E.; Lax, A.J. Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor from Escherichia Coli Induces RhoA-Dependent Expression of the Cyclooxygenase-2 Gene. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 6839–6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raptis, L.; Arulanandam, R.; Geletu, M.; Turkson, J. The R(h)Oads to Stat3: Stat3 Activation by the Rho GTPases. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 1787–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doye, A.; Mettouchi, A.; Bossis, G.; Clément, R.; Buisson-Touati, C.; Flatau, G.; Gagnoux, L.; Piechaczyk, M.; Boquet, P.; Lemichez, E. CNF1 Exploits the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Machinery to Restrict Rho GTPase Activation for Bacterial Host Cell Invasion. Cell 2002, 111, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lerm, M.; Pop, M.; Fritz, G.; Aktories, K.; Schmidt, G. Proteasomal Degradation of Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1-Activated Rac. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 4053–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daugaard, M.; Nitsch, R.; Razaghi, B.; McDonald, L.; Jarrar, A.; Torrino, S.; Castillo-Lluva, S.; Rotblat, B.; Li, L.; Malliri, A. Hace1 Controls ROS Generation of Vertebrate Rac1-Dependent NADPH Oxidase Complexes. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Munro, P.; Flatau, G.; Doye, A.; Boyer, L.; Oregioni, O.; Mege, J.-L.; Landraud, L.; Lemichez, E. Activation and Proteasomal Degradation of Rho GTPases by Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor-1 Elicit a Controlled Inflammatory Response. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 35849–35857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- May, M.; Kolbe, T.; Wang, T.; Schmidt, G.; Genth, H. Increased Cell-Matrix Adhesion upon Constitutive Activation of Rho Proteins by Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factors from E. Coli and Y. Pseudotuberculosis. J. Signal Transduct. 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerhard, R.; Schmidt, G.; Hofmann, F.; Aktories, K. Activation of Rho GTPases by Escherichia Coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 Increases Intestinal Permeability in Caco-2 Cells. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 5125–5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hopkins, A.M.; Walsh, S.V.; Verkade, P.; Boquet, P.; Nusrat, A. Constitutive Activation of Rho Proteins by CNF-1 Influences Tight Junction Structure and Epithelial Barrier Function. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 725–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hofman, P.; Flatau, G.; Selva, E.; Gauthier, M.; Le Negrate, G.; Fiorentini, C.; Rossi, B.; Boquet, P. Escherichia Coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 Effaces Microvilli and Decreases Transmigration of Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes in Intestinal T84 Epithelial Cell Monolayers. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 2494–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rippere-Lampe, K.E.; Lang, M.; Ceri, H.; Olson, M.; Lockman, H.A.; O’Brien, A.D. Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor Type 1-Positive Escherichia Coli Causes Increased Inflammation and Tissue Damage to the Prostate in a Rat Prostatitis Model. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 6515–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hofman, P.; Le Negrate, G.; Mograbi, B.; Hofman, V.; Brest, P.; Alliana-Schmid, A.; Flatau, G.; Boquet, P.; Rossi, B. Escherichia Coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor-1 (CNF-1) Increases the Adherence to Epithelia and the Oxidative Burst of Human Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes but Decreases Bacteria Phagocytosis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2000, 68, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fiorentini, C.; Falzano, L.; Fabbri, A.; Stringaro, A.; Logozzi, M.; Travaglione, S.; Contamin, S.; Arancia, G.; Malorni, W.; Fais, S. Activation of Rho GTPases by Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 Induces Macropinocytosis and Scavenging Activity in Epithelial Cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 2061–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Travaglione, S.; Falzano, L.; Fabbri, A.; Stringaro, A.; Fais, S.; Fiorentini, C. Epithelial Cells and Expression of the Phagocytic Marker CD68: Scavenging of Apoptotic Bodies Following Rho Activation. Toxicol. In Vitro 2002, 16, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvikis, O.; Boyer, L.; Torrino, S.; Doye, A.; Lemonnier, M.; Lorès, P.; Rolando, M.; Flatau, G.; Mettouchi, A.; Bouvard, D. Escherichia Coli Producing CNF1 Toxin Hijacks Tollip to Trigger Rac1-dependent Cell Invasion. Traffic 2011, 12, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.A.; Wang, Y.; Kim, K.J.; Chung, J.W.; Wass, C.A.; Kim, K.S. Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor-1 Contributes to Escherichia Coli K1 Invasion of the Central Nervous System. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 15607–15612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, B.Y.; Kang, J.; Kim, K.S. Invasion Processes of Pathogenic Escherichia Coli. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 295, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capo, C.; Meconi, S.; Sanguedolce, M.-V.; Bardin, N.; Flatau, G.; Boquet, P.; Mege, J.-L. Effect of Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor-1 on Actin Cytoskeleton in Human Monocytes: Role in the Regulation of Integrin-Dependent Phagocytosis. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 4301–4308. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, A.C.; Krishnan, S.; Prasadarao, N.V. The Effects of Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 Expression in the Uptake of Escherichia Coli K1 by Macrophages and the Onset of Meningitis in Newborn Mice. Virulence 2016, 7, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falzano, L.; Quaranta, M.G.; Travaglione, S.; Filippini, P.; Fabbri, A.; Viora, M.; Donelli, G.; Fiorentini, C. Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 Enhances Reactive Oxygen Species-Dependent Transcription and Secretion of Proinflammatory Cytokines in Human Uroepithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 4178–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nougayrède, J.-P.; Taieb, F.; De Rycke, J.; Oswald, E. Cyclomodulins: Bacterial Effectors That Modulate the Eukaryotic Cell Cycle. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rycke, J.; Mazars, P.; Nougayrede, J.-P.; Tasca, C.; Boury, M.; Herault, F.; Valette, A.; Oswald, E. Mitotic Block and Delayed Lethality in HeLa Epithelial Cells Exposed to Escherichia Coli BM2-1 Producing Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor Type 1. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 1694–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Aung, K.M.; Uhlin, B.E.; Wai, S.N. Reversible Senescence of Human Colon Cancer Cells after Blockage of Mitosis/Cytokinesis Caused by the CNF1 Cyclomodulin from Escherichia Coli. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malorni, W.; Fiorentini, C. Is the Rac GTPase-activating Toxin CNF1 a Smart Hijacker of Host Cell Fate? FASEB J. 2006, 20, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miraglia, A.G.; Travaglione, S.; Meschini, S.; Falzano, L.; Matarrese, P.; Quaranta, M.G.; Viora, M.; Fiorentini, C.; Fabbri, A. Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 Prevents Apoptosis via the Akt/IκB Kinase Pathway: Role of Nuclear Factor-ΚB and Bcl-2. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 2735–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Travaglione, S.; Loizzo, S.; Rizza, T.; Del Brocco, A.; Ballan, G.; Guidotti, M.; Vona, R.; Di Nottia, M.; Torraco, A.; Carrozzo, R.; et al. Enhancement of Mitochondrial ATP Production by the Escherichia Coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 3473–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augspach, A.; List, J.H.; Wolf, P.; Bielek, H.; Schwan, C.; Elsässer-Beile, U.; Aktories, K.; Schmidt, G. Activation of RhoA,B,C by Yersinia Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor (CNFy) Induces Apoptosis in LNCaP Prostate Cancer Cells. Toxins 2013, 5, 2241–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, M.; Meysick, K.C.; O’Brien, A.D. Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor Type 1 of Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli Kills Cultured Human Uroepithelial 5637 Cells by an Apoptotic Mechanism. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 5869–5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fabbri, A.; Travaglione, S.; Ballan, G.; Loizzo, S.; Fiorentini, C. The Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 from E. Coli: A Janus Toxin Playing with Cancer Regulators. Toxins 2013, 5, 1462–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fabbri, A.; Travaglione, S.; Rosadi, F.; Ballan, G.; Maroccia, Z.; Giambenedetti, M.; Guidotti, M.; Ødum, N.; Krejsgaard, T.; Fiorentini, C. The Escherichia Coli Protein Toxin Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 Induces Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition. Cell Microbiol. 2020, 22, e13138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falzano, L.; Filippini, P.; Travaglione, S.; Miraglia, A.G.; Fabbri, A.; Fiorentini, C. Escherichia Coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 Blocks Cell Cycle G2/M Transition in Uroepithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 3765–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, H.; Wang, J.; Lv, J.; Zhang, K.; Keller, E.T.; Yao, Z.; Wang, Q. Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 Promotes Prostate Cancer Progression through Activating the Cdc42–PAK1 Axis. J. Pathol. 2017, 243, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, K.; Lv, J.; Wang, L.; Gao, S.; Keller, E.T.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Yao, Z. Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 Promotes Bladder Cancer Angiogenesis through Activating RhoC. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 7927–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Travaglione, S.; Fabbri, A.; Fiorentini, C. The Rho-Activating CNF1 Toxin from Pathogenic E. Coli: A Risk Factor for Human Cancer Development? Infect. Agent. Cancer 2008, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mou, S.; Cote, C.K.; Worsham, P.L. Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor Is an Effective Immunogen in a Yersinia Pseudotuberculosis Aerosol Mouse Model. In Advances in Yersinia Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 179–181. [Google Scholar]
- Fournout, S.; Dozois, C.M.; Odin, M.; Desautels, C.; Pérès, S.; Hérault, F.; Daigle, F.; Segafredo, C.; Laffitte, J.; Oswald, E.; et al. Lack of a Role of Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 Toxin from Escherichia Coli in Bacterial Pathogenicity and Host Cytokine Response in Infected Germfree Piglets. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keestra, A.M.; Winter, M.G.; Auburger, J.J.; Fräßle, S.P.; Xavier, M.N.; Winter, S.E.; Kim, A.; Poon, V.; Ravesloot, M.M.; Waldenmaier, J.F. Manipulation of Small Rho GTPases Is a Pathogen-Induced Process Detected by NOD1. Nature 2013, 496, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stuart, L.M.; Boyer, L. RhoGTPases—NODes for Effector-Triggered Immunity in Animals. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 980–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diabate, M.; Munro, P.; Garcia, E.; Jacquel, A.; Michel, G.; Obba, S.; Goncalves, D.; Luci, C.; Marchetti, S.; Demon, D. Escherichia Coli α-Hemolysin Counteracts the Anti-Virulence Innate Immune Response Triggered by the Rho GTPase Activating Toxin CNF1 during Bacteremia. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yang, J.; Gao, W.; Li, L.; Li, P.; Zhang, L.; Gong, Y.-N.; Peng, X.; Xi, J.J.; Chen, S. Innate Immune Sensing of Bacterial Modifications of Rho GTPases by the Pyrin Inflammasome. Nature 2014, 513, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heine, W.; Beckstette, M.; Heroven, A.K.; Thiemann, S.; Heise, U.; Nuss, A.M.; Pisano, F.; Strowig, T.; Dersch, P. Loss of CNFY Toxin-Induced Inflammation Drives Yersinia Pseudotuberculosis into Persistency. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolters, M.; Boyle, E.C.; Lardong, K.; Trülzsch, K.; Steffen, A.; Rottner, K.; Ruckdeschel, K.; Aepfelbacher, M. Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor-Y Boosts Yersinia Effector Translocation by Activating Rac Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 23543–23553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rippere-Lampe, K.E.; O’Brien, A.D.; Conran, R.; Lockman, H.A. Mutation of the Gene Encoding Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor Type 1 (Cnf 1) Attenuates the Virulence of Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 3954–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Lv, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.-S.; Yao, Z.; Wang, Q. Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 Downregulates CD36 Transcription in Macrophages to Induce Inflammation During Acute Urinary Tract Infections. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, T.A.; Ventura, C.L.; Smith, M.A.; Merrell, D.S.; O’Brien, A.D. Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 and Hemolysin from Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli Elicit Different Host Responses in the Murine Bladder. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.-H.; Kim, K. Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 Contributes to Escherichia Coli Meningitis. Toxins 2013, 5, 2270–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carter, S.R.; Seiff, S.R. Cosmetic Botulinum Toxin Injections. Int. Ophthalmol. Clin. 1997, 37, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- França, K.; Kumar, A.; Fioranelli, M.; Lotti, T.; Tirant, M.; Roccia, M.G. The History of Botulinum Toxin: From Poison to Beauty. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 2017, 167, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, A.V. Commentary: Botulinum Toxin in Clinical Medicine. Clin. Dermatol. 2003, 21, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, G.; Valentini, G.; Travaglione, S.; Falzano, L.; Pieri, M.; Zona, C.; Meschini, S.; Fabbri, A.; Fiorentini, C. Enhancement of Learning and Memory after Activation of Cerebral Rho GTPases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fabbri, A.; Travaglione, S.; Fiorentini, C. Escherichia Coli Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 (CNF1): Toxin Biology, in Vivo Applications and Therapeutic Potential. Toxins 2010, 2, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musilli, M.; Nicolia, V.; Borrelli, S.; Scarpa, S.; Diana, G. Behavioral Effects of Rho GTPase Modulation in a Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 237, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizzo, S.; Rimondini, R.; Travaglione, S.; Fabbri, A.; Guidotti, M.; Ferri, A.; Campana, G.; Fiorentini, C. CNF1 Increases Brain Energy Level, Counteracts Neuroinflammatory Markers and Rescues Cognitive Deficits in a Murine Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65898. [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli, S.; Musilli, M.; Martino, A.; Diana, G. Long-Lasting Efficacy of the Cognitive Enhancer Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1. Neuropharmacology 2013, 64, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viti, S.D.; Martino, A.; Musilli, M.; Fiorentini, C.; Diana, G. The Rho GTPase Activating CNF1 Improves Associative Working Memory for Object-in-Place. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 212, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malchiodi-Albedi, F.; Paradisi, S.; Di Nottia, M.; Simone, D.; Travaglione, S.; Falzano, L.; Guidotti, M.; Frank, C.; Cutarelli, A.; Fabbri, A.; et al. CNF1 Improves Astrocytic Ability to Support Neuronal Growth and Differentiation In Vitro. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerri, C.; Fabbri, A.; Vannini, E.; Spolidoro, M.; Costa, M.; Maffei, L.; Fiorentini, C.; Caleo, M. Activation of Rho GTPases Triggers Structural Remodeling and Functional Plasticity in the Adult Rat Visual Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 15163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, A.; Ettorre, M.; Musilli, M.; Lorenzetto, E.; Buffelli, M.; Diana, G. Rho GTPase-Dependent Plasticity of Dendritic Spines in the Adult Brain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Filippis, B.; Valenti, D.; de Bari, L.; De Rasmo, D.; Musto, M.; Fabbri, A.; Ricceri, L.; Fiorentini, C.; Laviola, G.; Vacca, R.A. Mitochondrial Free Radical Overproduction Due to Respiratory Chain Impairment in the Brain of a Mouse Model of Rett Syndrome: Protective Effect of CNF1. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 83, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musilli, M.; Ciotti, M.T.; Pieri, M.; Martino, A.; Borrelli, S.; Dinallo, V.; Diana, G. Therapeutic Effects of the Rho GTPase Modulator CNF1 in a Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neuropharmacology 2016, 109, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travaglione, S.; Ballan, G.; Fortuna, A.; Ferri, A.; Guidotti, M.; Campana, G.; Fiorentini, C.; Loizzo, S. CNF1 Enhances Brain Energy Content and Counteracts Spontaneous Epileptiform Phenomena in Aged DBA/2J Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fabbri, A.; Travaglione, S.; Maroccia, Z.; Guidotti, M.; Pierri, C.L.; Primiano, G.; Servidei, S.; Loizzo, S.; Fiorentini, C. The Bacterial Protein CNF1 as a Potential Therapeutic Strategy against Mitochondrial Diseases: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vannini, E.; Panighini, A.; Cerri, C.; Fabbri, A.; Lisi, S.; Pracucci, E.; Benedetto, N.; Vannozzi, R.; Fiorentini, C.; Caleo, M. The Bacterial Protein Toxin, Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 (CNF1) Provides Long-Term Survival in a Murine Glioma Model. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannini, E.; Maltese, F.; Olimpico, F.; Fabbri, A.; Costa, M.; Caleo, M.; Baroncelli, L. Progression of Motor Deficits in Glioma-Bearing Mice: Impact of CNF1 Therapy at Symptomatic Stages. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 23539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Filippis, B.; Fabbri, A.; Simone, D.; Canese, R.; Ricceri, L.; Malchiodi-Albedi, F.; Laviola, G.; Fiorentini, C. Modulation of RhoGTPases Improves the Behavioral Phenotype and Reverses Astrocytic Deficits in a Mouse Model of Rett Syndrome. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Sonnenwald, T.; Sprenger, A.; Hansen, U.; Dengjel, J.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Schmidt, G.; Has, C. RhoA Activation by CNFy Restores Cell-Cell Adhesion in Kindlin-2-Deficient Keratinocytes: Kindlin-2 in Cell-Cell Adhesion. J. Pathol. 2014, 233, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gall-Mas, L.; Fabbri, A.; Namini, M.; Givskov, M.; Fiorentini, C.; Krejsgaard, T. The Bacterial Toxin CNF1 Induces Activation and Maturation of Human Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michel, G.; Ferrua, B.; Munro, P.; Boyer, L.; Mathal, N.; Gillet, D.; Marty, P.; Lemichez, E. Immunoadjuvant Properties of the Rho Activating Factor CNF1 in Prophylactic and Curative Vaccination against Leishmania Infantum. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156363. [Google Scholar]
- Munro, P.; Flatau, G.; Anjuere, F.; Hofman, V.; Czerkinsky, C.; Lemichez, E. The Rho GTPase Activators CNF1 and DNT Bacterial Toxins Have Mucosal Adjuvant Properties. Vaccine 2005, 23, 2551–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, P.; Flatau, G.; Lemichez, E. Intranasal Immunization with Tetanus Toxoid and CNF1 as a New Mucosal Adjuvant Protects BALB/c Mice against Lethal Challenge. Vaccine 2007, 25, 8702–8706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, V.; Loizzo, S.; Travaglione, S.; Bertuccini, L.; Condello, M.; Superti, F.; Guidotti, M.; Alano, P.; Silvestrini, F.; Fiorentini, C. The Bacterial Protein CNF1 as a New Strategy against Plasmodium Falciparum Cytoadherence. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavone, F.; Luvisetto, S.; Marinelli, S.; Straface, E.; Fabbri, A.; Falzano, L.; Fiorentini, C.; Malorni, W. The Rac GTPase-Activating Bacterial Protein Toxin CNF1 Induces Analgesia up-Regulating μ-Opioid Receptors. PAIN® 2009, 145, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryou, J.; Sohn, Y.; Hwang, D.; Park, W.; Kim, N.; Heo, W.; Kim, M.; Kim, H. Engineering of Bacterial Exotoxins for Highly Efficient and Receptor-specific Intracellular Delivery of Diverse Cargos. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 1639–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaoprasid, P.; Dersch, P. The Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factors (CNFs)—A Family of Rho GTPase-Activating Bacterial Exotoxins. Toxins 2021, 13, 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13120901
Chaoprasid P, Dersch P. The Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factors (CNFs)—A Family of Rho GTPase-Activating Bacterial Exotoxins. Toxins. 2021; 13(12):901. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13120901
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaoprasid, Paweena, and Petra Dersch. 2021. "The Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factors (CNFs)—A Family of Rho GTPase-Activating Bacterial Exotoxins" Toxins 13, no. 12: 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13120901
APA StyleChaoprasid, P., & Dersch, P. (2021). The Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factors (CNFs)—A Family of Rho GTPase-Activating Bacterial Exotoxins. Toxins, 13(12), 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13120901




