Abstract
Lobster species can accumulate paralytic shellfish toxins (PST) in their hepatopancreas following the consumption of toxic prey. The Southern Rock Lobster (SRL), Jasus edwardsii, industry in Tasmania, Australia, and New Zealand, collectively valued at AUD 365 M, actively manages PST risk based on toxin monitoring of lobsters in coastal waters. The SRL supply chain predominantly provides live lobsters, which includes wet holding in fishing vessels, sea-cages, or processing facilities for periods of up to several months. Survival, quality, and safety of this largely exported high-value product is a major consideration for the industry. In a controlled experiment, SRL were exposed to highly toxic cultures of Alexandrium catenella at field relevant concentrations (2 × 105 cells L−1) in an experimental aquaculture facility over a period of 21 days. While significant PST accumulation in the lobster hepatopancreas has been reported in parallel experiments feeding lobsters with toxic mussels, no PST toxin accumulated in this experiment from exposure to toxic algal cells, and no negative impact on lobster health was observed as assessed via a wide range of behavioural, immunological, and physiological measures. We conclude that there is no risk of PST accumulation, nor risk to survival or quality at the point of consumption through exposure to toxic algal cells.
Key Contribution:
Lobsters exposed to toxic algae during wet storage in long supply chains do not take up paralytic shellfish toxins. Furthermore, exposure does not cause health issues for lobsters and will therefore not have an impact on their survival and health in the supply chain.
1. Introduction
The Southern Rock Lobster (Jasus edwardsii Hutton) is sold in high value live export fisheries in Tasmania, Australia, and New Zealand worth AUD 97 M and AUD 268 M, respectively [1,2]. Lobsters are known to accumulate paralytic shellfish toxins (PST) during blooms of PST-producing algal species in Tasmanian and New Zealand coastal waters [3,4]. The causative alga in Tasmania is Alexandrium catenella (Whedon and Kofoid) Balech, whilst New Zealand blooms may be A. minutum Halim, A. pacificum Litaker (previously identified as A. catenella) and Gymnodinium catenatum Graham [5,6]. The toxins accumulate in the lobster hepatopancreas via the consumption of contaminated prey but are not found in the tail meat [7,8].
Whilst there is no Australian or New Zealand food standard for PST in lobster, several key export markets such as China and Hong Kong stipulate a maximum level of 0.8 mg saxitoxin (STX) equivalents kg−1. Furthermore, human health risk assessment has shown a risk of illness for consumers if consuming large quantities of lobster hepatopancreas. This risk is significantly reduced if the bivalve regulatory level of 0.8 mg STX equivalents kg−1 is applied [9]. In both Tasmania and New Zealand, the public health and market access risks associated with PST in J. edwardsii are managed during high-risk periods through weekly or fortnightly biotoxin monitoring of bivalve sentinel species in coastal waters, followed by direct monitoring of lobster hepatopancreases when bivalves indicate risk.
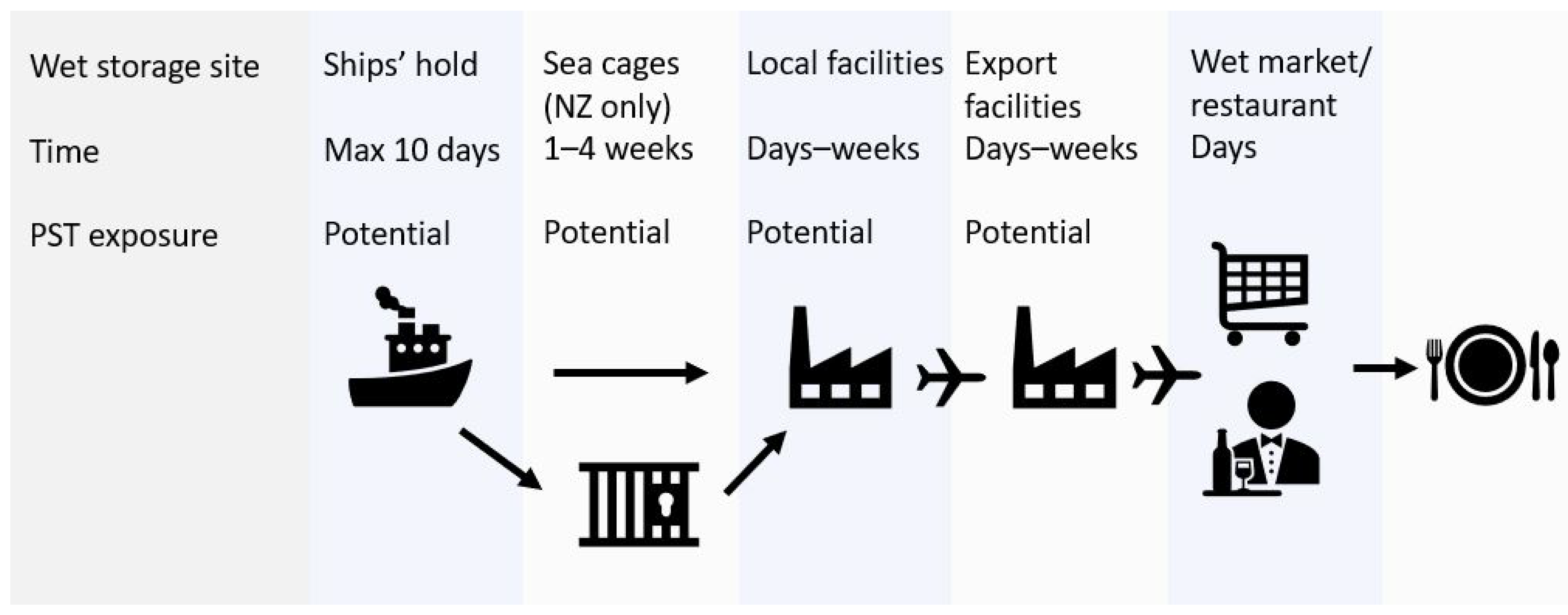
The J. edwardsii supply chain is focused on live seafood markets in Asia. Wet storage is employed to maintain animal quality and facilitate maximum price return during market fluctuations. Animals are moved into wet storage immediately after capture and remain in specialised holding facilities as they move through the supply chain [10], as depicted in Figure 1. The seawater used for wet storage is sourced from local coastal waters.
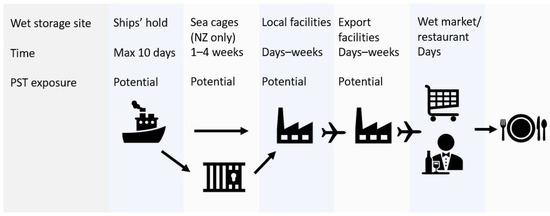
Figure 1.
Supply chain for J. edwardsii from Tasmania and New Zealand to Asian markets, showing wet storage and potential paralytic shellfish toxin (PST) exposure sites. Biotoxin risk monitoring occurs in coastal waters prior to entry into the supply chain.
Wet storage times may range from a few days to several weeks depending on the time of year and market demands. If PST-producing algal blooms are present in coastal waters, these algae will be inadvertently pumped into holding compartments on-vessel, in sea cages (New Zealand only), or in local/export holding facilities. As a result, J. edwardsii may be exposed to PST in the supply chain, post regulatory monitoring programs.
Crustacean gills have multiple functions, such as ionic transport mediating haemolymph osmoregulation, acid–base balance, and ammonia excretion. Heavy metal accumulation in crustaceans also occurs via the gills [11]. No studies have examined the potential for PST uptake in lobsters when directly exposed to toxic algae. Furthermore, lobsters may be in the supply chain for significant periods of time and subjected to more than one period of emersion during transport. To maximise value in the market, lobsters need to survive the rigours of international transport and thus it is integral that they start their journey in strong health [12]. Whilst a recent study showed no impact of PST feeding-related accumulation on J. edwardsii health [13], no studies have so far examined the sensitivity of lobster gill cells to the superoxide radicals, exudate phycotoxins, and fatty acids that are known to be produced by toxic Alexandrium spp. and to have a deleterious impact on fish gill cells [14,15].
A range of indicators have been used to assess stress and predict mortality in commercially-important crustacean species [12]. In this study, we have taken a holistic approach to determine the impact of PST, examining both whole organism indicators (survival, nutritional condition, reflex, behaviour, and health) and cellular indicators (haemolymph immunity, biochemical parameters, and gill histopathology).
Commercial operators assess J. edwardsii health during grading using a subjective vitality scale which is based on lobster reflex and behavioural responses [16]. Reflex actions are consistent, involuntary, nearly instantaneous responses to stimuli which can reliably indicate crustacean whole-body health status independently of animal size, strength, motivation and gender [12]. Crustacean reflex scores have been previously used to provide an accurate indicator of crustacean performance in supply chain studies [12,17,18,19,20]. Other commonly used methods to assess lobster gross or whole-body performance include survival and nutritional condition [16,19,21,22]
Physiological indicators for the assessment of the health and vitality of crustaceans commonly include immune responses (raised bacteraemia levels and changes in haemocyte counts [21,23,24,25,26]; and haemolymph concentration of ions (e.g., potassium, sodium, magnesium, calcium, bicarbonate, pH), metabolites (e.g., ammonia, urea, glucose, lactate) and hormones (e.g., crustacean hyperglycaemic hormone) [21,25,27,28].
The present study aimed to determine if J. edwardsii could accumulate PST through exposure to PST-producing algae, and to ascertain whether direct exposure to these algae could impact lobster health and vitality. In a biosecure experimental aquaculture facility, lobsters were exposed to field-relevant concentrations of toxin-producing A. catenella algae for 21 days. PST concentrations in the hepatopancreas were measured, as well as a range of measures commonly employed to assess survivability and lobster health.
2. Results
2.1. Stocking Animals
Lobsters arrived in good condition, with vitalities on receipt ranging from 4–5 (maximum score possible is 5). There was no significant difference in the lobster harvest wet weights (514 ± 34 g; p value = 0.59) or carapace lengths (104 ± 3 mm; p value = 0.37) between each treatment group. No lobsters moulted during the experiment, but two lobsters in the high exposure treatment groups died; one on day 10, and one on day 11.
2.2. Specific Feed Intake
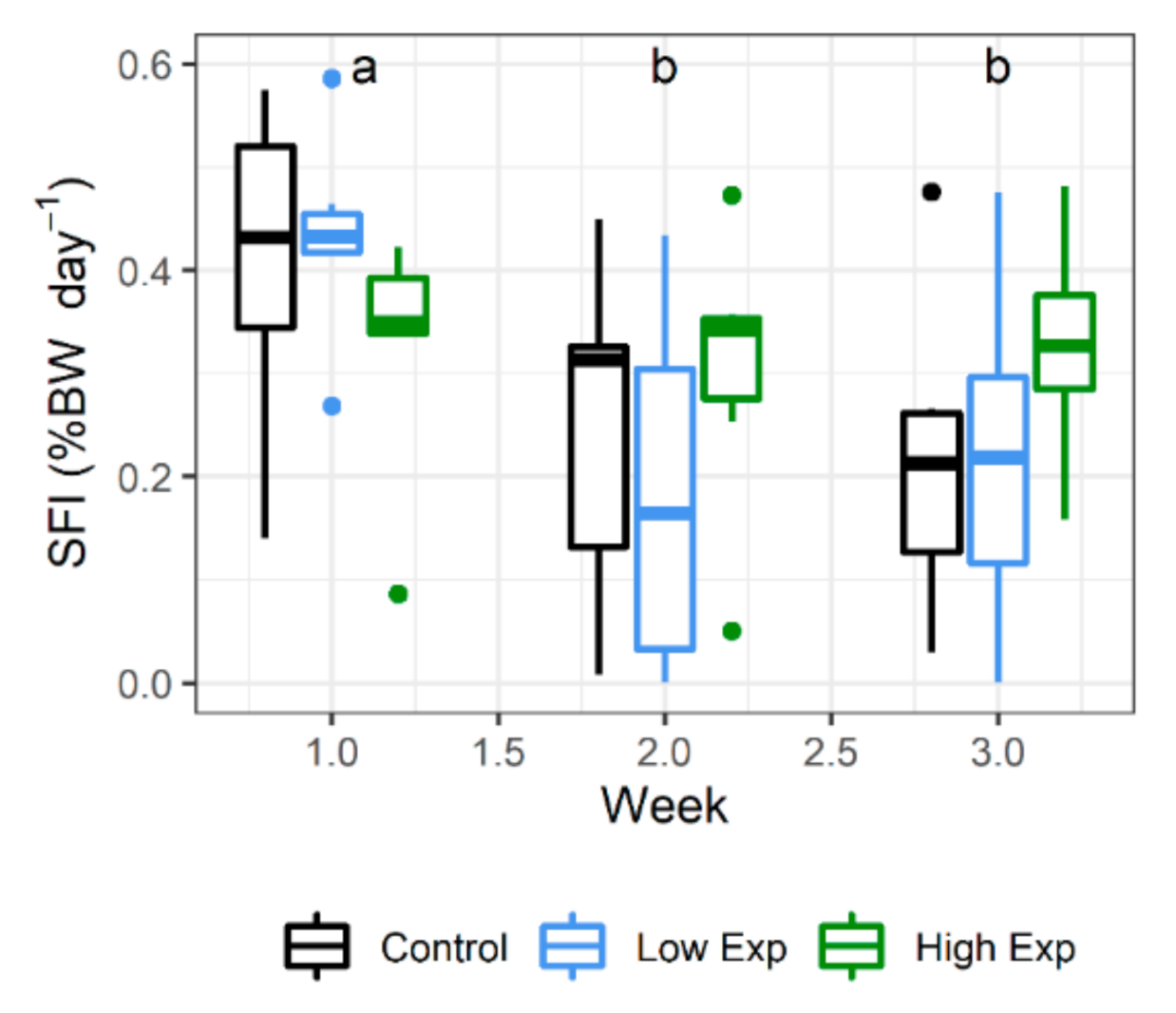
Lobsters from all treatment groups ate well during the experiment, with no significant difference in the specific feed intake (SFI) between treatment groups. Feed consumption decreased during the experiment, with SFI during weeks 2 and 3 being significantly less than that at week 1 (Figure 2; p value = 0.0009).
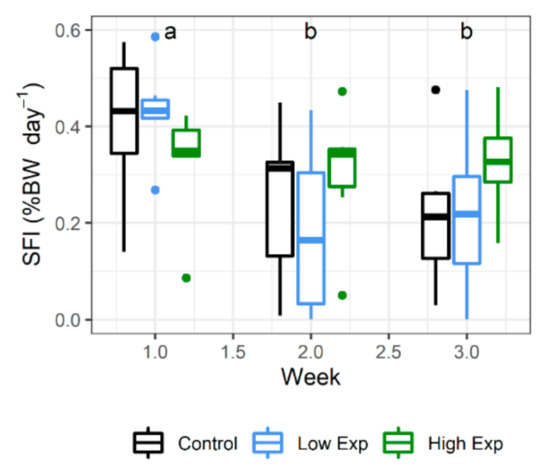
Figure 2.
Weekly specific feed intake (SFI) of J. edwardsii lobsters exposed to 0, 1 × 105 or 2 × 105 cells of A. catenella per litre of tank water (control, low, or high exposure (exp) groups, respectively) across three weeks of exposure. Weeks where SFI is not significantly different share the same letter. BW: body weight.
2.3. PST Accumulation
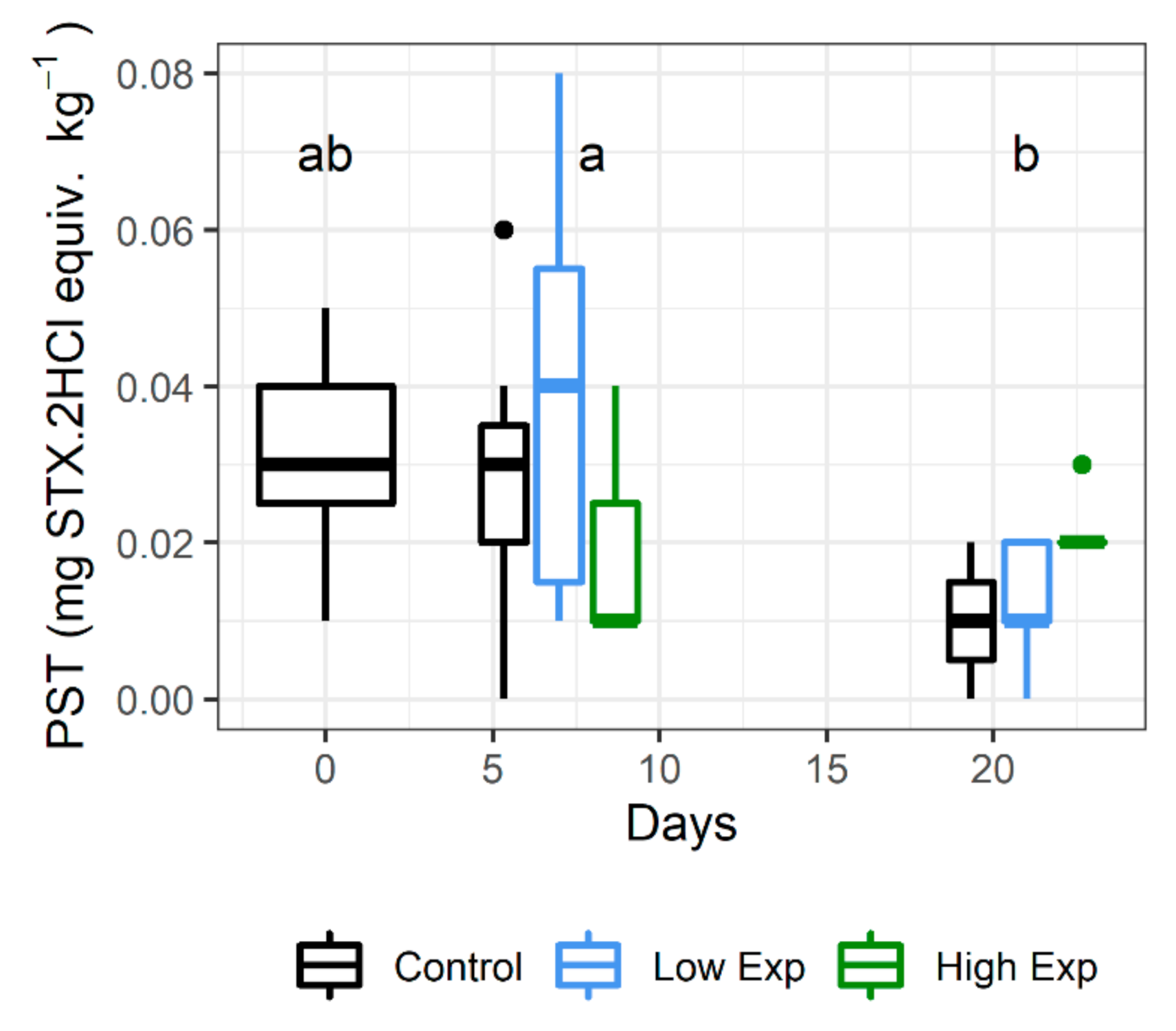
Lobsters had low concentrations of PST in the hepatopancreas on receipt (mean 0.03 ± 0.01 mg STX.2HCl equiv. kg−1). Lobsters harvested on day 21 had significantly lower PST than those harvested on day 7 (p value = 0.001), but not on day 0 (p value = 0.53; Figure 3; Supplementary Table S1). There was no significant difference between PST levels among treatment groups (p value = 0.64).
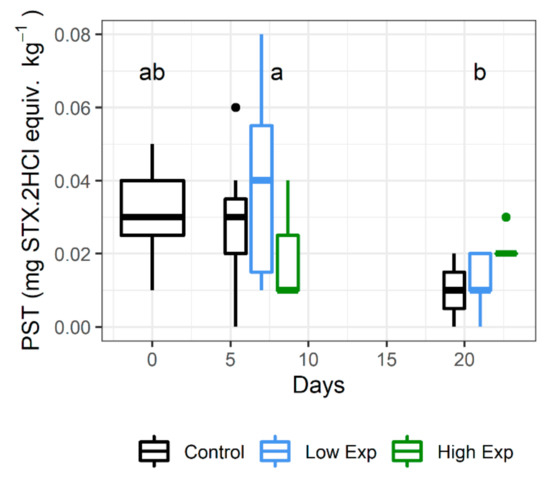
Figure 3.
PST concentrations in the hepatopancreas of J. edwardsii lobsters harvested on days 0, 7 and 21 after exposure to 0, 1 × 105 or 2 × 105 cells of A. catenella per litre of tank water (control, low, or high exposure groups respectively). Days where the PST concentration is not significantly different share the same letter. STX: saxitoxin.
2.4. Lobster Health Responses
There was minimal difference between treatment groups across a wide range of behavioural, immunological, and physiological parameters measured, as summarised in Table 1. The means and standard deviations of continuous variables are provided in Supplementary Table S2.

Table 1.
Summary of differences in behavioural, reflex, immunological, and blood chemistry parameters between control and exposed J. edwardsii (Treatment); across days; and for the interaction between treatment and days, as measured by ANOVA, ordinal logistic regression (OLR) or logistic regression (LR). Significant differences are marked with asterisks (* p = 0.05–0.01, ** p = 0.01–0.001, *** p < 0.001). ZMA: Zobell’s marine agar, TCBS: thiosulphate-citrate-bile salts agar.
2.5. Behavioural Responses
No significant difference between treatments or across days in the experimental system was seen in any of the behaviour measures tested (other than SFI, as discussed above). Lobster vitality remained high throughout the experiment, with 36 animals scoring the maximum vitality score (5), seven scoring a vitality of 4, and three scoring a vitality of 3. All lobsters responded quickly to being placed ventrum-up, righting within 28 s. Impairment of reflexes was low, with 32 lobsters showing impairment of three or less reflexes (Supplementary Table S2). Reflex impairment scores were significantly related to vitality scores (p value = 0.0003; Supplementary Table S3).
2.6. Immune Health Response
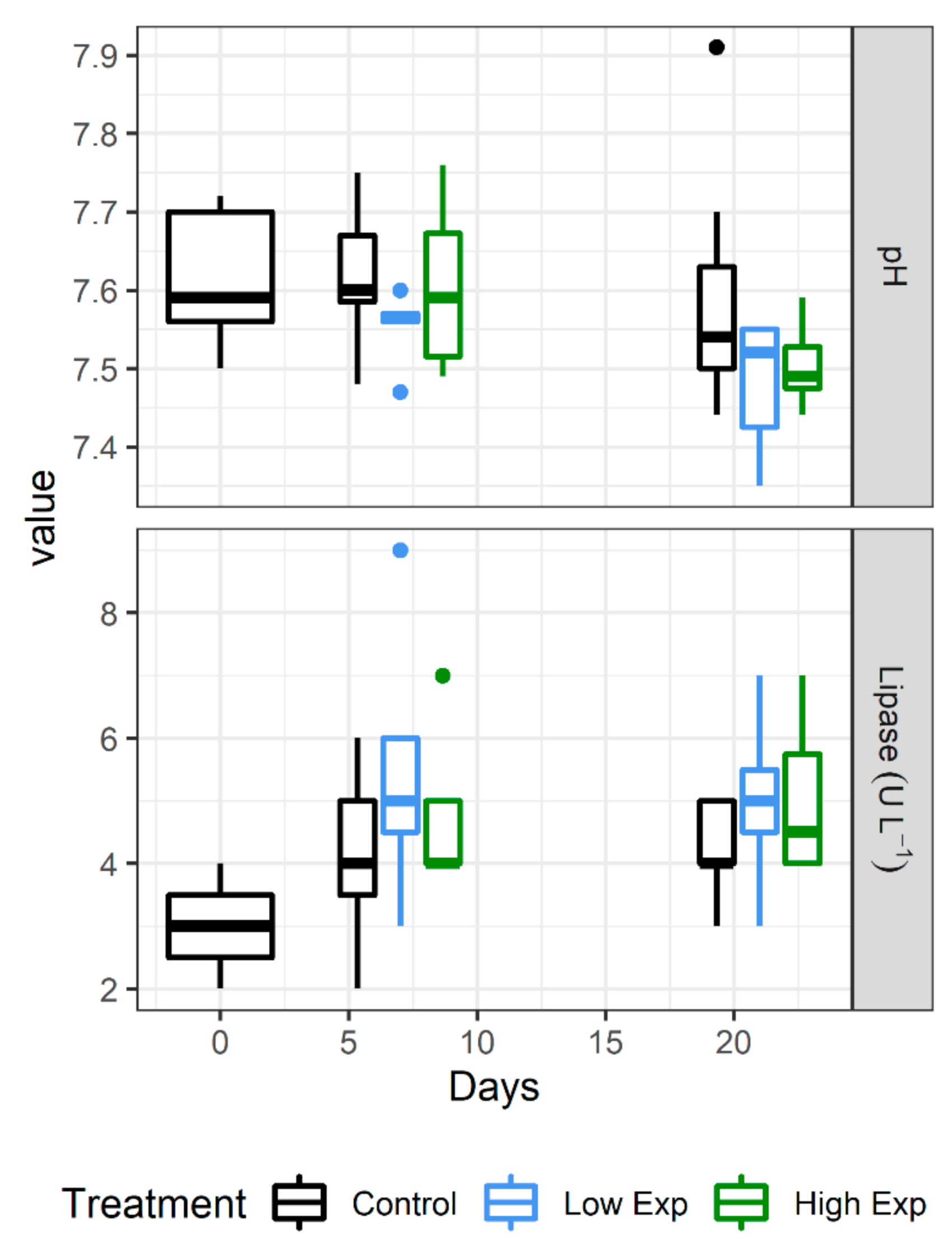
There was no change to bacteraemia concentrations or the prevalence of necrosis between treatment groups or days, however haemocyte counts did increase significantly across all treatment groups at day 21 compared to days 0 and 7 (Table 1, Figure 4; p values = 0.0007 and 0.002, respectively).
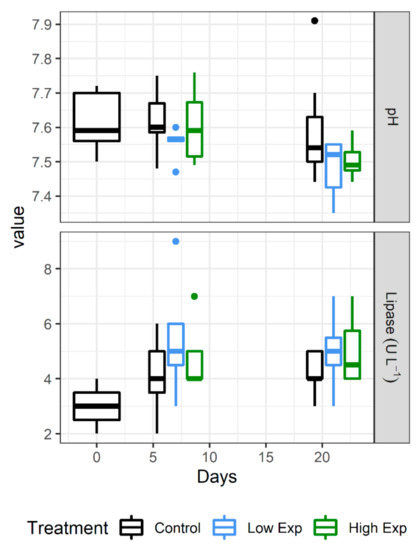
Figure 4.
Haemolymph biochemical parameters that showed significant differences between J. edwardsii treatment groups. Low exposed (dark grey) lobsters had significantly lower pH than the control group (p value = 0.02). Both high and low exposed lobster groups had significantly higher lipase than the control group (p values = 0.03 and 0.02, respectively).
2.7. Nutritional Response
There were no significant differences between the nutritional indicators of Brix and hepatopancreas index across treatments or across days (Table 1, Supplementary Table S3).
2.8. Haemolymph Biochemical Response
Of the range of electrolytes, minerals, metabolites, and enzymes examined, only pH and lipase showed any significant difference between treatments (Figure 4). The low exposure treatment group showed significantly lower pH than the control group (p value = 0.02), whilst both low and high exposure groups showed significantly higher lipase concentrations than the control group (p value = 0.03 and 0.02, respectively).
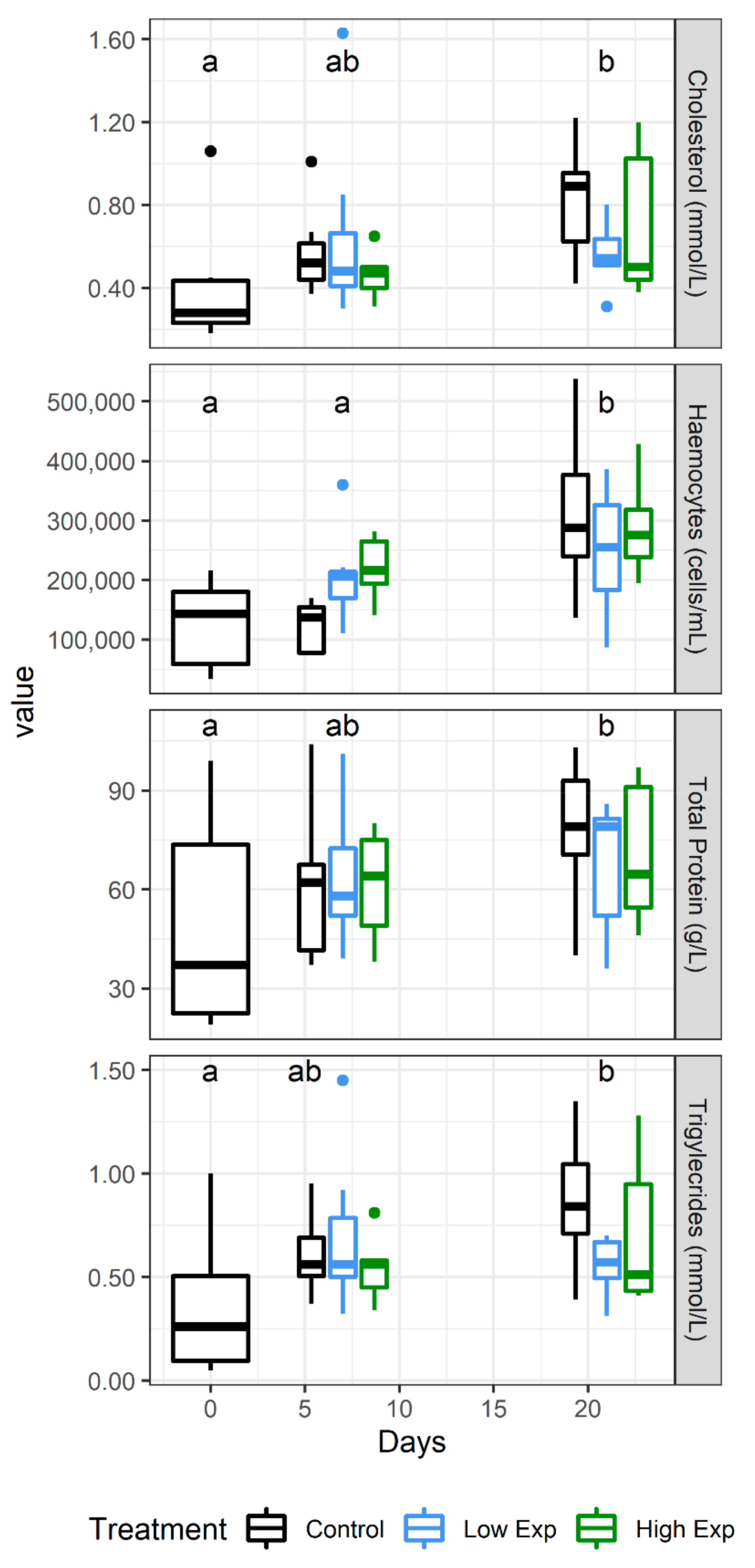
No difference was observed in electrolyte, mineral, or enzyme levels across the course of the experiment, but the metabolites cholesterol, total protein, and triglycerides all increased significantly across the duration of the experiment (Figure 5).
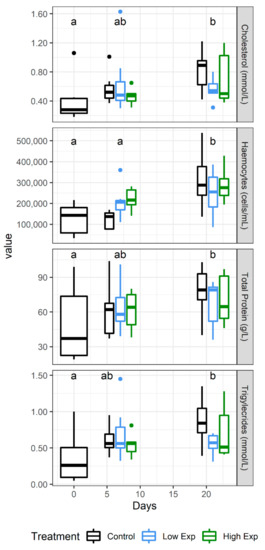
Figure 5.
J. edwardsii haemolymph parameters that changed significantly over the course of the experiment in control (black), low (blue), and high (red) algal exposure treatments (0, 1 × 105, 2 × 105 A. catenella cells/L, respectively). Days which are not significantly different from each other share the same letter.
2.9. Histopathological Findings in Gills
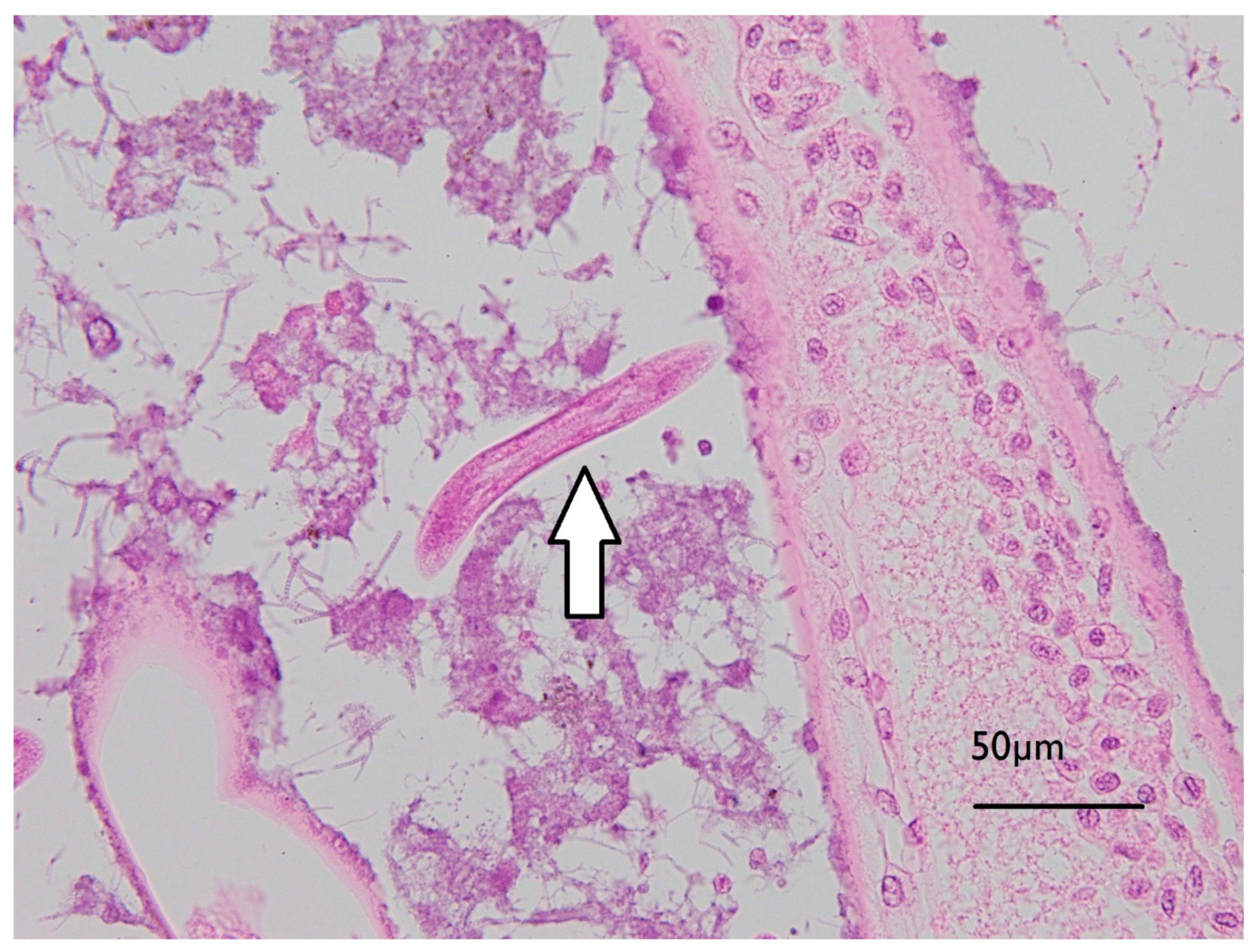
Initial examination of gill filaments from the six high exposed and three of the control animals showed no differences in histopathological findings, so no further examinations of other lobster gills occurred. Diffuse pooling of haemolymph was observed in the lamellae and central axis of all gills examined, consistent with agonal change. All gills examined also showed multifocal deposits of rod and/or filamentous bacteria and low to moderate numbers of ciliated protozoa. Low numbers of free-living larval nematodes were found between lamellae on three of the six samples of gill tissues examined from exposed lobsters, and one of the three gill tissues from control lobsters. The gills of two of the high exposure lobsters and one control lobster showed microvesicles in reserve inclusion cells (Figure 6), likely storing lipids [29].
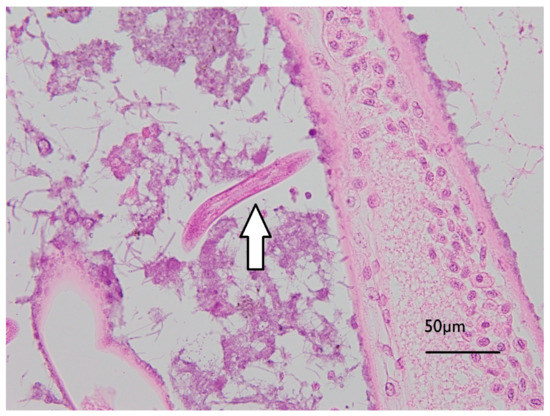
Figure 6.
Micrograph of J. edwardsii gill filament with biofouling (mixed bacterial colonies, including Leucothrix-like organisms, adhered to filaments) and a free-living nematode between filaments as indicated by the arrow.
3. Discussion
No uptake of PST was detected in J. edwardsii exposed to high but field-relevant concentrations of A. catenella in an experimental setting over a three-week period. This was in striking contrast to significant PST accumulation in the lobster hepatopancreas (reaching a maximum of 9.0 mg STX.2HCl equiv. kg−1) observed in parallel experiments involving feeding lobsters with toxic mussels [8], and uptake of PST by abalone when exposed to toxic algal cells in a similar experiment to the current study [30]. In the latter experiment, abalone were exposed to the same highly toxic strain of A. catenella (AT. TR/F) at the same level of the high exposure group in this experiment (2 × 105 cells L−1). Abalone were able to accumulate up to 128 µg STX.2HCl equiv. kg−1 in this experiment, although it is unknown if this accumulation occurred across the gills, epipodium, via the viscera, or a combination of these routes.
Furthermore, the minimal impact on lobster health, demonstrated in this experiment across a range of organismal and cellular levels, indicates that there is no detrimental effect on the survivability and vitality of these animals as a result of exposure to toxic cells. Minimal whole organism and cellular responses were observed in J. edwardsii following the accumulation of high levels of PST in their hepatopancreas [13] and when exposed to toxic cells (current experiment), indicating that lobsters are relatively resistant to the action of PST. However, this response is in contrast to significant histopathology and mortality experienced by Blue mussel and Pacific oyster larvae when exposed to extracellular exudates of the same Tasmanian A. catenella strain at equivalent cell concentrations of 100 to 1000 cells mL−1 [31].
The present study exposed lobsters to aliquots of cultured algae and replicated environmental conditions where animals would be exposed to both cells and cell exudates. The toxic cells were presented to the algae at the highest level recorded from the Tasmanian blooms [3]. It is likely that toxins in wet storage would be equal to or less than those found in the field, as wet storage areas either draw directly from coastal waters in a continuous flow through systems or recirculate sea water through filtration and sedimentation systems to maintain water conditions.
The cultured A. catenella strain (AT. TR/F) was originally isolated from a bloom on the east coast of Tasmania and contained up to 21.2 pg STX.2HCl equiv. cell−1, a relatively high PST cell quota from cultured algae [32,33,34,35]. The toxin profiles of the A. catenella cells were predominantly di-sulfated carbomoyl (C) 1,2 and gonyautoxin (GTX) 1,4, with minor levels of C3,4, neosaxitoxin (Neo), GTX2,3, STX, decarbamyolated gonyautoxin (dcGTX) 2,3, and GTX5,6 (see Section 4.2 below). These analogues are the same as those found in toxic shellfish from the east coast of Tasmania [36,37] and are thus considered representative of the Tasmanian A. catenella blooms. The same PST analogues are also found in New Zealand A. pacificum, A. minutum and G. catenatum isolates, although toxin proportions vary [5,38]. In particular, the proportion of C3,4 toxins tends to be higher in A. pacificum isolates, Neo and STX higher in A. minutum isolates, and C3,4 and GTX2,3 higher in G. catenatum isolates. Absolute concentrations present at any time will vary with the cell number and toxin content of the cells, and the amount of cell exudate.
Bioactive exudates from ichthyotoxic species have been demonstrated to have harmful impacts on the gills of adult Pacific oysters [39] and a range of fish species [15,40,41]. Compromised gills show necrotising degeneration of the epithelium of the secondary lamellae and sloughing and swelling of the primary lamellar epithelium with congestion of branchial vessels [42,43,44]. None of these effects were seen in the lobster gills exposed to high concentrations of A. catenella in this experiment.
A wide range of indicators used to predict the health of lobsters throughout the supply chain were assessed in this study. The only characteristics that demonstrated significant differences between treatment groups was haemolymph pH and lipase concentration. A difference in pH was found between control and low exposure groups, with the control group showing higher pH. A decrease in pH is a common stress response in lobsters caused by respiratory and metabolic acidosis. Other studies found a decrease in pH associated with emersion and high temperature [25,45,46,47]. Given that the high exposure group was not significantly different to the control and low exposure group, it is unlikely this difference was caused by the exposure to A. catenella.
Lipase plays an important role in the digestion of fats. The increase seen between the control and exposed groups of lobsters was influenced by the relatively low level of lipase measured in the control group at the start of the experiment. No significant differences were seen between control and the two treatment groups if the lobsters on day 0 were excluded from the analysis (p value = 0.21). This observed difference could be related to the improved nutritional condition of the lobsters across the experiment, as shown by significant increases in cholesterol, protein, and triglyceride levels. This increase in nutritional status was also detected in similar experiments involving feeding J. edwardsii mussels to excess daily [13] and was also associated with a similar decrease in feed intake during the course of the experiment as seen here.
The only immune response indicator that showed variation across the experiment was haemocyte levels, which increased with time in the system in all treatment groups. Other studies looking at stress in lobster supply chains have found varying results; some have found an increase in haemocyte levels with starvation, capture, emersion, storage and transport [21,25,26]; and others have found a decrease [18,24,48,49,50]. No difference in haemocyte levels was seen in a similar experimental study looking at the impact of PST accumulation on J. edwardsii health [13]. It is possible that the increase over time in all treatment groups may be related to the static experimental system.
In conclusion, we have conducted the first reported experiment to examine the uptake of PST by lobsters during exposure to PST-producing algal cells, as would potentially occur in lobster supply chains. The algal culture used was highly toxic, produced a range of commonly found PST analogues, and was presented at relatively high concentrations. The lobsters were exposed to toxic cells for three weeks, longer than would normally be experienced in the J. edwardsii supply chain in Tasmania and New Zealand. From the lack of uptake of PST in lobsters during this study and the lack of impact on animal health, we conclude that the wet storage of lobsters in coastal waters contaminated with the PST-producing algae typically found in Tasmania and New Zealand, as occurs in the J. edwardsii supply chain, does not pose a human health risk, nor an animal health risk. Therefore, no market access or risk to commercial returns through ill health exists from this practice.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental System
The experimental system used is described in detail in Turnbull et al. [8], with the exception that in this case, a static system was employed with total daily water exchange. Briefly, 450–600 g adult J. edwarsdii, (n = 48 male and 1 female) were sourced directly from South Australian fishing vessels from a mix of shallow and deep habitats with no known bloom activity. The lobsters were transported to the South Australian Aquatic Biosecurity Centre at Roseworthy, where they were held in individual 30 L tanks maintained between 13.1 and 16.3 °C, salinity of less than 37 ppt, and pH between 7.7–8.2 (supplementing the seawater supply with bicarbonate soda as necessary). Water quality was maintained using pre-conditioned sponge biofilters. Dissolved oxygen was >90% saturation and 10 lumens of light was provided on a 12:12 h light:dark cycle. Lobsters were acclimated for 7 days prior to exposure.
4.2. Algal Cultures
Batch cultures of A. catenella strain AT.TR/F (previously known as A. tamarense group 1; isolated from Triabunna, Tasmania at the Institute for Marine and Antarctic Studies, Hobart, Australia) were cultivated in 15 L carboys following the method of Seger et al. [30]. Cultures were maintained in sterile filtered seawater (0.22 µm) supplemented with modified GSe nutrient concentrations (final media = 3/4 GSe nutrients, 5 mM sodium bicarbonate and 7.5 pM H2SeO3 to replace the soil extract in the basal recipe). Cultures were grown at 18 ± 1 °C under 120 µmol photons m−2 s−1 of light supplied by low temperature light emitting diodes on a 12:12 h light:dark cycle. During the dark period, the carboys were gently aerated (0.15 L min−1) with ambient air, which was enriched with 1.5–2.5% (v/v) CO2 in the light.
Cultures used for the exposure experiments were in late exponential/early stationary phase (>2 × 107 cells L−1, 2.5% CO2 aeration) and contained 3.5–21.2 pg STX.2HCl equiv. cells−1 [30]. Cell PST quotas were determined in parallel experiments by Seger et al. [27] to be 3.5–21.2 pg STX.2HCl equiv. cell− 1. Briefly, suspensions of toxic cells were concentrated from four different batches of the same monoclonal source culture in late exponential/early stationary phase through centrifugation. Extracts of these suspensions were produced by lysis and further centrifugation to remove cell fragments. The toxin content of the extracts was determined via LCMS-MS analysis by the Cawthron Institute, New Zealand, as described below. The average toxin profile on a molar basis was 55% C1, 2, 36% GTX1,4, 3% C3,4, 2% Neo, 2% GTX2,3, 2% dcGTX2,3, and small percentages (<2% each) of STX, GTX5, GTX6, and doSTX.
4.3. Lobster Treatments
Lobsters were fed to excess (3 in-shell blue mussels, Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck) at the same time each day during the 7 day acclimation period and for the course of the experiment. The mussels were sourced from Coffin Bay, South Australia and were confirmed to be free of toxins via LCMS-MS [51,52] at the Cawthron Institute, New Zealand.
Lobsters were randomly allocated to three treatment groups: control (n = 21), low exposure (n = 14) and high exposure (n = 14). Each treatment group was further divided into harvest groups of seven replicates each. One control group was harvested on day 0, and the control, low, and high exposure groups were each harvested on days 7 and 21. Seven replicates were used in each group to minimise the number of experimental animals for ethical reasons whilst still allowing statistical rigour. The cell density of the A. catenella culture was determined daily via haemocytometer counts, and aliquots of culture were added to the low and high exposed lobsters at final concentrations of 1 × 105 cells/L and 2 × 105 cells/L, respectively, immediately after the morning water exchange each day.
4.4. Specific Feed Intake
The apparent feed intake (AFI) of lobsters were measured each week following the method of Fitzgibbon et al. [53]. Feed control tanks for the control, low, and high exposure groups were included in the random allocation, with no lobsters placed in these tanks. The feed control tanks each received 3 mussels at the same time as the lobster tanks each afternoon. Uneaten mussel meat from each tank (control and exposed animals, and feed control tanks) was collected at the beginning of each day. The shucked meat was frozen cumulatively over the period of a week. Subsequently, the uneaten mussel meat was dried at 105 °C for 24 h and weighed. The AFI of each lobster was calculated (dry weight of the uneaten food in the treatment tank subtracted from that of the respective control tank, divided by 7) and converted to SFI by dividing by the wet weight of the lobster.
4.5. Lobster Harvest Protocols
The harvest protocols and tests are described in detail in Turnbull et al. [13]. Briefly, lobster behavioural responses and tissue collection were conducted in the same order by the same researchers on each harvest day. Following behavioural measurements, lobsters were euthanised in an ice slurry, and then haemolymph samples (5–15 mL) were taken from the sinus under the right fifth leg joint. The animals were kept on ice overnight, then weighed, and the carapace length was measured prior to tissue dissection and collection. Gill tissue samples from each animal were immediately placed in Davidson’s fixative for 24 h, which was then replaced with 70% ethanol. Hepatopancreases were stored at −80 °C prior to PST analysis.
4.6. Behavioural Responses
Lobsters were first assessed for 7 reflex responses following Turnbull et al. [13]: primary and secondary pereopod lift, antennae and secondary antennal lift, and tail arch via photography whilst emersed; rapid (<1 sec) eye stalk return to normal after gently squeezing together; and rapid antennal touch of hand placed directly in front of immersed animal. Two behavioural responses were then assessed (righting response time measured by placing each animal ventrum-up in a tank of saltwater and recording the time taken to return to dorsum-up [54]; and vitality visually assessed on a lobster commercial operator 1–5 scale similar to that described by Spanoghe and Bourne [16]; 1 = dead; 2 = limp tail, no escape response, no response to handling; 3 = limp tail, some response to handling, i.e., leg movement; 4 = mostly alert, tail held erect; 5 = alert with vigorous escape behaviour). Each reflex response was scored (positive response = 0, negative response = 1) and summed into a reflex impairment score for each animal, as described by Stoner et al. [19]. Potential scores ranged from 0–7, with 0 indicating maximum vigour.
4.7. Immune Health Response
Haemolymph samples were preserved immediately after extraction by adding 200–300 μL chilled anticoagulant Lillie’s formol calcium (1.3 M formalin, 126 mM calcium acetate) and haemocytes were counted in an Improved Neubauer haemocytometer at 40× magnification (Olympus CX41 RF) within 48 h. To assess bacteraemia levels, 100 μL of haemolymph was sterilely plated onto each of Zobell’s marine and thiosulphate-citrate-bile salts agars (ZMA and TCBS, Thermofisher), which were incubated at 26 °C for 48 h prior to colonies being counted. Shell necrosis was visually noted as present/absent during dissection.
4.8. Nutritional Health Response
Nutritional responses were assessed via Brix index (Hanna Refractometer H196801) and hepatopancreas index (the ratio of hepatopancreas wet weight to lobster wet weight [55,56]).
4.9. Haemolymph Biochemical Response
Haemolymph pH was measured using a Radiometer Analytical pH meter PHM210 with micro-electrode B10C162, following which the haemolymph was spun at 10,000× g for 5 min (Sigma Microcentrifuge 1–14). The supernatant was snap frozen in liquid nitrogen, stored at −80 °C and sent to Crustipath Laboratories, Canada, for analysis using a Cobas c501 automated biochemistry analyser (Roche Diagnostics Corporation, Indianopolis, IN, USA) as described by Day et al. [21] and Fitzgibbon et al. [22]. Sodium (Na+), chloride (Cl−), and potassium (K+) were measured using an Ion-Selective Electrode, whilst Mg and bicarbonate (bicarb) were measured photometrically. The minerals calcium (Ca) and phosphorous (P); metabolites glucose (Gluc), lactate (Lact), cholesterol (Chol), triglycerides (Trig), total protein (TP), albumin (Alb), globulin (Glob), urea, and uric acid (UA); and enzymes lipase (Lip), amylase (Amy), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), sorbital (SDH), glutamate dehydrogenases (GD) and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) were measured photometrically. Osmolality was measured on a Micro-Osmette (Precision Systems Inc., Natick, MA, USA) via freezing point depression.
4.10. PST Analysis
Paralytic shellfish toxins in the hepatopancreas were analysed at the Cawthron Institute, New Zealand by LC-MS/MS (Waters Acquity UPLC i-Class system coupled to a Waters Xevo TQ-S triple quadrupole mass spectrometer with electrospray ionization), following the methods of Boundy et al. [51] and Turner et al. [52], with minor variations as detailed in Turnbull et al. [8]. Results were calculated using Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (FAO) toxicity equivalency factors [57]. Results reported as part of this study were corrected based on spike recoveries observed for the different sample matrices analysed. The limit of reporting for each PST analogue differed for each matrix tested.
4.11. Gill Histology
Histopathological analysis of gill tissues was conducted at the Animal Health Laboratory, Department of Primary Industries, Parks, Water and Environment in Tasmania. Gills stored in ethanol were embedded in paraffin, cut at 5 µm thickness, mounted and stained with haematoxylin and eosin using standard techniques. All slides were read by the same American College of Veterinary Pathologists (ACVP) board-certified veterinary pathologist.
4.12. Data Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using R Software (R Core Development Team version 3.6, April 2019). Continuous datasets were checked for normality and homoscedasticity using the Shapiro–Wilk test and Levene’s test respectively, with appropriate transformations if necessary (no transformation: SFC, haemocyte count, brix, pH, Na, Cl, TP, Glob, Alb:Glob (A:G), and GD; log transformations: time to right, Ca, Gluc, Chol, and Alb; square root transformations: P, bicarb, Trig, and UA). Analysis of variance was used to test for significant differences between groups for data with normal distributions, followed by post-hoc analysis using Tukey honestly significant difference (HSD) tests. Prior to transformations, P, Lact, bicarb, Trig, UA concentrations that were reported as less than the level of detection (LOD) were replaced with 0.5* LOD (n = 1, 12, 1, 2, 1 respectively). Two-way random permutation tests were used to test for significant differences in continuous data that could not be transformed to a normal distribution (bacterial counts on ZMA and TCBS, K, Na:K, Mg, Lact and measured osmolality).
Ordinal logistic regression was used to test for significant differences between discrete and ordinal datasets (reflex impairment score and vitality respectively), with p values calculated by comparing the t-value against the standard normal distribution. Ordinal chi-squared analysis was used to test for association between vitality and RIS. Significant differences between groups in binary datasets (necrosis and gill parasites) were tested using logistic regression.
Analytes where most of the data were below the LOD were not tested for significant differences between groups (creatinine, urea, ALT, ALP, AMY, AST, GGT, and SDH). Differences were considered statistically significant when p values < 0.05.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6651/13/2/129/s1, Table S1: The median and standard deviation of behavioural, immunological and biochemical parameters measured in control and PST exposed J. edwardsii over different time periods, Table S2: Frequency table of reflex impairment scores (RIS) for J. edwardsii control low and high exposure treatment groups (0, 1 × 105 and 2 × 105 cells A. catenella respectively) on days 0, 7 and 21, Table S3: Reflex impairment scores in relation to vitality in J. edwardsii. All treatment groups combined.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.T., G.H. and Q.F.; methodology, A.T., J.J., A.S., G.K. and Q.F.; formal analysis, A.T.; investigation, A.T., A.S., G.K.; data curation, A.T.; writing—original draft preparation, A.T.; writing—review and editing, J.J., A.S., G.H., G.K. and Q.F.; project administration, A.T.; funding acquisition, A.T. and G.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Fisheries Research and Development Corporation, grant numbers 2017-051 and 2017-086.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval for studies on crustacea are not required in South Australia. The study used the minimum number of animals required to ensure statistical rigour and used ethical procedures to euthanise all animals.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the supplementary material.
Acknowledgments
This research was conducted at the South Australian Aquatic Animal Biosecurity Centre. We thank Navreet Malhi, Geoff Holds, Jan Lee and Elliot Brown for technical support at the South Australian Aquatic Biosecurity Centre; Dane Hayes and Wendy Allen from the Department of Primary Industries Parks Water and Environment Animal Health Laboratory for histological preparation of slides.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Patterson, H.; Williams, A.; Woodhams, J.; Curtotti, R. Fishery Status Reports 2019; Australian Bureau of Agricultural and Resource Economics: Canberra, Australia, 2019.
- Williams, J.; Stokes, F.; Dixon, H.; Hurren, K. The Economic Contribution of Commercial Fishing to the New Zealand Economy; BERL: Wellington, New Zealand, 2017; pp. 1–53.
- Condie, S.A.; Oliver, E.C.J.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Environmental drivers of unprecedented Alexandrium catenella dinoflagellate blooms off eastern Tasmania, 2012–2018. Harmful Algae 2019, 87, 101628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallegraeff, G.; Bolch, C.; Condie, S.; Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; Murray, S.; Quinlan, R.; Ruvindy, R.; Turnbull, A.; Ugalde, S.; Wilson, K. Unprecedented Alexandrium blooms in a previously low biotoxin risk area of Tasmania, Australia. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Harmful Algae 2016; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Paris, France, 2017; pp. 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie, A.L. The risk to New Zealand shellfish aquaculture from paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) toxins. New Zealand J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2014, 48, 430–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.; Smith, K.F.; MacKenzie, L.; Wood, S.A.; Ponikla, K.; Harwood, D.T.; Packer, M.; Munday, R. The Cawthron Institute Culture Collection of Micro-algae: A significant national collection. New Zealand J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2016, 50, 291–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, T.; Malhi, N.; Tan, J.; McLeod, C.; Stewart, I.; Harwood, T.; Mann, G.; Turnbull, A. Experimental uptake and depuration of paralytic shellfish toxins in Southern Rock Lobster, Jasus edwardsii. Toxicon 2018, 143, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbull, A.; Malhi, N.; Seger, A.; Harwood, T.; Jolley, J.; Fitzgibbon, Q.; Hallegraeff, G. Paralytic shellfish toxin uptake, tissue distribution, and depuration in the Southern Rock Lobster Jasus edwardsii Hutton. Harmful Algae 2020, 95, 101818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, C.; Kiermeier, A.; Stewart, I.; Tan, J.; Turnbull, A.; Madigan, T. Paralytic shellfish toxins in Australian Southern Rock Lobster (Jasus edwardsii): Acute human exposure from consumption of hepatopancreas. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2018, 24, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.K.; Fitzgibbon, Q.; Caraguel, C.G.B. Investigation of risk factors associated with sub-optimal holding survival in southern rock lobster (Jasus edwardsii) in Australia. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 183, 105122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, R.P.; Lucu, C.; Onken, H.; Weihrauch, D. Multiple functions of the crustacean gill: Osmotic/ionic regulation, acid-base balance, ammonia excretion, and bioaccumulation of toxic metals. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, A.W. Assessing stress and predicting mortality in economically significant crustaceans. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2012, 20, 111–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, A.; Malhi, N.; Seger, A.; Jolley, J.; Hallegraeff, G.; Fitzgibbon, Q. Accumulation of paralytic shellfish toxins by Southern Rock Lobster Jasus edwardsii causes minimal impact on lobster health. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; Seger, A.; Mardones, J.I.; Nichols, P.D.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Progress in understanding algal bloom-mediated fish kills: The role of superoxide radicals, phycotoxins and fatty acids. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardones, J.I.; Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; Nichols, P.D.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Fish gill damage by the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella from Chilean fjords: Synergistic action of ROS and PUFA. Harmful Algae 2015, 49, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanoghe, P.T.; Bourne, P.K. Relative influence of environmental factors and processing techniques on Panulirus cygnus morbidity and mortality during simulated live shipments. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1997, 48, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, P.; Izquierdo-Gómez, D.; Siikavuopio, S.I. Use of reflex indicators for measuring vitality and mortality of the snow crab (Chionoecetes opilio) in captivity. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, B.D.; Spanoghe, P.T.; Davidson, G.W.; Hosking, W.; Nottingham, S.; Jussila, J.; Evans, L.H. Predicting survival of western rock lobsters Panulirus cygnus using discriminant analysis of haemolymph parameters taken immediately following simulated handling treatments. New Zealand J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2005, 39, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, A.W.; Rose, C.S.; Munk, J.E.; Hammond, C.F.; Davis, M.W. An assessment of discard mortality for two Alaskan crab species, Tanner crab (Chionoecetes bairdi) and snow crab (C. opilio), based on reflex impairment. Fish. Bull. 2008, 106, 337. [Google Scholar]
- Stoner, A.W. Prediction of discard mortality for Alaskan crabs after exposure to freezing temperatures, based on a reflex impairment index. Fish. Bull. 2009, 107, 451. [Google Scholar]
- Day, R.D.; Fitzgibbon, Q.P.; Gardner, C. The impact of holding stressors on the immune function and haemolymph biochemistry of Southern Rock Lobsters (Jasus edwardsii). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 89, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgibbon, Q.P.; Day, R.D.; McCauley, R.D.; Simon, C.J.; Semmens, J.M. The impact of seismic air gun exposure on the haemolymph physiology and nutritional condition of spiny lobster, Jasus edwardsii. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 125, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotedar, S.; Evans, L.; Jones, B. Effect of holding duration on the immune system of western rock lobster, Panulirus cygnus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A 2006, 143, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotedar, S.; Tsvetnenko, E.; Evans, L. Effect of air exposure on the immune system of the rock lobster Panulirus cygnus. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2001, 52, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, C.J.; Mendo, T.C.; Green, B.S.; Gardner, C. Predicting transport survival of brindle and red rock lobsters Jasus edwardsii using haemolymph biochemistry and behaviour traits. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A 2016, 201, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvetnenko, E.; Fotedar, S.; Evans, L. Antibacterial activity in the haemolymph of western rock lobster, Panulirus cygnus. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2001, 52, 1407–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrapavan, A.; Gardner, C.; Green, B.S. Haemolymph condition of deep-water southern rock lobsters (Jasus edwardsii) translocated to inshore reefs. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2011, 44, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.; Oliver, S. Circulatory, respiratory and metabolic response to emersion and low temperature of Jasus edwardsii: Simulation studies of commercial shipping methods. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 1999, 122, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, D.F. The moulting cycle of the spiny lobster, Panulirus argus Latreille. II. Pre-ecdysial histological and histochemical changes in the hepatopancreas and integumental tissues. Biol. Bull. 1954, 108, 88–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seger, A.; Hallegraeff, G.; Stone, D.; Bansemer, M.; Harwood, T.D.; Turnbull, A. Uptake of paralytic shellfish toxins by blacklip abalone (Haliotis rubra rubra leach) from direct exposure to Alexandrium catenella microalgal cells and toxic aquaculture feed. Harmful Algae 2020, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supono, S.; Knowles, G.; Bolch, C. Toxicity and histopathological effects of toxic dinoflagellate, Alexandrium catenella exudates on larvae of blue mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis, and Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. J. Ilm. Perikan. Dan Kelaut. 2020, 12, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jester, R.; Rhodes, L.; Beuzenberg, V. Uptake of paralytic shellfish poisoning and spirolide toxins by paddle crabs (Ovalipes catharus) via a bivalve vector. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilly, E.L.; Kulis, D.M.; Gentien, P.; Anderson, D.M. Paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in France linked to a human-introduced strain of Alexandrium catenella from the western Pacific: Evidence from DNA and toxin analysis. J. Plankton Res. 2002, 24, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, K.; Ogata, T.; Kaga, S.; Yoshida, M.; Fukuyo, Y.; Kodama, M. Accumulation of paralytic shellfish toxins in the scallop Patinopecten yessoensis caused by the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella in Otsuchi Bay, Iwate Prefecture, northern Pacific coast of Japan. Fish. Sci. 2001, 67, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, D.; Paredes, J.; Alves-de-Souza, C.; Seguel, M.; Sfeir, A.; Frangópulos, M. Intraregional variation among Alexandrium catenella (Dinophyceae) strains from southern Chile: Morphological, toxicological and genetic diversity. Harmful Algae 2012, 15, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; Tan, J.Y.C.; Hallegraeff, G.M.; Campbell, K.; Ugalde, S.C.; Harwood, D.T.; Bartlett, J.K.; Campàs, M.; Crooks, S.; Gerssen, A.; et al. Detection of paralytic shellfish toxins in mussels and oysters using the qualitative Neogen Lateral-Flow Immunoassay: An interlaboratory study. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbull, A.R.; Tan, J.Y.C.; Ugalde, S.C.; Hallegraeff, G.M.; Campbell, K.; Harwood, D.T.; Dorantes-Aranda, J.J. Single-laboratory validation of the Neogen Qualitative Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the detection of paralytic shellfish toxins in mussels and oysters. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwood, D.T.; Boundy, M.; Selwood, A.I.; van Ginkel, R.; MacKenzie, L.; McNabb, P.S. Refinement and implementation of the Lawrence method (AOAC 2005.06) in a commercial laboratory: Assay performance during an Alexandrium catenella bloom event. Harmful Algae 2013, 24, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrec, J.; Soudant, P.; Payton, L.; Tran, D.; Miner, P.; Lambert, C.; Le Goïc, N.; Huvet, A.; Quillien, V.; Boullot, F.; et al. Bioactive extracellular compounds produced by the dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum are highly detrimental for oysters. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 199, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Chou, H.-N. Ichthyotoxicity studies of milkfish Chanos chanos fingerlings exposed to a harmful dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2001, 262, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Krock, B.; Tillmann, U.; Bickmeyer, U.; Graeve, M.; Cembella, A. Mode of action of membrane-disruptive lytic compounds from the marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Toxicon 2011, 58, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, M.; Imahayashi, T.; Ozaki, H.S.; Murakami, T.H.; Toyoshima, T.; Okaichi, T. Effects of sea bloom, Chattonella antiqual, on gill primary lamellae of the young yellowtail, Seriola quinqueradiata. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 1983, 16, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegraeff, G.; Dorantes-Aranda, J.; Mardones, J.I.; Seger, A. Review of progress in our understanding of fish-killing microalgae: Implications for management and mitigation. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Harmful Algae 2016; International Society for the Study of Harmful Algae and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Paris, France, 2017; pp. 150–155. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, R.J.; Bullock, A.M.; Turners, M.; Jones, K.; Tett, P. Mortalities of Salmo gairdneri exposed to cultures of Gyrodinium aureolum. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U.K. 1983, 63, 741–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dove, A.D.M.; Allam, B.; Powers, J.J.; Sokolowski, M.S. A prolonged thermal stress experiment on the American Lobster Homarus americanus. J. Shellfish Res. 2005, 24, 761–765. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzon, S.; Giulianini, P.G.; Martinis, M.; Ferrero, E.A. Stress effect of different temperatures and air exposure during transport on physiological profiles in the American lobster Homarus americanus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 147, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteley, E.; Taylor, E. Oxygen and acid-base disturbances in the hemolymph of the lobster Homarus gammarus during commercial transport and storage. J. Crustacean Biol. 1992, 12, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.E.; Cornick, J.W.; Foley, D.M.; Li, M.F.; Bishop, C.M. Muscle weight relationship to serum proteins, hemocytes and hepatopancreas in the lobster, Homarus americanus. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1967, 24, 2339–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jussila, J.; Jago, J.; Tsvetnenko, E.; Dunstan, B.; Evans, L.H. Total and differential haemocyte counts in western rock lobsters (Panulirus cygnus George) under post-harvest stress. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1997, 48, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basti, D.; Hoyt, K.; Bouchard, D.; Bricknell, I.; Chang, E.S.; Halteman, W. Factors affecting post-capture survivability of lobster Homarus americanus. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2010, 90, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boundy, M.J.; Selwood, A.I.; Harwood, T.D.; McNabb, P.S.; Turner, A.D. Development of a sensitive and selective liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry method for high throughput analysis of paralytic shellfish toxins using graphitised carbon solid phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1387, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.D.; McNabb, P.S.; Harwood, T.; Selwood, A.I.; Boundy, M.J. Single-laboratory validation of a multitoxin ultra-performance LC-hydrophilic interaction LC-MS/MS method for quantitation of paralytic shellfish toxins in bivalve shellfish. J. AOAC Int. 2015, 98, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgibbon, Q.P.; Simon, C.J.; Smith, G.G.; Carter, C.G.; Battaglene, S.C. Temperature dependent growth, feeding, nutritional condition and aerobic metabolism of juvenile spiny lobster, Sagmariasus verreauxi. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2017, 207, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, R.D.; McCauley, R.D.; Fitzgibbon, Q.P.; Hartmann, K.; Semmens, J.M. Seismic air guns damage rock lobster mechanosensory organs and impair righting reflex. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, C.J.; Fitzgibbon, Q.P.; Battison, A.; Carter, C.G.; Battaglene, S.C. Bioenergetics of nutrient reserves and metabolism in spiny lobster juveniles Sagmariasus verreauxi: Predicting nutritional condition from hemolymph biochemistry. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. Ecol. Evol. Approaches 2015, 88, 266–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landman, M.J.; Fitzgibbon, Q.P.; Wirtz, A.; Codabaccus, B.M.; Ventura, T.; Smith, G.G.; Carter, C.G. Physiological status and nutritional condition of cultured juvenile Thenus australiensis over the moult cycle. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 250, 110504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and World Health Organisation. Technical Paper on Toxicity Equivalency Factors for Marine Biotoxins Associated with Bivalve Molluscs; FAO/WHO: Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).