Abstract
Breast reconstruction after mastectomy is commonly performed using transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous (TRAM) flap. Previous studies have demonstrated that botulinum neurotoxin injections in TRAM flap surgeries lower the risk of necrosis and allow further expansion of arterial cross-sectional diameters. The study was designed to determine the ideal injection points for botulinum neurotoxin injection by exploring the arborization patterns of the intramuscular nerves of the rectus abdominis muscle. A modified Sihler’s method was performed on 16 rectus abdominis muscle specimens. Arborization of the intramuscular nerves was determined based on the most prominent point of the xyphoid process to the pubic crest. All 16 rectus abdominis muscle specimens were divided into four muscle bellies by the tendinous portion. The arborized portions of the muscles were located on the 5–15%, 25–35%, 45–55%, and 70–80% sections of the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th muscle bellies, respectively. The tendinous portion was located at the 15–20%, 35–40%, 55–60%, and 90–100% sections. These results suggest that botulinum neurotoxin injections into the rectus abdominis muscles should be performed in specific sections.
Key Contribution:
The research proposes a guide for effective botulinum neurotoxin injection for rectus muscles.
1. Introduction
Breast reconstruction after mastectomy is commonly performed using the transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous (TRAM) flap. The TRAM flap uses an autologous myocutaneous flap consisting of skin, subcutaneous fat, blood vessels, and the rectus abdominis muscle [1]. The benefits of using autologous tissue, such as in TRAM, include superior cosmetic results and avoidance of implant-associated complications [2]. However, TRAM flap surgery still carries the risk of postoperative complications, such as tissue necrosis.
Previous studies have demonstrated that botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) injections in TRAM flap surgeries lower the risk of necrosis and allow further expansion of arterial cross-sectional diameters [3]. The identified mechanism of action of BoNT is a prolonged inhibition of acetylcholine release in the neuromuscular junction of the rectus abdominis muscle; as a result, muscle contraction is blocked and the risk of tissue ischemia is decreased [4,5,6,7]. The main objective in reconstructive procedures is ensuring tissue survival after transplantation using pedicled or free flaps. Furthermore, muscle contractions after TRAM surgery can cause pain in patients, and BoNT injections are known to relieve pain by decreasing muscle tone [8].
Presently, the main treatment for reducing muscle contractions is through the injection of BoNT, which is recognized as one of the most effective and safest treatment options for this purpose [9,10,11]. When injecting BoNT, the dose administered should be sufficient to allow toxin buildup in the arborized neural network [8,12,13]. The effectiveness of injections that target neural arborized sections, which contain the most neuromuscular junctions, has been investigated in clinical studies on psoas major and biceps brachii muscles [14,15]. Furthermore, injections directed at sections of arborization have been demonstrated to result in significantly greater reductions in muscle volume than injections performed on conventional sites [14,15].
Clinicians should be aware of several factors when using BoNT, since high doses can cause undesirable paralysis as the toxin reaches adjacent muscles [16,17]. Furthermore, the use of high doses and repeated BoNT injections accelerates the production of antibodies, which leads to decreased toxin efficacy [16,17,18]. Consequently, BoNT must be injected into sections of neural arborization to maximize efficiency and reduce adverse effects. Previous studies have revealed the location of intramuscular arborization sections in other muscles; these sections have been suggested as the ideal sites for BoNT injections [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26].
To date, no study has been able to pinpoint the locations of intramuscular neural arborizations in the rectus abdominis. In this study, we used the whole-mount staining method first suggested by Sihler to demonstrate intramuscular neural distributions without injuring the nerves [27,28]. The findings of this study allow for the identification of injection points for BoNT in TRAM flaps.
2. Results
2.1. Intramuscular Arborization Patterns of the Rectus Abdominis Muscle
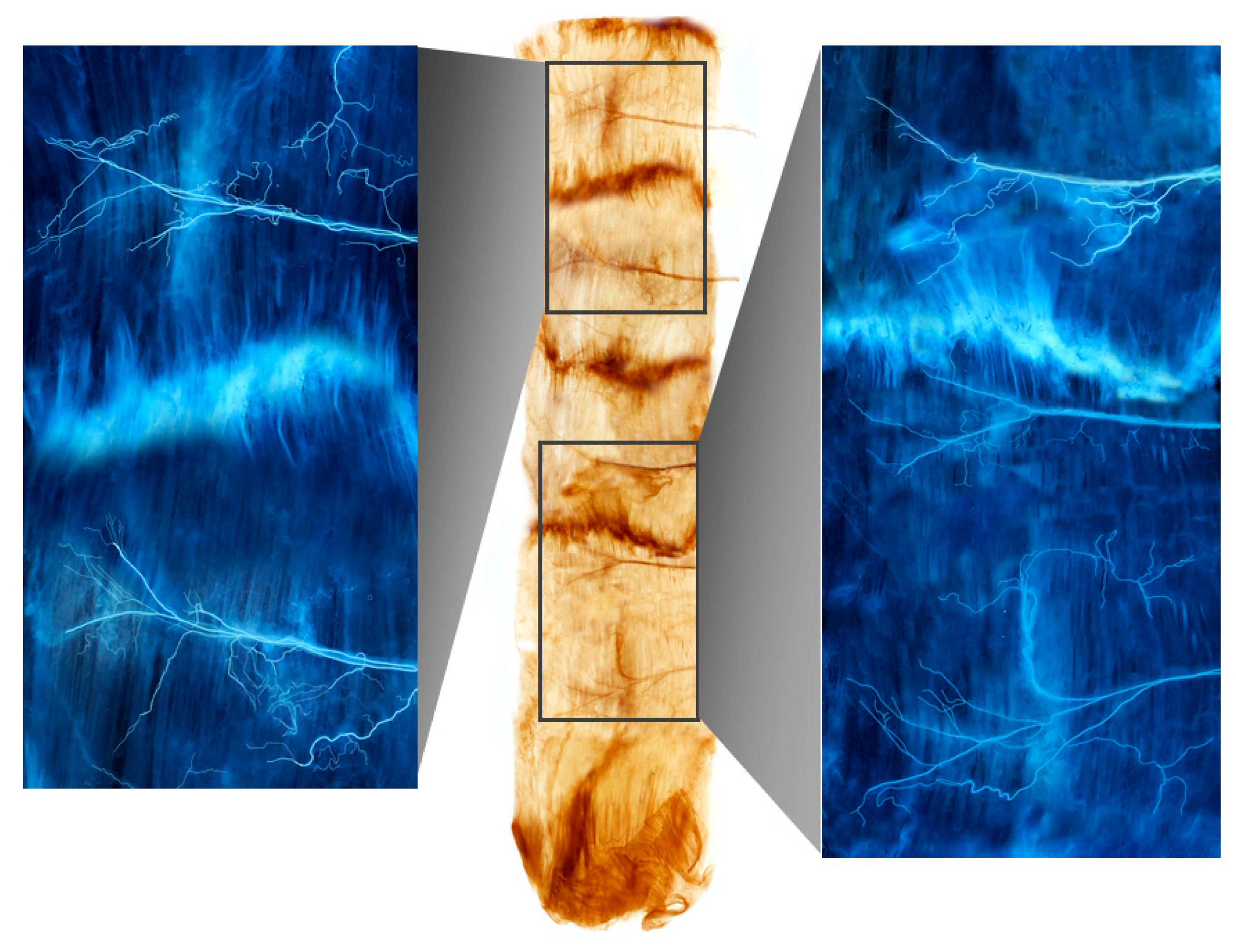
Ten of the 16 rectus abdominis muscle specimens were divided into four muscle bellies. Based on the distance from the xyphoid process to the pubic crest, the arborizations of the intramuscular nerves were largest in sections 5–15%, 25–35%, 45–55%, and 70–80% from the 1st to the 4th muscle belly, respectively (Figure 1). Three specimens had the largest arborizations in the 5–15%, 30–35%, 45–55%, and 70–85% sections. Two specimens had the largest arborizations in the 10–15%, 30–35%, 45–55%, and 75–85% sections. Finally, one specimen had the largest arborizations in the 5–15%, 30–35%, 45–55%, and 75–85% sections.
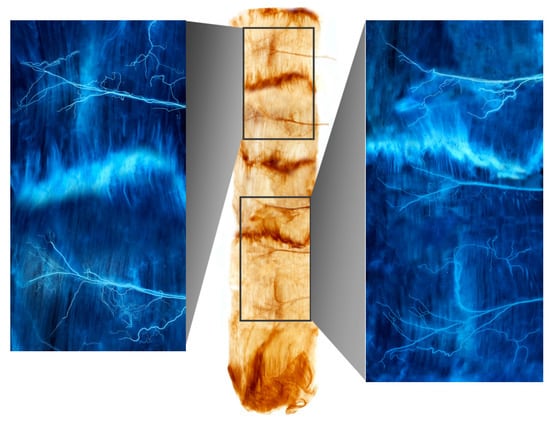
Figure 1.
A Sihler-stained rectus abdominis muscle. Note the intramuscular arborizations shown in the enlarged panels.
2.2. Tendinous Portion of the Rectus Abdominis Muscle
Fourteen out of the 16 rectus abdominis muscle specimens had the tendinous portion located in the 15–20%, 35–40%, 55–60%, and 90–100% sections, relative to the distance from the xyphoid process of the sternum to the crest of the pubis. Two specimens had the tendinous portion located in the 15–20%, 35–40%, 55–65%, and 90–100% sections.
3. Discussion
The rectus abdominis is a flat and strap muscle that extends along the whole length of the anterior wall of the abdomen and is separated into two portions by the linea alba. Tendinous intersections subdivide each rectus abdominis muscle into smaller muscle bellies [29]. The 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th muscle bellies of the rectus abdominis are innervated by the 8th, 9th, 10th, and 12th intercostal nerves, respectively, which enter the muscles from the deeper side. The 11th intercostal nerve innervates parts of the 3rd and 4th muscle bellies near the third tendon. The 8th, 9th, 10th, and 12th intercostal nerves enter the muscles at the mid parallel line of each muscle belly. The rectus abdominis has dual blood supply: the superior and inferior epigastric arteries. The TRAM flap procedure can be achieved as a free flap based on the inferior epigastric artery or pedicled flap based on the superior epigastric artery [30,31,32].
A free TRAM is wholly detached and implanted to the breast and anastomosed to internal mammary or the thoracodorsal vessels. In a pedicled TRAM, the tissues are bulkily rotated and relocated in a state of one side attached. In most of the cases, the free TRAM flaps have better results in shaping and lesser risk of insufficient blood supply than the pedicled flap.
Previous studies have suggested that TRAM flap surgery results in a severe painful symptomatology, which necessitates the use of pain medications, [33] and post-transplantation muscle contractions and spasms are considered to be the underlying causes [34,35,36]. Recently, muscle tissue changes due to contraction-induced hypoxia in the muscle have been identified, and the association of a low oxygen level with pain has been described [37]. Additionally, deposits of glycogen and resulting interstitial fibrosis in the muscles with hypoxia have been reported. Several studies revealed that BoNT infiltration of the flap muscle in breast reconstruction surgery had produced prolonged inhibition of muscle contraction and postoperative pain [38,39,40]. Schweizer et al. demonstrated that BoNT injection increased flap survival through enhanced blood flow and oxygen supply to the tissues [41,42]. Studies examining the positive effects of BoNT on tissue perfusion and flap survival from the last decade have already been published [4,42,43,44].
BoNT irreversibly blocks neurotransmitter release in the presynaptic neuron by coupling with the presynaptic cell membrane [45]. Thus, clinicians not only need to manage the toxin precisely in the target rectus abdominis muscle, but must also inject the toxin close to the site of action; specifically, in the arborized section of the muscle. Furthermore, the large amounts of BoNT into the body can lead to the creation of antibodies against the toxin, which reduces its therapeutic effect. The rectus abdominis muscle, which is a multiply-banded, superficial abdominal muscle, requires multiple injections; this increases the risk of developing complications in nearby organs. This study made several important contributions in the discovery of the ideal injection sites in the rectus abdominis to maximize the effect of BoNT while using the smallest dose possible.
Furthermore, the method of exposing the arborization patterns of intramuscular neural networks used in this study can be applied to electromyography studies of the rectus abdominis and may also find use in sports medicine, respiratory studies, and in the diagnosis of neuromuscular injuries [46,47].
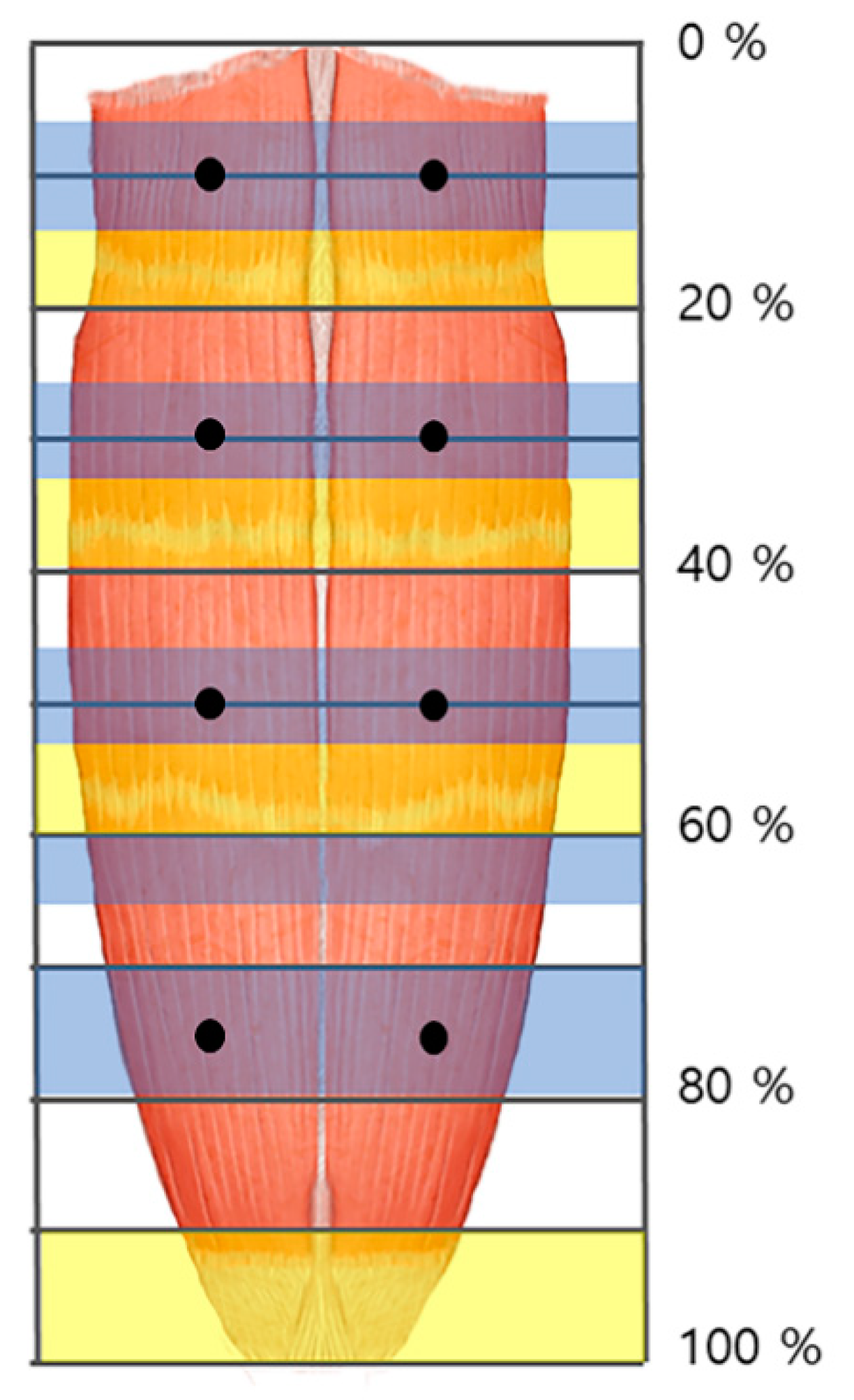
We propose that practitioners perform low dose BoNT injections at several points to achieve maximum therapeutic effect while minimizing side effects (Figure 2). Furthermore, we suggest that BoNT injections and electromyography be performed in the arborized sections of the rectus abdominis muscle and to avoid the tendinous portion.
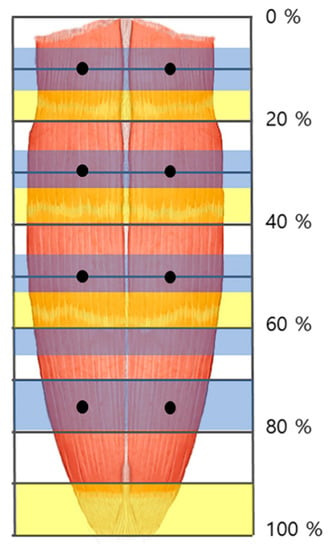
Figure 2.
The arborized portions of the rectus abdominis muscle were located in the 5–15%, 25–35%, 45–55%, and 70–80% sections (blue shaded) from the 1st to the 4th muscle belly, respectively. The tendinous portions were located in the 15–20%, 35–40%, 55–60%, and 90–100% sections (yellow shaded). The injection points of the rectus abdominis muscle are at both sides of the midpoint at 10%, 30%, 50%, and 75% (dark dot).
Previous studies administered amounts of BoNT injection to the rectus abdominis muscle ranging from 200–600 units with one to six injection sites [48,49,50]. However, according to the result, we recommend an injection of BoNT in pedicled flap at eight points, and free flap at the lower four points (Figure 2). Additionally, we suggest each injection dosed 25 units, since the average thickness of the rectus abdominis muscle is 10 mm [29], and BoNT usually spreads up to 2–4 cm from the injection site [13].
4. Materials and Methods
This study was conducted in compliance with the principles set forth in the Declaration of Helsinki. Permission and approval were obtained from the families of the cadavers before beginning the dissections. A total of 16 rectus abdominis muscles from Korean cadavers (five men and five women with a mean age of 74.6 years; range, 63–83 years) were dissected in Yonsei University medical center from May 2020 to October 2020. Modified Sihler staining was performed on all specimens to highlight the sections of arborization of the intramuscular nerves.
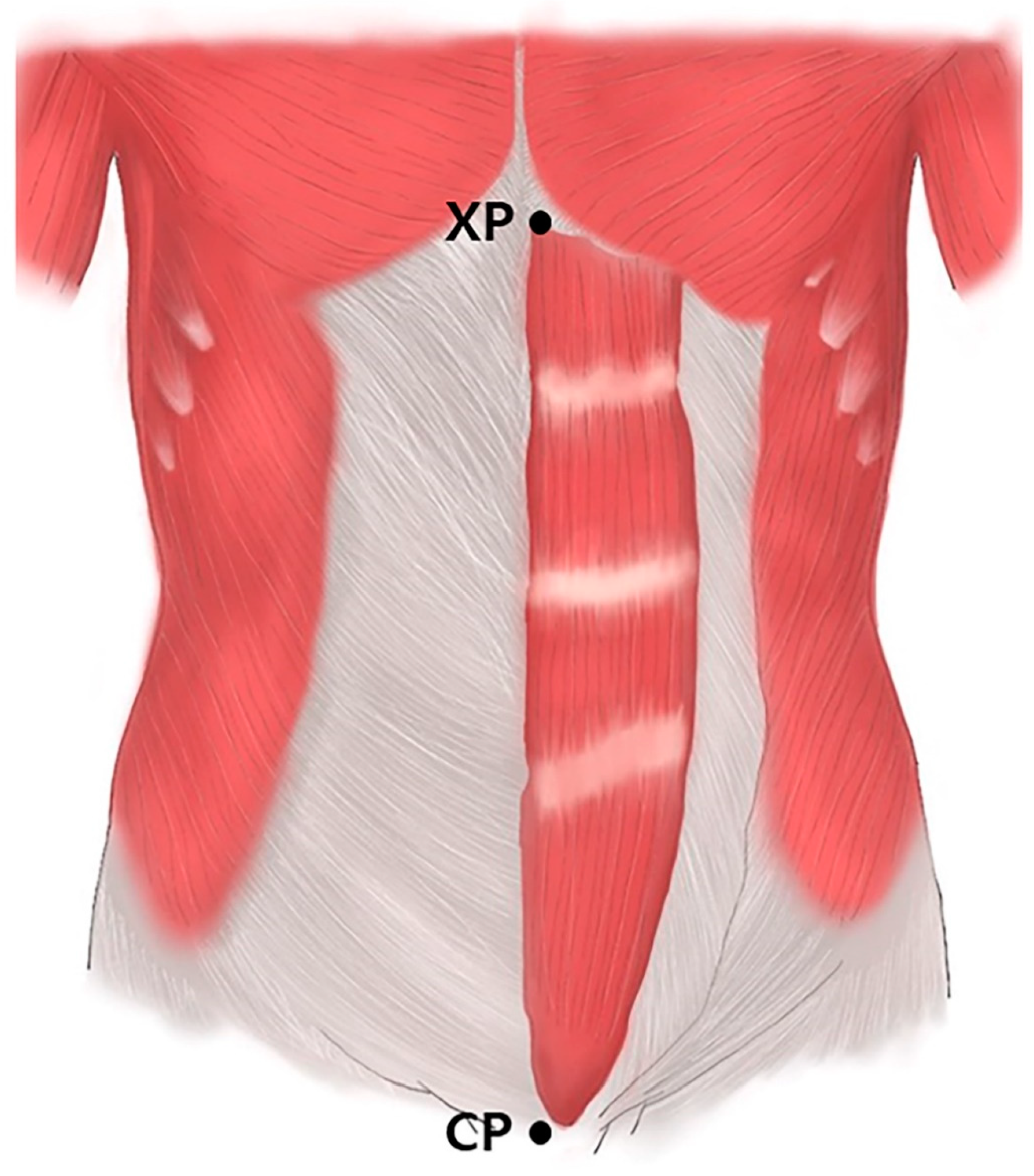
Prior to the dissection, the rectus abdominis muscles were aligned within their anatomical positions. The arborization patterns were tracked based on two landmarks: the xyphoid process of the sternum (0%) and the crest of the pubis (100%) (Figure 3). The muscles were divided transversely into 20 sections with each section representing a value of 5%, and the distribution of the intramuscular nerves was tracked with microscopic dissection prior to the staining procedure.
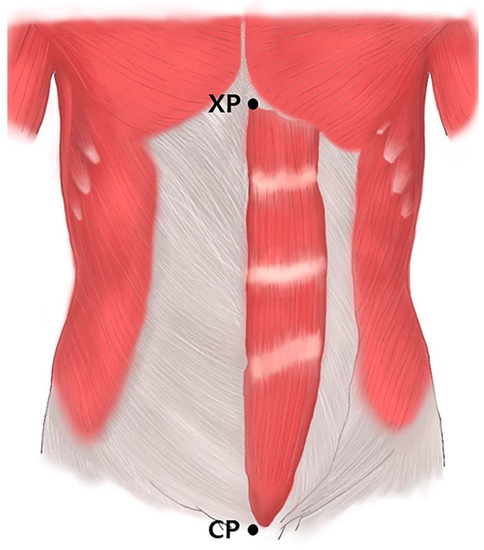
Figure 3.
Rectus abdominis muscles. Specimens were harvested from the xyphoid process of the sternum (XP) to the crest of pubis (CP).
The muscle specimens underwent Sihler staining as modified by Liem and Douwe van Willigen [51]. This method includes several phases to visualize the arborization pattern of the intramuscular nerves. After staining, the muscles were measured from the xyphoid process of the sternum (0%) to the crest of the pubis (100%).
Modified Sihler Staining
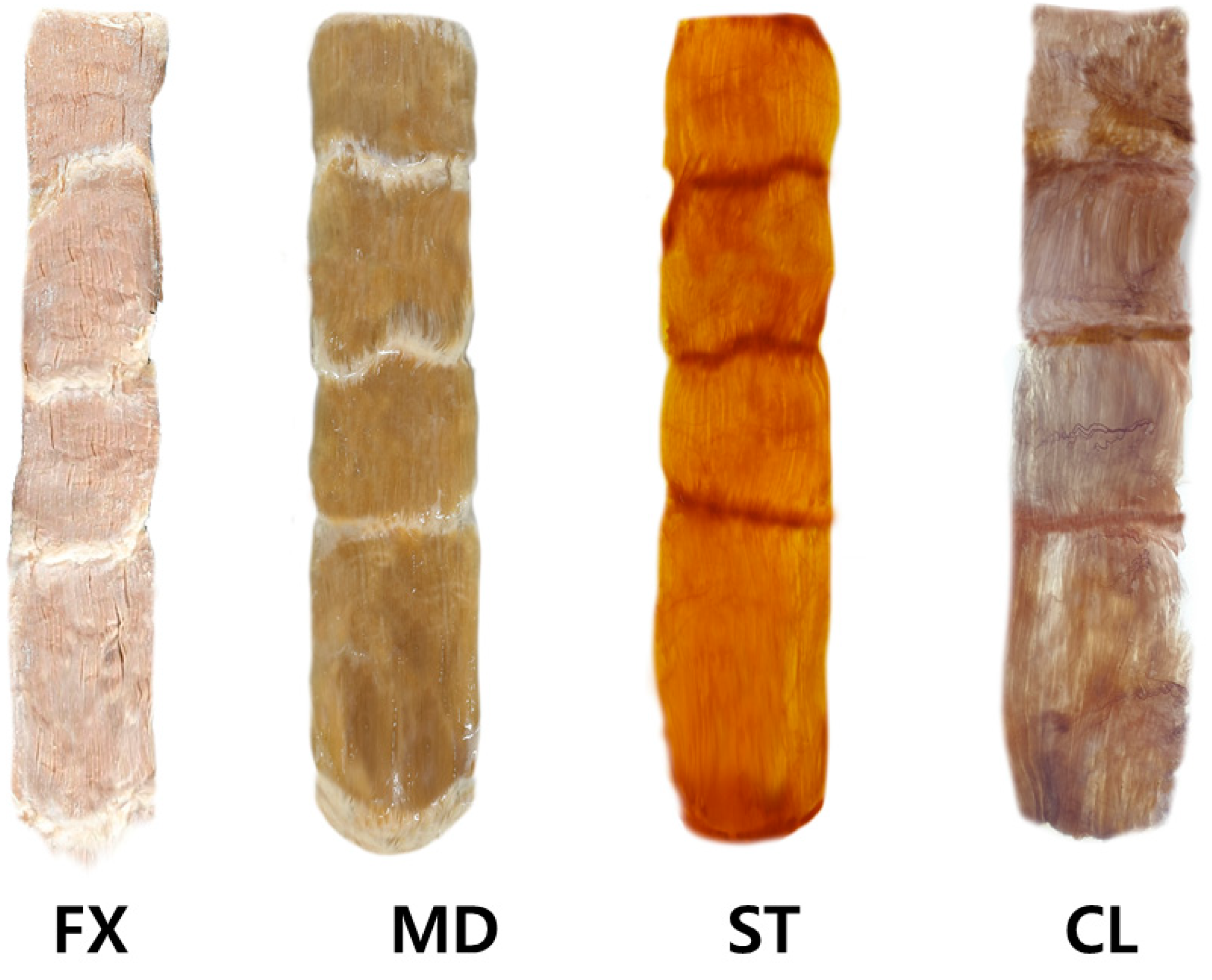
The steps involved in performing the modified Sihler staining on the rectus abdominis muscles are presented in Figure 4, described as follows:
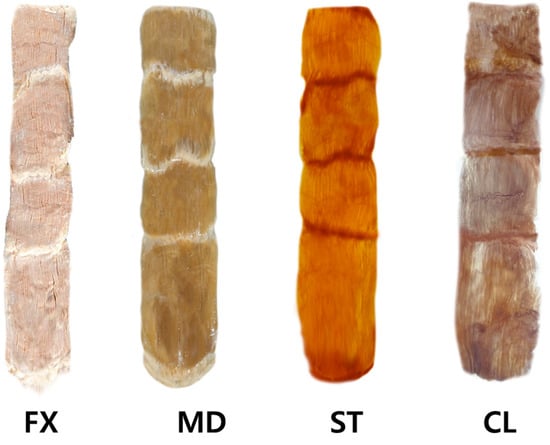
Figure 4.
The rectus abdominis muscle underwent the modified Sihler’s method. The method consists of stages of fixation (FX), maceration and depigmentation (MD), decalcification, staining (ST), and clearing (CL).
Fixation phase: The harvested rectus abdominis muscles were fixated for 30 days in 10% un-neutralized formalin solution. This solution was changed every time it became opaque.
Maceration and depigmentation phase: The fixed rectus abdominis muscle specimens were cleaned in pure water for an hour. Afterward, the samples were depigmented for four weeks in a solution containing hydrogen peroxide and 3% aqueous potassium hydroxide.
Decalcification phase: The macerated specimens were placed in Sihler I solution (glycerin, aqueous chloral hydrate, and glacial acetic acid) for one day.
Staining phase: After decalcification, the specimens were immediately placed in Sihler II solution (glycerin, aqueous chloral hydrate, and acetic acid) for four weeks.
Destaining phase: The stained muscle specimens were then destained in Sihler I solution for an hour.
Neutralization phase: The destained specimens were then neutralized in flowing water for half an hour and subsequently placed in 0.05% lithium carbonate for an hour.
Clearing phase: The neutralized rectus abdominis muscle specimens were finally washed with increasing concentrations (20% to 100%) of glycerin for four days.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.-H.Y.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, J.-H.L. and K.K.S.; Writing—Review and Editing, K.K.S. and H.-J.L.; Visualization, H.-J.L.; Supervision, H.-J.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIP) (NRF-2019R1C1C1010776).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Yonsei University College of Medicine (approval number 20-007, approved date: 22 January 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely thank those who donated their bodies to science so that anatomical research could be performed. The results from such research can potentially increase mankind’s overall knowledge that can then improve patient care. Therefore, these donors and their families deserve our highest gratitude. The authors thank Eun-Byul Yi from the Eonbuk elementary school for illustrations.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kampe, S.; Warm, M.; Kasper, S.M.; Diefenbach, C. Concept for postoperative analgesia after pedicled TRAM flaps: Continuous wound instillation with 0.2% ropivacaine via multilumen catheters. A report of two cases. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 2003, 56, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.G.; Ramakrishnan, V. Microsurgical Tissue Transfer in Breast Reconstruction. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2017, 44, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temiz, G.; Yesiloglu, N.; Sirinoglu, H.; Akpinar, A.C.; Sarici, M.; Filinte, D.; Filinte, G.T.; Bozkurt, M. Increasing the survival of transverse rectus abdominis musculocutaneous flaps with a Botulinum toxin-A injection: A comparison of surgical and chemical flap delay methods. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2016, 69, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Roh, T.S.; Lee, W.J.; Yoo, W.M.; Tark, K.C. The effect of botulinum toxin A on skin flap survival in rats. Wound Repair Regen. 2009, 17, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.K.; Oh, E.J.; Chung, J.Y.; Park, J.W.; Cho, B.C.; Chung, H.Y. The effects of botulinum toxin A on the survival of a random cutaneous flap. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2009, 62, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, P.B.; Fang, T.; Songcharoen, S.J.; Ziakas, G.; Zhang, F. Inflammatory response and survival of pedicled abdominal flaps in a rat model after perivascular application of botulinum toxin type A. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 133, 491e–498e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcal, A.; Sevim, K.Z.; Yesilada, A.; Kiyak, V.; Sucu, D.O.; Tatlidede, H.S.; Sakiz, D.; Kaya, H. Comparison of perivascular and intramuscular applied botulinum toxin a pretreatment on muscle flap ischemia-reperfusion injury and chemical delay. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2013, 24, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childers, M.K. Targeting the neuromuscular junction in skeletal muscles. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 83, S38–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, C.H.; Teive, H.A.; Zonta, M.; Silva, G.C.; Oliveira, M.R.; Roriz, M.M.; Brandi, I.V.; Becker, N.; Scola, R.H.; Werneck, L.C. Botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of lower-limb spasticity in children with cerebral palsy. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2009, 67, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ade-Hall, R.A.; Moore, A.P. Botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of lower limb spasticity in cerebral palsy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westhoff, B.; Seller, K.; Wild, A.; Jaeger, M.; Krauspe, R. Ultrasound-guided botulinum toxin injection technique for the iliopsoas muscle. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2003, 45, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childers, M.K.; Brashear, A.; Jozefczyk, P.; Reding, M.; Alexander, D.; Good, D.; Walcott, J.M.; Jenkins, S.W.; Turkel, C.; Molloy, P.T. Dose-dependent response to intramuscular botulinum toxin type A for upper-limb spasticity in patients after a stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 85, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Castaneda, J.; Jankovic, J.; Comella, C.; Dashtipour, K.; Fernandez, H.H.; Mari, Z. Diffusion, spread, and migration of botulinum toxin. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 1775–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracies, J.M.; Lugassy, M.; Weisz, D.J.; Vecchio, M.; Flanagan, S.; Simpson, D.M. Botulinum toxin dilution and endplate targeting in spasticity: A double-blind controlled study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2009, 90, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Campenhout, A.; Verhaegen, A.; Pans, S.; Molenaers, G. Botulinum toxin type A injections in the psoas muscle of children with cerebral palsy: Muscle atrophy after motor end plate-targeted injections. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2013, 34, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinnett, D. Botulinum toxin A injections in children: Technique and dosing issues. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 83, S59–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.S.; Dover, J.S.; Arndt, K.A. Effect of volume and concentration on the diffusion of botulinum exotoxin A. Arch. Dermatol. 2004, 140, 1351–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepage, D.; Parratte, B.; Tatu, L.; Vuiller, F.; Monnier, G. Extra- and intramuscular nerve supply of the muscles of the anterior antebrachial compartment: Applications for selective neurotomy and for botulinum toxin injection. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2005, 27, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rha, D.W.; Yi, K.H.; Park, E.S.; Park, C.; Kim, H.J. Intramuscular nerve distribution of the hamstring muscles: Application to treating spasticity. Clin. Anat. 2016, 29, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Cong, L.; Lee, K.L.; Hu, K.S.; Kim, H.J. Effective botulinum toxin injection guide for treatment of cervical dystonia. Clin. Anat. 2020, 33, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.H.; Cong, L.; Bae, J.H.; Park, E.S.; Rha, D.W.; Kim, H.J. Neuromuscular structure of the tibialis anterior muscle for functional electrical stimulation. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2017, 39, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.H.; Rha, D.W.; Lee, S.C.; Cong, L.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, Y.W.; Kim, H.J.; Hu, K.S. Intramuscular nerve distribution pattern of ankle invertor muscles in human cadaver using sihler stain. Muscle Nerve 2016, 53, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.H.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, J.H.; Hu, K.S.; Kim, H.J. Intramuscular Neural Distribution of Rhomboid Muscles: Evaluation for Botulinum Toxin Injection Using Modified Sihler’s Method. Toxins 2020, 12, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.H.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, K.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.J. Anatomical guide for botulinum neurotoxin injection: Application to cosmetic shoulder contouring, pain syndromes, and cervical dystonia. Clin. Anat. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, K.H.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, K.L.; Kim, H.J. Effective botulinum neurotoxin injection in treating iliopsoas spasticity. Clin. Anat. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, K.H.; Lee, K.L.; Lee, J.H.; Hu, H.W.; Lee, K.; Seo, K.K.; Kim, H.J. Guidelines for botulinum neurotoxin injections in piriformis syndrome. Clin. Anat. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Campenhout, A.; Hubens, G.; Fagard, K.; Molenaers, G. Localization of motor nerve branches of the human psoas muscle. Muscle Nerve 2010, 42, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddy, M.J.; Brown, C.; Mistry, R.; Eastwood, D.M. Botulinum toxin injection site localization for the tibialis posterior muscle. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2006, 15, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lim, H.; Lee, S.I.; Kim, Y.J. Thickness of rectus abdominis muscle and abdominal subcutaneous fat tissue in adult women: Correlation with age, pregnancy, laparotomy, and body mass index. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2012, 39, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartrampf, C.R., Jr.; Bennett, G.K. Autogenous tissue reconstruction in the mastectomy patient. A critical review of 300 patients. Ann. Surg. 1987, 205, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheflan, M.; Dinner, M.I. The transverse abdominal island flap: Part I. Indications, contraindications, results, and complications. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1983, 10, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, S.L.; Ducic, I.; Cuoco, F.; Taylor, N. Effect of obesity on flap and donor-site complications in pedicled TRAM flap breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2007, 119, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, S.S.; Sharma, S.; Koutz, C.; Langstein, H.N.; Evans, G.R.D.; Robb, G.L.; Chang, D.W.; Reece, G.P. Postoperative morphine requirements of free TRAM and DIEP flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2001, 107, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.P.; Haribhakti, V.; Loree, T.R.; Sutaria, P. Complications of the pectoralis major myocutaneous flap in head and neck reconstruction. Am. J. Surg. 1990, 160, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merve, A.; Mitra, I.; Swindell, R.; Homer, J.J. Shoulder morbidity after pectoralis major flap reconstruction for head and neck cancer. Head Neck 2009, 31, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, S.; Sarkar, S.; Kavarana, N.; Bhathena, H.; Mehta, A. Complications of the pectoralis major myocutaneous flap in the oral cavity: A prospective evaluation of 220 cases. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1996, 98, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gur, E.; Hanna, W.; Andrighetti, L.; Semple, J.L. Light and electron microscopic evaluation of the pectoralis major muscle following tissue expansion for breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1998, 102, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W. Botulinum Toxin A Plays an Important Role in the Placement of Implants Deep Within the Pectoralis Major Muscle for Mammaplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Aesthetic Plast. 2018, 42, 1519–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winocour, S.; Murad, M.H.; Bidgoli-Moghaddam, M.; Jacobson, S.R.; Bite, U.; Saint-Cyr, M.; Tran, N.V.; Lemaine, V. A systematic review of the use of Botulinum toxin type A with subpectoral breast implants. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2014, 67, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.; Champaneria, M.C.; Maxwell, G.P. The efficacy of botulinum toxin A in post-mastectomy breast reconstruction: A pilot study. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2015, 35, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, D.F.; Schweizer, R.; Zhang, S.; Kamat, P.; Contaldo, C.; Rieben, R.; Eberli, D.; Giovanoli, P.; Erni, D.; Plock, J.A. Botulinum toxin A and B raise blood flow and increase survival of critically ischemic skin flaps. J. Surg. Res. 2013, 184, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Rah, D.K.; Kim, S.Y. Presurgical Botulinum Toxin A Treatment Increases Angiogenesis by Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1alpha/Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Subsequent Superiorly Based Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous Flap Survival in a Rat Model. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2016, 76, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.; Fathi, H.; Mazloumi, M.; Khalilzadeh, O.; Amanpour, S.; Meysamie, A.; Mashali, L.; Kardar, M.H. Preventive effect of botulinum toxin A in microanastomotic thrombosis: A rabbit model. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2010, 63, e720–e724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, M.W.; Higgins, J.P.; Wilgis, E.F. Prevention of anastomotic thrombosis by botulinum toxin a in an animal model. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 123, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melling, J.; Hambleton, P.; Shone, C.C. Clostridium botulinum toxins: Nature and preparation for clinical use. Eye 1988, 2, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Nonaka, K.; Ogaya, S.; Ogi, A.; Matsunaka, C.; Horie, J. Surface electromyography activity of the rectus abdominis, internal oblique, and external oblique muscles during forced expiration in healthy adults. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2016, 28, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.M.; Lehr, R.P.; Millar, A.B.; Silver, J.R. An electromyographic study of the abdominal muscles during postural and respiratory manoeuvres. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1987, 50, 866–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azher, S.N.; Jankovic, J. Camptocormia: Pathogenesis, classification, and response to therapy. Neurology 2005, 65, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.J.; Li, B.; Pan, Y.G.; Zhang, X.L.; Jin, L.J. Botulinum Toxin A for Treatment of Diaphragmatic Myoclonus. Chin. Med. J. 2017, 130, 753–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshubaili, A.; Abou-Al-Shaar, H.; Santhamoorthy, P.; Attia, H.; Bohlega, S. Ultrasound-guided botulinum toxin A injection in the treatment of belly dancer’s dyskinesia. BMC Neurol. 2016, 16, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liem, R.S.; Douwe van Willigen, J. In toto staining and preservation of peripheral nervous tissue. Stain Technol. 1988, 63, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).