The Roles of IL-17, IL-21, and IL-23 in the Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gastrointestinal Inflammation: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Bacterial Antigen Induced Immune Response
3. Overview of IL-17, IL-21, and IL-23
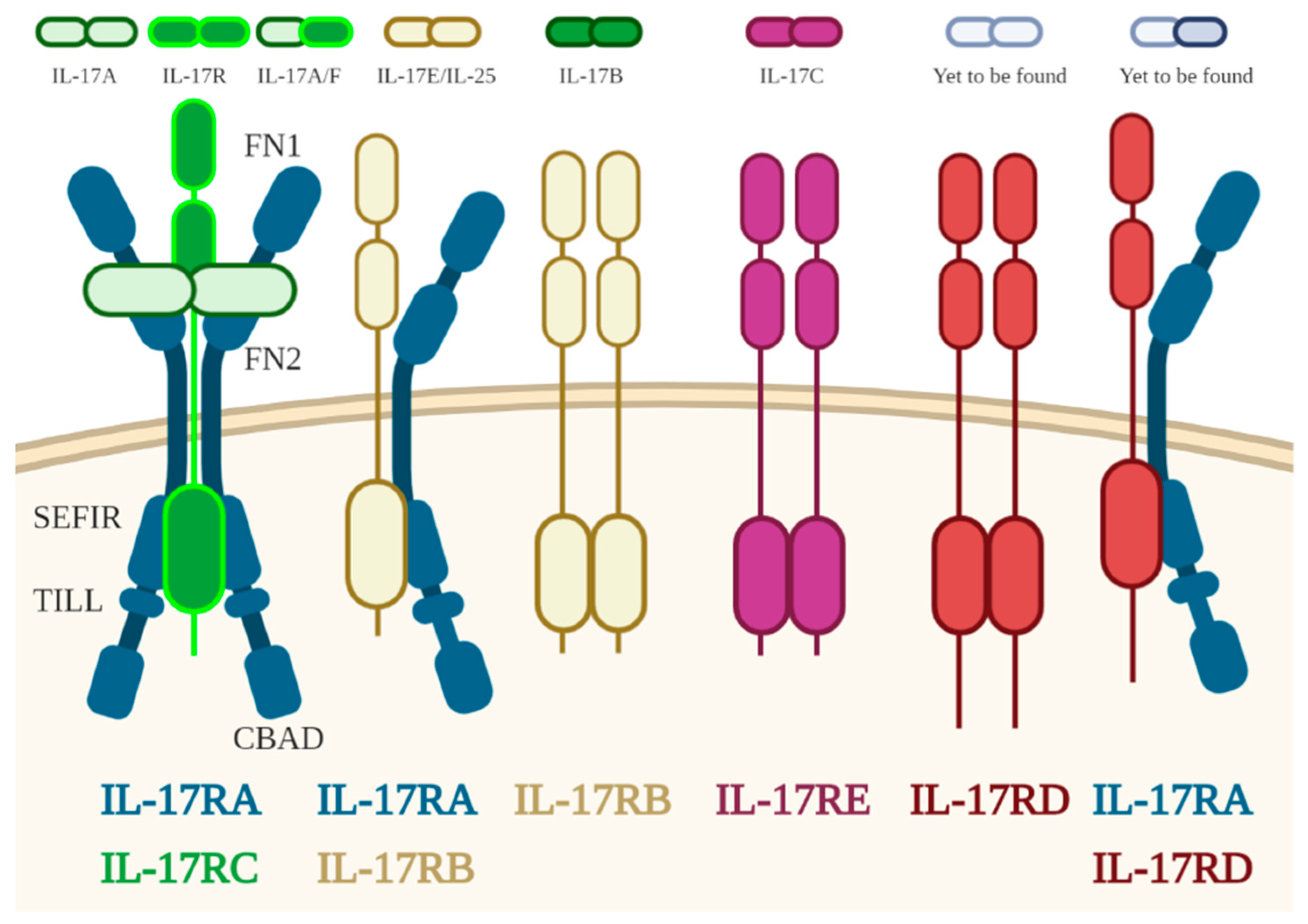
3.1. IL17
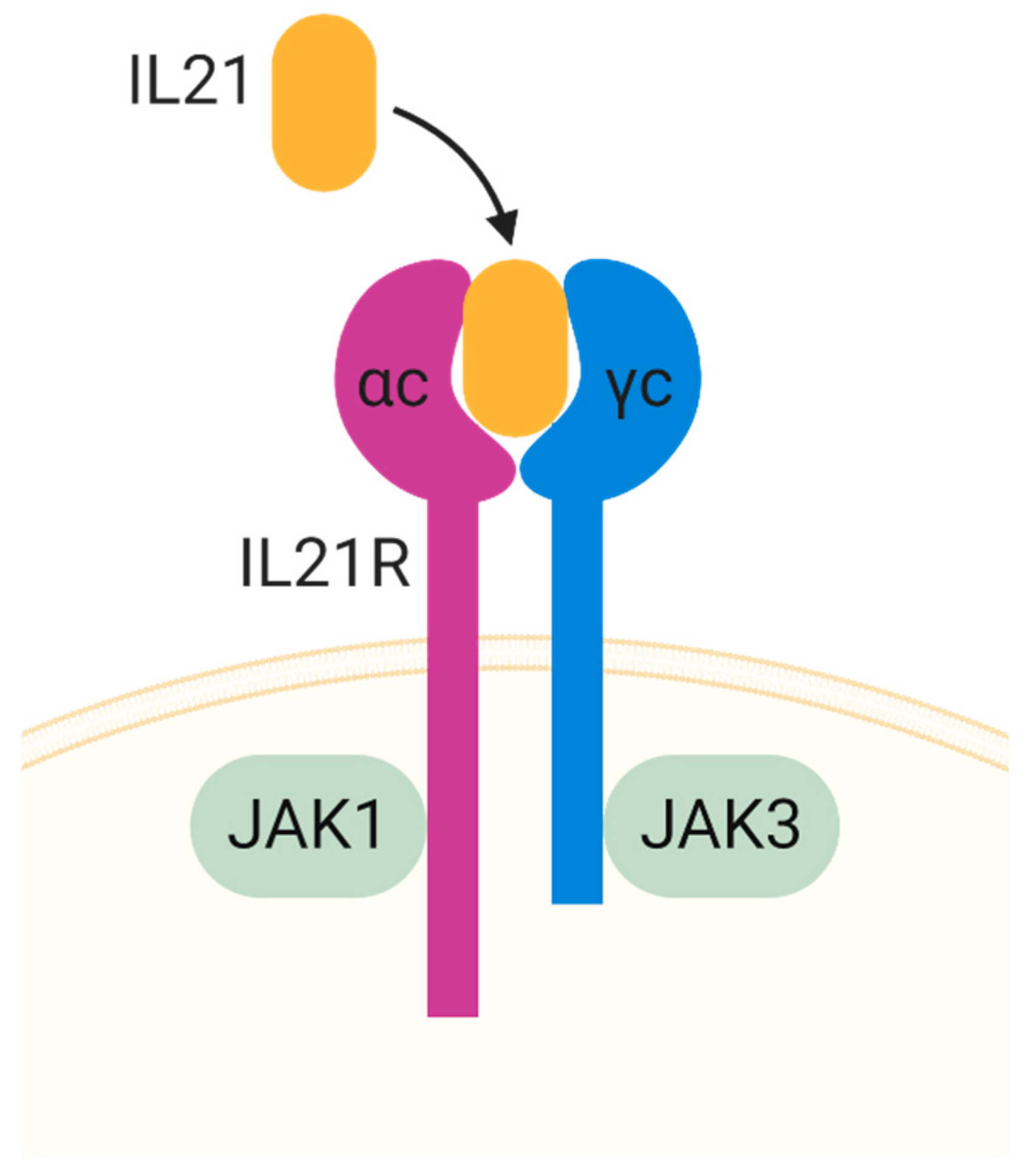
3.2. IL-21
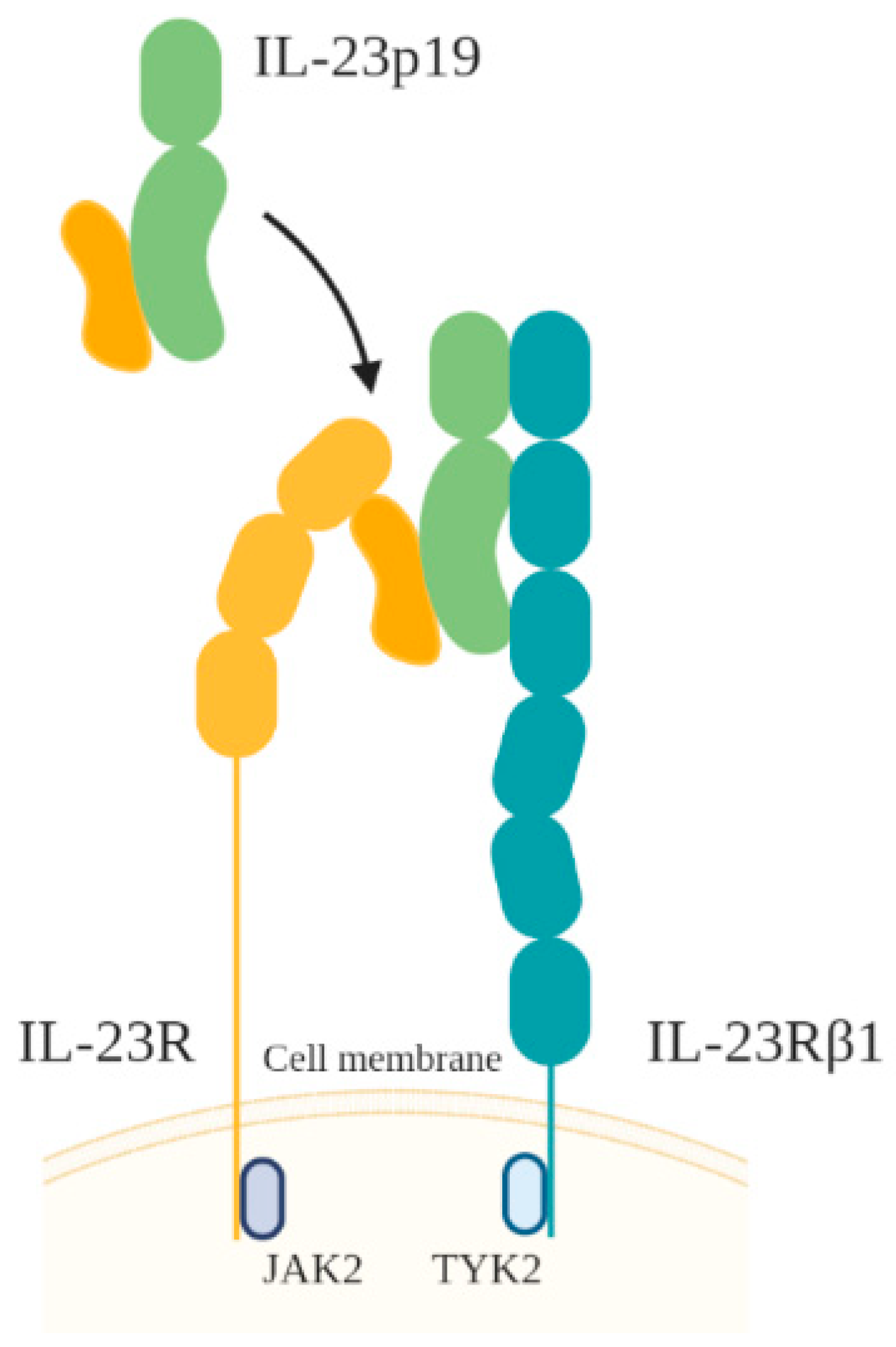
3.3. IL-23
4. The Role of IL-17, IL-21, and IL-23 in Gastrointestinal Inflammation
5. Th17 Roles in H. pylori Infection
6. IL-17 and IL-21 Axis in H. pylori Infection
7. IL-17 and IL-23 Axis in H. pylori Infection
8. IL-17, IL-21, and IL-23 Role in GC Development
9. Interleukin Polymorphism and the Development of Gastrointestinal Cancer
10. Expert Opinion
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Correa, P.; Houghton, J. Carcinogenesis of Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suerbaum, S.; Smith, J.M.; Bapumia, K.; Morelli, G.; Smith, N.H.; Kunstmann, E.; Dyrek, I.; Achtman, M. Free recombination within Helicobacter pylori. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 12619–12624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatakeyama, M.; Higashi, H. Helicobacter pylori CagA: A new paradigm for bacterial carcinogenesis. Cancer Sci. 2005, 96, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watabe, H.; Mitsushima, T.; Yamaji, Y.; Okamoto, M.; Wada, R.; Kokubo, T.; Doi, H.; Yoshida, H.; Kawabe, T.; Omata, M. Predicting the development of gastric cancer from combining Helicobacter pylori antibodies and serum pepsinogen status: A prospective endoscopic cohort study. Gut 2005, 54, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miftahussurur, M.; Waskito, L.A.; Syam, A.F.; Nusi, I.A.; Wibawa, I.D.N.; Rezkitha, Y.A.A.; Siregar, G.; Yulizal, O.K.; Akil, F.; Uwan, W.B.; et al. Analysis of risks of gastric cancer by gastric mucosa among Indonesian ethnic groups. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoldi, A.; Carrara, E.; Graham, D.Y.; Conti, M.; Tacconelli, E. Prevalence of Antibiotic Resistance in Helicobacter pylori: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis in World Health Organization Regions. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1372–1382.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caruso, R.; Fina, D.; Paoluzi, O.A.; Blanco, G.D.V.; Stolfi, C.; Rizzo, A.; Caprioli, F.; Sarra, M.; Andrei, F.; Fantini, M.C.; et al. IL-23-mediated regulation of IL-17 production inHelicobacter pylori-infected gastric mucosa. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, X.-F.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Liu, T.; Yin, Z.; Wu, C.; Mao, X.-H.; Jia, K.-R.; Wang, F.-J.; et al. Helicobacter pylori-Induced Th17 Responses Modulate Th1 Cell Responses, Benefit Bacterial Growth, and Contribute to Pathology in Mice. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 5121–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shabgah, A.G.; Fattahi, E.; Shahneh, F.Z. Interleukin-17 in human inflammatory diseases. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2014, 31, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bagheri, N.; Azadegan-Dehkordi, F.; Shirzad, H.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Rahimian, G.; Razavi, A. The biological functions of IL-17 in different clinical expressions of Helicobacter pylori-infection. Microb. Pathog. 2015, 81, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.S.; Cox, M.A.; Zajac, A.J. Interleukin-21: A multifunctional regulator of immunity to infections. Microbes Infect. 2010, 12, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hue, S.; Ahern, P.; Buonocore, S.; Kullberg, M.C.; Cua, D.J.; McKenzie, B.S.; Powrie, F.; Maloy, K.J. Interleukin-23 drives innate and T cell–mediated intestinal inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2473–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caruso, R.; Pallone, F.; Monteleone, G. Emerging role of IL-23/IL-17 axis in H pylori-associated pathology. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 5547–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morrison, P.J.; Ballantyne, S.J.; Kullberg, M.C. Interleukin-23 and T helper 17-type responses in intestinal inflammation: From cytokines to T-cell plasticity. Immunology 2011, 133, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koussoulas, V.; Vassiliou, S.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Tassias, G.; Kotsaki, A.; Barbatzas, C.; Tzivras, M. Implications for a role of interleukin-23 in the pathogenesis of chronic gastritis and of peptic ulcer disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 156, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ümit, H.; Tezel, A.; Bukavaz, S.; Unsal, G.; Otkun, M.; Soylu, A.R.; Tucer, D.; Otkun, M.; Bilgi, S. The Relationship Between Virulence Factors of Helicobacter pylori and Severity of Gastritis in Infected Patients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 54, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmiela, M.; Walczak, N.; Rudnicka, K. Helicobacter pylori outer membrane vesicles involvement in the infection development and Helicobacter pylori-related diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-K.; Zhu, H.-F.; He, B.-S.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Chen, Z.-T.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Wu, G.-L. CagA+ H pylori infection is associated with polarization of T helper cell immune responses in gastric carcinogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 2923–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, S.; Kwok, T.; Hartig, R.; König, W.; Backert, S. NF-κB activation and potentiation of proinflammatory responses by the Helicobacter pylori CagA protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, C.; Sillén, A.; Eriksson, L.; Strand, M.-L.; Enroth, H.; Normark, S.; Falk, P.; Engstrand, L. Correlation between cag Pathogenicity Island Composition and Helicobacter pylori-Associated Gastroduodenal Disease. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 6573–6581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, S.; Nagashima, H.; Cruz, M.; Uchida, T.; Uotani, T.; Abreu, J.A.J.; Mahachai, V.; Vilaichone, R.-K.; Ratanachu-Ek, T.; Tshering, L.; et al. Interleukin-17C in Human Helicobacter pylori Gastritis. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00389-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lina, T.T.; Pinchuk, I.V.; House, J.; Yamaoka, Y.; Graham, D.Y.; Beswick, E.J.; Reyes, V.E. CagA-dependent downregulation of B7-H2 expression on gastric mucosa and inhibition of Th17 responses during Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 3838–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caruso, R.; Fina, D.; Peluso, I.; Fantini, M.C.; Tosti, C.; Blanco, G.D.V.; Paoluzi, O.A.; Caprioli, F.; Andrei, F.; Stolfi, C.; et al. IL-21 Is Highly Produced inHelicobacter pylori-Infected Gastric Mucosa and Promotes Gelatinases Synthesis. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 5957–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagheri, N.; Azadegan-Dehkordi, F.; Shirzad, M.; Zamanzad, B.; Rahimian, G.; Taghikhani, A.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Shirzad, H. Clinical immunology Mucosal interleukin-21 mRNA expression level is high in patients with Helicobacter pylori and is associated with the severity of gastritis. Central Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 1, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranzer, K.; Eckhardt, A.; Aigner, M.; Knoll, G.; Deml, L.; Speth, C.; Lehn, N.; Rehli, M.; Schneider-Brachert, W. Induction of Maturation and Cytokine Release of Human Dendritic Cells by Helicobacter pylori. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 4552–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andres, S.; Schmidt, H.M.; Mitchell, H.; Rhen, M.; Maeurer, M.; Engstrand, L. Helicobacter pylori defines local immune response through interaction with dendritic cells. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, J.Y.; Zhang, M.; Miller, M.J.; Mills, J.C.; Wang, B.; Liu, M.; Eaton, K.A.; Zou, W.; Berndt, B.E.; Cole, T.S.; et al. Helicobacter pylori Immune Escape Is Mediated by Dendritic Cell–Induced Treg Skewing and Th17 Suppression in Mice. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shiu, J.; Blanchard, T.G. Dendritic cell function in the host response to Helicobacter pylori infection of the gastric mucosa. Pathog. Dis. 2013, 67, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.M.; Kim, J.S.; Yoo, D.Y.; Ko, S.H.; Kim, N.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y.-J. Stimulation of dendritic cells with Helicobacter pylori vacuolating cytotoxin negatively regulates their maturation via the restoration of E2F1. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 166, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Liu, T.; Guo, H.; Liu, X.-F.; Zhuang, Y.; Yu, S.; Chen, L.; Wu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, B.; et al. Induction of a Th17 cell response by Helicobacter pylori Urease subunit B. Immunobiology 2011, 216, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, Z.; Cheng, L.; Ren, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Fu, X.-Y.; Chang, Z. Interleukin-17F signaling requires ubiquitination of interleukin-17 receptor via TRAF6. Cell Signal. 2007, 19, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffen, S.L. Structure and signalling in the IL-17 receptor family. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mangan, P.R.; Harrington, L.E.; O’Quinn, D.B.; Helms, W.S.; Bullard, D.C.; Elson, C.O.; Hatton, R.D.; Wahl, S.M.; Schoeb, T.R.; Weaver, C.T. Transforming growth factor-beta induces development of the T(H)17 lineage. Nature 2006, 441, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, E.; Servant, N.; Zollinger, R.; Bogiatzi, S.I.; Hupe, P.; Barillot, E.; Soumelis, V. A critical function for transforming growth factor-beta, interleukin 23 and proinflammatory cytokines in driving and modulating human T(H)-17 responses. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.; Fanslow, W.C.; Seldin, M.F.; Rousseau, A.-M.; Painter, S.L.; Comeau, M.R.; Cohen, J.I.; Spriggs, M.K. Herpesvirus saimiri encodes a new cytokine, IL-17, which binds to a novel cytokine receptor. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 4392–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awane, M.; Andres, P.G.; Li, D.J.; Reinecker, H.C. NF-kappa B-inducing kinase is a common mediator of IL-17-, TNF-alpha-, and IL-1 beta-induced chemokine promoter activation in intestinal epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 5337–5344. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.H.; Sun, S.C. Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor-Associated Factor Regulation of Nuclear Factor kappaB and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwandner, R.; Yamaguchi, K.; Cao, Z. Requirement of Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor–Associated Factor (Traf)6 in Interleukin 17 Signal Transduction. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louten, J.; Boniface, K.; Malefyt, R.D.W. Development and function of TH17 cells in health and disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, B.R.E.A.; Hossain, R.; Patel, R.V.; Algood, H.M.S. Th17 Cells in Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Dichotomy of Help and Harm. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asao, H.; Okuyama, C.; Kumaki, S.; Ishii, N.; Tsuchiya, S.; Foster, D.; Sugamura, K. Cutting edge: The common gamma-chain is an indispensable subunit of the IL-21 receptor complex. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carbo, A.; Olivares-Villagómez, D.; Hontecillas, R.; Bassaganya-Riera, J.; Chaturvedi, R.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Delgado, A.; Washington, M.K.; Wilson, K.T.; Algood, H.M.S. Systems Modeling of the Role of Interleukin-21 in the Maintenance of Effector CD4+ T Cell Responses during Chronic Helicobacter pylori Infection. mBio 2014, 5, e01243-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fina, D.; Sarra, M.; Fantini, M.C.; Rizzo, A.; Caruso, R.; Caprioli, F.; Stolfi, C.; Cardolini, I.; Dottori, M.; Boirivant, M.; et al. Regulation of gut inflammation and th17 cell response by interleukin-21. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korn, T.; Bettelli, E.; Gao, W.; Awasthi, A.; Jager, A.; Strom, T.B.; Oukka, M.; Kuchroo, V.K. IL-21 initiates an alternative pathway to induce proinflammatory T(H)17 cells. Nature 2007, 448, 484–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, M.; Yi, H.; Rosenblatt, H.M.; Filipovich, A.H.; Adelstein, S.; Modi, W.S.; McBride, O.W.; Leonard, W.J. Interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain mutation results in X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency in humans. Cell 1993, 73, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, T.; Senadheera, S.; Weinberg, K.; Kaushansky, K. The common gamma chain (gamma c) is a required signaling component of the IL-21 receptor and supports IL-21-induced cell proliferation via JAK3. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 8725–8731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, W.J.; Zeng, R.; Spolski, R. Interleukin 21: A cytokine/cytokine receptor system that has come of age. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 84, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duvallet, E.; Semerano, L.; Assier, E.; Falgarone, G.; Boissier, M.-C. Interleukin-23: A key cytokine in inflammatory diseases. Ann. Med. 2011, 43, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parham, C.; Chirica, M.; Timans, J.; Vaisberg, E.; Travis, M.; Cheung, J.; Pflanz, S.; Zhang, R.; Singh, K.P.; Vega, F.; et al. A receptor for the heterodimeric cytokine IL-23 is composed of IL-12Rbeta1 and a novel cytokine receptor subunit, IL-23R. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 5699–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghoreschi, K.; Laurence, A.; Yang, X.P.; Tato, C.M.; McGeachy, M.J.; Konkel, J.E.; Ramos, H.L.; Wei, L.; Davidson, T.S.; Bouladoux, N.; et al. Generation of pathogenic T(H)17 cells in the absence of TGF-beta signalling. Nature 2010, 467, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coccia, M.; Harrison, O.J.; Schiering, C.; Asquith, M.J.; Becher, B.; Powrie, F.; Maloy, K.J. IL-1beta mediates chronic intestinal inflammation by promoting the accumulation of IL-17A secreting innate lymphoid cells and CD4(+) Th17 cells. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1595–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cua, D.J.; Sherlock, J.P.; Chen, Y.; Murphy, C.A.; Joyce, B.; Seymour, B.W.P.; Lucian, L.; To, W.; Kwan, S.; Churakova, T.; et al. Interleukin-23 rather than interleukin-12 is the critical cytokine for autoimmune inflammation of the brain. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 421, 744–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigame, H.; Kakuta, S.; Nagai, T.; Kadoki, M.; Nambu, A.; Komiyama, Y.; Fujikado, N.; Tanahashi, Y.; Akitsu, A.; Kotaki, H.; et al. Differential Roles of Interleukin-17A and -17F in Host Defense against Mucoepithelial Bacterial Infection and Allergic Responses. Immunity 2009, 30, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solaymani-Mohammadi, S.; Berzofsky, J.A. Interleukin 21 collaborates with interferon-gamma for the optimal expression of interferon-stimulated genes and enhances protection against enteric microbial infection. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castaño-Rodríguez, N.; Kaakoush, N.O.; Lee, W.S.; Mitchell, H.M. Dual role of Helicobacter and Campylobacter species in IBD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut 2017, 66, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.W.; Ji, H.Z.; Yang, M.F.; Wu, L.; Wang, F.Y. Helicobacter pylori infection and inflammatory bowel disease in Asians: A meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 4750–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Li, P.; Min, L.; Zhang, S. Helicobacter pylori infection and inflammatory bowel disease: A crosstalk between upper and lower digestive tract. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokkas, T.; Gisbert, J.P.; Niv, Y.; O’Morain, C. The association between Helicobacter pylori infection and inflammatory bowel disease based on meta-analysis. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2015, 3, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ueno, A.; Jijon, H.; Chan, R.; Ford, K.; Hirota, C.; Kaplan, G.G.; Beck, P.L.; Iacucci, M.; Gasia, M.F.; Barkema, H.W.; et al. Increased Prevalence of Circulating Novel IL-17 Secreting Foxp3 Expressing CD4+ T Cells and Defective Suppressive Function of Circulating Foxp3+ Regulatory Cells Support Plasticity Between Th17 and Regulatory T Cells in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 2522–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Su, J.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, J.; Shi, R.; Zhang, H. Elevated levels of Th17 cells and Th17-related cytokines are associated with disease activity in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Res. 2014, 63, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, J.H.; Seo, J.W.; Cho, M.-S.; Ahn, J.-H.; Sung, H.Y. Role of Treg and TH17 Cells of the Gastric Mucosa in Children with Helicobacter pylori Gastritis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 58, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Dai, Y.; Liu, M.Y.; Wu, T.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, W. Helicobacter pylori Colonization Protects Against Chronic Experimental Colitis by Regulating Th17/Treg Balance. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 1481–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, B.R.E.A.; Radin, J.N.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Contreras, D.C.; Algood, H.M.S. IL-17a and IL-22 Induce Expression of Antimicrobials in Gastrointestinal Epithelial Cells and May Contribute to Epithelial Cell Defense against Helicobacter pylori. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, C.; Cho, J. Interleukin-23/Th17 pathways and inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2009, 15, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bank, S.; Andersen, P.S.; Burisch, J.; Pedersen, N.; Roug, S.; Galsgaard, J.; Turino, S.Y.; Brodersen, J.B.; Rashid, S.; Rasmussen, B.K.; et al. Polymorphisms in the Toll-Like Receptor and the IL-23/IL-17 Pathways Were Associated with Susceptibility to Inflammatory Bowel Disease in a Danish Cohort. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Tato, C.M.; Joyce-Shaikh, B.; Gulen, M.F.; Cayatte, C.; Chen, Y.; Blumenschein, W.M.; Judo, M.; Ayanoglu, G.; McClanahan, T.K.; et al. Interleukin-23-Independent IL-17 Production Regulates Intestinal Epithelial Permeability. Immunity 2015, 43, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stritesky, G.L.; Yeh, N.; Kaplan, M.H. IL-23 promotes maintenance but not commitment to the Th17 lineage 1. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 5948–5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahern, P.P.; Schiering, C.; Buonocore, S.; McGeachy, M.J.; Cua, D.J.; Maloy, K.J.; Powrie, F. Interleukin-23 Drives Intestinal Inflammation through Direct Activity on T Cells. Immunity 2010, 33, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monteleone, G.; Pallone, F.; Macdonald, T.T. Interleukin-21 (IL-21)-mediated pathways in T cell-mediated disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009, 20, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, K.; Yoshitomi, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Maeda, S.; Teradaira, S.; Sugimoto, N.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nomura, T.; Ito, H.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Preferential recruitment of CCR6-expressing Th17 cells to inflamed joints via CCL20 in rheumatoid arthritis and its animal model. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 2803–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, M. Immune Responses Mediated by Th17 Cells in Helicobacter pylori Infection. Integr. Med. Int. 2016, 3, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakura, Y.; Nakae, S.; Saijo, S.; Ishigame, H. The roles of IL-17A in inflammatory immune responses and host defense against pathogens. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 226, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Lopes, J.E.; Chong, M.M.W.; Ivanov, I.I.; Min, R.; Victora, G.D.; Shen, Y.; Du, J.; Rubtsov, Y.P.; Rudensky, A.Y.; et al. TGF-β-induced Foxp3 inhibits TH17 cell differentiation by antagonizing RORγt function. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 453, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeLyria, E.S.; Redline, R.W.; Blanchard, T.G. Vaccination of Mice Against H pylori Induces a Strong Th-17 Response and Immunity That Is Neutrophil Dependent. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagheri, N.; Shirzad, H.; Elahi, S.; Azadegan-Dehkordi, F.; Rahimian, G.; Shafigh, M.; Rashidii, R.; Sarafnejad, A.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Faridani, R.; et al. Downregulated regulatory T cell function is associated with increased peptic ulcer in Helicobacter pylori-infection. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 110, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebkova, L.; Pellicanò, A.; Monteleone, G.; Grazioli, B.; Guarnieri, G.; Imeneo, M.; Pallone, F.; Luzza, F. Extracellular Signal-Regulated Protein Kinase Mediates Interleukin 17 (IL-17)-Induced IL-8 Secretion in Helicobacter pylori-Infected Human Gastric Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 5019–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddique, I.; Al-Qabandi, A.; Al-Ali, J.; Alazmi, W.; Memon, A.; Mustafa, A.S.; Junaid, T.A. Association between Helicobacter pylori genotypes and severity of chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer disease and gastric mucosal interleukin-8 levels: Evidence from a study in the Middle East. Gut Pathog. 2014, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bagheri, N.; Razavi, A.; Pourgheysari, B.; Azadegan-Dehkordi, F.; Rahimian, G.; Pirayesh, A.; Shafigh, M.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Fereidani, R.; Tahmasbi, K.; et al. Up-regulated Th17 cell function is associated with increased peptic ulcer disease in Helicobacter pylori -infection. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 60, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andoh, A.; Takaya, H.; Makino, J.; Sato, H.; Bamba, S.; Araki, Y.; Hata, K.; Shimada, M.; Okuno, T.; Fujiyama, Y.; et al. Cooperation of interleukin-17 and interferon-gamma on chemokine secretion in human fetal intestinal epithelial cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2001, 125, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.E.; Khoi, P.N.; Xia, Y.; Park, J.S.; Joo, Y.E.; Kim, K.K.; Choi, S.Y.; Jung, Y.D. Helicobacter pylori and interleukin-8 in gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 8192–8202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butcher, L.D.; Hartog, G.D.; Ernst, P.B.; Crowe, S.E. Oxidative Stress Resulting From Helicobacter pylori Infection Contributes to Gastric Carcinogenesis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 3, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iwakura, Y.; Ishigame, H. The IL-23/IL-17 axis in inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Cong, X.; Gao, H.; Lan, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Song, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; et al. Tumor-associated neutrophils induce EMT by IL-17a to promote migration and invasion in gastric cancer cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezalotfi, A.; Ahmadian, E.; Aazami, H.; Solgi, G.; Ebrahimi, M. Gastric Cancer Stem Cells Effect on Th17/Treg Balance; A Bench to Beside Perspective. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Wu, X.; Bian, Z.; Gao, Q. Interleukin 17A promotes gastric cancer invasiveness via NF-kappaB mediated matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 expression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96678. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, K.W.; Letley, D.P.; Ingram, R.J.M.; Staples, E.; Skjoldmose, H.; Atherton, J.C.; Robinson, K. CCL20/CCR6-mediated migration of regulatory T cells to theHelicobacter pylori-infected human gastric mucosa. Gut 2014, 63, 1550–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vogelzang, A.; McGuire, H.M.; Yu, D.; Sprent, J.; Mackay, C.R.; King, C. A Fundamental Role for Interleukin-21 in the Generation of T Follicular Helper Cells. Immunity 2008, 29, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yasmin, S.; Dixon, B.R.E.A.; Olivares-Villagómez, D.; Algood, H.M.S. Interleukin-21 (IL-21) Downregulates Dendritic Cell Cytokine Responses to Helicobacter pylori and Modulates T Lymphocyte IL-17A Expression in Peyer’s Patches during Infection. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Algood, H.M.S.; Allen, S.S.; Washington, M.K.; Peek, R.M.; Miller, G.G.; Cover, T.L. Regulation of Gastric B Cell Recruitment Is Dependent on IL-17 Receptor A Signaling in a Model of Chronic Bacterial Infection. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 5837–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaffen, S.L.; Jain, R.; Garg, A.V.; Cua, D.J. The IL-23–IL-17 immune axis: From mechanisms to therapeutic testing. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinchuk, I.V.; Morris, K.T.; Nofchissey, R.A.; Earley, R.B.; Wu, J.-Y.; Ma, T.Y.; Beswick, E.J. Stromal Cells Induce Th17 during Helicobacter pylori Infection and in the Gastric Tumor Microenvironment. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Blanchard, T.G.; Ernst, P.B. Host Inflammatory Response to Infection. In Helicobacter Pylori: Physiology and Genetics; Mobley, H.L.T., Mendz, G.L., Hazell, S.L., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Negrini, R.; Lisato, L.; Zanella, I.; Cavazzini, L.; Gullini, S.; Villanacci, V.; Poiesi, C.; Albertini, A.; Ghielmi, S. Helicobacter pylori infection induces antibodies cross-reacting with human gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology 1991, 101, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhiani, A.A.; Schön, K.; Franzén, L.E.; Pappo, J.; Lycke, N. Helicobacter pylori-Specific Antibodies Impair the Development of Gastritis, Facilitate Bacterial Colonization, and Counteract Resistance against Infection. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 5024–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontarini, E.; Murray-Brown, W.J.; Croia, C.; Lucchesi, D.; Conway, J.; Rivellese, F.; Fossati-Jimack, L.; Astorri, E.; Prediletto, E.; Corsiero, E.; et al. Unique expansion of IL-21+ Tfh and Tph cells under control of ICOS identifies Sjögren’s syndrome with ectopic germinal centres and MALT lymphoma. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1588–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamri, W.; Walker, M.M.; Clark, P.; Atherton, J.C.; Thursz, M.R.; Bamford, K.B.; Lechler, R.I.; Lombardi, G. Helicobacter pylori Stimulates Dendritic Cells To Induce Interleukin-17 Expression from CD4+ T Lymphocytes. Infect. Immun. 2009, 78, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horvath, D.J.J.; Washington, M.K.; Cope, V.A.; Algood, H.M.S. IL-23 Contributes to Control of Chronic Helicobacter Pylori Infection and the Development of T Helper Responses in a Mouse Model1. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, M.L.; Kang, J.W.; Moon, Y.M.; Nam, H.J.; Jhun, J.Y.; Heo, S.B.; Jin, H.T.; Min, S.Y.; Ju, J.H.; Park, K.S.; et al. STAT3 and NF-kappaB signal pathway is required for IL-23-mediated IL-17 production in spontaneous arthritis animal model IL-1 receptor antagonist-deficient mice. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 5652–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Ivanov, I.I.; Spolski, R.; Min, R.; Shenderov, K.; Egawa, T.; Levy, D.E.; Leonard, W.J.; Littman, D.R. IL-6 programs T(H)-17 cell differentiation by promoting sequential engagement of the IL-21 and IL-23 pathways. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, N.; Okamoto, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Matsumura, N.; Yamaguchi, S.; Yamakido, M.; Taniyama, K.; Sasaki, N.; Schlemper, R.J. Helicobacter pyloriInfection and the Development of Gastric Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.; Kono, K.; Mizukami, Y.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Mimura, K.; Watanabe, M.; Izawa, S.; Fujii, H. Distribution of Th17 cells and FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, tumor-draining lymph nodes and peripheral blood lymphocytes in patients with gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 1947–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Tan, B.; Ai, J.; Zhang, Z.; Song, J.; Shan, B. Prevalence of Th17 and Treg cells in gastric cancer patients and its correlation with clinical parameters. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Rong, G.; Wei, H.; Zhang, M.; Bi, J.; Ma, L.; Xue, X.; Wei, G.; Liu, X.; Fang, G. The prevalence of Th17 cells in patients with gastric cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 374, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.M.; Zhang, T.S.; Lin, S.; Zhang, W.G.; Liu, J.; Cao, X.M.; Li, H.B.; Wang, M.; Liu, X.H.; Liu, K.; et al. Role of IL-17A rs2275913 and IL-17F rs763780 polymorphisms in risk of cancer development: An updated meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amedei, A.; Munari, F.; Della Bella, C.; Niccolai, E.; Benagiano, M.; Bencini, L.; Cianchi, F.; Farsi, M.; Emmi, G.; Zanotti, G.; et al. Helicobacter pylori secreted peptidyl prolyl cis, trans-isomerase drives Th17 inflammation in gastric adenocarcinoma. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2012, 9, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Zhang, J.; Guo, D.; Ma, J.; Shui, S.-F.; Han, X.-W. IL-21R functions as an oncogenic factor and is regulated by the lncRNA MALAT1/miR-125a-3p axis in gastric cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 54, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Błogowski, W.; Madej-Michniewicz, A.; Marczuk, N.; Dołęgowska, B.; Starzyńska, T. Interleukins 17 and 23 in patients with gastric neoplasms. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wan, Q.; Peng, H.; Zhu, W. Interleukin-23A is associated with tumor growth in Helicobacter-pylori-related human gastric cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2014, 14, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Yang, C.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Li, P.; Shi, Y.; Yu, P. Interleukin-23 promotes the migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via the STAT3 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 499, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mommersteeg, M.C.; Yu, J.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Fuhler, G.M. Genetic host factors in Helicobacter pylori -induced carcinogenesis: Emerging new paradigms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2018, 1869, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Qiu, L.-X.; Cheng, L.; Wang, M.-Y.; Li, J.; Sun, M.-H.; Yang, Y.-J.; Wang, J.-C.; Jin, L.; Wang, Y.-N.; et al. Associations of genotypes and haplotypes of IL-17 with risk of gastric cancer in an eastern Chinese population. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 82384–82395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elshazli, R.M.; Salman, D.O.; Kamel, M.M.; Toraih, E.A.; Fawzy, M.S. Genetic polymorphisms of IL-17A rs2275913, rs3748067 and IL-17F rs763780 in gastric cancer risk: Evidence from 8124 cases and 9873 controls. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2018, 45, 1421–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, B.; Fan, Y.; Wang, W.; Yao, G.; Zhai, J. IL-17A G197A and C1249T polymorphisms in gastric carcinogenesis. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 9977–9985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.-F.; Zhang, H.; Lv, J.; Wang, L.; Fan, Y.-Y. Associations of the IL-17A rs2275913 and IL-17F rs763780 polymorphisms with the risk of digestive system neoplasms: A meta-analysis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 67, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-Q.; Li, Y.; Terry, P.D.; Kou, W.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Hui, Z.-Z.; Ren, X.-H.; Wang, M.-X. Association between interleukin-21 gene rs907715 polymorphism and gastric precancerous lesions in a Chinese population. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2020, 12, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Pan, B.; Pan, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Sun, H.; Xu, T.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. Polymorphisms of IL-23R predict survival of gastric cancer patients in a Chinese population. Cytokine 2019, 117, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.; Kenefeck, R.; Pidgeon, E.L.; Shakib, S.; Patel, S.; Polson, R.J.; Zaitoun, A.M.; Atherton, J.C. Helicobacter pylori-induced peptic ulcer disease is associated with inadequate regulatory T cell responses. Gut 2008, 57, 1375–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, R.; Brenner, L.; Bauer, S.; Schwendy, S.; Layland, L.; da Costa, C.P.; Reindl, W.; Dossumbekova, A.; Friedrich, M.; Saur, D.; et al. CD25+/Foxp3+ T Cells Regulate Gastric Inflammation and Helicobacter pylori Colonization In Vivo. Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, H.; Hirata, I.; Okubo, M.; Arima, Y.; Kamiya, Y.; Fujita, H.; Yoshioka, D.; Nakamura, M.; Nagasaka, M.; Shibata, T.; et al. Genetic polymorphisms of molecules associated with inflammation and immune response in Japanese subjects with functional dyspepsia. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 20, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meliț, L.E.; Mărginean, C.O.; Mărginean, C.D.; Mărginean, M.O. The Relationship between Toll-like Receptors and Helicobacter pylori-Related Gastropathies: Still a Controversial Topic. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 8197048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fauny, M.; Moulin, D.; D’Amico, F.; Netter, P.; Petitpain, N.; Arnone, D.; Jouzeau, J.-Y.; Loeuille, D.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Paradoxical gastrointestinal effects of interleukin-17 blockers. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allocca, M.; Furfaro, F.; Fiorino, G.; Gilardi, D.; D’Alessio, S.; Danese, S. Can IL-23 be a good target for ulcerative colitis? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2018, 32–33, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bockerstett, K.A.; Osaki, L.H.; Petersen, C.P.; Cai, C.W.; Wong, C.F.; Nguyen, T.-L.M.; Ford, E.L.; Hoft, D.F.; Mills, J.C.; Goldenring, J.R.; et al. Interleukin-17A Promotes Parietal Cell Atrophy by Inducing Apoptosis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 5, 678–690.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Cytokine | Cell Producers | Played Roles | Mechanism of Action | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-17A, IL-17F | Th17 | Mucosal protection | Increases bacterial elimination | [53,54] |
| Induces claudin, mucin production | [14,63] | |||
| Gastric inflammation | Recruitment of neutrophils | [74,82,83] | ||
| Synergize with IFNγ & IL-8 | [8,76,79] | |||
| Progression of ulcer | Increases mucosal damages | [71] | ||
| Progression of gastric cancer | Expression of angiogenic factors | [84] | ||
| Promotes cancer cells’ growth | [85] | |||
| Exacerbation of colitis | Increases chemokine | [36,70] | ||
| Recruitment of neutrophil | [32,51] | |||
| IL-21 | Th17, Th1, Tfh, NK, | Promotion to inflammation | Maintains Th17 and Th1 proliferation | [42] |
| Induces CCL20 | [70,86] | |||
| Induction of H. pylori-specific antibodies | Autocrine loop of Tfh cell | [87] | ||
| Drives B cell to produce antibodies | [88,89] | |||
| ECM degradation | Induces MMPs | [11] | ||
| IL-23 | Macrophage, DCs, neutrophil | Promotion to inflammation | Maintains Th17 and Th1 proliferation | [66,67,90] |
| Recruitment of neutrophils | [14,82] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dewayani, A.; Fauzia, K.A.; Alfaray, R.I.; Waskito, L.A.; Doohan, D.; Rezkitha, Y.A.A.; Abdurachman, A.; Kobayashi, T.; I’tishom, R.; Yamaoka, Y.; et al. The Roles of IL-17, IL-21, and IL-23 in the Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gastrointestinal Inflammation: A Review. Toxins 2021, 13, 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13050315
Dewayani A, Fauzia KA, Alfaray RI, Waskito LA, Doohan D, Rezkitha YAA, Abdurachman A, Kobayashi T, I’tishom R, Yamaoka Y, et al. The Roles of IL-17, IL-21, and IL-23 in the Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gastrointestinal Inflammation: A Review. Toxins. 2021; 13(5):315. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13050315
Chicago/Turabian StyleDewayani, Astri, Kartika Afrida Fauzia, Ricky Indra Alfaray, Langgeng Agung Waskito, Dalla Doohan, Yudith Annisa Ayu Rezkitha, Abdurachman Abdurachman, Takashi Kobayashi, Reny I’tishom, Yoshio Yamaoka, and et al. 2021. "The Roles of IL-17, IL-21, and IL-23 in the Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gastrointestinal Inflammation: A Review" Toxins 13, no. 5: 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13050315
APA StyleDewayani, A., Fauzia, K. A., Alfaray, R. I., Waskito, L. A., Doohan, D., Rezkitha, Y. A. A., Abdurachman, A., Kobayashi, T., I’tishom, R., Yamaoka, Y., & Miftahussurur, M. (2021). The Roles of IL-17, IL-21, and IL-23 in the Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gastrointestinal Inflammation: A Review. Toxins, 13(5), 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13050315








