Asynchrony of Gambierdiscus spp. Abundance and Toxicity in the U.S. Virgin Islands: Implications for Monitoring and Management of Ciguatera
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
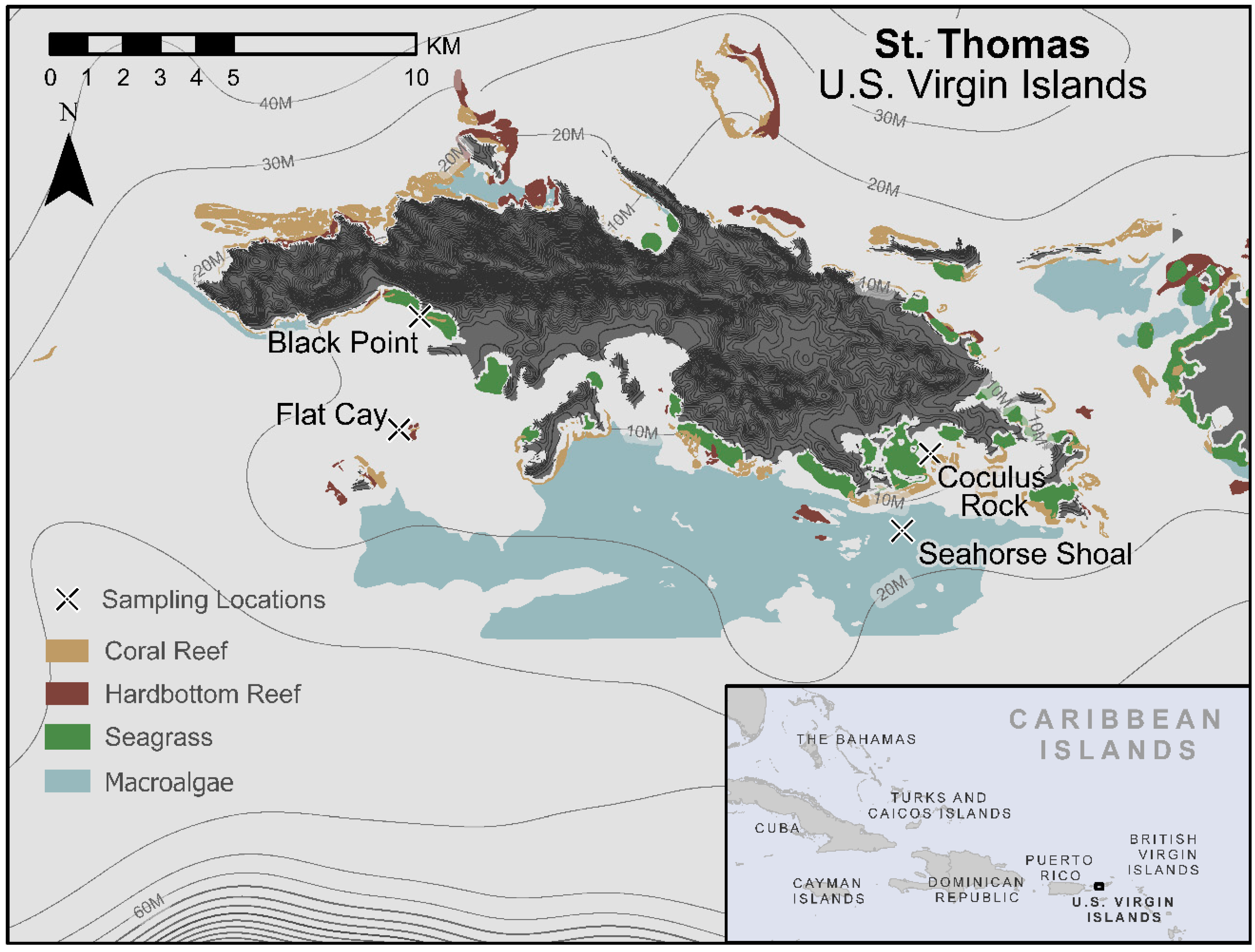
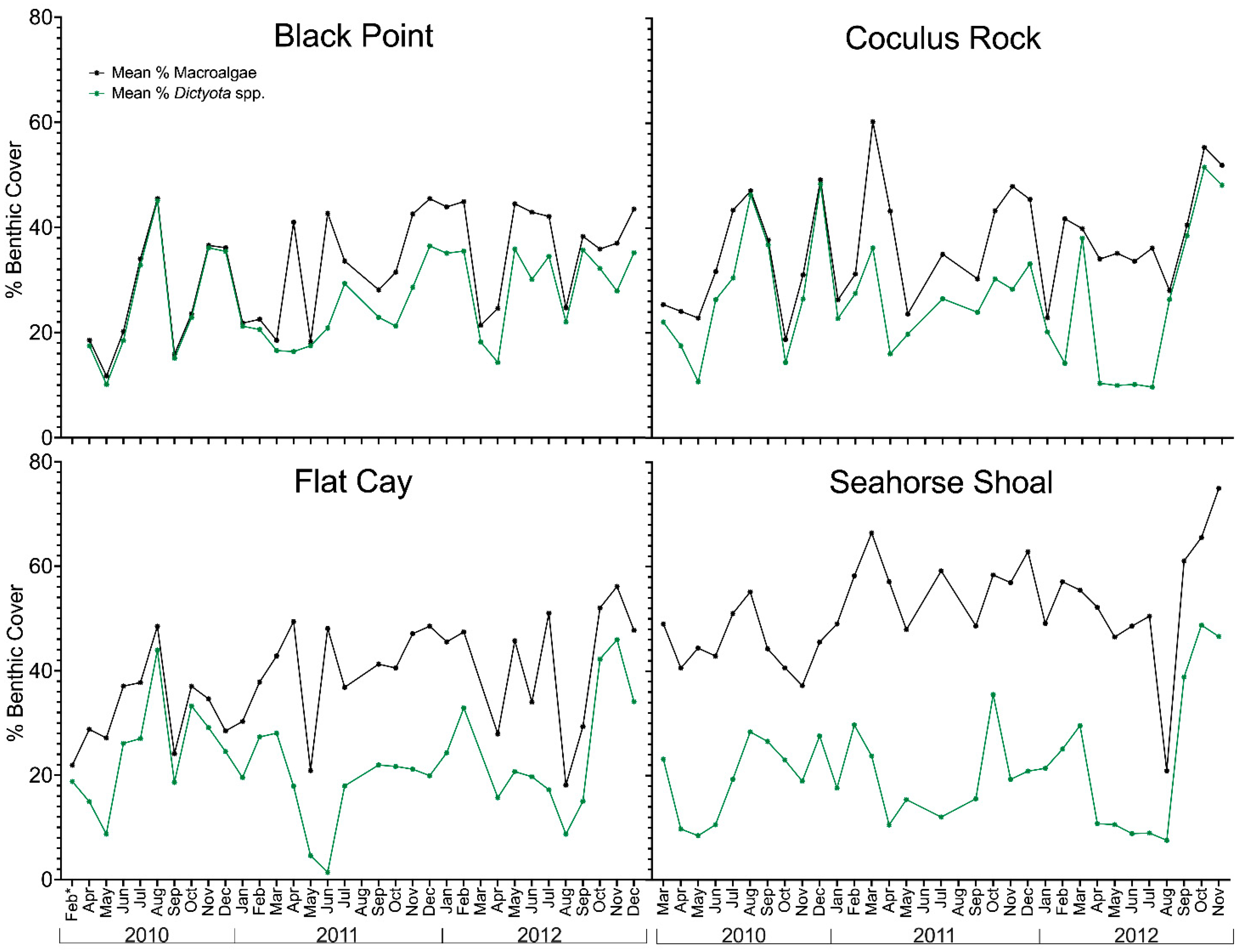
2.1. Variation in Environmental Conditions and Benthic Composition
2.2. Gambierdiscus spp. Abundance
2.3. Detection of Ciguatoxins in Field Samples
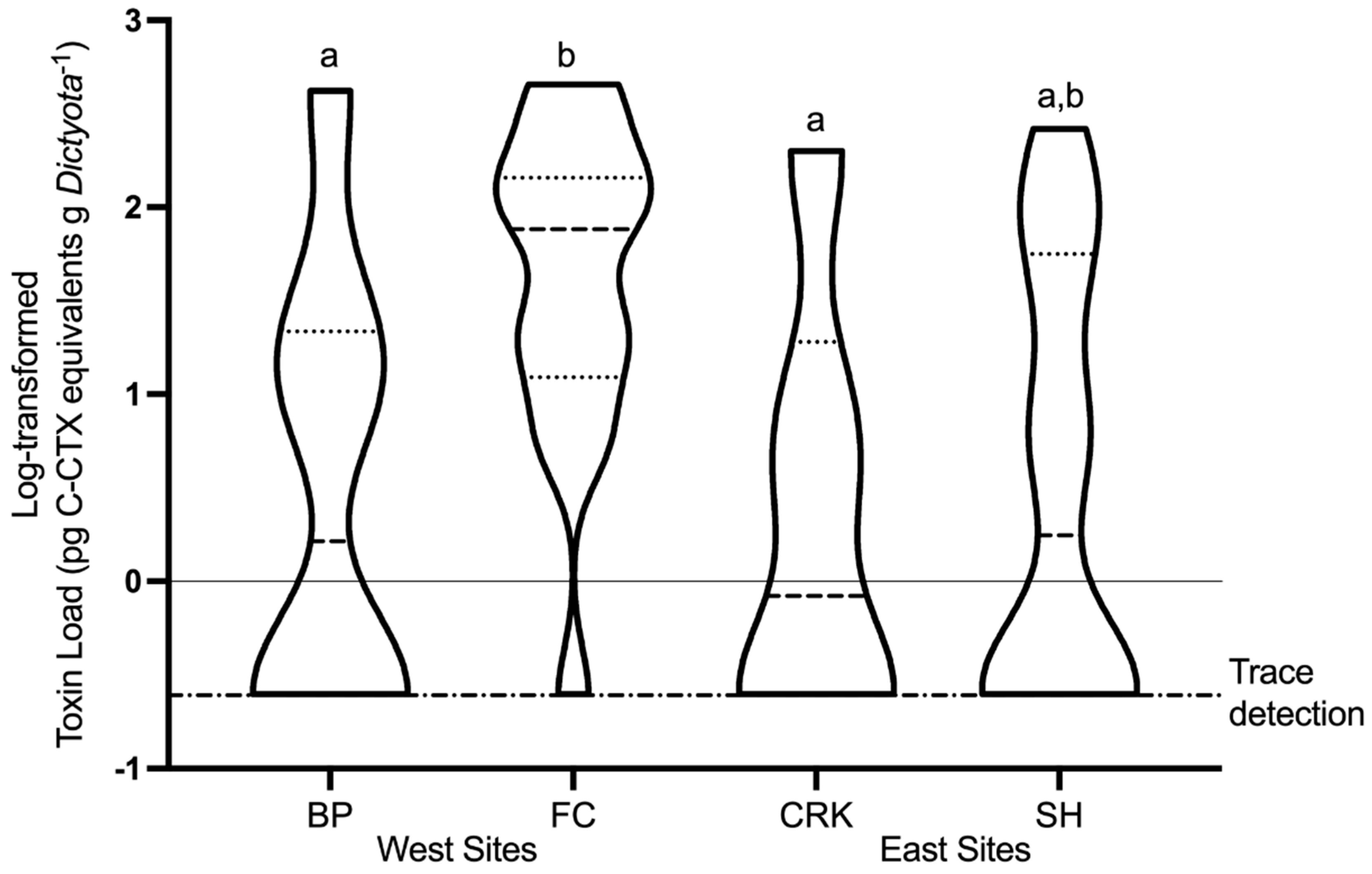
2.4. Spatial and Temporal Variability of In Situ Ciguatoxin Levels
3. Discussion
3.1. Relative Toxicity of In Situ Gambierdiscus
3.2. Cellular CTX Quota and Not Gambierdiscus Abundance Determines CTX Production
3.3. Nearshore vs. Offshore Sites
3.4. Seasonality of CTX Production
3.5. Implications for Assessing CTX Exposure Risk
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Site Descriptions
4.2. Environmental Sampling
4.2.1. Oceanographic Measurements
4.2.2. Benthic Temperatures
4.2.3. Precipitation
4.2.4. Nutrient Analyses
4.2.5. Benthic Community Composition
4.3. Biological Sampling
4.3.1. Collection of Gambierdiscus Epiphytes
4.3.2. Gambierdiscus Cell Enumeration
4.4. Toxin Extraction and Analyses
4.4.1. Cell Pellet Extraction
4.4.2. Quantitation of CTX by In Vitro N2a Cytotoxicity Assay
4.4.3. Sample Screening and Dose Determination
4.4.4. Tests of Matrix Effects and Sample Purification
4.5. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedman, M.A.; Fernandez, M.; Backer, L.C.; Dickey, R.W.; Bernstein, J.; Schrank, K.; Kibler, S.; Stephan, W.; Gribble, M.O.; Bienfang, P. An updated review of ciguatera fish poisoning: Clinical, epidemiological, environmental, and public health management. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, M.L.; Aligizaki, K.; Bottein, M.Y.D.; Fraga, S.; Morton, S.L.; Penna, A.; Rhodes, L. Gambierdiscus and Ostreopsis: Reassessment of the state of knowledge of their taxonomy, geography, ecophysiology, and toxicology. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 107–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Rivera, E.; Villareal, T.A. Macroalgal palatability and the flux of ciguatera toxins through marine food webs. Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 497–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, S.T.; Kohler, C.C. Dead bleached coral provides new surfaces for dinoflagellates implicated in ciguatera fish poisonings. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1992, 35, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, A.; Fukui, M.; Cruchet, P.; Yasumoto, T. Progress on chemical knowledge of ciguatoxins. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 1992, 85, 467–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pottier, I.; Vernoux, J.-P.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J. Characterisation of multiple Caribbean ciguatoxins and congeners in individual specimens of horse-eye jack (Caranx latus) by high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Toxicon 2002, 40, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinain, M.; Darius, H.T.; Ung, A.; Cruchet, P.; Wang, Z.H.; Ponton, D.; Laurent, D.; Pauillac, S. Growth and toxin production in the ciguatera-causing dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus polynesiensis (Dinophyceae) in culture. Toxicon 2010, 56, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinain, M.; Gatti, C.; Darius, H.; Quod, J.-P.; Tester, P. Ciguatera poisonings: A global review of occurrences and trends. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, F.; Fraga, S.; Ramilo, I.; Rial, P.; Figueroa, R.I.; Riobó, P.; Bravo, I. Canary Islands (NE Atlantic) as a biodiversity ‘hotspot’of Gambierdiscus: Implications for future trends of ciguatera in the area. Harmful Algae 2017, 67, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.L.; Smith, K.F.; Murray, J.S.; Nishimura, T.; Finch, S.C. Ciguatera fish poisoning: The risk from an Aotearoa/New Zealand perspective. Toxins 2020, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, T.; Sato, S.; Tawong, W.; Sakanari, H.; Uehara, K.; Shah, M.M.R.; Suda, S.; Yasumoto, T.; Taira, Y.; Yamaguchi, H. Genetic diversity and distribution of the ciguatera-causing dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus spp. (Dinophyceae) in coastal areas of Japan. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tester, P.A.; Vandersea, M.W.; Buckel, C.A.; Kibler, S.R.; Holland, W.C.; Davenport, E.D.; Clark, R.D.; Edwards, K.F.; Taylor, J.C.; Vander Pluym, J.L. Gambierdiscus (Dinophyceae) species diversity in the Flower Garden Banks National Marine Sanctuary, Northern Gulf of Mexico, USA. Harmful Algae 2013, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, L.E.; Baden, D.G.; Bean, J.A.; Weisman, R.; Blythe, D.G. Seafood toxin diseases: Issues in epidemiology & community outreach. In Proceedings of the VIII International Conference on Harmful Algae, Vigo, Spain, 25–29 June 1997; Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernández, M., Wyatt, T., Eds.; Xunta de Galicia and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Galicia, Spain, 1998; pp. 245–248. [Google Scholar]
- Ting, J.; Brown, A. Ciguatera poisoning: A global issue with common management problems. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 2001, 8, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litaker, R.W.; Vandersea, M.W.; Faust, M.A.; Kibler, S.R.; Nau, A.W.; Holland, W.C.; Chinain, M.; Holmes, M.J.; Tester, P.A. Global distribution of ciguatera causing dinoflagellates in the genus Gambierdiscus. Toxicon 2010, 56, 711–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinain, M.; Faust, M.A.; Pauillac, S. Morphology and molecular analyses of three toxic species of Gambierdiscus (Dinophyceae): G. pacificus, sp. nov., G. australes, sp. nov., and G. polynesiensis, sp. nov. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 1282–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litaker, R.W.; Holland, W.C.; Hardison, D.R.; Pisapia, F.; Hess, P.; Kibler, S.R.; Tester, P.A. Ciguatoxicity of Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa species from the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, L.; Harwood, T.; Smith, K.; Argyle, P.; Munday, R. Production of ciguatoxin and maitotoxin by strains of Gambierdiscus australes, G. pacificus and G. polynesiensis (Dinophyceae) isolated from Rarotonga, Cook Islands. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisapia, F.; Holland, W.C.; Hardison, D.R.; Litaker, R.W.; Fraga, S.; Nishimura, T.; Adachi, M.; Nguyen-Ngoc, L.; Séchet, V.; Amzil, Z. Toxicity screening of 13 Gambierdiscus strains using neuro-2a and erythrocyte lysis bioassays. Harmful Algae 2017, 63, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Richlen, M.L.; Liefer, J.D.; Robertson, A.; Kulis, D.; Smith, T.B.; Parsons, M.L.; Anderson, D.M. Influence of Environmental Variables on Gambierdiscus spp. (Dinophyceae) Growth and Distribution. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibler, S.R.; Litaker, R.W.; Holland, W.C.; Vandersea, M.W.; Tester, P.A. Growth of eight Gambierdiscus (Dinophyceae) species: Effects of temperature, salinity and irradiance. Harmful Algae 2012, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosteson, T. Caribbean ciguatera: A changing paradigm. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2004, 52, 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Chinain, M.; Germain, M.; Deparis, X.; Pauillac, S.; Legrand, A.M. Seasonal abundance and toxicity of the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus spp. (Dinophyceae), the causative agent of ciguatera in Tahiti, French Polynesia. Mar. Biol. 1999, 135, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chateau-Degat, M.-L.; Chinain, M.; Cerf, N.; Gingras, S.; Hubert, B.; Dewailly, E. Seawater temperature, Gambierdiscus spp. variability and incidence of ciguatera poisoning in French Polynesia. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinain, M.; Darius, H.T.; Ung, A.; Fouc, M.T.; Revel, T.; Cruchet, P.; Pauillac, S.; Laurent, D. Ciguatera risk management in French Polynesia: The case study of Raivavae Island (Australes Archipelago). Toxicon 2010, 56, 674–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Asencio, L.; Clausing, R.J.; Vandersea, M.; Chamero-Lago, D.; Gómez-Batista, M.; Hernández-Albernas, J.I.; Chomérat, N.; Rojas-Abrahantes, G.; Litaker, R.W.; Tester, P. Ciguatoxin occurrence in food-web components of a Cuban coral reef ecosystem: Risk-assessment implications. Toxins 2019, 11, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeffler, C.R.; Robertson, A.; Flores Quintana, H.A.; Silander, M.C.; Smith, T.B.; Olsen, D. Ciguatoxin prevalence in 4 commercial fish species along an oceanic exposure gradient in the US Virgin Islands. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 1852–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, J.E. A review of ciguatera, tropical fish poisoning, with a tentative explanation of its cause. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1958, 8, 236–267. [Google Scholar]
- Longo, S.; Sibat, M.; Viallon, J.; Darius, H.T.; Hess, P.; Chinain, M. Intraspecific variability in the toxin production and toxin profiles of in vitro cultures of Gambierdiscus polynesiensis (Dinophyceae) from French Polynesia. Toxins 2019, 11, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudó, À.; Toldrà, A.; Rey, M.; Todolí, I.; Andree, K.B.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Campàs, M.; Sureda, F.X.; Diogène, J. Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa as potential indicators of ciguatera risk in the Balearic Islands. Harmful Algae 2020, 99, 101913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, A.; Richlen, M.L.; Erdner, D.; Smith, T.B.; Anderson, D.M.; Liefer, J.D.; Xu, Y.; McCarron, P.; Miles, C.O.; Parsons, M.L. Toxicity, chemistry, and implications of Gamberdiscus silvae: A ciguatoxin superbug in the Greater Caribbean Region. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference for Harmful Algae, Nantes, France, 21–26 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rossignoli, A.E.; Tudó, A.; Bravo, I.; Díaz, P.A.; Diogène, J.; Riobó, P. Toxicity characterisation of Gambierdiscus species from the Canary Islands. Toxins 2020, 12, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, E.G.; Grattan, L.M.; Cook, R.L.; Smith, T.B.; Anderson, D.M.; Morris, J.G., Jr. Ciguatera incidence in the US Virgin Islands has not increased over a 30-year time period despite rising seawater temperatures. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hygeine 2013, 88, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Richlen, M.L.; Sehein, T.R.; Chinain, M.; Adachi, M.; Nishimura, T.; Xu, Y.; Parsons, M.L.; Smith, T.B.; Zheng, T. LSU rDNA based RFLP assays for the routine identification of Gambierdiscus species. Harmful Algae 2017, 66, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NOAA. Environmental Sensitivity Index (ESI) and Geographical Information System (GIS) Mapping. Virgin Islands: U.S. and British Virgin Islands. 2000. Available online: https://response.restoration.noaa.gov/oil-and-chemical-spills/oil-spills/download-esi-maps-and-gis-data#VirginIslands (accessed on 19 March 2021).
- Kendall, M. Benthic Habitat Mapping in Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands for a Baseline Inventory. Benthic Habitat Map of St. Thomas and St. John, USVI in GIS Format. 2000. Available online: https://coastalscience.noaa.gov/project/benthic-habitat-mapping-puerto-rico-virgin-islands/ (accessed on 19 March 2021).
- Yogi, K.; Oshiro, N.; Inafuku, Y.; Hirama, M.; Yasumoto, T. Detailed LC-MS/MS Analysis of Ciguatoxins Revealing Distinct Regional and Species Characteristics in Fish and Causative Alga from the Pacific. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8886–8891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryuchkov, F.; Robertson, A.; Miles, C.O.; Mudge, E.M.; Uhlig, S. LC–HRMS and Chemical Derivatization Strategies for the Structure Elucidation of Caribbean Ciguatoxins: Identification of C-CTX-3 and -4. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottier, I.; Hamilton, B.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J.; Vernoux, J.P. Identification of slow and fast-acting toxins in a highly ciguatoxic barracuda (Sphyraena barracuda) by HPLC/MS and radiolabelled ligand binding. Toxicon 2003, 42, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caillaud, A.; De la Iglesia, P.; Darius, H.T.; Pauillac, S.; Aligizaki, K.; Fraga, S.; Chinain, M.; Diogène, J. Update on methodologies available for ciguatoxin determination: Perspectives to confront the onset of ciguatera fish poisoning in Europe. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1838–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lartigue, J.; Jester, E.L.E.; Dickey, R.W.; Villareal, T.A. Nitrogen source effects on the growth and toxicity of two strains of the ciguatera-causing dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. Scientific Opinion on marine biotoxins in shellfish–Emerging toxins: Ciguatoxin group. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, N.W. Ciguatera research in the northwestern Hawaiian Islands: Laboratory and field studies on ciguatoxigenic dinoflagellates in the Hawaiian Archipelago. In Proceedings of the Second Symposium on Resource Investigations in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–27 May 1983; pp. 144–156. [Google Scholar]
- Chinain, M.; Ung, A.; Cruchet, P.; Revel, T.; Viallon, J.; Sibat, M.; Varney, P.; Laurent, V.; Hess, P.; Darius, H.T. Evidence for the Range Expansion of Ciguatera in French Polynesia: A Revisit of the 2009 Mass-Poisoning Outbreak in Rapa Island (Australes Archipelago). Toxins 2020, 12, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnis, R.; Chanteau, S.; Chungue, E.; Hurtel, J.; Yasumoto, T.; Inoue, A. Origins of ciguatera fish poisoning: A new dinoflagellate, Gambierdiscus toxicus Adachi and Fukuyo, definitively involved as a causal agent. Toxicon 1980, 18, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnis, R.; Legrand, A.-M.; Inoue, A. Follow-up of a bloom of the toxic dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus on a fringing reef of Tahiti. In Toxic Marine Phytoplankton; Graneli, E., Sundstrom, B., Edler, L., Anderson, D.M., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto, T.; Nakajima, I.; Oshima, Y.; Bagnis, R. A new toxic dinoflagellate [Algae, Gambier Islands] found in association with ciguatera [Ciguatoxin, maitotoxin, French Polynesia]. In Toxic Dinoflagellate Blooms; Taylor, L., Seliger, H.H., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, M.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Sellin, M.; Street, R. The origin of ciguatera in Platypus Bay, Australia. Mem. Qld. Mus. 1994, 34, 505–512. [Google Scholar]
- Darius, H.; Ponton, D.; Revel, T.; Cruchet, P.; Ung, A.; Fouc, M.T.; Chinain, M. Ciguatera risk assessment in two toxic sites of French Polynesia using the receptor-binding assay. Toxicon 2007, 50, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowiez, R.; Darius, H.T.; Cruchet, P.; Rossi, F.; Caillaud, A.; Laurent, D.; Chinain, M. Evaluation of seafood toxicity in the Australes archipelago (French Polynesia) using the neuroblastoma cell-based assay. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. 2013, 30, 567–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, J.P.; Hoffman, P.A.; Granade, H. Gambierdiscus toxicus from the Caribbean: A source of toxins involved in ciguatera. Mar. Fish. Rev. 1986, 48, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Durand-Clement, M. Study of production and toxicity of cultured Gambierdiscus toxicus. Biol. Bull. 1987, 172, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomber, J.W.; Guillard, R.R.; Nelson, W.G. Roles of temperature, salinity, and light in seasonality, growth, and toxicity of ciguatera-causing Gambierdiscus toxicus Adachi et Fukuyo (Dinophyceae). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1988, 115, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, S.; Rodriguez, F.; Caillaud, A.; Diogene, J.; Raho, N.; Zapata, M. Gambierdiscus excentricus sp. nov. (Dinophyceae), a benthic toxic dinoflagellate from the Canary Islands (NE Atlantic Ocean). Harmful Algae 2011, 11, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeffler, C.R.; Richlen, M.L.; Brandt, M.E.; Smith, T.B. Effects of grazing, nutrients, and depth on the ciguatera-causing dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus in the US Virgin Islands. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 531, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richlen, M.L.; Lobel, P.S. Effects of depth, habitat, and water motion on the abundance and distribution of ciguatera dinoflagellates at Johnston Atoll, Pacific Ocean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 421, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, S.; Bomber, J.; Tindall, D.; Aikman, K. Response of Gambierdiscus toxicus to light: Cell physiology and toxicity. In Toxic Phytoplankton Blooms in the Sea; Smayda, T., Shimizu, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 541–546. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, M.L.; Settlemier, C.J.; Ballauer, J.M. An examination of the epiphytic nature of Gambierdiscus toxicus, a dinoflagellate involved in ciguatera fish poisoning. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rains, L.K.; Parsons, M.L. Gambierdiscus species exhibit different epiphytic behaviors toward a variety of macroalgal hosts. Harmful Algae 2015, 49, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapa, N.I.; Yong, H.L.; Lee, L.K.; Lim, Z.F.; Lim, H.C.; Teng, S.T.; Luo, Z.; Gu, H.; Leaw, C.P.; Lim, P.T. Growth and epiphytic behavior of three Gambierdiscus species (Dinophyceae) associated with various macroalgal substrates. Harmful Algae 2019, 89, 101671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, M.L.; Settlemier, C.J.; Bienfang, P.K. A simple model capable of simulating the population dynamics of Gambierdiscus, the benthic dinoflagellate responsible for ciguatera fish poisoning. Harmful Algae 2010, 10, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, P.A.; Feldman, R.L.; Nau, A.W.; Kibler, S.R.; Litaker, R.W. Ciguatera fish poisoning and sea surface temperatures in the Caribbean Sea and the West Indies. Toxicon 2010, 56, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibler, S.R.; Davenport, E.D.; Tester, P.A.; Hardison, D.R.; Holland, W.C.; Litaker, R.W. Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa species in the greater Caribbean: Regional growth projections for ciguatera-associated dinoflagellates. Ecol. Model. 2017, 360, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitz, K.J.; Richlen, M.L.; Fachon, E.; Smith, T.B.; Parsons, M.L.; Anderson, D.M. Development of fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) probes to detect and enumerate Gambierdiscus species. Harmful Algae 2021, 101, 101914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandersea, M.W.; Kibler, S.R.; Holland, W.C.; Tester, P.A.; Schultz, T.F.; Faust, M.A.; Holmes, M.J.; Chinain, M.; Wayne Litaker, R. Development of semi-quantitative pcr assays for the detection and enumeration of Gambierdiscus species (gonyaulacales, dinophyceae) 1. J. Phycol. 2012, 48, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, P.A.; Litaker, R.W.; Berdalet, E. Climate change and harmful benthic microalgae. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and World Health Organization. Report of the Expert Meeting on Ciguatera Poisoning. In Food Safety and Quality Series; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2020; Volume 9, p. 133. [Google Scholar]
- Ennis, R.; Kadison, E.; Heidmann, S.; Brandt, M.; Henderson, L.; Smith, T. The United States Virgin Islands Territorial Coral Reef Monitoring Program: 2019 Annual Report; University of the Virgin Islands: St Thomas, VI, USA, 2019; p. 295. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, T.B.; Gyory, J.; Brandt, M.E.; Miller, W.J.; Jossart, J.; Nemeth, R.S. Caribbean mesophotic coral ecosystems are unlikely climate change refugia. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 2756–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.; Kadison, E.; Ennis, R.; Gyory, J.; Brandt, M.; Wright, V.; Nemeth, R.; Henderson, L. The United States Virgin Islands Territorial Coral Reef Monitoring Program; University of the Virgin Islands: St Thomas, VI, USA, 2014; p. 273. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, T.; Brandt, M.; Calnan, J.; Nemeth, R.; Blondeau, J.; Kadison, E.; Taylor, M.; Rothenberger, P. Convergent mortality responses of Caribbean coral species to seawater warming. Ecosphere 2013, 4, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, K.E.; Gill, S.M. Coral Point Count with Excel extensions (CPCe): A Visual Basic program for the determination of coral and substrate coverage using random point count methodology. Comput. Geosci. 2006, 32, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, M.A.; Gulledge, R.A. Identifying harmful marine dinoflagellates. In Contributions from the United States National Herbarium; National Museum of Natural History: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; Volume 42, pp. 1–144. [Google Scholar]
- Manger, R.L.; Leja, L.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Hungerford, J.M.; Hokama, Y.; Dickey, R.W.; Granade, H.R.; Lewis, R.; Yasumoto, T.; Wekell, M.M. Detection of sodium-channel toxins—Directed cytotoxicity assays of purified ciguatoxins, brevetoxins, saxitoxins, and seafood extracts. J. AOAC Int. 1995, 78, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, A.; Garcia, A.C.; Quintana, H.A.F.; Smith, T.B.; Castillo, B.F.; Reale-Munroe, K.; Gulli, J.A.; Olsen, D.A.; Hooe-Rollman, J.I.; Jester, E.L. Invasive lionfish (Pterois volitans): A potential human health threat for ciguatera fish poisoning in tropical waters. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinain, M.; Gatti, C.M.; Roué, M.; Darius, H.T.; Subba Rao, D. Ciguatera-causing dinoflagellates in the genera Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa: Distribution, ecophysiology and toxicology. In Dinoflagellates: Morphology, Life History and Ecological Significance; Subba Rao, D., Ed.; Nova Science: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 405–457. [Google Scholar]
- Peres-Neto, P.R.; Jackson, D.A.; Somers, K.M. Giving meaningful interpretation to ordination axes: Assessing loading significance in Principal Component Analysis. Ecology 2003, 84, 2347–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Field Site | Black Point | Flat Cay | Coculus Rock | Seahorse Shoal | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Samples Collected | 30 | 32 | 31 | 32 | 125 |
| No. Positive Samples | 8 | 15 | 7 | 16 | 46 |
| No. Quantifiable Samples | 4 | 14 | 3 | 9 | 30 |
| % Total Positive Samples | 17.4 | 32.6 | 15.2 | 34.8 | % of total |
| % Total Quantifiable Samples | 13.3 | 46.7 | 10 | 30 | % of total |
| Mean Cell Toxin Quota (pg C-CTX-1 eq. cell−1) | 0.3 ± 1.5 | 0.7 ± 1.4 | 0.4 ± 2.3 | 0.5 ± 1.3 | 0.5 ± 1.63 |
| Cell Toxin Quota Range (pg C-CTX-1 eq. cell−1) | 0–8.3 | 0–6.4 | 0–12.6 | 0–5.4 | 0–12.6 |
| Mean Toxin Load (pg C-CTX-1 eq. g Dictyota−1) | 15.1 ± 75.2 | 59.4 ± 121.3 | 6.8 ± 35.8 | 20.5 ± 55.5 | 25.5 ± 72.0 |
| Toxin Load Range (pg C-CTX-1 eq. g Dictyota−1) | 0–419.4 | 0–453.8 | 0–199.5 | 0–262.2 | 0–453.8 |
| Location | Cell Toxin Quota (pg CTX eq. Cell−1) | Method | N | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Mean | ||||
| Northwest Hawaiian Is., Hawaii | - | 24 | 1 MBA | 1 | [43] |
| Papara, Tahiti, French Polynesia | 0.09–3.60 | 0.25 ± 0.18 | 1 MBA | 34 | [23] |
| Rapa Island, French Polynesia | 0.5–13.5 | - | 2 RBA | 4 | [44] |
| Gambier Islands, French Polynesia | 0.03–1.00 | 0.15 ± 0.26 | 1 MBA | 6 | [45] |
| Hitiaa Reef, Tahiti, French Polynesia | 0.05–1.35 | 0.16 ± 0.20 | 1 MBA | 10 | [46] |
| Gambier Islands, French Polynesia | 0.96–1.42 | 1.15 ± 0.32 | 1 MBA | 2 | [47] |
| Platypus Bay, Australia | - | 0.23 | 1 MBA | 1 | [48] |
| Nuku Hiva, French Polynesia | 0.85–3.90 | 2.38 ± 2.15 | 2 RBA | [49] | |
| Rapa, French Polynesia | - | 0.03 ± 0.004 | 3 N2a | 1 | [50] |
| ^ St. Thomas, US Virgin Islands | 1.14–5.14 | 1.54 ± 0.94 | 1 MBA | 3 | [51] |
| ^ St. Thomas, US Virgin Islands | 0.00–12.62 | 0.56 ± 1.75 | 3 N2a | 125 | This Study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liefer, J.D.; Richlen, M.L.; Smith, T.B.; DeBose, J.L.; Xu, Y.; Anderson, D.M.; Robertson, A. Asynchrony of Gambierdiscus spp. Abundance and Toxicity in the U.S. Virgin Islands: Implications for Monitoring and Management of Ciguatera. Toxins 2021, 13, 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13060413
Liefer JD, Richlen ML, Smith TB, DeBose JL, Xu Y, Anderson DM, Robertson A. Asynchrony of Gambierdiscus spp. Abundance and Toxicity in the U.S. Virgin Islands: Implications for Monitoring and Management of Ciguatera. Toxins. 2021; 13(6):413. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13060413
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiefer, Justin D., Mindy L. Richlen, Tyler B. Smith, Jennifer L. DeBose, Yixiao Xu, Donald M. Anderson, and Alison Robertson. 2021. "Asynchrony of Gambierdiscus spp. Abundance and Toxicity in the U.S. Virgin Islands: Implications for Monitoring and Management of Ciguatera" Toxins 13, no. 6: 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13060413
APA StyleLiefer, J. D., Richlen, M. L., Smith, T. B., DeBose, J. L., Xu, Y., Anderson, D. M., & Robertson, A. (2021). Asynchrony of Gambierdiscus spp. Abundance and Toxicity in the U.S. Virgin Islands: Implications for Monitoring and Management of Ciguatera. Toxins, 13(6), 413. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13060413






