The Dragon’s Paralysing Spell: Evidence of Sodium and Calcium Ion Channel Binding Neurotoxins in Helodermatid and Varanid Lizard Venoms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
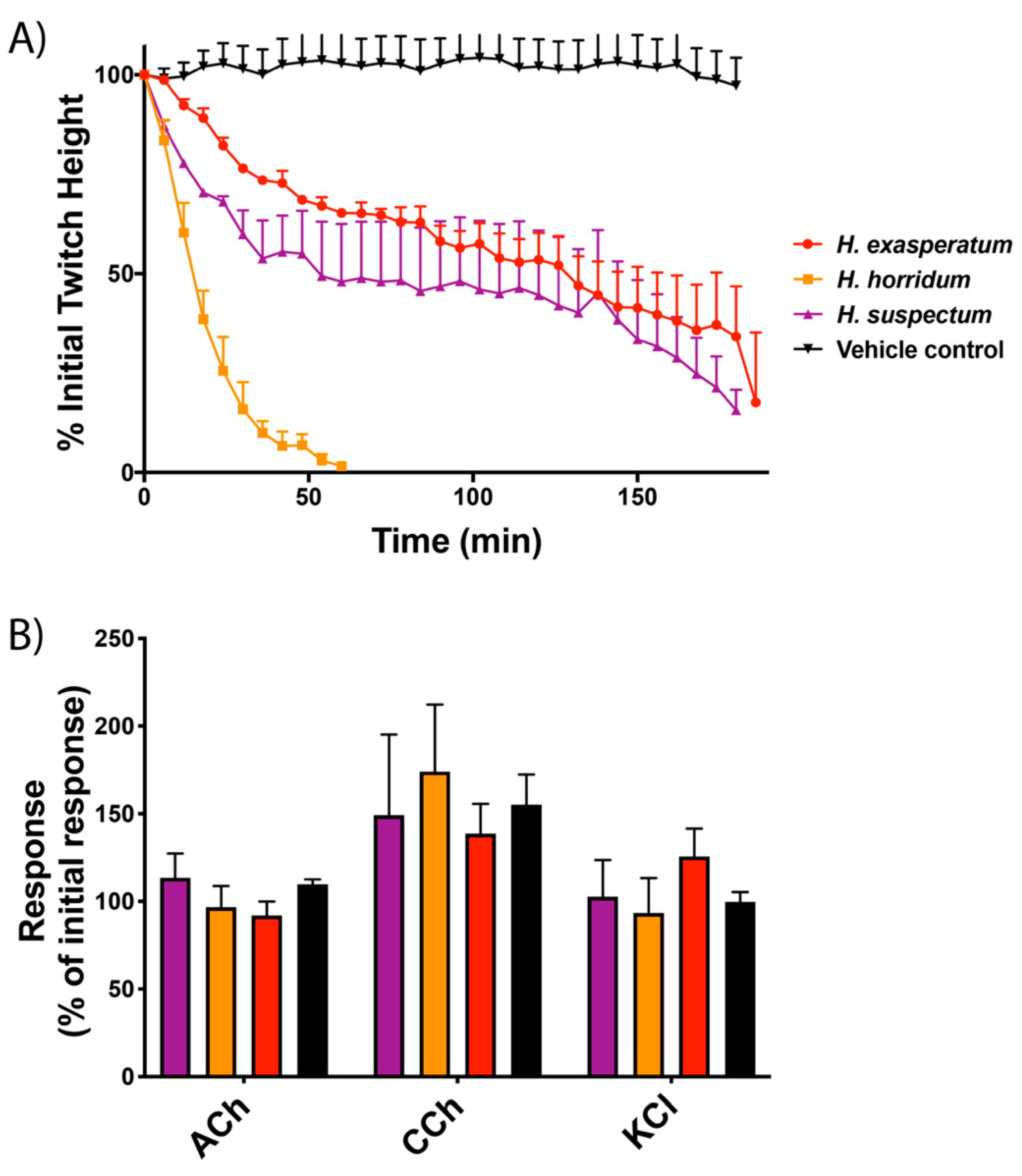
2. Results
2.1. Gallus gallus Chick Biventer Cervicis Nerve–Muscle Assays
2.2. Biolayer Interferometry Assays
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Acquisition
4.2. Gallus Gallus Chick Biventer Cervicis Nerve–Muscle Assays
4.3. Biolayer Interferometry
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ertel, E.A.; Campbell, K.P.; Harpold, M.M.; Hofmann, F.; Mori, Y.; Perez-reyes, E.; Schwartz, A.; Snutch, T.P.; Tanabe, T.; Birnbaumer, L.; et al. Nomenclature of Voltage-Gated Calcium Channles. Neuron 2000, 25, 533–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, P.A.V.; Greenberg, R.M. Phylogeny of Ion Channels: Clues to Structure and Function. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B 2001, 129, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, C.A.; Payandeh, J.; Bosmans, F.; Chanda, B. The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Galaxy. J. Gen. Physiol. 2016, 147, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chanda, B.; Bezanilla, F. Tracking Voltage-Dependent Conformational Changes in Skeletal Muscle Sodium Channel during Activation. J. Gen. Physiol. 2002, 120, 629–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldschen-ohm, M.P.; Capes, D.L.; Oelstrom, K.M.; Chanda, B. Multiple Pore Conformations Driven by Asynchronous Movements of Voltage Sensors in a Eukaryotic Sodium Channel. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pantazis, A.; Savalli, N.; Sigg, D.; Neely, A.; Olcese, R.; Pantazisa, A.; Savalli, N.; Siggbf, D.; Neelycf, A.; Olcesea, R. Functional Heterogeneity of the Four Voltage Sensors of a Human L-type Calcium Channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 111, 18381–18386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beyl, S.; Depil, K.; Hohaus, A.; Stary-weinzinger, A.; Linder, T.; Timin, E.; Hering, S. Neutralisation of a Single Voltage Sensor Affects Gating Determinants in All Four Pore-Forming S6 Segments of CaV1.2: A Cooperative Gating Model. Pflügers Arch.-Eur. J. Physiol. 2012, 464, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Catterall, W.A.; Goldin, A.L.; Waxman, S.G. International Union of Pharmacology. XLVII. Nomenclature and Structure-Function Relationships of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolphin, A.C. Calcium Channel Diversity: Multiple Roles of Calcium Channel Subunits. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2009, 19, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W.A. Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W.A. Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels at 60: Structure, Function and Pathophysiology. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 2577–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.L.J. Inherited Disorders of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1990–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, S.C. Pathomechanisms in Channelopathies of Skeletal Muscle and Brain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 29, 387–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waxman, S.G.; Merkies, I.S.J.; Gerrits, M.M.; Dib-hajj, S.D.; Lauria, G.; Cox, J.J.; Wood, J.N.; Woods, C.G.; Drenth, J.P.H.; Faber, C.G. Sodium Channel Genes in Pain-Related Disorders: Phenotype–Genotype Associations and Recommendations for Clinical Use. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B.G.; Roelants, K.; Champagne, D.E.; Scheib, H.; Tyndall, J.D.A.; King, G.F.; Nevalainen, T.J.; Norman, J.A.; Lewis, R.J.; Norton, R.S.; et al. The Toxicogenomic Multiverse: Convergent Recruitment of Proteins Into Animal Venoms. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2009, 10, 483–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bosmans, F.; Swartz, K.J. Targeting Voltage Sensors in Sodium Channels with Spider Toxins. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 31, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bosmans, F.; Martin-Eauclaire, M.F.; Swartz, K.J. Deconstructing Voltage Sensor Function and Pharmacology in Sodium Channels. Nature 2008, 456, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.C.; Deuis, J.R.; Dashevsky, D.; Dobson, J.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Brust, A.; Xie, B.; Koludarov, I.; Debono, J.; Hendrikx, I.; et al. The Snake with the Scorpion’s Sting: Novel Three-Finger Toxin Sodium Channel Activators from the Venom of the Long-Glanded Blue Coral Snake (Calliophis bivirgatus). Toxins 2016, 8, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourinet, E.; Stotz, S.C.; Spaetgens, R.L.; Dayanithi, G.; Lemos, J.; Nargeot, J.; Zamponi, G.W. Interaction of SNX482 with Domains III and IV Inhibits Activation Gating of α1E (CaV2. 3) calcium channels. Biophys. J. 2001, 81, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilchrist, J.; Bosmans, F. Using Voltage-Sensor Toxins and their Molecular Targets to Investigate NaV1.8 Gating. J. Physiol. 2018, 10, 1863–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hooker, K.R.; Caravati, M.E. Gila Monster Envenomation. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1994, 24, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, R.N.E.; Ash, J.; Brooks, D.E.; French, R.N.E.; Ash, J.; Brooks, D.E. Gila Monster Bite. Clin. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 151–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amri, K.; Chippaux, J. Report of a Severe Heloderma suspectum Envenomation. Clin. Toxicol. 2020, 59, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B.G.; Winter, K.; Norman, J.A.; Roelants, K.; Nabuurs, R.J.A.; van Osch, M.J.P.; Teeuwisse, W.M.; van der Weerd, L.; Mcnaughtan, J.E.; Kwok, H.F.; et al. Functional and Structural Diversification of the Anguimorpha Lizard Venom System. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2010, 9, 2369–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, F.E.; Bogert, C.M. Gila Monster: Its Biology, Venom and Bite-A Review. Toxicon 1981, 19, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, R.; Brooks, D.; Ruha, A.; Shirazi, F.; Boesen, K.; Walter, F.; French, R.; Brooks, D.; Ruha, A.; Shirazi, F.; et al. Gila Monster (Heloderma suspectum) Envenomation: Descriptive Analysis of Calls to United States Poison Centers with Focus on Arizona Cases. Clin. Toxicol. 2015, 53, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lino-López, G.J.; Valdez-Velázquez, L.L.; Corzo, G.; Romero-Gutiérrez, M.T.; Jiménez-Vargas, J.M.; Rodríguez-Vázquez, A.; Vazquez-Vuelvas, O.F.; Gonzalez-Carrillo, G. Venom Gland Transcriptome from Heloderma horridum horridum by High-Throughput Sequencing. Toxicon 2020, 180, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koludarov, I.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Sunagar, K.; Nouwens, A.; Hendrikx, I.; Fry, B.G. Fossilized Venom: The Unusually Conserved Venom Profiles of Heloderma Species (Beaded Lizards and Gila Monsters). Toxins 2014, 6, 3582–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwok, H.F.; Ivanyi, C.; Morris, A.; Shaw, C. Proteomic and Genomic Studies on Lizard Venoms in the Last Decade. Proteom. Insights 2010, 3, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanggaard, K.W.; Dyrlund, T.F.; Thomsen, L.R.; Nielsen, T.A.; Brøndum, L.; Wang, T.; Thøgersen, I.B.; Enghild, J.J. Characterization of the Gila Monster (Heloderma suspectum suspectum) Venom Proteome. J. Proteom. 2015, 117, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mochca-Morales, J.; Martin, B.M.; Possani, L.D. Isolation and Characterization of Helothermine, a Novel Txin from Heloderma horridum horridum (Mexican Beaded Lizard) Lenom. Toxicon 1990, 28, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissette, J.; Krätzschmar, J.; Haendler, B.; El-Hayek, R.; Mochca-Morales, J.; Martin, B.M.; Patel, J.R.; Moss, R.L.; Schleuning, W.D.; Coronado, R.; et al. Primary Structure and Properties of Helothermine, a Peptide Toxin that Blocks Ryanodine Receptors. Biophys. J. 1995, 68, 2280–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nobile, M.; Magnelli, V.; Lagostena, L.; Mochca-Morales, J.; Possani, L.D.; Prestipino, G. The Toxin Helothermine Affects Potassium Currents in Newborn Rat Cerebellar Granule Cells. J. Membr. Biol. 1994, 139, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile, M.; Noceti, F.; Prestipino, G.; Possani, L.D. Helothermine, a Lizard Venom Toxin, Inhibits Calcium Current in Cerebellar Granules. Exp. Brain Res. 1996, 110, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komori, Y.; Nikai, T.; Sugihara, H. Purification and Characterization of a Lethal Toxin from the Venom of Helodermahorridumhorridum. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1988, 154, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B.G.; Roelants, K.; Winter, K.; Hodgson, W.C.; Griesman, L.; Kwok, H.F.; Scanlon, D.; Karas, J.; Shaw, C.; Wong, L.; et al. Novel Venom Proteins Produced by Differential Domain-Expression Strategies in Beaded Lizards and Gila Monsters (Genus Heloderma). Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koludarov, I.; Jackson, T.N.W.; op den Brouw, B.; Dobson, J.; Dashevsky, D.; Arbuckle, K.; Clemente, C.J.; Stockdale, E.J.; Cochran, C.; Debono, J.; et al. Enter the Dragon: The Dynamic and Multifunctional Evolution of Anguimorpha Lizard Venoms. Toxins 2017, 9, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobson, J.S.; Zdenek, C.N.; Hay, C.; Violette, A.; Fourmy, R.; Cochran, C.; Fry, B.G. Varanid Lizard Venoms Disrupt the Clotting Ability of Human Fibrinogen through Destructive Cleavage. Toxins 2019, 11, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fry, B.G.; Wroe, S.; Teeuwisse, W.; Van Osch, M.J.P.; Moreno, K.; Ingle, J.; Mchenry, C.; Ferrara, T.; Clausen, P.; Scheib, H.; et al. A Central Role for Venom in Predation by Varanus komodoensis (Komodo Dragon) and the Extinct Giant Varanus (Megalania) priscus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 8969–8974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fry, B.G.; Vidal, N.; Norman, J.A.; Vonk, F.J.; Scheib, H.; Ramjan, S.F.R.; Kuruppu, S.; Fung, K.; Hedges, S.B.; Richardson, M.K.; et al. Early Evolution of the Venom System in Lizards and Snakes. Nature 2006, 439, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koludarov, I.; Sunagar, K.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Ruder, T.; Whitehead, D.; Saucedo, A.C.; Mora, G.R.; Alagon, A.C.; King, G.; et al. Structural and Molecular Diversification of the Anguimorpha Lizard Mandibular Venom Gland System in the Arboreal Species Abronia graminea. J. Mol. Evol. 2012, 75, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, S.; Swan, G. A Complete Guide to Reptiles of Australia, 5th ed.; Reed New Holland Publishers: Chatswood, Australia, 2017; ISBN 9781925546026. [Google Scholar]
- Pianka, E.R.; King, D.; King, R. Varanoid Lizards of the World; Pianka, E.R., King, D.R., King, R.A., Eds.; Indiana University Press: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Pianka, E.R.; Sweet, S.S. Field Observations by Two American Varanophiles. In Proceedings of the 2015 Interdisciplinary World Conference on Monitor Lizards; Cota, M., Ed.; Institute for Research and Development, Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University: Bangkok, Thailand, 2016; pp. 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- Arbuckle, K. Ecological Function of Venom in Varanus, with a Compilation of Dietary Records from the Literature. Biawak 2009, 3, 46–56. [Google Scholar]
- Sopiev, O.; Makeev, V.M.; Kudryavcev, S.V.; Makarov, A.N. The Case of Intoxication with the Bite of the Gray Monitor Lizard Varanus. Izvestia Academii nauk Turkmenskoi SSR. Seriya Biol. Nauk 1987, 598, 615. (In Rissian) [Google Scholar]
- Ballard, V.; Antonio, F.B. Varanus griseus (Desert Monitor) Toxicity. Herpetol. Rev. 2001, 32, 261. [Google Scholar]
- Zima, Y.A. On the Toxicity of the Bite of the Caspian Desert Monitor Lizard (Varanus griseus caspius). Biawak 2019, 13, 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- Sweet, S.S. Chasing Flamingos: Toxicofera and the Misinterpretation of Venom in Varanid Lizards. In Proceedings of the 2015 Interdisciplinary World Conference on Monitor Lizards; Cota, M., Ed.; Institute for Research and Development, Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University: Bangkok, Thailand, 2016; pp. 123–149. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.-F.; Chiang, H.-S. Effect on Human Platelet Aggregation of Phospholipase A2 Purified from Heloderma horridum (Beaded Lizard) Venom. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Lipids Lipid Metab. 1994, 1211, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utaisincharoenso, P.; Mackessyn, S.P.; Miller, R.A.; Tusii, A.T. Complete Primary Structure and Biochemical Properties of Gilatoxin, a Serine Protease with Kallikrein-like and Angiotensin-Degrading Activities. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 21975–21983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelov, Y.K. On the Toxicity of Saliva Varanus griseus. Izvestia Academii nauk Turkmenskoi SSR. Seriya Biol. Nauk 1971, 6, 75–76. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.C.; Dobson, J.; Cochran, C.; Dashevsky, D.; Arbuckle, K.; Benard, M.; Boyer, L.; Alagón, A.; Hendrikx, I.; Hodgson, W.C.; et al. The Bold and the Beautiful: A Neurotoxicity Comparison of New World Coral Snakes in the Micruroides and Micrurus Genera and Relative Neutralization by Antivenom. Neurotox. Res. 2017, 32, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B.G.; Lumsden, N.G.; Wuster, W.; Wickramaratna, J.C.; Hodgson, W.C.; Kini, R.M. Isolation of a Neurotoxin (Alpha-Colubritoxin) from a Nonvenomous Colubrid: Evidence for Early Origin of Venom in Snakes. J. Mol. Evol. 2003, 57, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Op den Brouw, B.; Coimbra, F.C.P.; Bourke, L.A.; Huynh, T.M.; Vlecken, D.H.W.; Ghezellou, P.; Visser, J.C.; Dobson, J.S.; Fernandez-Rojo, M.A.; Ikonomopoulou, M.P.; et al. Extensive Variation in the Activities of Pseudocerastes and Eristicophis Viper Venoms Suggests Divergent Envenoming Strategies Are Used for Prey Capture. Toxins 2021, 13, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumsden, N.G.; Fry, B.G.; Manjunatha Kini, R.; Hodgson, W.C. In Vitro Neuromuscular Activity of ‘Colubrid’ Venoms: Clinical and Evolutionary Implications. Toxicon 2004, 43, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.J.; Youngman, N.J.; Chan, W.; Bosmans, F.; Cheney, K.L.; Fry, B.G. Getting Stoned: Characterisation of the Coagulotoxic and Neurotoxic Effects of Reef Stonefish (Synanceia verrucosa) Venom. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 346, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, L.; Harris, R.J.; Fry, B.G. Not Goanna Get Me: Mutations in the Savannah Monitor Lizard (Varanus exanthematicus) Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Confer Reduced Susceptibility to Sympatric Cobra Venoms. Neurotox. Res. 2021, 39, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdenek, N.C.; Harris, J.R.; Kuruppu, S.; Youngman, J.N.; Dobson, S.J.; Debono, J.; Khan, M.; Smith, I.; Yarski, M.; Harrich, D.; et al. A Taxon-Specific and High-Throughput Method for Measuring Ligand Binding to Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Toxins 2019, 11, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, R.J.; Youngman, N.J.; Zdenek, C.N.; Huynh, T.M.; Nouwens, A.; Hodgson, W.C.; Harrich, D.; Dunstan, N.; Portes-junior, J.A.; Fry, B.G. Assessing the Binding of Venoms from Aquatic Elapids to the Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Orthosteric Site of Di ff erent Prey Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, R.J.; Fry, B.G. Electrostatic Resistance to Alpha-Neurotoxins Conferred by Charge Reversal Mutations in Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Proc. R. Soc. B 2021, 288, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.J.; Zdenek, C.N.; Debono, J.; Harrich, D.; Fry, B.G. Evolutionary Interpretations of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Targeting Venom Effects by a Clade of Asian Viperidae Snakes. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 38, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngman, N.J.; Harris, R.J.; Huynh, T.M.; Coster, K.; Sundman, E.; Braun, R.; Naude, A.; Hodgson, W.C.; Fry, B.G. Widespread and Differential Neurotoxicity in Venoms from the Bitis Genus of Viperid Snakes. Neurotox. Res. 2021, 39, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modahl, C.; Mrinalini; Frietze, S.; Mackessy, S.P. Adaptive Evolution of Distinct Prey-Specific Toxin Genes in Rear-Fanged Snake Venom. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20181003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.J.; Zdenek, C.N.; Harrich, D.; Frank, N.; Fry, B.G. An Appetite for Destruction: Detecting Prey-Selective Binding of α-Neurotoxins in the Venom of Afro-Asian Elapids. Toxins 2020, 12, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heyborne, W.H.; Mackessy, S.P. Identification and Characterization of a Taxon-Specific Three- Finger Toxin from the Venom of the Green Vinesnake (Oxybelis fulgidus; family Colubridae). Biochimie 2013, 95, 1923–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, J.; Mackessy, S.P.; Fry, B.G.; Bhatia, M.; Mourier, G.; Fruchart-gaillard, C.; Servent, D.; Stura, E.; Ménez, A.; Kini, R.M. Denmotoxin, a Three-finger Toxin from the Colubrid Snake Boiga dendrophila (Mangrove Catsnake) with Bird-specific Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 29030–29041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Youngman, N.J.; Chowdhury, A.; Zdenek, C.N.; Coster, K.; Sundman, E.; Braun, R.; Fry, B.G. Utilising Venom Activity to infer Dietary Composition of the Kenyan Horned Viper (Bitis worthingtoni). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C 2021, 240, 108921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngman, N.J.; Zdenek, C.N.; Dobson, J.S.; Bittenbinder, M.A.; Gillett, A.; Hamilton, B.; Dunstan, N.; Allen, L.; Veary, A.; Veary, E.; et al. Mud in the Blood: Novel Potent Anticoagulant Coagulotoxicity in the Venoms of the Australian Elapid Snake Genus Denisonia (Mud Adders) and Relative Antivenom Efficacy. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 302, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cipriani, V.; Debono, J.; Goldenberg, J.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Arbuckle, K.; Dobson, J.; Koludarov, I.; Li, B.; Hay, C.; Dunstan, N.; et al. Correlation Between Ontogenetic Dietary Shifts and Venom Variation in Australian Brown Snakes (Pseudonaja). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 197, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daltry, J.C.; Wüster, W.; Thorpe, R.S. Diet and Snake Venom Evolution. Nature 1996, 379, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Fiedler, B.; Green, B.R.; Catlin, P.; Watkins, M.; Garrett, J.E.; Smith, B.J.; Yoshikami, D.; Olivera, B.M.; Bulaj, G. Structural and Functional Diversities among µ-Conotoxins Targeting TTX-Resistant Sodium Channels. Biochem. 2019, 13, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.J.; Yoshikami, D.; Azam, L.; Gajewiak, J.; Olivera, B.M.; Bulaj, G. μ -Conotoxins that Differentially Block Sodium Channels NaV1.1 through 1.8 Identify those Responsible for Action Potentials in Sciatic Nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10302–10307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beck, D.D.; Lowe, C.H. Ecology of the Beaded Lizard, Heloderma horridum, in a Tropical Dry Forest in Jalisco, México. J. Herpetol. 1991, 25, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensley, M. Mammal Diet of Heloderma. Herpetologica 1949, 5, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chippaux, J.-P.; Amri, K. Severe Heloderma spp. Envenomation: A Review of the Literature. Clin. Toxicol. 2021, 59, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abroug, F.; Souheil, E.; Ouanes, I.; Dachraoui, F.; Fekih-Hassen, M.; Besbes, L.O. Scorpion-Related Cardiomyopathy: Clinical Characteristics, Pathophysiology, and Treatment. Clin. Toxicol. 2015, 53, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, J.; Olivera, B.M.; Bosmans, F. Animal Toxins Influence Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Function. In Voltage Gated Sodium Channels; Ruben, P.C., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 203–229. ISBN 978-3-642-41588-3. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, F.C.; Castro, J.; Grundy, L.; Schober, G.; Garcia-caraballo, S.; Zhao, T.; Herzig, V.; King, G.F.; Brierley, S.M.; Lewis, R.J. A Spider-Venom Peptide with Multitarget Activity on Sodium and Calcium Channels Alleviates Chronic Visceral Pain in a Model of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Pain 2021, 162, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, J.; Yang, D.C.; op den Brouw, B.; Cochran, C.; Huynh, T.; Kurrupu, S.; Sánchez, E.E.; Massey, D.J.; Baumann, K.; Jackson, T.N.W.; et al. Rattling the Border Wall: Pathophysiological Implications of Functional and Proteomic Venom Variation between Mexican and US Subspecies of the Desert Rattlesnake Crotalus scutulatus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 205, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin-Eauclaire, M.F.; Ferracci, G.; Bosmans, F.; Bougis, P.E. A Surface Plasmon Resonance Approach to Monitor Toxin Interactions with an Isolated Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Paddle Motif. J. Gen. Physiol. 2015, 145, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dobson, J.S.; Harris, R.J.; Zdenek, C.N.; Huynh, T.; Hodgson, W.C.; Bosmans, F.; Fourmy, R.; Violette, A.; Fry, B.G. The Dragon’s Paralysing Spell: Evidence of Sodium and Calcium Ion Channel Binding Neurotoxins in Helodermatid and Varanid Lizard Venoms. Toxins 2021, 13, 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13080549
Dobson JS, Harris RJ, Zdenek CN, Huynh T, Hodgson WC, Bosmans F, Fourmy R, Violette A, Fry BG. The Dragon’s Paralysing Spell: Evidence of Sodium and Calcium Ion Channel Binding Neurotoxins in Helodermatid and Varanid Lizard Venoms. Toxins. 2021; 13(8):549. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13080549
Chicago/Turabian StyleDobson, James S., Richard J. Harris, Christina N. Zdenek, Tam Huynh, Wayne C. Hodgson, Frank Bosmans, Rudy Fourmy, Aude Violette, and Bryan G. Fry. 2021. "The Dragon’s Paralysing Spell: Evidence of Sodium and Calcium Ion Channel Binding Neurotoxins in Helodermatid and Varanid Lizard Venoms" Toxins 13, no. 8: 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13080549
APA StyleDobson, J. S., Harris, R. J., Zdenek, C. N., Huynh, T., Hodgson, W. C., Bosmans, F., Fourmy, R., Violette, A., & Fry, B. G. (2021). The Dragon’s Paralysing Spell: Evidence of Sodium and Calcium Ion Channel Binding Neurotoxins in Helodermatid and Varanid Lizard Venoms. Toxins, 13(8), 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13080549






