Production of Alternaria Toxins in Yellow Peach (Amygdalus persica) upon Artificial Inoculation with Alternaria alternate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Performance of UHPLC-MS/MS Method
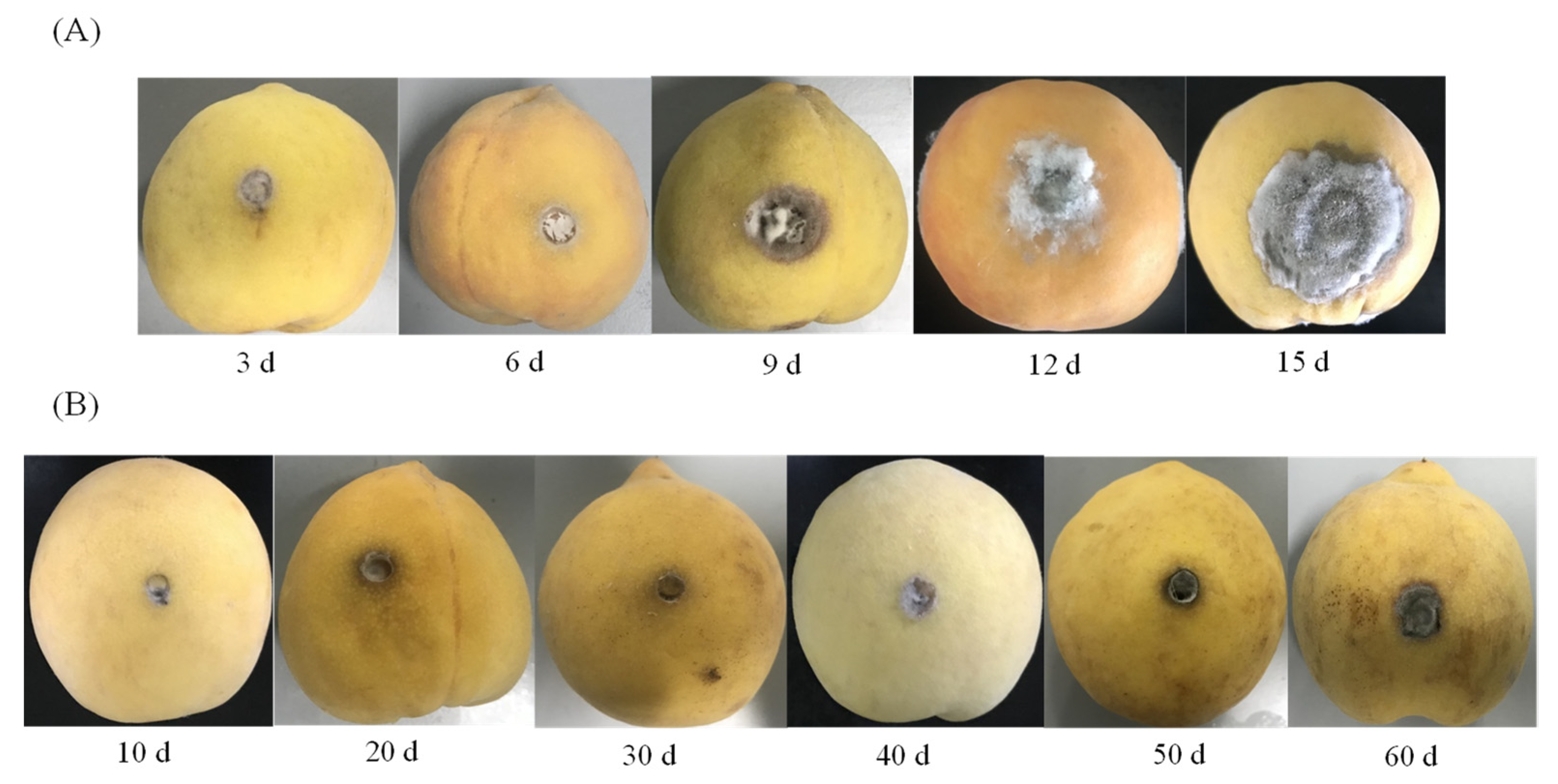
2.2. The Visual Appearance of Yellow Peaches Decay upon Inoculation with A. alternate
2.3. Production of Alternaria Toxins upon Inoculation with A. alternate
2.3.1. Production of Alternaria Toxins Stored at 28 °C upon Inoculation with A. alternate
2.3.2. Production of Alternaria Toxins Stored at 4 °C upon Inoculation with A. alternate
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Reagents and Chemicals
5.2. Fungal Material and the Preparation of Spore Suspension
5.3. Artificial Inoculation
5.4. UHPLC-MS/MS Analysis
5.5. Sample Preparation
5.6. Method Validation
5.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, Z.J.; Ma, R.J.; Cai, Z.X.; Yu, M.L.; Zhang, Z. Diversity, population structure, and evolution of local peach cultivars in China identified by simple sequence repeats. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chen, S.; Kong, W.; Li, S.; Archbold, D.D. Salicilyc acid pretreatment alleviates chilling injury and effects the antioxidant system and heat shock proteins of peaches during cold storage. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2006, 41, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Cao, J. Study on occurrence of peach black spot (Alternaria alternata) and disease disposition. J. Hebei Agric. Univ. 1995, 18, 53–58. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, K.; Nasu, H. Black spot of peach caused by Alternaria alternata (Fr.) Keissler. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2000, 66, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Holb, I.J.; Schnabel, G. A new selective medium for the recovery and enumeration of Monilinia fructicola, M. fructigena, and M. laxa from stone fruits. Phytopathology 2009, 99, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.H.; Brannen, P.M.; Schnabel, G. Resistance in Alternaria alternata to SDHI fungicides causes rare disease outbreak in peach orchards. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ushijima, K.; Yamamoto, M. A sequence resource of autosomes and additional chromosomes in the peach pathotype of Alternaria alternata. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2019, 32, 1273–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ostry, V. Alternaria mycotoxins: An overview of chemical characterization, producers, toxicity, analysis and occurrence in foodstuffs. World Mycotoxin J. 2008, 1, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crudo, F.; Varga, E.; Aichinger, G.; Galaverna, G.; Marko, D.; Dall’Asta, C.; Dellafiora, L. Co-occurrence and combinatory effects of Alternaria mycotoxins and other xenobiotics of food origin: Current scenario and future perspectives. Toxins 2019, 11, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Berardis, S.; De Paola, E.L.; Montevecchi, G.; Garbini, D.; Masino, F.; Antonelli, A.; Melucci, D. Determination of four Alternaria alternata mycotoxins by QuEChERS approach coupled with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in tomato-based and fruit-based products. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tölgyesi, Á.; Stroka, J.; Tamosiunas, V.; Zwickel, T. Simultaneous analysis of Alternaria toxins and citrinin in tomato: An optimised method using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2015, 32, 1512–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magnani, R.F.; De Souza, G.D.; Rodrigues-Filho, E. Analysis of alternariol and alternariol monomethyl ether on flavedo and albedo tissues of tangerines (Citrus reticulata) with symptoms of alternaria brown spot. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4980–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, P.M.; Lawrence, G.A.; Lau, B.P. Analysis of wines, grape juices and cranberry juices for Alternaria toxins. Mycotoxin Res. 2006, 22, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noser, J.; Schneider, P.; Rother, M.; Schmutz, H. Determination of six Alternaria toxins with UPLC-MS/MS and their occurrence in tomatoes and tomato products from the Swiss market. Mycotoxin Res. 2011, 27, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Shao, B.; Yang, D.; Li, F. Natural occurrence of four Alternaria mycotoxins in tomato- and citrus-based foods in China. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.G.; Liu, G.T.; Dong, Z.M.; Qian, Y.Z.; An, Y.H.; Miao, J.A.; Zhen, Y.Z. Induction of mutagenesis and transformation by the extract of Alternaria alternata isolated from grainsin Linxian, China. Carcinogenesis 1987, 8, 989–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solfrizzo, M.; Girolamo, A.D.; Vitti, C.; Tylkowska, K.; Grabarkiewicz-Szczesna, J.; Szopińska, D.; Dorna, H. Toxigenic profile of Alternaria alternata and Alternaria radicina occurring on umbelliferous plants. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Scientific opinion on the risks for animal and public health related to the presence of Alternaria toxins in feed and food. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraeyman, S.; Croubels, S.; Devreese, M.; Antonissen, G. Emerging Fusarium and Alternaria mycotoxins: Occurrence, toxicity and toxicokinetics. Toxins 2017, 9, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walravens, J.; Mikula, H.; Rychlik, M.; Asam, S.; Devos, T.; Ediage, E.N.; Di Mavungu, J.D.; Jacxsens, L.; Van Landschoot, A.; Vanhaecke, L.; et al. Validated UPLC-MS/MS methods to quantitate free and conjugated Alternaria toxins in commercially available tomato products, fruit and vegetable juices in Belgium. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 5101–5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiao, X.T.; Yin, J.; Yang, Y.J.; Zhang, J.; Shao, B.; Li, H.; Chen, H.B. Determination of Alternaria mycotoxins in fresh sweet cherries and cherry-based products: Method validation and occurrence. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 11846–11853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcella, D.; Eskola, M.; Ruiz, J.A.G. Dietary exposure assessment to Alternaria toxins in the European population. EFSA J. 2016, 14, 4654. [Google Scholar]
- Sanzani, S.M.; Reverberi, M.; Geisen, R. Mycotoxins in harvested fruits and vegetables: Insights in producing fungi, biological role, conducive conditions, and tools to manage postharvest contamination. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 122, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, F.N. Role of controlled environments in suppression of postharvest diseases. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 1985, 7, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.; Oueslati, S.; Mañes, J. Evaluation of Alternaria mycotoxins in strawberries: Quantification and storage condition. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2016, 33, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo, M.S.; Ramirez, M.L.; Barros, G.G.; Chulze, S.N. Impact of water activity and temperature on growth and alternariol and alternariol monomethyl ether production of Alternaria alternata isolated from soybean. J. Food Protect. 2010, 73, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robiglio, A.L.; López, S.E. Mycotoxin production by Alternaria alternata strains isolated from red delicious apples in Argentina. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1995, 24, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation 401/2006. European Commission Regulation (EC) No 401/2006 of 23 February 2006 Laying down the methods of sampling and analysis for the official control of the levels of mycotoxins in foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 2006, L70, 12–34. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2006/401/oj (accessed on 7 August 2021).
- Guo, W.; Fan, K.; Nie, D.; Meng, J.; Huang, Q.; Yang, J.; Shen, Y.; Tangni, E.K.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Y.; et al. Development of a QuEChERS-Based UHPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of six Alternaria toxins in grapes. Toxins 2019, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pose, G.; Patriarca, A.; Kyanko, V.; Pardo, A.; Pinto, V.F. Water activity and temperature effects on mycotoxin production by Alternaria alternata on a synthetic tomato medium. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 142, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaquera, S.; Patriarca, A.; Pinto, V.F. Water activity and temperature effects on growth of Alternaria arborescens on tomato medium. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 185, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, L.D.; Rodriguez, A.; Andrade, M.J.; Patriarca, A.; Delgado, J. Effect of Debaryomyces hansenii and the antifungal PgAFP protein on Alternaria spp. growth, toxin production, and RHO1 gene expression in a tomato-based medium. Food Microbiol. 2021, 97, 103741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Gong, L.; Ge, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liang, M.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, C.; Jiao, B. Production and distribution of Alternaria mycotoxins in Satsuma Mandarin (Citrus unshiu Marc.) artificially inoculated with Alternaria alternate. Food Sci. 2017, 3, 251–257. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Stinson, E.; Osman, S.; Heisler, E.; Siciliano, J.; Bills, D. Mycotoxin production in whole tomatoes, apples, oranges, and lemons. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1981, 29, 790–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwickel, T.; Kahl, S.M.; Klaffke, H.; Rychlik, M.; Müller, M.E. Spotlight on the underdogs-an analysis of underrepresented Alternaria mycotoxins formed depending on varying substrate, time and temperature conditions. Toxins 2016, 8, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, A.; Mao, X.; Sun, Q.; Wei, Z.; Li, J.; You, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, G.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Alternaria mycotoxins: An overview of toxicity, metabolism, and analysis in food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7817–7830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffo, A.; Nardo, N.; Tabilio, M.R.; Paoletti, F. Effects of cold storage on aroma compounds of white- and yellow-fleshed peaches. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 226, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.M.; Wei, D.Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M. Distribution of Alternaria mycotoxins in decayed locations and their extension tissues of tomato infected with Alternaria alternate. J. Food Saf. Food Qual. 2018, 9, 5858–5862. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]





| Alternaria Toxins | Linear Range | Linear Equation | Correlation Coefficient (R2) | LOD (µg kg−1) | LOQ (µg kg−1) | Matrix Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AME | 0.3–200 | y = 2662.59x + 718.912 | 0.998 | 0.07 | 0.18 | 74.65 |
| AOH | 0.3–200 | y = 3335.09x + 540.209 | 0.999 | 0.11 | 0.28 | 110.91 |
| TeA | 0.2–200 | y = 1082.09x + 67.7107 | 0.998 | 0.07 | 0.20 | 41.05 |
| Alternaria Toxins | Spiked Levels (µg kg−1) | Recovery (Mean ± SD, %) | Intra-Day Precision (RSD, %) | Inter-Day Precision (RSD, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AME | 10 | 104.9 ± 1.2 | 5.5 | 6.0 |
| 50 | 96.3 ± 7.6 | 5.6 | 4.1 | |
| 100 | 98.6 ± 6.2 | 4.1 | 3.3 | |
| AOH | 10 | 96.0 ± 7.4 | 5.7 | 9.7 |
| 50 | 91.1 ± 6.0 | 3.1 | 8.1 | |
| 100 | 97.8 ± 3.5 | 1.9 | 6.0 | |
| TeA | 10 | 77.5 ± 0.9 | 1.8 | 11.2 |
| 50 | 97.3 ± 4.7 | 2.7 | 4.7 | |
| 100 | 85.0 ± 7.0 | 0.7 | 2.2 |
| Alternaria Toxins | Precursor Ions (m/z) | Product Ions (m/z) | Dwell Times (s) | Cone Voltage (V) | Collision Energy (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AME | 273.0 [M + H]+ | 128.1/258.0 * | 0.018 | 54/54 | 26/25 |
| AOH | 259.0 [M + H]+ | 185.1 */213.1 | 0.018 | 64/64 | 28/24 |
| TeA | 198.1 [M + H]+ | 125.0/153.1 * | 0.018 | 42/42 | 16/12 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, J.; Guo, W.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Nie, D.; Tangni, E.K.; Han, Z. Production of Alternaria Toxins in Yellow Peach (Amygdalus persica) upon Artificial Inoculation with Alternaria alternate. Toxins 2021, 13, 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13090656
Meng J, Guo W, Zhao Z, Zhang Z, Nie D, Tangni EK, Han Z. Production of Alternaria Toxins in Yellow Peach (Amygdalus persica) upon Artificial Inoculation with Alternaria alternate. Toxins. 2021; 13(9):656. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13090656
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Jiajia, Wenbo Guo, Zhihui Zhao, Zhiqi Zhang, Dongxia Nie, Emmanuel K. Tangni, and Zheng Han. 2021. "Production of Alternaria Toxins in Yellow Peach (Amygdalus persica) upon Artificial Inoculation with Alternaria alternate" Toxins 13, no. 9: 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13090656
APA StyleMeng, J., Guo, W., Zhao, Z., Zhang, Z., Nie, D., Tangni, E. K., & Han, Z. (2021). Production of Alternaria Toxins in Yellow Peach (Amygdalus persica) upon Artificial Inoculation with Alternaria alternate. Toxins, 13(9), 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13090656






