Thermal Stability and Degradation Kinetics of Patulin in Highly Acidic Conditions: Impact of Cysteine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
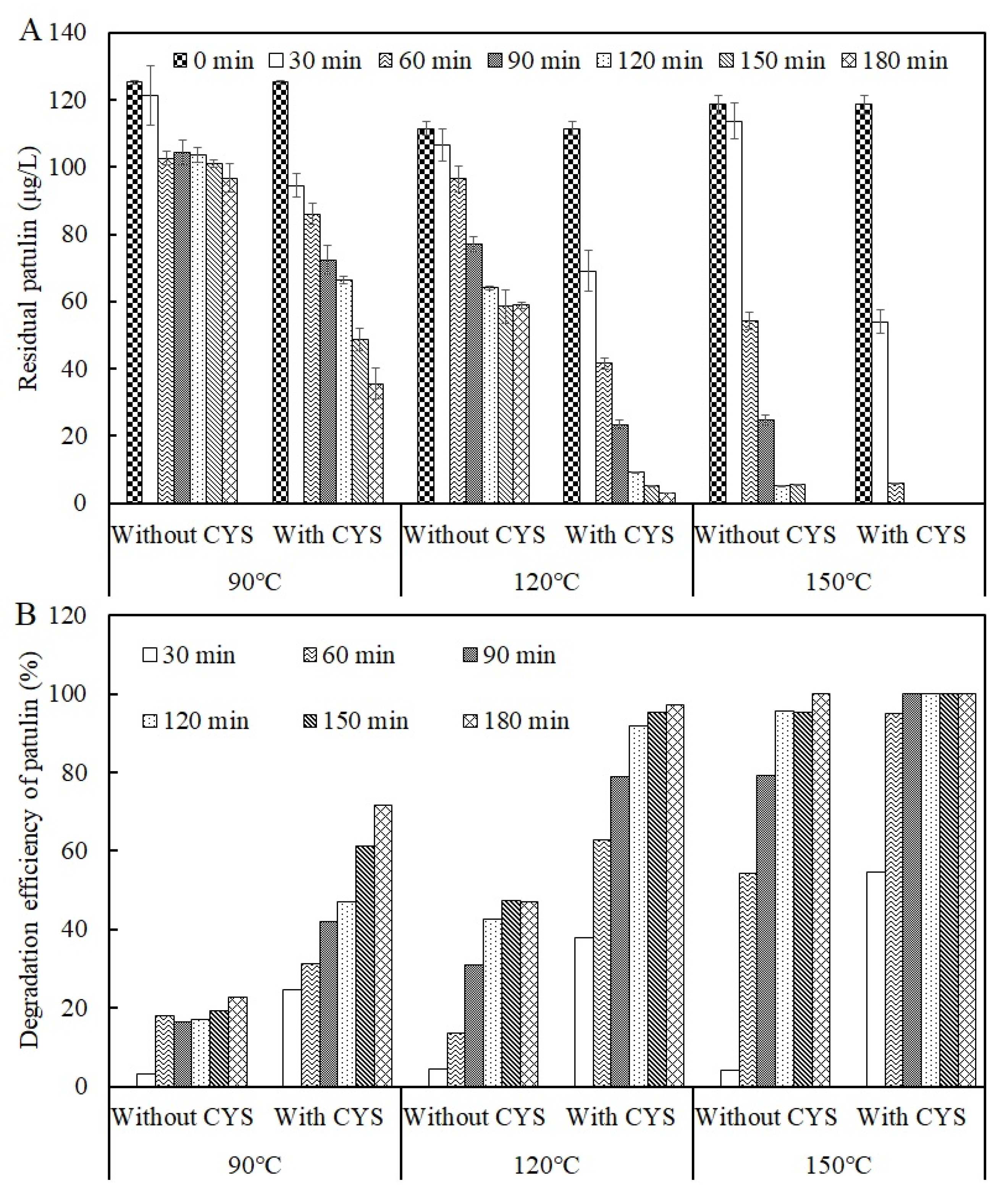
2.1. Thermal Stability of Patulin in Highly Acidic Conditions
2.2. Effect of Cysteine on the Degradation Efficiency of Patulin
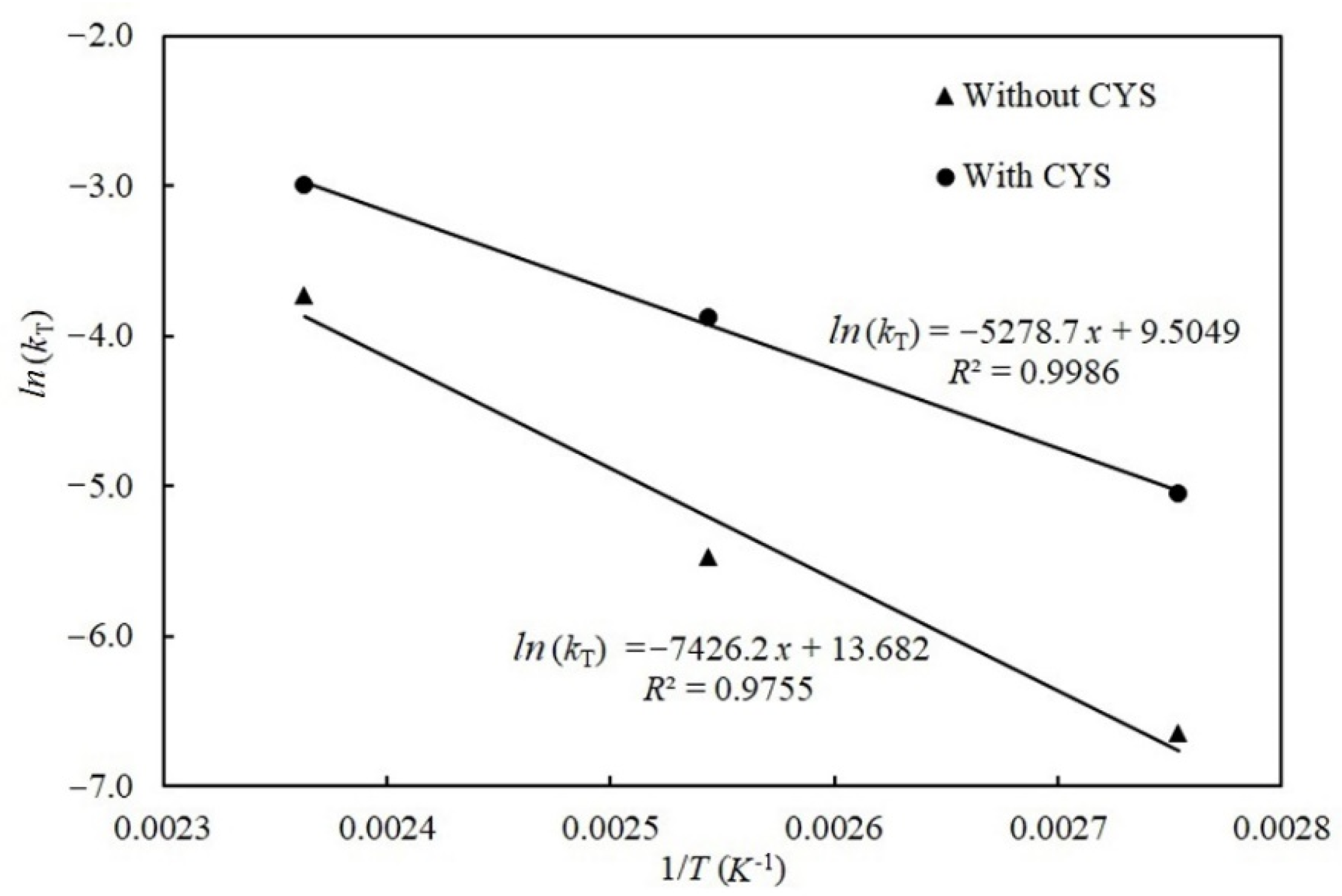
2.3. Degradation Kinetic Models of Patulin with and without Cysteine
3. Discussion
3.1. Thermal Stability of Patulin without and with Cysteine
3.2. Thermal Degradation Kinetic Models of Patulin
4. Conclusions
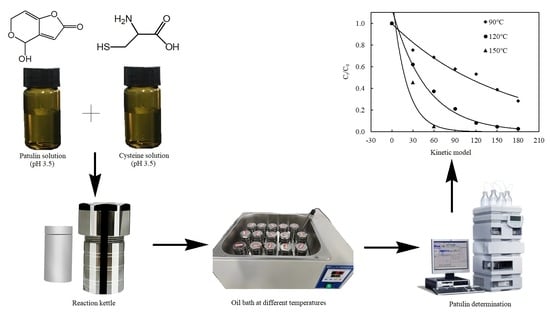
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Materials
5.2. Methods
5.2.1. Preparation of Patulin and Cysteine Solutions
5.2.2. Reaction of Patulin and Cysteine
5.2.3. Determination of Patulin in Reaction Solutions
5.2.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saleh, I.; Goktepe, I. The characteristics, occurrence, and toxicological effects of patulin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 129, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, A.; Ouhibi, S.; Ghali, R.; Hedhili, A.; Saeger, S.D.; Boevre, M.D. The mycotoxin patulin: An updated short review on occurrence, toxicity and analytical challenges. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 129, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moake, M.M.; Padilla-Zakour, O.I.; Worobo, R.W. Comprehensive review of patulin control methods in Foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2005, 4, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agriopoulou, S.; Stamatelopoulou, E.; Varzakas, T. Advances in occurrence, importance, and mycotoxin control strategies: Prevention and detoxification in foods. Foods 2020, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioi, J.D.; Zhou, T.; Tsao, R.; Marcone, M.F. Mitigation of patulin in fresh and processed foods and beverages. Toxins 2017, 9, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coton, M.; Bregier, T.; Poirier, E.; Debaets, S.; Arnich, N.; Coton, E.; Dantigny, P. Production and migration of patulin in Penicillium expansum molded apples during cold and ambient storage. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 313, 108377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vansteelandt, M.; Kerzaon, I.; Blanchet, E.; Tankoua, O.F.; Pont, T.R.D.; Joubert, Y.; Monteau, F.; Bizec, B.L.; Frisvad, J.C.; Pouchus, Y.F.; et al. Patulin and secondary metabolite production by marine-derived Penicillium strains. Fungal Biol. 2012, 116, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Li, R.; Yang, H.; Qi, P.; Xiao, Y.; Qian, M. Occurrence of patulin in various fruit products and dietary exposure assessment for consumers in China. Food Control 2017, 78, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piqué, E.; Vargas-Murga, L.; Gómez-Catalán, J.; Lapuente, J.D.; Llobet, J.M. Occurrence of patulin in organic and conventional apple-based food marketed in Catalonia and exposure assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 60, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.Z.; Malik, S.; Asi, M.R.; Selamat, J.; Malik, N. Natural occurrence of patulin in different fruits, juices and smoothies and evaluation of dietary intake in Punjab, Pakistan. Food Control 2018, 84, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants. In 44th Report of the Joint Food and Agriculture Organization/World Health Organization Expert Committee on Food Additives; WHO Technical Report Series 859; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995; pp. 36–38. [Google Scholar]
- Diao, E.J.; Hou, H.X.; Hu, W.C.; Dong, H.Z.; Li, X.Y. Removing and detoxifying methods of patulin: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 81, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.B.; Young, J.M. Carcinogenicity of lactones. III. The reaction of unsaturated γ-lactones with L-cysteine. J. Med. Chem. 1978, 11, 1176–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fliege, R.; Metzler, M. Electrophilic properties of patulin. N-acetylcysteine and glutathione adducts. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2000, 13, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciegler, A.; Beckwith, A.C.; Jackson, L.K. Teratogenicity of patulin and patulin adducts formed with cysteine. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1976, 31, 664–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindroth, S.; Wright, A.V. Comparison of the toxicities of patulin and patulin adducts formed with cysteine. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1978, 35, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sogvar, O.B.; Razavi, F.; Rabiei, V.; Gohari, G. Postharvest application of L-cysteine to prevent enzymatic browning of “Stanley” plum fruit during cold storage. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Ren, W.; Yang, G.; Duan, J.; Huang, X.; Fang, R.; Li, C.; Li, T.; Yin, Y.; Hou, Y.; et al. L-cysteine metabolism and its nutritional implications. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackebaei, D.; King, N.; Shukla, B.; Suleiman, M.S. Mechanisms underlying the cardioprotective effect of L-cysteine. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2005, 277, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoica, A.; Popescu, C.; Barascu, E.; Lordan, M. L-cysteine influence on the physical properties of bread from high extraction flours with normal gluten. Ann. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 11, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Yun, Z.; Duan, X.; Jiang, Y. L-Cysteine hydrochloride delays senescence of harvested longan fruit in relation to modification of redox status. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 143, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackett, R.E.; Marth, E.H. Ascorbic acid and ascorbate cause disappearance of patulin from buffer solutions and apple juice. J. Food Protect. 1979, 42, 864–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovett, J.; Peeler, J.T. Effect of pH on the thermal destruction kinetics of patulin in aqueous solution. J. Food Sci. 1973, 38, 1094–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadakal, Ç.; Nas, S. Effect of heat treatment and evaporation on patulin and some other properties of apple juice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2003, 83, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, S.; Bodart, E.; Badot, C.; Bouseta, A.; Nizet, S. Identification of the main degradation products of patulin generated through heat detoxification treatments. J. Inst. Brew. 2008, 114, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welke, J.E.; Hoeltz, M.; Dottori, H.A.; Noll, I.B. Effect of processing stages of apple juice concentrate on patulin levels. Food Control 2009, 20, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, W.; Yao, X.; Su, L.; Sun, J.; Yue, T.; Wang, J.L. Highly efficient and cost-effective removal of patulin from apple juice by surface engineering of diatomite with sulfur-functionalized graphene oxide. Food Chem. 2019, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Yang, Q.; Hu, N.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, W.; Wang, R.; Suo, Y.; Wang, J.L. Patulin removal from apple juice using a novel cysteine-functionalized metal-organic framework adsorbent. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paimard, G.; Mohammadi, R.; Bahrami, R.; Khosravi-Darani, K.; Sarlak, Z.; Rouhi, M. Detoxification of patulin from juice simulator and apple juice via cross-linked Se-chitosan/L-cysteine nanoparticles. LWT 2021, 143, 111146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarz, R.; Garvín, A.; Ibarz, A. Kinetic and thermodynamic study of the photochemical degradation of patulin. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


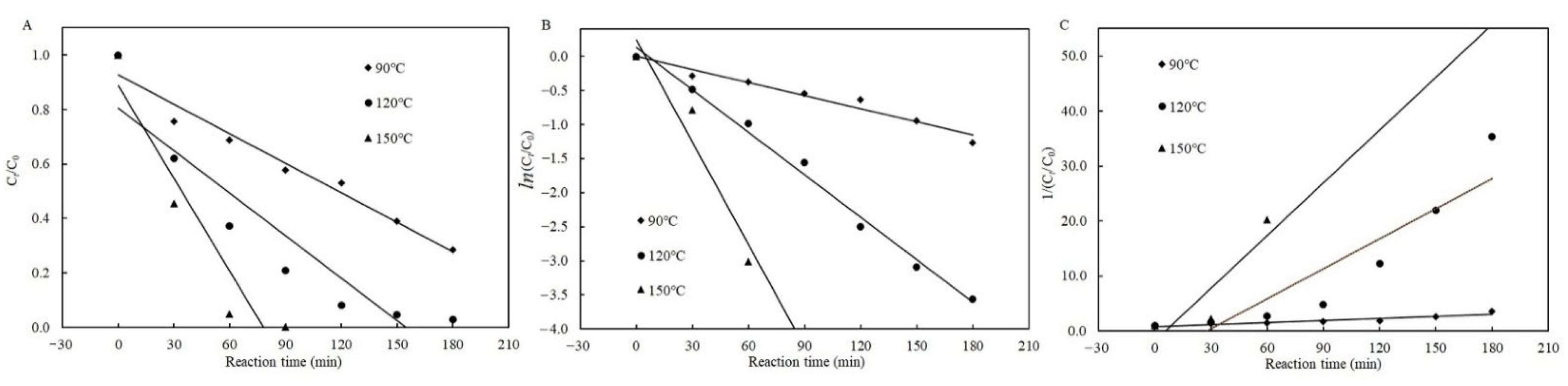


| Kinetic Model | Temperature (°C) | Kinetic Equation | kT (μg/L·min) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-order | 90 | Ct/C0 = −0.0012t + 0.9684 | 0.0012 | 0.7868 |
| 120 | Ct/C0 = −0.0031t + 1.0095 | 0.0031 | 0.9400 | |
| 150 | Ct/C0 = −0.0062t + 0.9491 | 0.0062 | 0.8731 | |
| First-order | 90 | ln(Ct/C0) = −0.0013t − 0.0328 | 0.0013 | 0.7988 |
| 120 | ln(Ct/C0) = −0.0042t + 0.0349 | 0.0042 | 0.9449 | |
| 150 | ln(Ct/C0) = −0.0241t + 0.3802 | 0.0241 | 0.9228 | |
| Second-order | 90 | 1/(Ct/C0) = 0.0015t + 1.0339 | 0.0015 | 0.8108 |
| 120 | 1/(Ct/C0) = 0.0059t + 0.9220 | 0.0059 | 0.9424 | |
| 150 | 1/(Ct/C0) = 0.1614t − 3.2556 | 0.1614 | 0.7711 |
| Kinetic Model | Temperature (°C) | Kinetic Equation | kT (μg/L·min) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-order | 90 | Ct/C0 = −0.0036t + 0.9289 | 0.0036 | 0.9652 |
| 120 | Ct/C0 = −0.0052t + 0.8039 | 0.0052 | 0.8662 | |
| 150 | Ct/C0 = −0.0114t + 0.8870 | 0.0114 | 0.9010 | |
| First-order | 90 | ln(Ct/C0) = −0.0064t − 0.0023 | 0.0064 | 0.9634 |
| 120 | ln(Ct/C0) = −0.0207t + 0.1271 | 0.0207 | 0.9910 | |
| 150 | ln(Ct/C0) = −0.0501t + 0.2379 | 0.0501 | 0.9300 | |
| Second-order | 90 | 1/(Ct/C0) = 0.0126t + 0.7976 | 0.0126 | 0.8805 |
| 120 | 1/(Ct/C0) = 0.1822t − 5.0421 | 0.1822 | 0.8307 | |
| 150 | 1/(Ct/C0) = 0.3200t − 1.7988 | 0.3200 | 0.7968 |
| Kinetic Model | Temperature (°C) | Kinetic Equation | kT (μg/L·min) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without cysteine | 90 | Ct/C0 = 0.9683 exp(−0.001t) | 0.001 | 0.7977 |
| 120 | Ct/C0 = 1.0358 exp(−0.004t) | 0.004 | 0.9450 | |
| 150 | Ct/C0 = 1.4633 exp(−0.024t) | 0.024 | 0.9227 | |
| With cysteine | 90 | Ct/C0 = 0.9971 exp(−0.006t) | 0.006 | 0.9641 |
| 120 | Ct/C0 = 1.1370 exp(−0.021t) | 0.021 | 0.9910 | |
| 150 | Ct/C0 = 1.2694 exp(−0.050t) | 0.050 | 0.9297 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diao, E.; Ma, K.; Zhang, H.; Xie, P.; Qian, S.; Song, H.; Mao, R.; Zhang, L. Thermal Stability and Degradation Kinetics of Patulin in Highly Acidic Conditions: Impact of Cysteine. Toxins 2021, 13, 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13090662
Diao E, Ma K, Zhang H, Xie P, Qian S, Song H, Mao R, Zhang L. Thermal Stability and Degradation Kinetics of Patulin in Highly Acidic Conditions: Impact of Cysteine. Toxins. 2021; 13(9):662. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13090662
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiao, Enjie, Kun Ma, Hui Zhang, Peng Xie, Shiquan Qian, Huwei Song, Ruifeng Mao, and Liming Zhang. 2021. "Thermal Stability and Degradation Kinetics of Patulin in Highly Acidic Conditions: Impact of Cysteine" Toxins 13, no. 9: 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13090662
APA StyleDiao, E., Ma, K., Zhang, H., Xie, P., Qian, S., Song, H., Mao, R., & Zhang, L. (2021). Thermal Stability and Degradation Kinetics of Patulin in Highly Acidic Conditions: Impact of Cysteine. Toxins, 13(9), 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13090662