Occurrence and Seasonal Monitoring of Domoic Acid in Three Shellfish Species from the Northern Adriatic Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Validation of Analytical Method
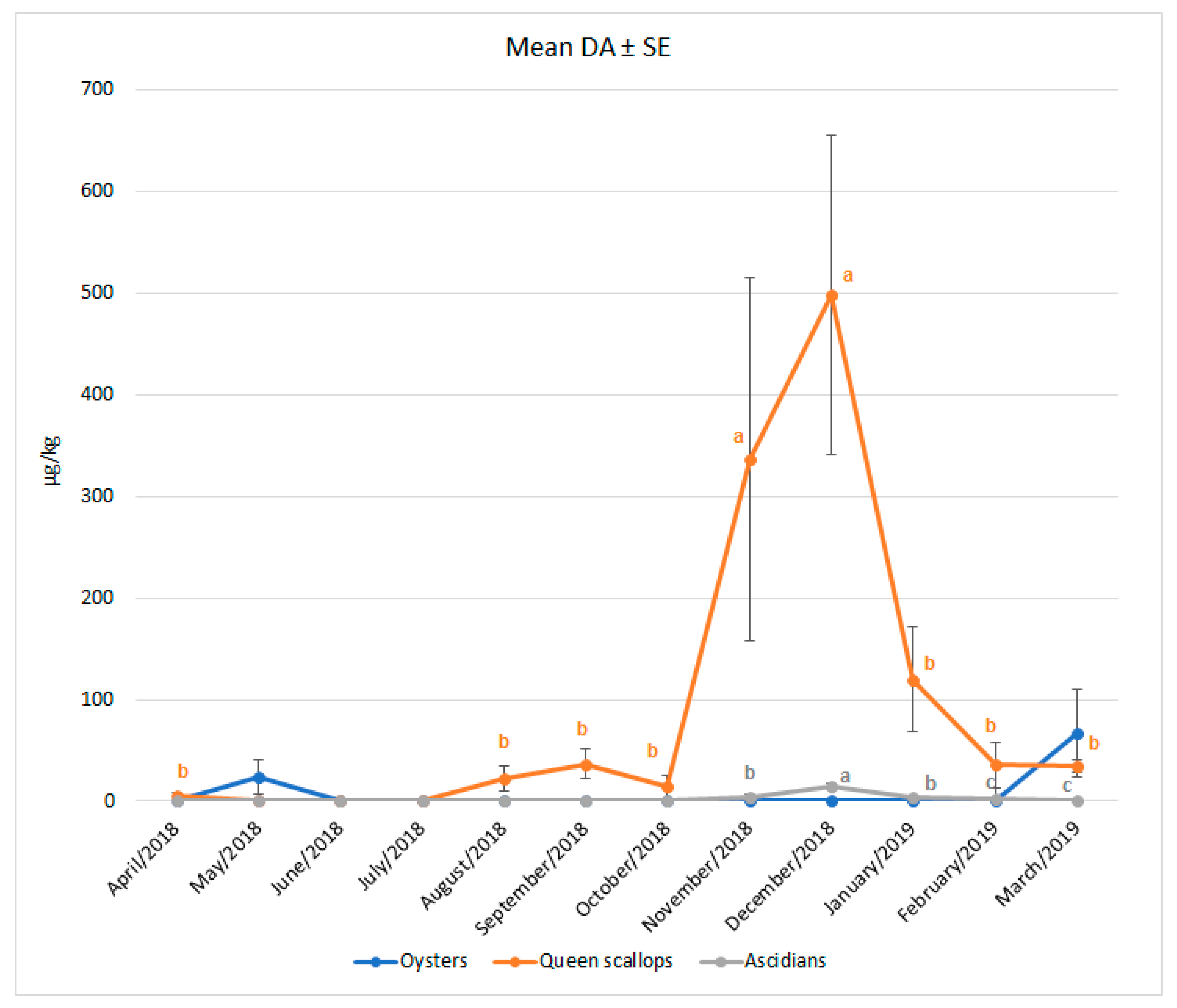
2.2. Domoic Acid in Bivalves and Ascidians
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. The Collection of Samples
4.2. Chemicals and Analytical Standard
4.3. Sample Preparation
4.4. LC-MS/MS Analyses
4.5. Validation
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, F.M. The Nutritional Value of Shellfish in Fisheries, Aquaculture and Seafood. Wash. Sea Grant. Available online: https://wsg.washington.edu/wordpress/wpcontent/uploads/publications/Nutritional-Value-of-Shellfish.pdf (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Phillips, K.M.; Ruggio, D.M.; Exler, J.; Patterson, K.Y. Sterol composition of shellfish species commonly consumed in the United States. Food Nutr. Res. 2012, 56, 18931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rittenschober, D.; Nowak, V.; Charrondiere, R. Review of availability of food composition data for fish and shellfish. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 4303–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). FAO/INFOODS Global Food Composition Database for Fish and Shellfish Version 1.0-uFiSh1.0. Available online: http://www.fao.org/infoods/infoods/tables-and-databases/faoinfoods-databases/en/ (accessed on 5 May 2018).
- Lambert, G.; Karney, R.C.; Rhee, W.Y.; Carman, M.R. Wild and cultured edible tunicates: A review. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2016, 7, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Mahony, M. EU Regulatory risk management of marine biotoxins in the marine bivalve mollusc food-chain. Toxins 2018, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolas, J.; Hoogenboom, R.L.A.P.; Hendriksen, P.J.M.; Bodero, M.; Bovee, T.F.H.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Gerssen, A. Marine biotoxins and associated outbreaks following seafood consumption: Prevention and surveillance in the 21st century. Glob. Food Secur. 2017, 15, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminiello, P.; Fattorusso, E. Bivalve molluscs as vectors of marine biotoxins involved in seafood poisoning. Progr. Mol. Subcell. Biol. 2006, 43, 53–82. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, A.F.; Awan, S.A.; Ling, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, S. Domoic acid: Attributes, exposure risks, innovative detection techniques and therapeutics. Algal Res. 2017, 24, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farabegoli, F.; Blanco, L.; Rodríguez, L.P.; Vieites, J.M.; Cabado, A.G. Phycotoxins in marine shellfish: Origin, occurrence and effects on humans. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bates, S.S.; Beach, D.G.; Comeau, L.A.; Haigh, N.; Lewis, N.I.; Locke, A.; Martin, J.L.; McCarron, P.; McKenzie, C.H.; Michel, C.; et al. Marine Harmful Algal Blooms and Phycotoxins of Concern to Canada; Fisheries and Oceans Canada: Moncton, NB, Canada, 2020; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343365663_Marine_harmful_algal_blooms_and_phycotoxins_of_concern_to_Canada_Can_Tech_Rep_Fish_Aquat_Sci (accessed on 8 May 2020).
- Ujević, I.; Roje-Busatto, R.; Ezgeta-Balić, D. Comparison of Amnesic, Paralytic and Lipophilic Toxins profiles in cockle (Acanthocardia tuberculata) and smooth clam (Callista chione) from the central Adriatic Sea (Croatia). Toxicon 2019, 159, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchouicha-Smida, D.; Lundholm, N.; Sahraoui, I.; Lambert, C.; Mabrouk, H.H.; Hlaili, A.S. Detection of domoic acid in Mytilus galloprovincialis and Ostrea edulis linked to the presence of Nitzschia bizertensis in Bizerte Lagoon (SW Mediterranean). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 165, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, Y.; Sato, S.; Viet Ha, D.; Montojo, U.M.; Lirdwitayaprasit, T.; Kamolsiripichaiporn, S.; Kotaki, Y.; Fukuyo, Y.; Kodama, M. Occurrence of domoic acid in tropical bivalves. Fish. Sci. 2009, 75, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picot, C.; Limon, G.; Durand, G.; Wesolek, N.; Parent-Massin, D.; Roudot, A.C. Domoic Acid, Okadaic Acid and Spirolides: Inter-Species Variability in Contamination and Cooking Effects. Food Public Health 2012, 2, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanco, J.; Mariño, C.; Martín, H.; Álvarez, G.; Rossignoli, A.E. Characterization of the Domoic Acid Uptake Mechanism of the Mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) Digestive Gland. Toxins 2021, 13, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novaczek, I.; Madhyastka, M.S.; Ablett, R.F.; Donald, A.; Johnson, G.; Nijjar, M.S.; Sims, D.E. Depuration of domoic acid from live blue mussels (Mytilus edulis). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1992, 49, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Bermúdez de la Puente, M.; Arévalo, F.; Salgado, C.; Moroño, Á. Depuration of mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) contaminated with domoic acid. Aquat. Living Resour. 2002, 15, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, G.; Uribe, E.; Regueiro, J.; Martin, H.; Gajardo, T.; Jara, L.; Blanco, J. Depuration and anatomical distribution of domoic acid in the surf clam Mesodesma donacium. Toxicon 2015, 102, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, G.; José Rengel, J.; Araya, M.; Álvarez, F.; Pino, R.; Uribe, E.; Díaz, P.A.; Rossignoli, A.E.; López-Rivera, A.; Blanco, J. Rapid Domoic Acid Depuration in the Scallop Argopecten purpuratus and Its Transfer from the Digestive Gland to Other Organs. Toxins 2020, 12, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainer, V.L.; Bill, B.D. Characterization of a domoic acid binding site from Pacific razor clam. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 69, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Acosta, C.P.; de la Puente, M.B.; Salgado, C. Depuration and anatomical distribution of the amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP) toxin domoic acid in the king scallop Pecten maximus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2002, 60, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventoso, P.; Pazos, A.J.; Pérez-Parallé, M.L.; Blanco, J.; Triviño, J.C.; Sánchez, J.L. RNA-Seq Transcriptome Profiling of the Queen Scallop (Aequipecten opercularis) Digestive Gland after Exposure to Domoic Acid-Producing Pseudo-nitzschia. Toxins 2019, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dizer, H.; Fischer, B.; Harabawy, A.S.A.; Hennion, M.-C.; Hansen, P.-D. Toxicity of domoic acid in the marine mussel Mytilus edulis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2001, 55, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.O.; Whyte, J.N.C.; Ginther, N.G.; Townsend, L.D.; Iwama, G.K. Haemocyte Changes In The Pacific Oyster, Crassostrea Gigas, Caused By Exposure To Domoic Acid In The Diatom Pseudonitzschia Pungens F. Multiseries. Toxicon 1995, 33, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.O.; Whyte, J.N.C.; Townsend, L.D.; Ginther, N.G.; Iwama, G.K. Effects of domoic acid on haemolymph pH, PCO, and PO, in the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas and the California mussel, Mytilus californianus. Aquat. Toxicol. 1995, 31, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Kelly, M.S.; Campbell, D.A.; Dong, S.L.; Zhua, J.X.; Wang, S.F. Exposure to domoic acid affects larval development of king scallop Pecten maximus (Linnaeus, 1758). Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 81, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Kelly, M.S.; Campbell, D.A.; Fang, J.; Zhu, J. Accumulation of domoic acid and its effect on juvenile king scallop Pecten maximus (Linnaeus, 1758). Aquaculture 2008, 284, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzl, T.; Haedrich, J.; Schaechtele, A.; Robouch, P.; Stroka, J. Guidance Document on the Estimation of LOD and LOQ for Measurements in the Field of Contaminants in Feed and Food. EUR 28099; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszewski, B.K.; Constanzer, M.L.; Chavez-Eng, C.M. Strategies for the assessment of matrix effect in quantitative bioanalytical methods based on HPLC-MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 3019–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, S.; Wang, P.G. Matrix effects and application of matrix effect factor. Bioanalysis 2017, 9, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panuwet, P.; Hunter, R.E., Jr.; D’Souza, P.E.; Chen, X.; Radford, S.A.; Cohen, J.R.; Marder, M.E.; Kartavenka, K.; Bary, R.P.; Boyd, B.D. Biological matrix effects in quantitative tandem mass spectrometry-based analytical methods: Advancing biomonitoring. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2016, 46, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The European Parliament; The Council of the European Union. Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 laying down specific hygiene rules for food of animal origin. Off. J. Eur. Union 2004, 139, 55–205. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2004/853/oj (accessed on 10 June 2018).
- Mafra, L.L., Jr.; Bricelj, M.; Ward, J.E. Mechanisms contributing to low domoic acid uptake by oysters feeding on Pseudo-nitzschia cells. II. Selective rejection. Aquat. Biol. 2009, 6, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafra, L.L., Jr.; Bricelj, M.; Ouellettea, C.; Bates, S.S. Feeding mechanics as the basis for differential uptake of the neurotoxin domoic acid by oysters, Crassostrea virginica, and mussels, Mytilus edulis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 97, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafra, L.L., Jr.; Bricelj, V.M.; Fennel, K. Domoic acid uptake and elimination kinetics in oysters and mussels in relation to body size and anatomical distribution of toxin. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 100, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blanco, J.; Mauríz, A.; Álvarez, G. Distribution of Domoic Acid in the Digestive Gland of the King Scallop Pecten maximus. Toxins 2020, 12, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Acosta, C.P.; Mariño, C.; Muñiz, S.; Martín, H.; Moroño, A.; Correa, J.; Arévalo, F.; Salgado, C. Depuration of domoic acid from different body compartments of the king scallop Pecten maximus grown in raft culture and natural bed. Aquat. Living Resour. 2006, 19, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlgeschaffen, G.D.; Mann, K.H.; Subba Rao, D.V.; Pocklington, R. Dynamics of the phycotoxin domoic acid: Accumulation and excretion in two commercially important bivalves. J. Appl. Phycol. 1992, 4, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, P.; Sampayo, M.A.M. Domoic acid in Portuguese shellfish and fish. Toxicon 2001, 39, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.E.; Marks, L.J.; Gilgan, M.W.; Pfeiffer, E.; Zwicker, B.M. Microbial utilization of the neurotoxin domoic acid: Blue mussels (Mytilus edulis) and soft shell clams (Mya arenaria) as sources of the microorganisms. Can. J. Microbiol. 1998, 44, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coma, R.; Ribes, M.; Gili, J.; Hughes, R.N. The ultimate opportunists: Consumers of seston. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 219, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, B.A.; Bricelj, V.M.; Shumway, S.E. Physiology: Energy Acquisition and Utilisation. In Scallops: Biology, Ecology and Aquaculture, 2nd ed.; Shumway, S., Parsons, G.J., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 40, pp. 417–492. [Google Scholar]
- Barillé, L.; Cognie, B. Revival Capacity of Diatoms in Bivalve Pseudofaeces and Faeces. Diatom Res. 2000, 15, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armsworthy, S.L.; MacDonald, B.A.; Ward, E. Feeding activity, absorption efficiency and suspension feeding processes in the ascidian, Halocynthia pyriformis (Stolidobranchia: Ascidiacea): Responses to variations in diet quantity and quality. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2001, 260, 41–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, I.J. Food Passage and Defaecation an Ciona intestinalis (L.); The Effects of Suspension Quantity and Quality. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1985, 89, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi, Y.; Shenkar, N.; Ward, J.E.; Rosa, M.; Ramon, G.Z.; Shavit, U.; Yahel, G. Evasive plankton: Size-independent particle capture by ascidians. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guéguen, M.; Lassus, P.; Laabir, M.; Bardouil, M.; Baron, R.; Séchet, V.; Truquet, P.; Amzil, Z.; Barillé, L. Gut passage times in two bivalve molluscs fed toxic microalgae: Alexandrium minutum, A. catenella and Pseudo-nitzschia calliantha. Aquat. Living Resour. 2008, 21, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauriz, A.; Blanco, J. Distribution and linkage of domoic acid (amnesic shellfish poisoning toxins) in subcellular fractions of the digestive gland of the scallop Pecten maximus. Toxicon 2010, 55, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, J.C.; Ogata, T.; Veit, C.H.; Kodama, M. Occurrence of Tetrodotoxin and Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Phallusia nigra (Tunicata, Ascidiacea) From the Brazilian Coast. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins 1996, 2, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rivera, A.; Pinto, M.; Insinilla, A.; Suárez Isla, B.; Uribe, E.; Alvarez, G.; Lehane, M.; Furey, A.; James, K.J. The occurrence of domoic acid linked to a toxic diatom bloom in a new potential vector: The tunicate Pyura chilensis (piure). Toxicon 2009, 54, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roje-Busatto, R.; Ujević, I. PSP toxins profile in ascidian Microcosmus vulgaris (Heller, 1877) after human poisoning in Croatia (Adriatic Sea). Toxicon 2014, 79, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M.; Magno, G.S.; Tartaglione, L.; Quilliam, M.A.; Tubaro, A.; Poletti, R. Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry for determination of domoic acid in Adriatic shellfish. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 2030–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arapov, J. A Review of shellfish phycotoxin profile and toxic phytoplankton species along Croatian coast of the Adriatic Sea. Acta Adriat. 2013, 54, 283–298. [Google Scholar]
- Ljubešić, Z.; Bosak, S.; Viličić, D.; Kralj Borojević, K.; Marić, D.; Godrijan, J.; Ujević, I.; Peharec, P.; Ðakovac, T. Ecology and taxonomy of potentially toxic Pseudo-nitzschia species in Lim Bay (north-eastern Adriatic Sea). Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujević, I.; Ninčević-Gladan, Ž.; Roje, R.; Skejić, S.; Arapov, J.; Marasović, I. Domoic Acid—A New Toxin in the Croatian Adriatic Shellfish Toxin Profile. Molecules 2010, 15, 6835–6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rijal Leblad, B.; Lundholm, N.; Goux, D.; Veron, B.; Sagou, R.; Taleb, A.; Nhhala, H.; Er-Raioui, H. Pseudo-nitzschia Peragallo (Bacillariophyceae) diversity and domoic acid accumulation in tuberculate cockles and sweet clams in M’diq Bay, Morocco. Acta Bot. Croat. 2013, 72, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassoun, A.E.R.; Ujević, I.; Mahfouz, C.; Fakhri, M.; Roje-Busatto, R.; Jemaa, S.; Nazlić, N. Occurrence of domoic acid and cyclic imines in marine biota from Lebanon-Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 755, 142542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stonik, I.V.; Orlova, T.Y. The Seasonal Accumulation of Amnesic Toxin (Domoic Acid) in Commercial Bivalves Mytilus trossulus Gould, 1850 and Mizuhopecten yessoensis Jay, 1850 in Vostok Bay, Sea of Japan. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2020, 46, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qin, J.G.; Abbott, C.A.; Li, X.; Benkendorff, K. Synergistic impacts of heat shock and spawning on the physiology and immune health of Crassostrea gigas: An explanation for summer mortality in Pacific oysters. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 293, 2353–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Qin, J.G.; Abbott, C.A.; Li, X.; Benkendorff, K. Monthly variation of condition index, energy reserves and antibacterial activity in Pacific oysters, Crassostrea gigas, in Stansbury (South Australia). Aquaculture 2009, 286, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qin, J.G.; Abbott, C.A.; Li, X.; Benkendorff, K. Spawning-dependent stress response to food deprivation in Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Aquaculture 2009, 286, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brokordt, K.; Pérez, H.; Herrera, C.; Gallardo, A. Reproduction reduces HSP70 expression capacity in Argopecten purpuratus scallops subject to hypoxia and heat stress. Aquat. Biol. 2015, 23, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brokordt, K.; Defranchi, Y.; Espósito, I.; Cárcamo, C.; Schmitt, P.; Mercado, L.; de la Fuente-Ortega, E.; Rivera-Ingraham, G.A. Reproduction Immunity Trade-Off in a Mollusk: Hemocyte Energy Metabolism Underlies Cellular and Molecular Immune Responses. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turon, X. The ascidians of Tossa de Mar (Girona, NE of Spain). II.-Biological cycles of the colonial species. Cah. Biol. Mar. 1988, 29, 407–418. [Google Scholar]
- Raijman Nagar, L.; Shenkar, N. From Tropical to Sub-Tropical: Prolonged Reproductive Activity of the Invasive Ascidian Microcosmus exasperatus in the Eastern Mediterranean. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 4, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amzil, Z.; Fresnel, J.; Dominique Le Gal, D.; Billard, C. Domoic acid accumulation in French shellfish in relation to toxic species of Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries and P. pseudodelicatissima. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viličić, D.; Đakovac, T.; Zrinka, B.; Bosak, S. Composition and annual cycle of phytoplankton assemblages in the northeastern Adriatic Sea. Bot. Mar. 2009, 52, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, D.G.; Liu, H.; Quilliam, M.A. Sensitive determination of domoic acid in mussel tissue using dansyl chloride derivatization and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2014, 7, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EC—European Commission. Commission Decision 2002/657/EC of 12th August 2002 implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC concerning the performance of analytical methods and the interpretation of results. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2002, 50, 8–36. [Google Scholar]

| Calibration Level (μg/kg) | sr (μg/kg) | Rsr (%) | swR (μg/kg) | RswR (%) | Recovery (%) | Δ (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 4.3 | 9.5 | 5.3 | 10.6 | 93 | 18 |
| 250 | 19.9 | 8.0 | 21.2 | 8.5 | 94 | 14 |
| 500 | 39.5 | 7.9 | 41.6 | 8.3 | 94 | 14 |
| 1000 | 78.9 | 7.9 | 7.9 | 8.3 | 94 | 14 |
| Species | n | % of Positives * | Mean ± SE of Positives * (μg/kg) | Maximum (μg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| European oysters | 46 | 17 | 65.6 ± 10.3 b | 212 |
| Queen scallops | 53 | 57 | 153 ± 32.1 a | 810 |
| Ascidians | 107 | 33 | 5.5 ± 0.6 b | 24.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kvrgić, K.; Lešić, T.; Džafić, N.; Pleadin, J. Occurrence and Seasonal Monitoring of Domoic Acid in Three Shellfish Species from the Northern Adriatic Sea. Toxins 2022, 14, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14010033
Kvrgić K, Lešić T, Džafić N, Pleadin J. Occurrence and Seasonal Monitoring of Domoic Acid in Three Shellfish Species from the Northern Adriatic Sea. Toxins. 2022; 14(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14010033
Chicago/Turabian StyleKvrgić, Kristina, Tina Lešić, Natalija Džafić, and Jelka Pleadin. 2022. "Occurrence and Seasonal Monitoring of Domoic Acid in Three Shellfish Species from the Northern Adriatic Sea" Toxins 14, no. 1: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14010033
APA StyleKvrgić, K., Lešić, T., Džafić, N., & Pleadin, J. (2022). Occurrence and Seasonal Monitoring of Domoic Acid in Three Shellfish Species from the Northern Adriatic Sea. Toxins, 14(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14010033






