Current Advances, Research Needs and Gaps in Mycotoxins Biomonitoring under the HBM4EU—Lessons Learned and Future Trends
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Human Exposure to Mycotoxins
1.2. Mycotoxins in the Context of the HBM4EU Initiative
1.3. Prioritized Mycotoxins: Occurrence, Toxicological Properties and Exposure Thresholds
2. Results Obtained for DON and FB1 in the Scope of the HBM4EU Initiative
2.1. Hazard Assessment
2.1.1. Toxicokinetics (TK)
2.1.2. Main Health Effects Identified for DON and FB1
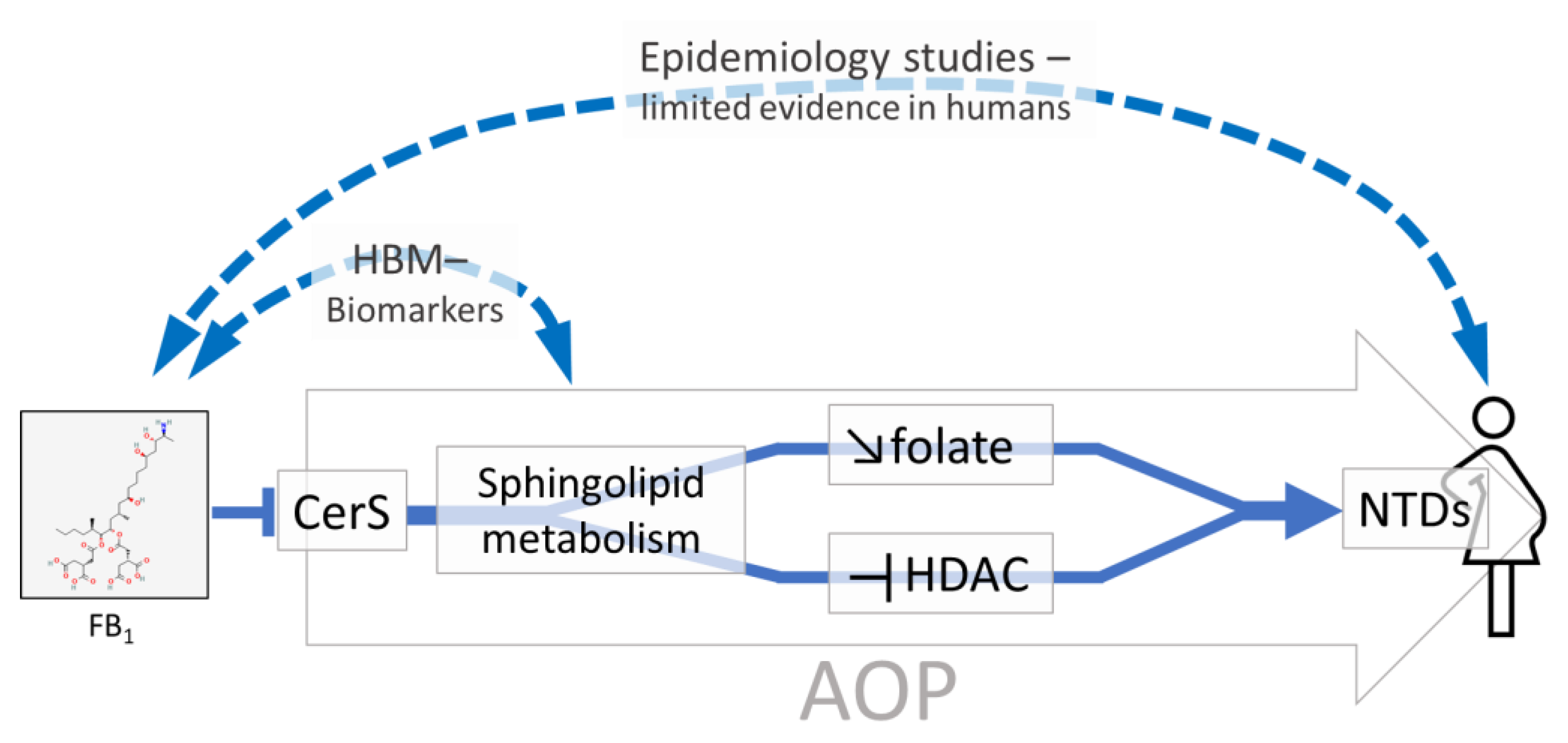
2.1.3. Development of AOPs for FB1 Based on Mechanistic Knowledge
2.1.4. Effect Biomarkers in HBM Studies
2.1.5. Derivation of a HBM-GV for DON
2.1.6. Responses to Policy Questions on Hazard Assessment
2.2. Exposure Assessment
2.2.1. Mycotoxin Exposure Biomarkers
2.2.2. Exposure Scenarios and Levels of the EU Population
Literature Search
Aligned Studies
2.2.3. Responses to Policy Questions on Exposure Assessment
2.3. Risk Characterization
2.3.1. Approaches to the Risk Characterization of DON
2.3.2. Responses to Policy Questions on Risk Characterization
3. Overview of the Main Achievements of the HBM4EU on Mycotoxins and Future Trends
3.1. Policy Relevance
3.2. Future Trends and Research Needs
4. Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 15-ADON | 15-acetyldeoxynivalenol |
| 3-ADON | 3-acetyldeoxynivalenol |
| AOP | Adverse Outcome Pathway |
| BMDL | Benchmark dose (lower confidence limit) |
| bw | Body weight |
| CerS | Ceramide synthase |
| crt | Creatinine |
| DG SANTE | Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety |
| DOM-1 | Deepoxy-deoxynivalenol |
| DON | Deoxynivalenol |
| DON-15-GlcA | Deoxynivalenol-15-glucuronide |
| DON-15-GlcA (fabs_excr) | DON-15-GlcA residence time and excreted fraction |
| DON-3G | Deoxynivalenol-3-glucoside |
| DON-3-GlcA | Deoxynivalenol-3-glucuronide |
| EFSA | European Food Safety Authority |
| EU | European |
| FB1–4 | Fumonisins B1,2,3,4 |
| fDON | free DON |
| HBM | Human Biomonitoring |
| HBM4EU | European Human Biomonitoring Initiative |
| HBM-GV | Human Biomonitoring Guidance Value |
| HDAC | Histone deacetylase |
| HFB1 | Hydrolysed FB1 |
| HQ | Hazard quotient |
| IARC | International Agency for Research on Cancer |
| ICI | Interlaboratory comparison investigation |
| LC-MS-MS | Liquid Chromatography with tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| LOQ | Limit of Quantification |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| MIE | Molecular Initiating Event |
| NCM-FB1 | N-(carboxymethyl)-FB1 |
| NDF-FB1 | N-(1-deoxy-D-fructos-1-yl)-FB1 |
| NTDs | Neural Tube Defects |
| pHFB1 | Partially hydrolysed FB1 |
| QA/QC | Quality Assurance/Quality Control |
| RA | Risk assessment |
| RDF | Reverse Dosimetry Factor |
| Sa | Sphinganine |
| So | Sphingosine |
| SWOT | Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats |
| TDI | Tolerable daily intake |
| tDON | total DON |
| TK | Toxicokinetics |
References
- Bennett, J.W.; Klich, M. Mycotoxins. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Groopman, J.D.; Pestka, J.J. Public Health Impacts of Foodborne Mycotoxins. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 5, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köppen, R.; Koch, M.; Siegel, D.; Merkel, S.; Maul, R.; Nehls, I. Determination of Mycotoxins in Foods: Current State of Analytical Methods and Limitations. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 1595–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louro, H.; Heinälä, M.; Bessems, J.; Buekers, J.; Vermeire, T.; Woutersen, M.; Van Engelen, J.; Borges, T.; Rousselle, C.; Ougier, E.; et al. International Journal of Hygiene and Human Biomonitoring in Health Risk Assessment in Europe: Current Practices and Recommendations for the Future. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viegas, S.; Viegas, C.; Oppliger, A. Occupational Exposure to Mycotoxins: Current Knowledge and Prospects. Ann. Work Expo. Health 2018, 62, 923–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission (EU). Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 Setting Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants in Foodstuffs. EFSA J. 2006, 364, 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA CONTAM Panel (EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain). Scientific Opinion on the Risks for Human and Animal Health Related to the Presence of Modified Forms of Certain Mycotoxins in Food and Feed. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber-Dorninger, C.; Novak, B.; Nagl, V.; Berthiller, F. Emerging Mycotoxins: Beyond Traditionally Determined Food Contaminants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7052–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekwomadu, T.I.; Akinola, S.A.; Mwanza, M. Fusarium Mycotoxins, Their Metabolites (Free, Emerging, and Masked), Food Safety Concerns, and Health Impacts. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvito, P.; Barcelo, J.; De Meester, J.; Rito, E.; Suman, M. Mitigation of Mycotoxins during Food Processing: Sharing Experience among Europe and South East Asia. Sci. Technol. Cereal. Oils Foods 2021, 29, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miraglia, M.; Marvin, H.J.P.; Kleter, G.A.; Battilani, P.; Brera, C.; Coni, E.; Cubadda, F.; Croci, L.; De Santis, B.; Dekkers, S.; et al. Climate Change and Food Safety: An Emerging Issue with Special Focus on Europe. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battilani, P.; Toscano, P.; Van Der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; Moretti, A.; Camardo Leggieri, M.; Brera, C.; Rortais, A.; Goumperis, T.; Robinson, T. Aflatoxin B 1 Contamination in Maize in Europe Increases Due to Climate Change. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assunção, R.; Martins, C.; Viegas, S.; Viegas, C.; Jakobsen, L.S.; Pires, S.; Alvito, P. Climate Change and the Health Impact of Aflatoxins Exposure in Portugal–an Overview. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 2018, 35, 1610–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvito, P.; Assunção, R. Climate Change and the Impact on Aflatoxin Contamination in Foods: Where Are We and What Should Be Expected? In Aflatoxins in Food; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; ISBN 9783030857615. [Google Scholar]
- Zingales, V.; Taroncher, M.; Martino, P.A.; Caloni, F. Climate Change and Effects on Molds and Mycotoxins. Toxins 2022, 14, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizjak, T.; Capodiferro, M.; Deepika, D.; Dinçkol, Ö.; Dzhedzheia, V.; Lopez-Suarez, L.; Petridis, I.; Runkel, A.A.; Schultz, D.R.; Kontić, B. Human Biomonitoring Data in Health Risk Assessments Published in Peer-Reviewed Journals between 2016 and 2021: Confronting Reality after a Preliminary Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Aarøe Mørck, T.; Polcher, A.; Knudsen, L.E.; Joas, A. Review of the State of the Art of Human Biomonitoring for Chemical Substances and Its Application to Human Exposure Assessment for Food Safety. EFSA Support. Publ. 2015, 12, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation (WHO). Biomarkers and Risk Assessment: Concepts and Principles. Environmental Health Criteria 155; WHO Library Cataloguing in Publication Data: Vammala, Finland, 1993; ISBN 9241571551.
- European Commission. EUR-Lex–52004DC0416–EN 2004. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=CELEX:52004DC0416&from=EN (accessed on 4 July 2022).
- Ganzleben, C.; Antignac, J.P.; Barouki, R.; Castaño, A.; Fiddicke, U.; Klánová, J.; Lebret, E.; Olea, N.; Sarigiannis, D.; Schoeters, G.R.; et al. Human Biomonitoring as a Tool to Support Chemicals Regulation in the European Union. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2017, 220, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormsby, J.-N.; Lecoq, P.; Ougier, E.; Rousselle, C.; Ganzleben, C. HBM4EU—Prioritisation, Strategy and Criteria, Deliverable Report D4.3; 2017. Available online: https://www.hbm4eu.eu/work-packages/deliverable-4-3-prioritisation-strategy-and-criteria/ (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Ougier, E.; Ganzleben, C.; Lecoq, P.; Bessems, J.; David, M.; Schoeters, G.; Lange, R.; Meslin, M.; Uhl, M.; Kolossa-gehring, M.; et al. Chemical Prioritisation Strategy in the European Human Biomonitoring Initiative (HBM4EU)—Development and Results. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 236, 113778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeters, G.; Rosa, L.; Kolossa, M.; Barouki, R.; Tarroja, E.; Uhl, M.; Klanova, J.; Melymuk, L.; Horvat, M.; Bocca, B.; et al. HBM4EU—Scoping Documents for 2021 for the First and Second Second Round HBM4EU Priority Substances Deliverable Report D4.9. 2021. Available online: https://www.hbm4eu.eu/work-packages/deliverable-4-9-scoping-documents-for-2021-for-the-first-and-second-second-round-hbm4eu-priority-substances/ (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Schoeters, G.; Lange, R.; Laguzzi, F.; Kadikis, N.; Wasowicz, W.; Santonen, T.; Mahiout, S.; Rudnai, P.; Katsonouri-Sazeides, A.; Alvito, P.; et al. HBM4EU—Scoping Documents for the Second Round Priority Substances Deliverable Report D4.6; 2019. Available online: https://www.hbm4eu.eu/work-packages/deliverable-4-6-scoping-documents-for-the-second-round-priority-substances/ (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Ankley, G.T.; Bennett, R.S.; Erickson, R.J.; Hoff, D.J.; Hornung, M.W.; Johnson, R.D.; Mount, D.R.; Nichols, J.W.; Russom, C.L.; Schmieder, P.K.; et al. Adverse Outcome Pathways: A Conceptual Framework to Support Ecotoxicology Research and Risk Assessment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 29, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA CONTAM Panel (EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain); Knutsen, H.K.; Alexander, J.; Barregård, L.; Bignami, M.; Brüschweiler, B.; Ceccatelli, S.; Cottrill, B.; Dinovi, M.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; et al. Risks to Human and Animal Health Related to the Presence of Deoxynivalenol and Its Acetylated and Modified Forms in Food and Feed. EFSA J. 2017, 15, 4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndossi, D.G.; Frizzell, C.; Tremoen, N.H.; Fæste, C.K.; Verhaegen, S.; Dahl, E.; Eriksen, G.S.; Sørlie, M.; Connolly, L.; Ropstad, E. An in Vitro Investigation of Endocrine Disrupting Effects of Trichothecenes Deoxynivalenol (DON), T-2 and HT-2 Toxins. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 214, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC. Some Naturally Occurring Susbtances: Food Items and Constituents, Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines and Mycotoxins; IARC: Lyon, France, 1993; ISBN 9283212568. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA CONTAM Panel (EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain); Knutsen, H.K.; Barregård, L.; Bignami, M.; Brüschweiler, B.; Ceccatelli, S.; Cottrill, B.; Dinovi, M.; Edler, L.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; et al. Appropriateness to Set a Group Health-Based Guidance Value for Fumonisins and Their Modified Forms. EFSA J. 2018, 16, 5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Some Traditional Herbal Medicines, Some Mycotoxins, Naphthalene and Styrene; IARC: Lyon, France, 2002; Volume 82, ISBN 9789283215875. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, P.C.; White, K.L.M.; Burley, V.J.; Hopton, R.P.; Rajendram, A.; Fisher, J.; Cade, J.E.; Wild, C.P. A Comparison of Deoxynivalenol Intake and Urinary Deoxynivalenol in UK Adults. Biomarkers 2010, 15, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warth, B.; Sulyok, M.; Berthiller, F.; Schuhmacher, R.; Krska, R. New Insights into the Human Metabolism of the Fusarium Mycotoxins Deoxynivalenol and Zearalenone. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 220, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fæste, C.K.; Ivanova, L.; Sayyari, A.; Hansen, U.; Sivertsen, T.; Uhlig, S. Prediction of Deoxynivalenol Toxicokinetics in Humans by in Vitro-to-in Vivo Extrapolation and Allometric Scaling of in Vivo Animal Data. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 2195–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, A.; Claeys, L.; Mengelers, M.; Vanhoorne, V.; Vervaet, C.; Huybrechts, B.; De Saeger, S.; De Boevre, M. Humans Significantly Metabolize and Excrete the Mycotoxin Deoxynivalenol and Its Modified Form Deoxynivalenol-3-Glucoside within 24 Hours. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengelers, M.; Zeilmaker, M.; Vidal, A.; De Boevre, M.; De Saeger, S.; Hoogenveen, R. Biomonitoring of Deoxynivalenol and Deoxynivalenol-3-Glucoside in Human Volunteers: Renal Excretion Profiles. Toxins 2019, 11, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyndrickx, E.; Sioen, I.; Huybrechts, B.; Callebaut, A.; De Henauw, S.; De Saeger, S. Human Biomonitoring of Multiple Mycotoxins in the Belgian Population: Results of the BIOMYCO Study. Environ. Int. 2015, 84, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, A.; Mengelers, M.; Yang, S.; De Saeger, S.; De Boevre, M. Mycotoxin Biomarkers of Exposure: A Comprehensive Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1127–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.; Vidal, A.; De Boevre, M.; De Saeger, S.; Nunes, C.; Torres, D.; Goios, A.; Lopes, C.; Assunção, R.; Alvito, P. Exposure Assessment of Portuguese Population to Multiple Mycotoxins: The Human Biomonitoring Approach. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Brand, A.D.; Hoogenveen, R.; Mengelers, M.J.B.; Zeilmaker, M.; Eriksen, G.S.; Uhlig, S.; Brantsæter, A.L.; Dirven, H.A.A.M.; Husøy, T. Modelling the Renal Excretion of the Mycotoxin Deoxynivalenol in Humans in an Everyday Situation. Toxins 2021, 13, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; del Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Leblanc, J.; Nielsen, E. Assessment of Information as Regards the Toxicity of Fumonisins for Pigs, Poultry and Horses. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, R.T.; Torres, O.; Showker, J.L.; Zitomer, N.C.; Matute, J.; Voss, K.A.; Gelineau-van Waes, J.B.; Maddox, J.R.; Gregory, S.G.; Ashley-Koch, A.E. The Kinetics of Urinary Fumonisin B1 Excretion in Humans Consuming Maize-Based Diets. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, J.K.S.; Vikström, A.C.; Turner, P.; Knudsen, L.E. Deoxynivalenol Transport across the Human Placental Barrier. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 2046–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundheim, L.; Lillegaard, I.; Fæste, C.; Brantsæter, A.-L.; Brodal, G.; Eriksen, G. Deoxynivalenol Exposure in Norway, Risk Assessments for Different Human Age Groups. Toxins 2017, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Technical Report Series: Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- Missmer, S.A.; Suarez, L.; Felkner, M.; Wang, E.; Jr, A.H.M.; Rothman, K.J.; Hendricks, K.A. Exposure to Fumonisins and the Occurrence of Neural Tube Defects along the Texas—Mexico Border. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasas, W.F.O.; Riley, R.T.; Hendricks, K.A.; Stevens, V.L.; Sadler, T.W.; Gelineau-van Waes, J.B.; Missmer, S.A.; Cabrera, J.; Torres, O.; Gelderblom, W.C.A.; et al. Fumonisins Disrupt Sphingolipid Metabolism, Folate Transport, and Neural Tube Development in Embryo Culture and In Vivo: A Potential Risk Factor for Human Neural Tube Defects among Populations Consuming Fumonisin-Contaminated Maize. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, T.J.; Stack, M.E.; Troy, A.L.; Chirtel, S.J. Assessment of the Embryotoxic Potential of the Total Hydrolysis Product of Fumonisin B1 Using Cultured Organogenesis-Staged Rat Embryos. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1997, 35, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelineau-van Waes, J.; Rainey, M.A.; Maddox, J.R.; Voss, K.A.; Sachs, A.J.; Gardner, N.M.; Wilberding, J.D.; Riley, R.T. Increased Sphingoid Base-1-Phosphates and Failure of Neural Tube Closure after Exposure to Fumonisin or FTY720. Birth Defects Res. Part A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2012, 94, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelineau-van Waes, J.; Starr, L.; Maddox, J.; Aleman, F.; Voss, K.A.; Wilberding, J.; Riley, R.T. Maternal Fumonisin Exposure and Risk for Neural Tube Defects: Mechanisms in an In Vivo Mouse Model. Birth Defects Res. 2005, 73, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, S.; Wu, S.; Huang, S.; Lin, J.; Chen, L.; Tang, P. Inhibition of Fumonisin B 1 Cytotoxicity by Nanosilicate Platelets during Mouse Embryo Development. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadler, T.W.; Merrill, A.H.; Stevens, V.L.; Sullards, M.C.; Wang, E.; Wang, P.; Hill, C.; Carolina, N. Prevention of Fumonisin B1-Induced Neural Tube Defects by Folic Acid. Teratology 2002, 176, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, K.A.; Riley, R.T.; Gelineau-van Waes, J.B. Fetotoxicity and Neural Tube Defects in CD1 Mice Exposed to the Mycotoxin Fumonisin B1. Mycotoxins 2006, 2006, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, K.A.; Riley, R.T.; Gelineau-van Waes, J.B. Fumonisin B 1 Induced Neural Tube Defects Were Not Increased in LM/Bc Mice Fed Folate-Deficient Diet. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, K.A.; Riley, R.T.; Snook, M.E.; Gelineau-van Waes, J. Reproductive and Sphingolipid Metabolic Effects of Fumonisin B 1 and Its Alkaline Hydrolysis Product in LM / Bc Mice: Hydrolyzed Fumonisin B 1 Did Not Cause Neural Tube Defects. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 112, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Brand, A.D.; Bajard, L.; Steffensen, I.-L.; Brantsæter, A.L.; Dirven, H.A.A.M.; Louisse, J.; Peijnenburg, A.; Ndaw, S.; Mantovani, A.; De Santis, B.; et al. Providing Biological Plausibility for Exposure–Health Relationships for the Mycotoxins Deoxynivalenol (DON) and Fumonisin B1 (FB1) in Humans Using the AOP Framework. Toxins 2022, 14, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarigiannis, D.; Karkitsios, S.; Frydas, I.; Karakoltzidis, A.; Renieri, E.; Huuskonen, P.; Santonen, T.; Horvat, M.; Tratnik, J.S.; Baken, K.; et al. HBM4EU Final Report on AOPs, Deliverable Report D13.6. 2022. Available online: https://www.hbm4eu.eu/work-packages/deliverable-13-6-final-report-on-aops/ (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Turner, N.; Lim, X.Y.; Toop, H.D.; Osborne, B.; Brandon, A.E.; Taylor, E.N.; Fiveash, C.E.; Govindaraju, H.; Teo, J.D.; Mcewen, H.P.; et al. A Selective Inhibitor of Ceramide Synthase 1 Reveals a Novel Role in Fat Metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Norred, W.P.; Bacon, C.W.; Rileygll, R.T.; Merrill, A.H.; Sl, J. Inhibition of Sphingolipid Biosynthesis by Fumonisins. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 14486–14490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, R.T.; Enongene, E.; Voss, K.A.; Norred, W.P.; Meredith, F.I.; Sharma, R.P.; Spitsbergen, J.; Williams, D.E.; Carlson, D.B.; Merrill, A.H. Sphingolipid Perturbations as Mechanisms for Fumonisin Carcinogenesis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, R.T.; Merrill, A.H. Ceramide Synthase Inhibition by Fumonisins: A Perfect Storm of Perturbed Sphingolipid Metabolism, Signaling, and Disease. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Smith, E.R.; Hanada, K.; Stevens, V.L.; Mayor, S. GPI Anchoring Leads to Sphingolipid-Dependent Retention of Endocytosed Proteins in the Recycling Endosomal Compartment. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hait, N.C.; Wise, L.E.; Allegood, J.C.; O’Brien, M.; Avni, D.; Reeves, T.; Knapp, P.; Lu, J.; Luo, C.; Miles, M.F.; et al. Active, Phosphorylated Fingolimod Inhibits Histone Deacetylases and Facilitates Fear Extinction Memory. Nat Neurosci. 2014, 17, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, N.M.; Riley, R.T.; Showker, J.L.; Voss, K.A.; Sachs, A.J.; Maddox, J.R.; Gelineau-van Waes, J.B. Elevated Nuclear Sphingoid Base-1-Phosphates and Decreased Histone Deacetylase Activity after Fumonisin B1 Treatment in Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 298, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustieles, V.; Rodríguez-Carrillo, A.; Olea, N.; Fernández, M.F. Selection Criteria and Inventory of Effect Biomarkers for the 2nd Set of Substances Deliverable Report D14.5. 2020. Available online: https://www.hbm4eu.eu/work-packages/deliverable-14-5-selection-criteria-and-inventory-of-effect-biomarkers-for-the-2nd-set-of-substances/ (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Rodríguez-Carrillo, A.; Mustieles, V.; Olea, N.; Fernández, M.F.; Cynthia, S.; Legoff, L.; Smagulova, F.; David, A.; Bonefeld-Jørgensen, E.C.; Wielsoe, M.; et al. Report on the State of Development of Task 14.3: Identification of Needs for the Implementation of Both Classical and New Biomarkers of Effect and Decision Criteria for Their Validation Additional Deliverable Report AD14.6. 2020. Available online: https://www.hbm4eu.eu/work-packages/additional-deliverable-14-6-report-on-the-state-of-development-of-task-14-3-identification-of-needs-for-the-implementation-of-both-classical-and-new-biomarkers-of-effect-and-decision-criteria-for-the/ (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Wangia, R.N.; Githanga, D.P.; Xue, K.S.; Tang, L.; Anzala, O.A.; Wang, J.S. Validation of Urinary Sphingolipid Metabolites as Biomarker of Effect for Fumonisins Exposure in Kenyan Children. Biomarkers 2019, 24, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, R.T.; Torres, O.; Matute, J.; Gregory, S.G.; Ashley-koch, A.E.; Showker, J.L.; Mitchell, T.; Voss, K.A.; Maddox, J.R.; Gelineau-van Waes, J.B. Evidence for Fumonisin Inhibition of Ceramide Synthase in Humans Consuming Maize-Based Foods and Living in High Exposure Communities in Guatemala. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 2209–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jaal, B.A.; Jaganjac, M.; Barcaru, A.; Horvatovich, P.; Latiff, A. Aflatoxin, Fumonisin, Ochratoxin, Zearalenone and Deoxynivalenol Biomarkers in Human Biological Fluids: A Systematic Literature Review, 2001–2018. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 129, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephard, G.S.; Van Der Westhuizen, L.; Sewram, V. Biomarkers of Exposure to Fumonisin Mycotoxins: A Review. Food Addit. Contam. 2007, 24, 1196–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, P.; Beausoleil, C.; Lamkarkach, F.; Meslin, M.; Voss, J.U.; Mengelers, M.; Lange, R.; David, M.; Rousselle, C.; Zeman, F.; et al. HBM4EU 3rd Substance Specific Derivation of EU-Wide Health-Based Guidance Values Deliverable Report D5.9. 2022. Available online: https://www.hbm4eu.eu/work-packages/deliverable-5-9-3rd-substance-specific-derivation-of-eu-wide-health-based-guidance-values/ (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Carballo, D.; Pallarés, N.; Ferrer, E.; Barba, F.J.; Berrada, H. Assessment of Human Exposure to Deoxynivalenol, Ochratoxin A, Zearalenone and Their Metabolites Biomarker in Urine Samples Using LC-ESI-qTOF. Toxins 2021, 13, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppa, C.F.S.C.; Cirelli, A.C.; Gonçalves, B.L.; Barnabé, E.M.B.; Petta, T.; Franco, L.T.; Javanmardi, F.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Lee, S.H.I.; Corassin, C.H.; et al. Mycotoxin Occurrence in Breast Milk and Exposure Estimation of Lactating Mothers Using Urinary Biomarkers in São Paulo, Brazil. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 279, 116938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, G.S.; Knutsen, H.K.; Sandvik, M.; Brantsæter, A.L. Urinary Deoxynivalenol as a Biomarker of Exposure in Different Age, Life Stage and Dietary Practice Population Groups. Environ. Int. 2021, 157, 106804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, G.S.; Pettersson, H.; Lindberg, J.E. Absorption, Metabolism and Excretion of 3-Acetyl Don in Pigs. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2003, 57, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbioni, G.; Castaño, A.; Esteban López, M.; Göen, T.; Mol, H.; Riou, M.; Tagne-Fotso, R. Literature Review and Evaluation of Biomarkers, Matrices and Analytical Methods for Chemicals Selected in the Research Program Human Biomonitoring for the European Union (HBM4EU). Environ. Int. 2022, 169, 107458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, A.; Bouzaghnane, N.; De Saeger, S.; De Boevre, M. Human Mycotoxin Biomonitoring: Conclusive Remarks on Direct or Indirect Assessment of Urinary Deoxynivalenol. Toxins 2020, 12, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahiout, S.; Santonen, T.; Joksić, A.Š.; Gerofke, A.; Scholten, B.; Martins, C.; Louro, H.; Tarazona, J.; Niemann, L.; Woutersen, M.; et al. Human Biomonitoring in Risk Assessment: 4th Set of Examples on the Use of HBM in Risk Assessments of HBM4EU Priority Chemicals Deliverable Report D5.11. 2022. Available online: https://www.hbm4eu.eu/work-packages/deliverable-5-11-human-biomonitoring-in-risk-assessment-4th-set-of-examples-on-the-use-of-hbm-in-risk-assessments-of-hbm4eu-priority-chemicals/ (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Lorenz, N.; Dänicke, S.; Edler, L.; Gottschalk, C.; Lassek, E.; Marko, D.; Rychlik, M.; Mally, A. A Critical Evaluation of Health Risk Assessment of Modified Mycotoxins with a Special Focus on Zearalenone. Mycotoxin Res. 2019, 35, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Policy Questions on Mycotoxins under HBM4EU | |
|---|---|
| Hazard assessment | Are there toxicokinetics data for the target mycotoxins and what are their limitations? What are the key events that determine the chronic health effects of the target mycotoxins? What are the most frequent AOP-based effect biomarkers for the prioritized mycotoxins? Is it possible to set HBM guidance values for the target mycotoxins? |
| Exposure assessment | Are there validated and harmonised analytical methods to assess the target mycotoxins’ exposure? Which are the current exposure levels of the European population to DON and FB1? Does the exposure to the target mycotoxins differ among different population groups? Which are the main exposure determinants? |
| Risk characterization | Is the risk associated with human exposure to these mycotoxins characterized? |
| Policy Relevance of Main Achievements |
|---|
| Total DON exposure assessment of the European population through human biomonitoring (internal exposure) using a harmonised and HBM4EU-qualified method was, for the first time, attained. |
| The characterization of the risk from exposure to DON was improved, given the possibility of directly comparing the internal dose measured with the newly derived human biomonitoring guidance value, although some associated uncertainties must still be considered. |
| The assessment of DON exposure and the associated risk characterization contributed to close a data gap on the Eastern European population exposure and evidenced some concern regarding the most exposed population groups that deserve further action. |
| Comparison of dietary exposure through food occurrence and the internal dose of DON is now possible due to the development of a toxicokinetics model, although some refinement might still be needed to evolve to a physiologically based TK model. |
| The characterization of the internal exposure to DON can be used as a baseline level to monitor exposure of the European population to this mycotoxin, e.g., considering climate changes expected. |
| The use of the AOP framework to organize mechanistic data on FB1 provided biological plausibility to the development of congenital anomalies (neural tube defects) associated with early life exposure to FB1. |
| Effect biomarkers have been rarely analysed in epidemiological studies concerning DON and FB1 (and other mycotoxins) exposure and need to be further developed. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.M.; Bajard, L.; Martins, C.; Mengelers, M.J.B.; Mol, H.; Namorado, S.; van den Brand, A.D.; Vasco, E.; Viegas, S.; et al. Current Advances, Research Needs and Gaps in Mycotoxins Biomonitoring under the HBM4EU—Lessons Learned and Future Trends. Toxins 2022, 14, 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120826
Alvito P, Assunção RM, Bajard L, Martins C, Mengelers MJB, Mol H, Namorado S, van den Brand AD, Vasco E, Viegas S, et al. Current Advances, Research Needs and Gaps in Mycotoxins Biomonitoring under the HBM4EU—Lessons Learned and Future Trends. Toxins. 2022; 14(12):826. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120826
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlvito, Paula, Ricardo Manuel Assunção, Lola Bajard, Carla Martins, Marcel J. B. Mengelers, Hans Mol, Sónia Namorado, Annick D. van den Brand, Elsa Vasco, Susana Viegas, and et al. 2022. "Current Advances, Research Needs and Gaps in Mycotoxins Biomonitoring under the HBM4EU—Lessons Learned and Future Trends" Toxins 14, no. 12: 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120826
APA StyleAlvito, P., Assunção, R. M., Bajard, L., Martins, C., Mengelers, M. J. B., Mol, H., Namorado, S., van den Brand, A. D., Vasco, E., Viegas, S., & Silva, M. J. (2022). Current Advances, Research Needs and Gaps in Mycotoxins Biomonitoring under the HBM4EU—Lessons Learned and Future Trends. Toxins, 14(12), 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120826








