Bioactivity Profiling of In Silico Predicted Linear Toxins from the Ants Myrmica rubra and Myrmica ruginodis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
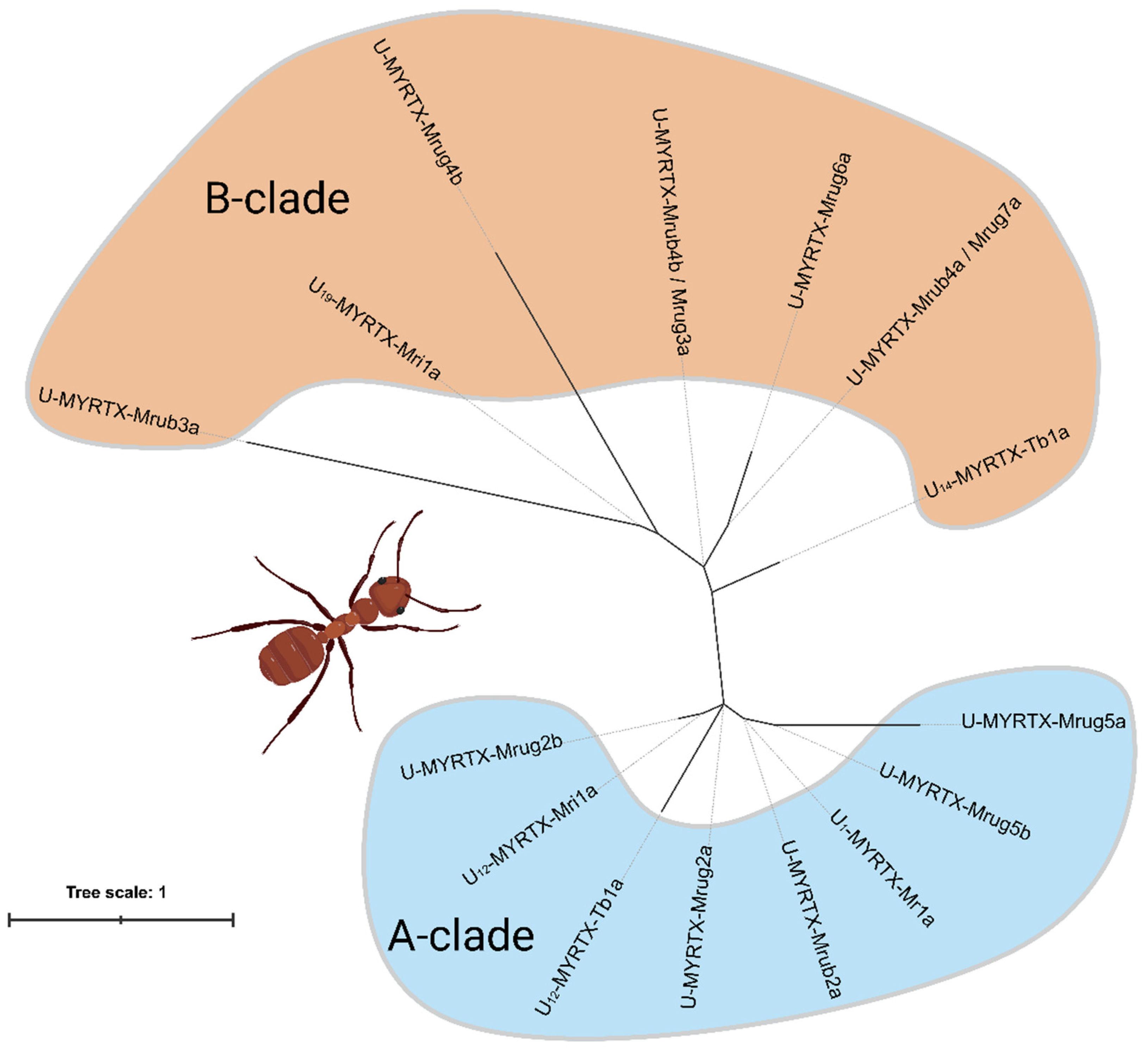
2.1. AMP-like Toxins Are Expressed in M. rubra and M. ruginodis Venom Glands
2.2. No Cytotoxicity but Partly Insecticidal Activity of Tested AMP-like Toxins
2.3. AMP-like Ant Toxins Exert No Protective Effect against Influenza Virus
2.4. Tested Peptides Display Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Effects
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Material and Methods
5.1. Identification of Peptides
5.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
5.3. Peptide Nomenclature
5.4. Peptide Synthesis
5.5. Cytotoxicity Assays
5.6. Antiviral Assay
5.7. Insecticidal Activity
5.8. Antimicrobial Activity
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- California Academy of Science AntWeb. Version 8.81. Available online: https://www.antweb.org/ (accessed on 12 October 2022).
- Bolton, B. AntCat: An Online Catalog of the Ants of the World. Available online: https://antcat.org/ (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Hölldobler, B.; Wilson, E.O. The Ants; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990; ISBN 978-0-674-04075-5. [Google Scholar]
- Eagles, D.A.; Saez, N.J.; Krishnarjuna, B.; Bradford, J.J.; Chin, Y.K.-Y.; Starobova, H.; Mueller, A.; Reichelt, M.E.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Norton, R.S.; et al. A Peptide Toxin in Ant Venom Mimics Vertebrate EGF-like Hormones to Cause Long-Lasting Hypersensitivity in Mammals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2112630119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aili, S.R.; Touchard, A.; Escoubas, P.; Padula, M.P.; Orivel, J.; Dejean, A.; Nicholson, G.M. Diversity of Peptide Toxins from Stinging Ant Venoms. Toxicon 2014, 92, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touchard, A.; Aili, S.; Fox, E.; Escoubas, P.; Orivel, J.; Nicholson, G.; Dejean, A. The Biochemical Toxin Arsenal from Ant Venoms. Toxins 2016, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wanandy, T.; Wilson, R.; Gell, D.; Rose, H.E.; Gueven, N.; Davies, N.W.; Brown, S.G.A.; Wiese, M.D. Towards Complete Identification of Allergens in Jack Jumper (Myrmecia pilosula) Ant Venom and Their Clinical Relevance: An Immunoproteomic Approach. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 1222–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, C.T. Hypersensitivity to Fire Ant Venom. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1996, 77, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-Q.; Yang, T.; Lan, L.-F.; Chen, X.-M.; Huang, D.-B.; Zeng, Z.-L.; Ye, X.-Y.; Wan, C.-L.; Li, L.-N. Ant Sting-Induced Whole-Body Pustules in an Inebriated Male: A Case Report. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 6695–6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aili, S.R.; Touchard, A.; Hayward, R.; Robinson, S.D.; Pineda, S.S.; Lalagüe, H.; Mrinalini; Vetter, I.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Kini, R.M.; et al. An Integrated Proteomic and Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Venom Complexity of the Bullet Ant Paraponera clavata. Toxins 2020, 12, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodou Lima, H.V.; de Paula Cavalcante, C.S.; Rádis-Baptista, G. Antifungal In Vitro Activity of Pilosulin- and Ponericin-Like Peptides from the Giant Ant Dinoponera quadriceps and Synergistic Effects with Antimycotic Drugs. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senetra, A.S.; Necelis, M.R.; Caputo, G.A. Investigation of the Structure-Activity Relationship in Ponericin L1 from Neoponera goeldii. Pept. Sci. 2020, 112, e24162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, S.A.; Robinson, S.D.; Agwa, A.J.; Walker, A.A.; Choudhary, S.; Touchard, A.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Robertson, A.; Vetter, I.; Schroeder, C.I.; et al. Multipurpose Peptides: The Venoms of Amazonian Stinging Ants Contain Anthelmintic Ponericins with Diverse Predatory and Defensive Activities. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 192, 114693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, D.B.; Mello, C.P.; Bandeira, I.C.J.; de Menezes, R.R.P.P.B.; Sampaio, T.L.; Falcão, C.B.; Morlighem, J.-É.R.L.; Rádis-Baptista, G.; Martins, A.M.C. The Dinoponeratoxin Peptides from the Giant Ant Dinoponera quadriceps Display in Vitro Antitrypanosomal Activity. Biol. Chem. 2018, 399, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rádis-Baptista, G.; Dodou, H.V.; Prieto-da-Silva, Á.R.B.; Zaharenko, A.J.; Kazuma, K.; Nihei, K.; Inagaki, H.; Mori-Yasumoto, K.; Konno, K. Comprehensive Analysis of Peptides and Low Molecular Weight Components of the Giant Ant Dinoponera quadriceps Venom. Biol. Chem. 2020, 401, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.F.C.; Huang, C.; Chong, C.-M.; Leung, S.W.; Prieto-da-Silva, Á.R.B.; Havt, A.; Quinet, Y.P.; Martins, A.M.C.; Lee, S.M.Y.; Rádis-Baptista, G. Transcriptome Analysis in Venom Gland of the Predatory Giant Ant Dinoponera quadriceps: Insights into the Polypeptide Toxin Arsenal of Hymenopterans. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guzman, J.; Téné, N.; Touchard, A.; Castillo, D.; Belkhelfa, H.; Haddioui-Hbabi, L.; Treilhou, M.; Sauvain, M. Anti-Helicobacter pylori Properties of the Ant-Venom Peptide Bicarinalin. Toxins 2018, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Téné, N.; Bonnafé, E.; Berger, F.; Rifflet, A.; Guilhaudis, L.; Ségalas-Milazzo, I.; Pipy, B.; Coste, A.; Leprince, J.; Treilhou, M. Biochemical and Biophysical Combined Study of Bicarinalin, an Ant Venom Antimicrobial Peptide. Peptides 2016, 79, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifflet, A.; Gavalda, S.; Téné, N.; Orivel, J.; Leprince, J.; Guilhaudis, L.; Génin, E.; Vétillard, A.; Treilhou, M. Identification and Characterization of a Novel Antimicrobial Peptide from the Venom of the Ant Tetramorium bicarinatum. Peptides 2012, 38, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.O. Chemistry, Pharmacology, and Chemical Ecology of Ant Venoms. In Venoms of the Hymenoptera: Biochemical, Pharmacological and Behavioural Aspects; Piek, T., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1986; pp. 425–508. ISBN 978-0-12-554770-3. [Google Scholar]
- Orivel, J.; Redeker, V.; Le Caer, J.-P.; Krier, F.; Revol-Junelles, A.-M.; Longeon, A.; Chaffotte, A.; Dejean, A.; Rossier, J. Ponericins, New Antibacterial and Insecticidal Peptides from the Venom of the Ant Pachycondyla Goeldii. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 17823–17829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lima, D.B.; Sousa, P.L.; Torres, A.F.C.; Rodrigues, K.A.d.F.; Mello, C.P.; de Menezes, R.R.P.P.B.; Tessarolo, L.D.; Quinet, Y.P.; de Oliveira, M.R.; Martins, A.M.C. Antiparasitic Effect of Dinoponera quadriceps Giant Ant Venom. Toxicon 2016, 120, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, D.B.; Fox, E.G.P.; dos Santos, D.G.; de Sousa, J.S.; Freire, D.M.G.; Nogueira, F.C.S.; Domont, G.B.; de Castilho, L.V.A.; Machado, E.d.A. Fire Ant Venom Alkaloids Inhibit Biofilm Formation. Toxins 2019, 11, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nixon, S.A.; Dekan, Z.; Robinson, S.D.; Guo, S.; Vetter, I.; Kotze, A.C.; Alewood, P.F.; King, G.F.; Herzig, V. It Takes Two: Dimerization Is Essential for the Broad-Spectrum Predatory and Defensive Activities of the Venom Peptide Mp1a from the Jack Jumper Ant Myrmecia pilosula. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüddecke, T.; Vilcinskas, A.; Lemke, S. Phylogeny-Guided Selection of Priority Groups for Venom Bioprospecting: Harvesting Toxin Sequences in Tarantulas as a Case Study. Toxins 2019, 11, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- von Reumont, B.M.; Campbell, L.I.; Jenner, R.A. Quo Vadis Venomics? A Roadmap to Neglected Venomous Invertebrates. Toxins 2014, 6, 3488–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Reumont, B.M.; Anderluh, G.; Antunes, A.; Ayvazyan, N.; Beis, D.; Caliskan, F.; Crnković, A.; Damm, M.; Dutertre, S.; Ellgaard, L.; et al. Modern Venomics—Current Insights, Novel Methods, and Future Perspectives in Biological and Applied Animal Venom Research. GigaScience 2022, 11, giac048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurka, S.; Brinkrolf, K.; Özbek, R.; Förster, F.; Billion, A.; Heep, J.; Timm, T.; Lochnit, G.; Vilcinskas, A.; Lüddecke, T. Venomics of the Central European Myrmicine Ants Myrmica rubra and Myrmica ruginodis. Toxins 2022, 14, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heep, J.; Klaus, A.; Kessel, T.; Seip, M.; Vilcinskas, A.; Skaljac, M. Proteomic Analysis of the Venom from the Ruby Ant Myrmica rubra and the Isolation of a Novel Insecticidal Decapeptide. Insects 2019, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heep, J.; Skaljac, M.; Grotmann, J.; Kessel, T.; Seip, M.; Schmidtberg, H.; Vilcinskas, A. Identification and Functional Characterization of a Novel Insecticidal Decapeptide from the Myrmicine Ant Manica rubida. Toxins 2019, 11, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Touchard, A.; Aili, S.R.; Téné, N.; Barassé, V.; Klopp, C.; Dejean, A.; Kini, R.M.; Mrinalini, M.; Coquet, L.; Jouenne, T.; et al. Venom Peptide Repertoire of the European Myrmicine Ant Manica rubida: Identification of Insecticidal Toxins. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 1800–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touchard, A.; Téné, N.; Song, P.C.T.; Lefranc, B.; Leprince, J.; Treilhou, M.; Bonnafé, E. Deciphering the Molecular Diversity of an Ant Venom Peptidome through a Venomics Approach. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 3503–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichberg, J.; Maiworm, E.; Oberpaul, M.; Czudai-Matwich, V.; Lüddecke, T.; Vilcinskas, A.; Hardes, K. Antiviral Potential of Natural Resources against Influenza Virus Infections. Viruses 2022, 14, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüddecke, T. The Venoms of Insects—Often Overlooked Chemical Arsenals. Antenna 2022, 46, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Krämer, J.; Lüddecke, T.; Marner, M.; Maiworm, E.; Eichberg, J.; Hardes, K.; Schäberle, T.F.; Vilcinskas, A.; Predel, R. Antimicrobial, Insecticidal and Cytotoxic Activity of Linear Venom Peptides from the Pseudoscorpion Chelifer Cancroides. Toxins 2022, 14, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tragust, S.; Herrmann, C.; Häfner, J.; Braasch, R.; Tilgen, C.; Hoock, M.; Milidakis, M.A.; Gross, R.; Feldhaar, H. Formicine Ants Swallow Their Highly Acidic Poison for Gut Microbial Selection and Control. eLife 2020, 9, e60287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, T.N.; Hughes, W.O.H. Adaptive Social Immunity in Leaf-Cutting Ants. Biol. Lett. 2009, 5, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tragust, S.; Mitteregger, B.; Barone, V.; Konrad, M.; Ugelvig, L.V.; Cremer, S. Ants Disinfect Fungus-Exposed Brood by Oral Uptake and Spread of Their Poison. Curr. Biol. CB 2013, 23, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tranter, C.; Graystock, P.; Shaw, C.; Lopes, J.F.S.; Hughes, W.O.H. Sanitizing the Fortress: Protection of Ant Brood and Nest Material by Worker Antibiotics. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2014, 68, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.J.; Papanicolaou, A.; Yassour, M.; Grabherr, M.; Blood, P.D.; Bowden, J.; Couger, M.B.; Eccles, D.; Li, B.; Lieber, M.; et al. De novo Transcript Sequence Reconstruction from RNA-Seq Using the Trinity Platform for Reference Generation and Analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1494–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teufel, F.; Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Johansen, A.R.; Gíslason, M.H.; Pihl, S.I.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 6.0 Predicts All Five Types of Signal Peptides Using Protein Language Models. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The UniProt Consortium UniProt: A Worldwide Hub of Protein Knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D506–D515. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.-T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A Fast Online Phylogenetic Tool for Maximum Likelihood Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An Online Tool for Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, G.F.; Gentz, M.C.; Escoubas, P.; Nicholson, G.M. A Rational Nomenclature for Naming Peptide Toxins from Spiders and Other Venomous Animals. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2008, 52, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miles, A.A.; Misra, S.S.; Irwin, J.O. The Estimation of the Bactericidal Power of the Blood. Epidemiol. Infect. 1938, 38, 732–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, S.M. Plater: Read, Tidy, and Display Data from Microtiter Plates. J. Open Source Softw. 2016, 1, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wickham, H. Reshaping Data with the reshape Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 21, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Toxin | Species | Sequence | Class | #AA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U12-MYRTX-Mri1a * | M. rubida | IDPKLLESLA | IDP | 10 |
| U1-MYRTX-Mr1a * | M. rubra | IDPKVLESLV | IDP | 10 |
| U-MYRTX-Mrub2a | M. rubra | IDPKLLESLA | IDP | 10 |
| U-MYRTX-Mrug2a | M. ruginodis | IDPKVLESLA | IDP | 10 |
| U-MYRTX-Mrug2b | M. ruginodis | IDPKVLESLL | IDP | 10 |
| U-MYRTX-Mrub3a | M. rubra | IDRSEKTERE | IDR | 10 |
| U-MYRTX-Mrub4a/Mrug7a | M. rubra and M. ruginodis | IDSDALKSLQ | IDS | 10 |
| U-MYRTX-Mrub4b/Mrug3a | M. rubra and M. ruginodis | IDSKAIKSLQ | IDS | 10 |
| U-MYRTX-Mrug4b | M. ruginodis | IDVYFILHLP | IDV | 10 |
| U-MYRTX-Mrug5a | M. ruginodis | INPKLWLKLF | INP | 10 |
| U-MYRTX-Mrug5b | M. ruginodis | INPKLLESL | INP | 9 |
| U-MYRTX-Mrug6a | M. ruginodis | KDSDSLKSFQ | KDS | 10 |
| Strain | MIC [µM] | MBC [µM] |
|---|---|---|
| Listeria monocytogenes | (50) | 50 |
| Micrococcus luteus | 6.25 | 6.25 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 50071 | None | None |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 1117 | None | None |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 100 | not to determine |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 50 | 50 |
| Escherichia coli DE3 | 50 | 50 |
| Name | Unique Identifier | OD600 for Assay | CFU/mL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Listeria monocytogenes | DSM 20600 | 0.000625 | 1.45 × 10⁶ |
| Micrococcus luteus | DSM 20030 | 0.005 | 2.20 × 10⁵ |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 50071 | DSM 50071 | 0.00125 | 4.83 × 108 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 1117 | DSM 1117 | 0.005 | 3.00 × 1013 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | DSM 2569 | 0.00125 | 9.00 × 10⁶ |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | ATCC 35984; DSM 28319 | 0.000625 | 1.73 × 10⁶ |
| Escherichia coli DE3 | BL21(DE3) | 0.000325 | 2.00 × 10⁶ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hurka, S.; Lüddecke, T.; Paas, A.; Dersch, L.; Schulte, L.; Eichberg, J.; Hardes, K.; Brinkrolf, K.; Vilcinskas, A. Bioactivity Profiling of In Silico Predicted Linear Toxins from the Ants Myrmica rubra and Myrmica ruginodis. Toxins 2022, 14, 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120846
Hurka S, Lüddecke T, Paas A, Dersch L, Schulte L, Eichberg J, Hardes K, Brinkrolf K, Vilcinskas A. Bioactivity Profiling of In Silico Predicted Linear Toxins from the Ants Myrmica rubra and Myrmica ruginodis. Toxins. 2022; 14(12):846. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120846
Chicago/Turabian StyleHurka, Sabine, Tim Lüddecke, Anne Paas, Ludwig Dersch, Lennart Schulte, Johanna Eichberg, Kornelia Hardes, Karina Brinkrolf, and Andreas Vilcinskas. 2022. "Bioactivity Profiling of In Silico Predicted Linear Toxins from the Ants Myrmica rubra and Myrmica ruginodis" Toxins 14, no. 12: 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120846
APA StyleHurka, S., Lüddecke, T., Paas, A., Dersch, L., Schulte, L., Eichberg, J., Hardes, K., Brinkrolf, K., & Vilcinskas, A. (2022). Bioactivity Profiling of In Silico Predicted Linear Toxins from the Ants Myrmica rubra and Myrmica ruginodis. Toxins, 14(12), 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120846






