Mechanism for the Potential Inhibition Effect of Microcystin-LR Disinfectant By-Products on Protein Phosphatase 2A
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
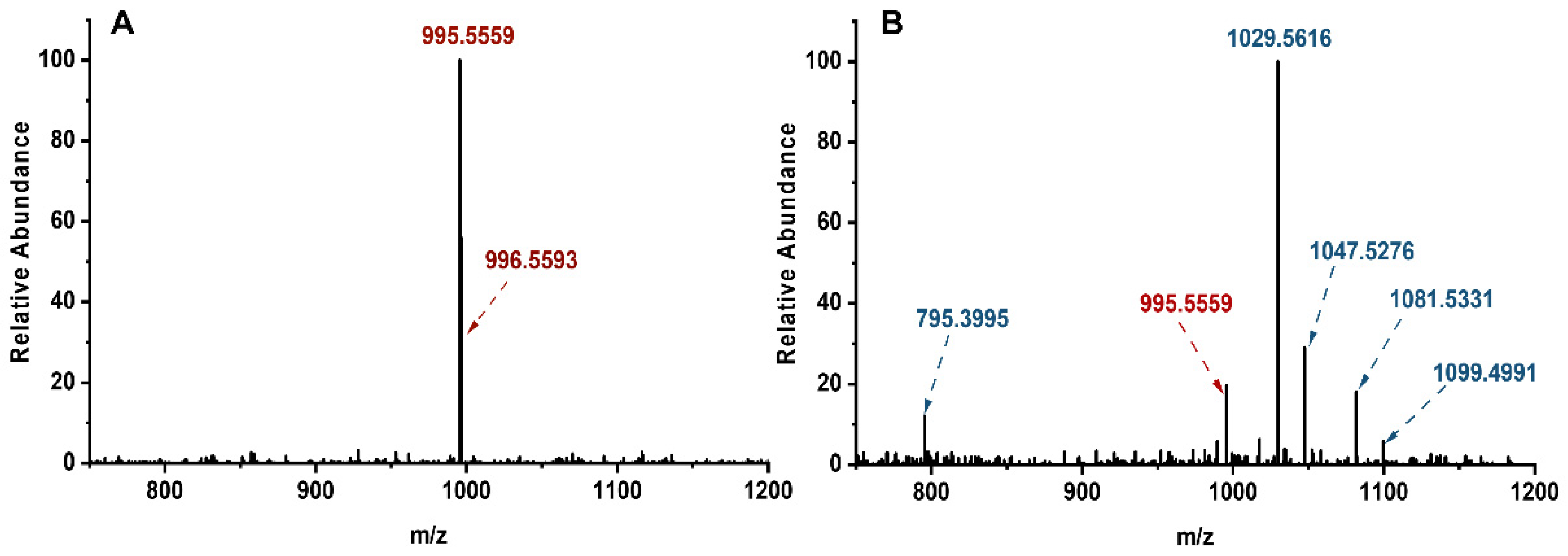
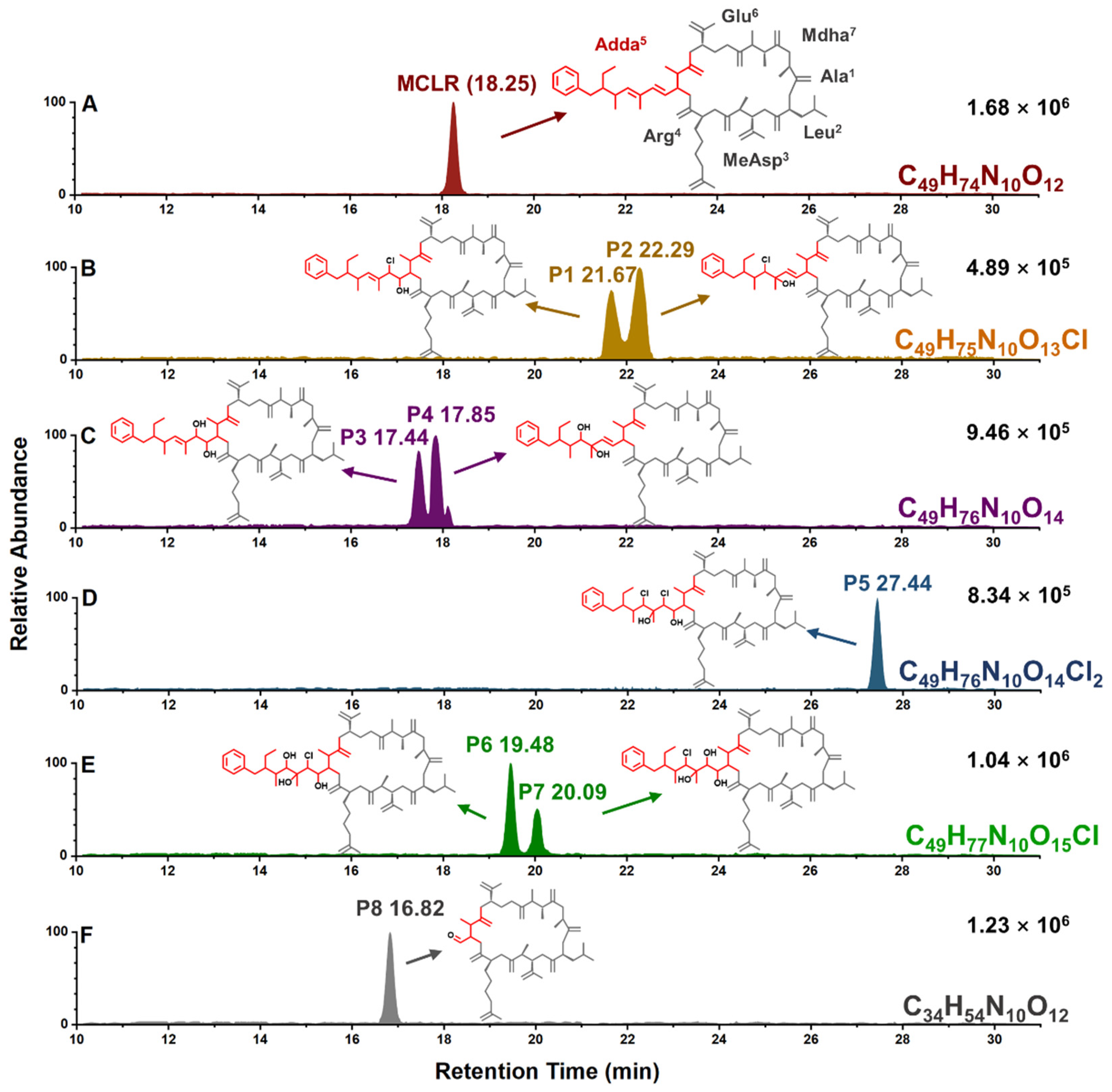
2.1. Typical MCLR-DBPs Identification Based on MS and HPLC Analysis
2.2. Potential Inhibition Effect for Typical MCLR-DBPs Target to PP2A
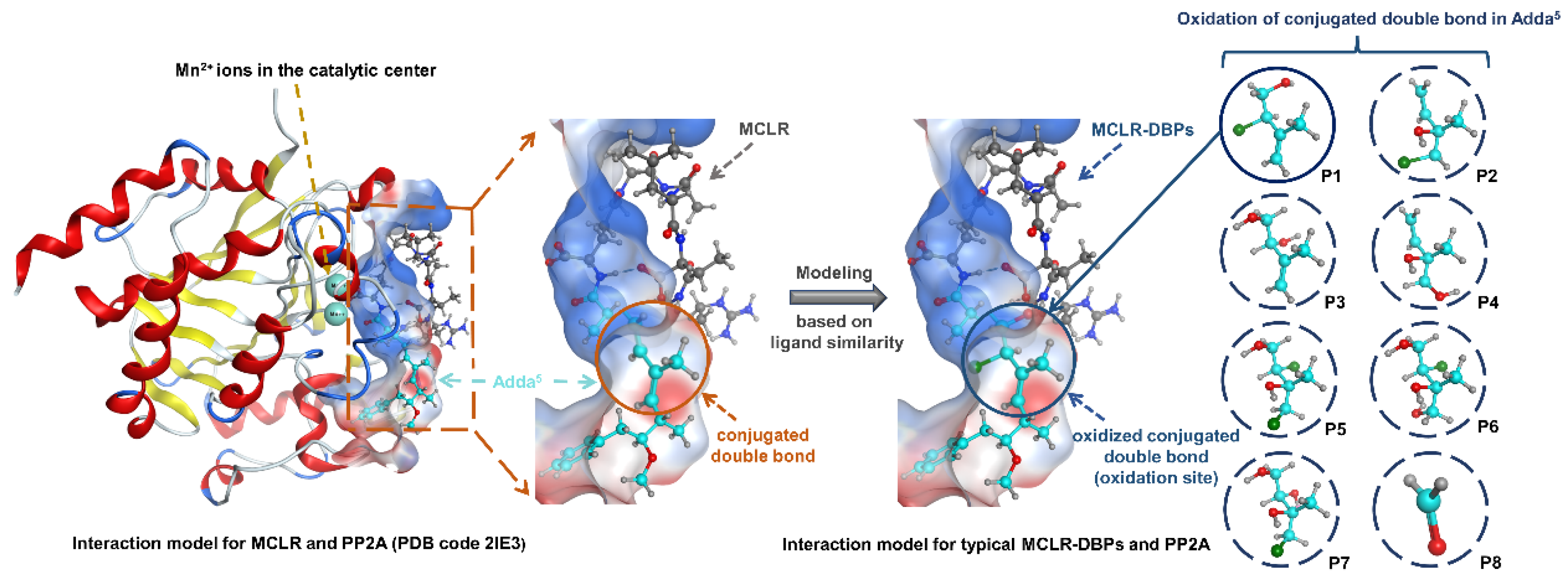
2.3. Simulation for the Interactions between Typical MCLR-DBPs and PP2A Based on Ligand Similarity Modeling and Molecular Docking
2.4. Pearson Correlation Analysis for the Candidate Interaction Parameters and Inhibition Data
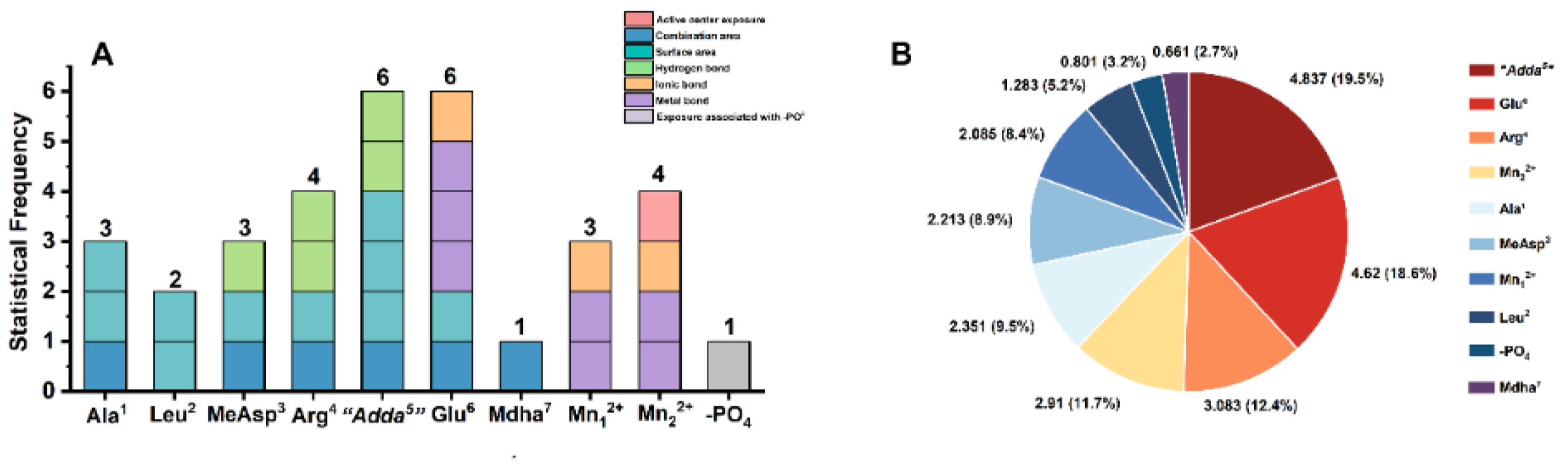
2.5. Molecular Mechanism Analysis for the Potential Inhibition Effect of Typical MCLR-DBPs Target to PP2A
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Chlorination Treatment of MCLR
4.3. Purification and Preparation of Typical MCLR-DBPs
4.3.1. MS Analysis of the Disinfection Samples
4.3.2. Purification of Typical MCLR-DBPs
4.3.3. Preparation of Typical MCLR-DBPs
4.4. PP2A Inhibition Assay for MCLR and Typical MCLR-DBPs
4.5. Molecular Simulation for the Interactions between MCLR/MCLR-DBPs and PP2A
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilhelm, S.W.; Bullerjahn, G.S.; McKay, R.M.L. The Complicated and Confusing Ecology of Microcystis Blooms. Mbio 2020, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; O’Brien, A.M.; Lins, T.F.; Shahmohamadloo, R.S.; Almirall, X.O.; Rochman, C.M.; Sinton, D. Effects of Hydrogen Peroxide on Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa in the Presence of Nanoplastics. ACS ES T Water 2021, 1, 1596–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortea, P.M.; Allis, O.; Healy, B.M.; Lehane, M.; Ni Shuilleabhain, A.; Furey, A.; James, K.J. Determination of toxic cyclic heptapeptides by liquid chromatography with detection using ultra-violet, protein phosphatase assay and tandem mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Xie, P. A review of reproductive toxicity of microcystins. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 301, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordasht, H.K.; Hassanpour, S.; Baradaran, B.; Nosrati, R.; Hashemzaei, M.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; la Guardia, M. Biosensing of microcystins in water samples; recent advances. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welten, R.D.; Meneely, J.P.; Elliott, C.T. A Comparative Review of the Effect of Microcystin-LR on the Proteome. Expo. Health 2019, 12, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.B.; Liu, G.F.; Ke, M.J.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zheng, M.; Lu, T.; Sun, L.W.; Qian, H.F. Proteomic analysis of the hepatotoxicity of Microcystis aeruginosa in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) and its potential mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svircev, Z.; Drobac, D.; Tokodi, N.; Mijovic, B.; Codd, G.A.; Meriluoto, J. Toxicology of microcystins with reference to cases of human intoxications and epidemiological investigations of exposures to cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 621–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulledge, B.M.; Aggen, J.B.; Eng, H.; Sweimeh, K.; Chamberlin, A.R. Microcystin analogues comprised only of Adda and a single additional amino acid retain moderate activity as PP1/PP2A inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 2907–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, M.; Luu, H.A.; McCready, T.L.; Holmes, C.F.B.; Williams, D.; Andersen, R.J. Molecular mechanisms underlying the interaction of motuporin and microcystins with type-1 and type-2A protein phosphatases. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1996, 74, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanillo, M.; Kohn, M. Microcystins: Synthesis and structure-activity relationship studies toward PP1 and PP2A. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, L.; You, Q.; Wang, L. Strategies for Targeting Serine/Threonine Protein Phosphatases with Small Molecules in Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 8916–8938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, A.; Vasconcelos, V. Molecular mechanisms of microcystin toxicity in animal cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 268–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiwaki-Matsushima, R.; Ohta, T.; Nishiwaki, S.; Suganuma, M.; Kohyama, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Carmichael, W.W.; Fujiki, H. Liver tumor promotion by the cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin-LR. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 1992, 118, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beasley, V.R.; Cook, W.O.; Dahlem, A.M.; Hooser, S.B.; Lovell, R.A.; Valentine, W.M. Algae intoxication in livestock and waterfowl. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 1989, 5, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, K.; Watanuki, T.; Kondo, F.; Watanabe, M.F.; Nakazawa, H.; Suzuki, M.; Uchida, H.; Harada, K. Stability of microcystins from cyanobacteria—IV. Effect of chlorination on decomposition. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 1997, 35, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Sanan, T.; de la Cruz, A.; He, X.; Kong, M.; Dionysiou, D.D. Susceptibility of the Algal Toxin Microcystin-LR to UV/Chlorine Process: Comparison with Chlorination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8252–8262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zong, W. Research on the discrepant inhibition mechanism of microcystin-LR disinfectant by-products target to protein phosphatase 1. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 45586–45595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, W.; Sun, F.; Sun, X. Evaluation on the generative mechanism and biological toxicity of microcystin-LR disinfection by-products formed by chlorination. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 252–253, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, W.; Sun, F.; Pei, H.; Hu, W.; Pei, R. Microcystin-associated disinfection by-products: The real and non-negligible risk to drinking water subject to chlorination. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, W.; Sun, F.; Sun, X. Oxidation by-products formation of microcystin-LR exposed to UV/H2O2: Toward the generative mechanism and biological toxicity. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3211–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Cui, J.; Yu, H.; Zong, W. Insight into the Molecular Mechanism for the Discrepant Inhibition of Microcystins (MCLR, LA, LF, LW, LY) on Protein Phosphatase 2A. Toxins 2022, 14, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.; Cho, M.; Ki, C.S. Correct Use of Repeated Measures Analysis of Variance. Korean J. Lab. Med. 2009, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yigit, O.; Soyuncu, S.; Eray, O.; Enver, S. Inhalational and dermal injury due to explosion of calcium hypochlorite. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2009, 28, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Carmichael, W.W. Use of a colorimetric protein phosphatase inhibition assay and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay for the study of microcystins and nodularins. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 1994, 32, 1495–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Pei, H.-Y.; Hu, W.-R.; Song, M.-M. A multi-technique approach for the quantification of Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB-905 biomass during high algae-laden periods. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.J.; Beattie, K.A.; Lee, E.Y.; Codd, G.A. Colorimetric protein phosphatase inhibition assay of laboratory strains and natural blooms of cyanobacteria: Comparisons with high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis for microcystins. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1997, 153, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Fu, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Lei, T.; Zhu, F.; Li, D.; Chang, S.; Xu, L.; Hou, T. Reliability of Docking-Based Virtual Screening for GPCR Ligands with Homology Modeled Structures: A Case Study of the Angiotensin II Type I Receptor. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 ,
,  ,
,  mean that the interaction parameters are extremely and significantly correlated with the inhibition data at the levels of 1, 10, and 100 nM, respectively (p < 0.01).
mean that the interaction parameters are extremely and significantly correlated with the inhibition data at the levels of 1, 10, and 100 nM, respectively (p < 0.01).  ,
,  ,
,  mean that the interaction parameters are significantly correlated with the inhibition data at the levels of 1, 10, and 100 nM, respectively (p < 0.05). A Student’s t-test was applied to the Pearson correlation analysis.
mean that the interaction parameters are significantly correlated with the inhibition data at the levels of 1, 10, and 100 nM, respectively (p < 0.05). A Student’s t-test was applied to the Pearson correlation analysis.
 ,
,  ,
,  mean that the interaction parameters are extremely and significantly correlated with the inhibition data at the levels of 1, 10, and 100 nM, respectively (p < 0.01).
mean that the interaction parameters are extremely and significantly correlated with the inhibition data at the levels of 1, 10, and 100 nM, respectively (p < 0.01).  ,
,  ,
,  mean that the interaction parameters are significantly correlated with the inhibition data at the levels of 1, 10, and 100 nM, respectively (p < 0.05). A Student’s t-test was applied to the Pearson correlation analysis.
mean that the interaction parameters are significantly correlated with the inhibition data at the levels of 1, 10, and 100 nM, respectively (p < 0.05). A Student’s t-test was applied to the Pearson correlation analysis.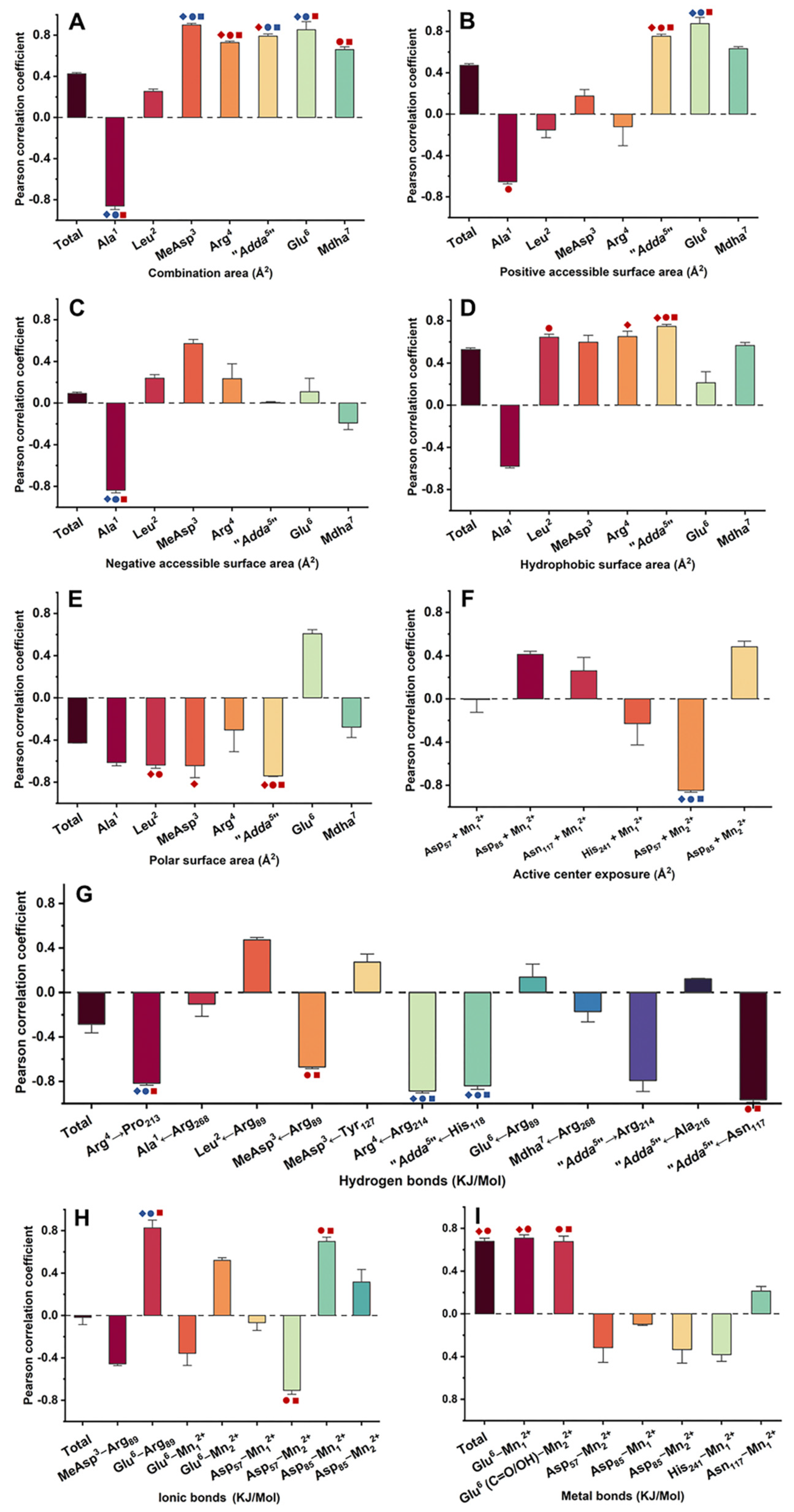


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.; Xu, Y.; Cui, J.; Zong, W. Mechanism for the Potential Inhibition Effect of Microcystin-LR Disinfectant By-Products on Protein Phosphatase 2A. Toxins 2022, 14, 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120878
Yu H, Xu Y, Cui J, Zong W. Mechanism for the Potential Inhibition Effect of Microcystin-LR Disinfectant By-Products on Protein Phosphatase 2A. Toxins. 2022; 14(12):878. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120878
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Huiqun, Yixue Xu, Jiyuan Cui, and Wansong Zong. 2022. "Mechanism for the Potential Inhibition Effect of Microcystin-LR Disinfectant By-Products on Protein Phosphatase 2A" Toxins 14, no. 12: 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120878
APA StyleYu, H., Xu, Y., Cui, J., & Zong, W. (2022). Mechanism for the Potential Inhibition Effect of Microcystin-LR Disinfectant By-Products on Protein Phosphatase 2A. Toxins, 14(12), 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120878




