New Insights into the Toxin Diversity and Antimicrobial Activity of the “Fire Coral” Millepora complanata
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
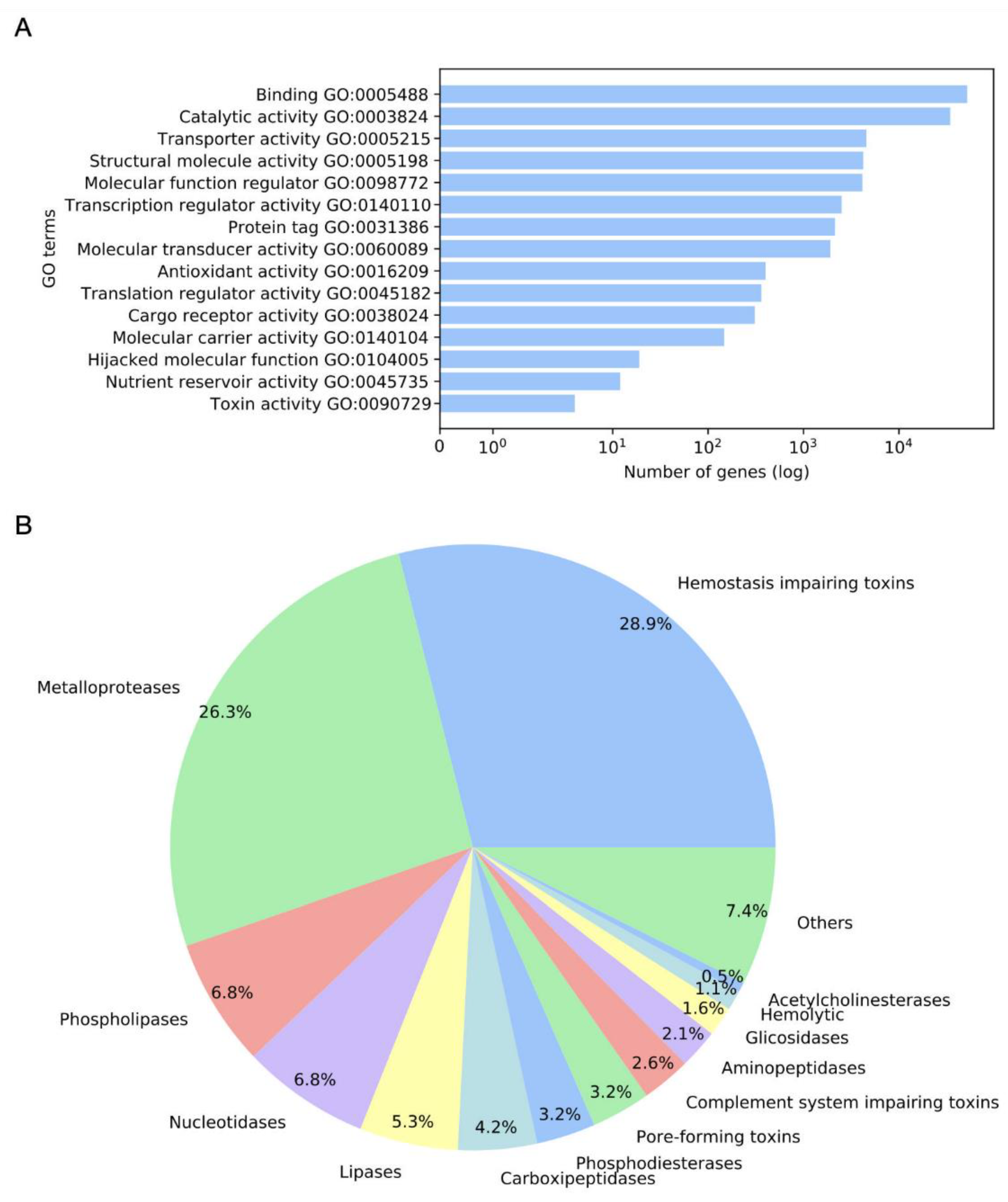
2.1. Annotation and GO Terms Assignment
2.2. Detected Putative Toxins
2.3. Virtual Screening of Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs)
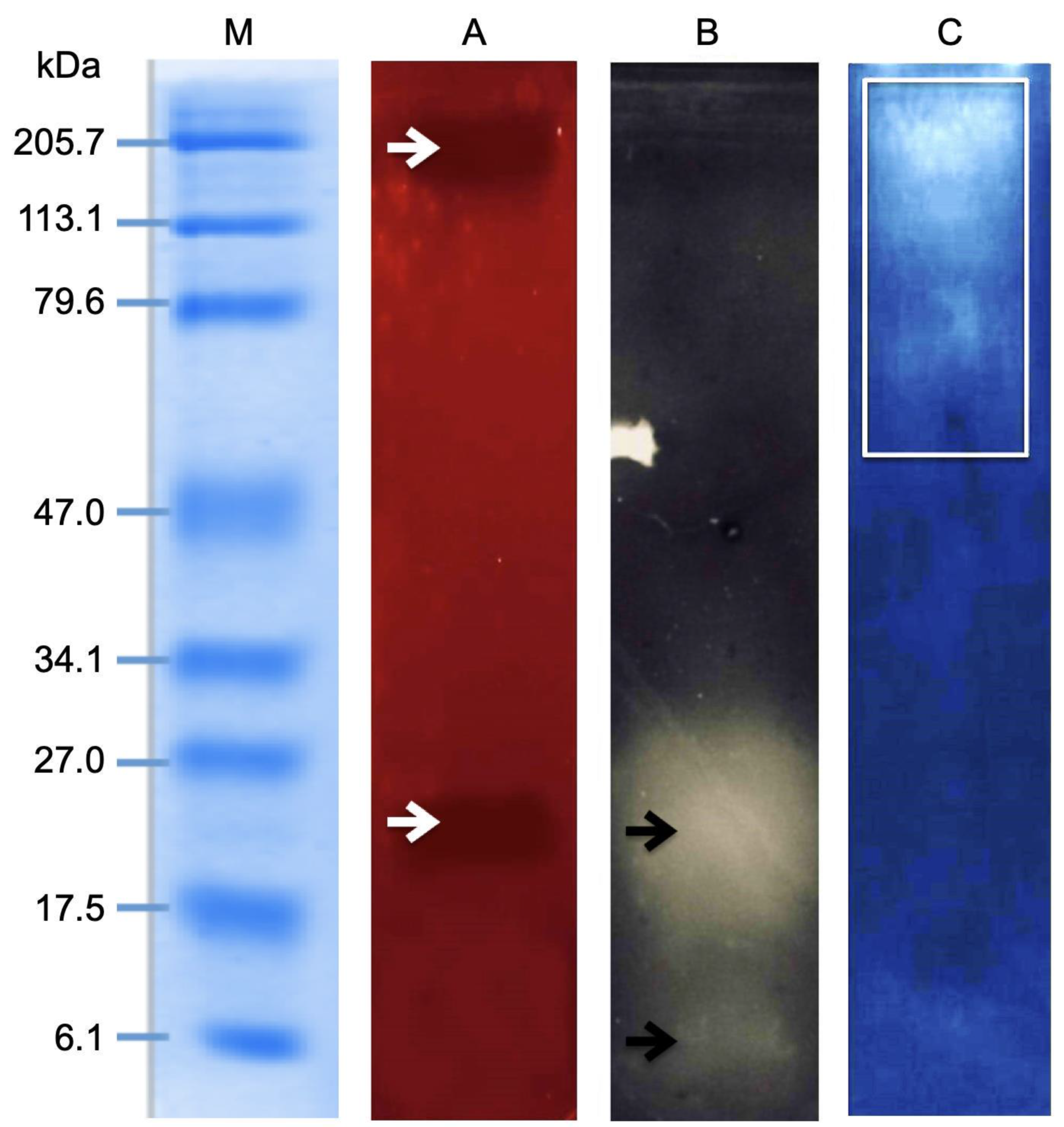
2.4. Electrophoretic Analysis of the M. complanata Nematocysts Proteome
2.5. Zymography Assay
2.6. Effect of Enzymatic Inhibitors on the Hemolytic Activity of the M. complanata Nematocysts Proteome
2.7. Antibacterial Activity Induced by M. complanata Nematocysts Peptidome
3. Discussion
3.1. Diversity of M. complanata Toxins and Prediction of Antimicrobial Peptides
3.2. Cytolysins from the Nematocyst Proteome of M. complanata
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Ethics Statement
5.2. Transcriptomic Data Acquisition
5.3. Functional Annotation and Gene Ontology
5.4. Identification of Putative toxins
5.5. Multiple Sequence Alignments
5.6. Prediction of AMPs
5.7. Sample Collection and M. complanata Nematocysts Proteome Preparation
5.8. One-Dimensional and Two-Dimensional Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
5.9. Zymographic Analysis
5.10. Hemolytic Activity Assay
5.11. Antibacterial Activity Assay
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jouiaei, M.; Yanagihara, A.A.; Madio, B.; Nevalainen, T.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Fry, B.G. Ancient Venom Systems: A Review on Cnidaria Toxins. Toxins 2015, 7, 2251–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Özbek, S. The cnidarian nematocyst: A miniature extracellular matrix within a secretory vesicle. Protoplasma 2011, 248, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevalainen, T.J.; Peuravuori, H.J.; Quinn, R.J.; Llewellyn, L.E.; Benzie, J.A.; Fenner, P.J.; Winkel, K.D. Phospholipase A2 in cnidaria. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 139, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podobnik, M.; Anderluh, G. Pore-forming toxins in Cnidaria. In Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 72, pp. 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariottini, G.L.; Bonello, G.; Giacco, E.; Pane, L. Neurotoxic and neuroactive compounds from Cnidaria: Five decades of research…and more. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambra, I.; Lauritano, C. A Review of Toxins from Cnidaria. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, J.E.; Dennis, E.A. Phospholipase A2 structure/function, mechanism, and signaling. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S237–S242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talvinen, K.A.; Nevalainen, T.J. Cloning of a novel phospholipase A2 from the cnidarian Adamsia carciniopados. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 132, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrander, J.; Daly, M. Evolution of the cytolytic pore-forming proteins (Actinoporins) in sea anemones. Toxins 2016, 8, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rojko, N.; Dalla Serra, M.; Maček, P.; Anderluh, G. Pore formation by actinoporins, cytolysins from sea anemones. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Biomembr. Pore-Form. Toxins Cell. Eff. Biotech Appl. 2016, 1858, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Feng, Y.; Yang, B.; Lee, S.M.-Y. Cnidarian peptide neurotoxins: A new source of various ion channel modulators or blockers against central nervous systems disease. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.; Peixe, L.; Gomes, N.C.M.; Calado, R. Cnidarians as a source of new marine bioactive compounds—An overview of the last decade and future steps for bioprospecting. Mar. Drugs. 2011, 9, 1860–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariottini, G.L.; Grice, I.D. Antimicrobials from Cnidarians. A New Perspective for Anti-Infective Therapy? Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bosch, T.C. The path less explored: Innate immune reactions in cnidarians. In Innate Immunity of Plants, Animals, and Humans; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 27–42. [Google Scholar]
- Mariottini, G.L.; Grice, I.D. Natural Compounds and Drug Discovery: Can Cnidarian Venom Play a Role? Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. Former. Curr. Med. Chem.-Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents 2019, 19, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Molina, A.; García-Arredondo, A.; Ibarra-Alvarado, C.; Bah, M. Millepora (“fire corals”) species: Toxinological studies until 2011. Adv. Environ. Res. 2012, 26, 133–148. [Google Scholar]
- Radwan, F.F. Comparative toxinological and immunological studies on the nematocyst venoms of the Red Sea fire corals Millepora dichotoma and M. platyphylla. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2002, 131, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiomi, K.; Hosaka, M.; Yanaike, N.; Yamanaka, H.; Kikuchi, T. Partial Characterization of Venoms from Two Species of Fire Corals Millepora platyphylla and Millepora dichotoma. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1989, 55, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlebrook, R.E.; Wittle, L.W.; Scura, E.D.; Lane, C.E. Isolation and purification of a toxin from Millepora dichotoma. Toxicon 1971, 9, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittle, L.W.; Scura, E.D.; Middlebrook, R.E. Stinging coral (Millepora tenera) toxin: A comparison of crude extracts with isolated nematocyst extracts. Toxicon 1974, 12, 481–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittle, L.W.; Middlebrook, R.E.; Lane, C.E. Isolation and partial purification of a toxin from Millepora alcicornis. Toxicon 1971, 9, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, A.; Torres, M.; Rojas, J.I.; Feregrino, A.; Heimer-de la Cotera, E.P. Calcium-dependent smooth muscle excitatory effect elicited by the venom of the hydrocoral Millepora complanata. Toxicon 2002, 40, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Arredondo, A.; Rojas-Molina, A.; Bah, M.; Ibarra-Alvarado, C.; Gallegos-Corona, M.A.; García-Servín, M. Systemic toxic effects induced by the aqueous extract of the fire coral Millepora complanata and partial purification of thermostable neurotoxins with lethal effects in mice. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 169, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Matehuala, R.; Rojas-Molina, A.; Vuelvas-Solórzano, A.A.; Garcia-Arredondo, A.; Alvarado, C.I.; Olguín-López, N.; Aguilar, M. Cytolytic and systemic toxic effects induced by the aqueous extract of the fire coral Millepora alcicornis collected in the Mexican Caribbean and detection of two types of cytolisins. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Trop. Dis. 2015, 21, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iguchi, A.; Iwanaga, S.; Nagai, H. Isolation and characterization of a novel protein toxin from fire coral. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 365, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Elizárraga, V.H.; Olguín-López, N.; Hernández-Matehuala, R.; Ocharán-Mercado, A.; Cruz-Hernández, A.; Guevara-González, R.G.; Caballero-Pérez, J.; Ibarra-Alvarado, C.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, J.; Rojas-Molina, A. Comparative Analysis of the Soluble Proteome and the Cytolytic Activity of Unbleached and Bleached Millepora complanata (“Fire Coral”) from the Mexican Caribbean. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olguín-López, N.; Hérnandez-Elizárraga, V.H.; Hernández-Matehuala, R.; Cruz-Hernández, A.; Guevara-González, R.; Caballero-Pérez, J.; Ibarra-Alvarado, C.; Rojas-Molina, A. Impact of El Niño-Southern Oscillation 2015–2016 on the soluble proteomic profile and cytolytic activity of Millepora alcicornis (“fire coral”) from the Mexican Caribbean. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Šuput, D. In vivo effects of cnidarian toxins and venoms. Toxicon Cnidarian Toxins Venoms 2009, 54, 1190–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Arredondo, A.; Rojas-Molina, A.; Ibarra-Alvarado, C.; Iglesias-Prieto, R. Effects of bleaching on the pharmacological and toxicological activities elicited by the aqueous extracts prepared from two “fire corals” collected in the Mexican Caribbean. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 396, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, F.F.; Aboul-Dahab, H.M. Milleporin-1, a new phospholipase A2 active protein from the fire coral Millepora platyphylla nematocysts. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2004, 139, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, P.G.; Beckmann, A.; Warnken, U.; Schnölzer, M.; Schüler, A.; Bornberg-Bauer, E.; Holstein, T.W.; Özbek, S. Proteome of Hydra Nematocyst. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 9672–9681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, Q.; Ruan, Z.; He, Q.; Zhang, L. Global transcriptome analysis of the tentacle of the jellyfish Cyanea capillata using deep sequencing and expressed sequence tags: Insight into the toxin-and degenerative disease-related transcripts. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klompen, A.M.; Macrander, J.; Reitzel, A.M.; Stampar, S.N. Transcriptomic analysis of four cerianthid (Cnidaria, Ceriantharia) venoms. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.-C.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, F.; Chen, Z.-M.; Liu, H.-W.; Wang, Y.-J.; Jiang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ding, J.-P. Venomic and transcriptomic analysis of centipede Scolopendra subspinipes dehaani. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 6197–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sher, D.; Fishman, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lebendiker, M.; Gaathon, A.; Mancheño, J.-M.; Zlotkin, E. Hydralysins, a New Category of β-Pore-forming Toxins in Cnidaria. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 22847–22855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seo, J.-K.; Lee, M.J.; Go, H.-J.; Kim, G.D.; Jeong, H.D.; Nam, B.-H.; Park, N.G. Purification and antimicrobial function of ubiquitin isolated from the gill of Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Mol. Immunol. 2013, 53, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Fischer, J.; Bartels, J.; Schröder, J.-M.; Meyer-Hoffert, U. Skin-Derived SPINK9 Kills Escherichia coli. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiemstra, P.S.; van den Barselaar, M.T.; Roest, M.; Nibbering, P.H.; van Furth, R. Ubiquicidin, a novel murine microbicidal protein present in the cytosolic fraction of macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1999, 66, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderluh, G.; Maček, P. Cytolytic peptide and protein toxins from sea anemones (Anthozoa: Actiniaria). Toxicon 2002, 40, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Arredondo, A.; Rojas-Molina, A.; Ibarra-Alvarado, C.; Lazcano-Pérez, F.; Arreguín-Espinosa, R.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, J. Composition and biological activities of the aqueous extracts of three scleractinian corals from the Mexican Caribbean: Pseudodiploria strigosa, Porites astreoides and Siderastrea siderea. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Trop. Dis. 2016, 22, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frazão, B.; Vasconcelos, V.; Antunes, A. Sea Anemone (Cnidaria, Anthozoa, Actiniaria) Toxins: An Overview. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1812–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, B.; Wang, Q.; Liu, G.; Wang, T.; He, Q.; Zhang, L. Unique Diversity of Sting-Related Toxins Based on Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analysis of the Jellyfish Cyanea capillata and Nemopilema nomurai (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa). J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, D.; Brinkman, D.L.; Potriquet, J.; Mulvenna, J. Tentacle Transcriptome and Venom Proteome of the Pacific Sea Nettle, Chrysaora fuscescens (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa). Toxins 2016, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riyas, A.; Kumar, A.; Chandran, M.; Jaleel, A.; Biju Kumar, A. The venom proteome of three common scyphozoan jellyfishes (Chrysaora caliparea, Cyanea nozakii and Lychnorhiza malayensis) (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) from the coastal waters of India. Toxicon 2021, 195, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderluh, G.; Sepčić, K.; Turk, T.; Maček, P. Cytolytic proteins from cnidarians—An overview. Acta Chim. Slov. 2011, 58, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mariottini, G.L.; Pane, L. Cytotoxic and cytolytic cnidarian venoms. A review on health implications and possible therapeutic applications. Toxins 2014, 6, 108–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-Arredondo, A.; Murillo-Esquivel, L.J.; Rojas, A.; Sanchez-Rodriguez, J. Characteristics of hemolytic activity induced by the aqueous extract of the Mexican fire coral Millepora complanata. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Trop. Dis. 2014, 20, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martins, R.D.; Alves, R.S.; Martins, A.M.C.; Barbosa, P.S.F.; Evangelista, J.S.A.M.; Evangelista, J.J.F.; Ximenes, R.M.; Toyama, M.H.; Toyama, D.O.; Souza, A.J.F.; et al. Purification and characterization of the biological effects of phospholipase A2 from sea anemone Bunodosoma caissarum. Toxicon 2009, 54, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, L.; Marcussi, S.; Marchi-Salvador, D.P.; Silva, F.P., Jr.; Fuly, A.L.; Stábeli, R.G.; da Silva, S.L.; González, J.; del Monte, A.; Soares, A.M. Enzymatic and structural characterization of a basic phospholipase A2 from the sea anemone Condylactis gigantea. Biochimie 2010, 92, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razpotnik, A.; Križaj, I.; Šribar, J.; Kordiš, D.; Maček, P.; Frangež, R.; Kem, W.R.; Turk, T. A new phospholipase A2 isolated from the sea anemone Urticina crassicornis—Its primary structure and phylogenetic classification. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2641–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yu, H.; Xue, W.; Yue, Y.; Liu, S.; Xing, R.; Li, P. Jellyfish venomics and venom gland transcriptomics analysis of Stomolophus meleagris to reveal the toxins associated with sting. J. Proteom. 2014, 106, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.-L.; Gröger, H.; Schmid, V.; Spring, J. A toxin homology domain in an astacin-like metalloproteinase of the jellyfish Podocoryne carnea with a dual role in digestion and development. Dev. Genes Evol. 1998, 208, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusmani, L.; Avian, M.; Galil, B.; Patriarca, P.; Rottini, G. Biologically active polypeptides in the venom of the jellyfish Rhopilema nomadica. Toxicon 1997, 35, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, Y.; Praher, D.; Schlesinger, A.; Ayalon, A.; Tal, Y.; Technau, U. Analysis of soluble protein contents from the nematocysts of a model sea anemone sheds light on venom evolution. Mar. Biotechnol. 2013, 15, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sher, D.; Knebel, A.; Bsor, T.; Nesher, N.; Tal, T.; Morgenstern, D.; Cohen, E.; Fishman, Y.; Zlotkin, E. Toxic polypeptides of the hydra—A bioinformatic approach to cnidarian allomones. Toxicon 2005, 45, 865–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gacesa, R.; Chung, R.; Dunn, S.R.; Weston, A.J.; Jaimes-Becerra, A.; Marques, A.C.; Morandini, A.C.; Hranueli, D.; Starcevic, A.; Ward, M.; et al. Gene duplications are extensive and contribute significantly to the toxic proteome of nematocysts isolated from Acropora digitifera (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Scleractinia). BMC Genom. 2016, 16, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernández-Elizárraga, V.H.; Olguín-López, N.; Hernández-Matehuala, R.; Caballero-Pérez, J.; Ibarra-Alvarado, C.; Rojas-Molina, A. Comprehensive Metatranscriptome Analysis of the Reef-Building Holobiont Millepora complanata. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, A.; Götz, S.; García-Gómez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Talón, M.; Robles, M. Blast2GO: A universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3674–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Charif, D.; Lobry, J.R. SeqinR 1.0-2: A contributed package to the R project for statistical computing devoted to biological sequences retrieval and analysis. In Structural Approaches to Sequence Evolution; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 207–232. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.; Zaretskaya, I.; Raytselis, Y.; Merezhuk, Y.; McGinnis, S.; Madden, T.L. NCBI BLAST: A better web interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W5–W9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega, accurate alignment of very large numbers of sequences. In Multiple Sequence Alignment Methods; Springer: Clifton, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- Clamp, M.; Cuff, J.; Searle, S.M.; Barton, G.J. The jalview java alignment editor. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 426–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawrence, T.J.; Carper, D.L.; Spangler, M.K.; Carrell, A.A.; Rush, T.A.; Minter, S.J.; Weston, D.J.; Labbé, J.L. amPEPpy 1.0: A portable and accurate antimicrobial peptide prediction tool. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 2058–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Dong, F.; Shi, C.; Liu, S.; Sun, J.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; Xu, H.; Lao, X.; Zheng, H. DRAMP 2.0, an updated data repository of antimicrobial peptides. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. APD3: The antimicrobial peptide database as a tool for research and education. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D1087–D1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marino, A.; Crupi, R.; Rizzo, G.; Morabito, R.; Musci, G.; La Spada, G. The unusual toxicity and stability properties of crude venom from isolated nematocysts of Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa). Cell. Mol. Biol. 2007, 53, 994–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Morabito, R.; Dossena, S.; La Spada, G.; Marino, A. Heavy metals affect nematocysts discharge response and biological activity of crude venom in the jellyfish Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa). Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ritz, C.; Baty, F.; Streibig, J.C.; Gerhard, D. Dose-response analysis using R. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0146021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| SeqID | Accession | Description | Activity | E-Value | Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mc1655639 | DRAMP03113 | SK84 | Anti-Gram+; antifungal; antiviral | 1.3 × 10−9 | LPSFSGSMFNPEGMPGSGAGKGGGGGGSVRDAGGSFGKMEAAREEEYFRRLQKEQLKSLQHQLDEEVDHHERELKQ |
| Mc2434582 | DRAMP03472 | cgUbiquitin | Anti-Gram+; anti-Gram−; antifungal | 1.5 × 10−37 | GGMQIFVKTLTGKTITLEVEPSDTIENVKAKIQDKEGIPPDQQRLIFAGKQLEDGRTLSDYNIQKESTLHLVLRLRGGMQIFVKTLTGKTITLEVEP |
| Mc1269566 | AP02096 | Ubiquicidin | Anti-Gram+; anti-Gram−; anti-MRSA | 6.1 × 10−23 | GIPNLSTINVVAQVLGGKVHGSLARAGKVKGQTPKVDKQDKKKKKTGGSHRRIQYNRRFVNVVPSFGRRRGPNSNNNS |
| Mc2063087 | AP02804 | Histone H2A | Anti-Gram+ | 2.6 × 10−17 | RHLKNRTTSHGRVGATAAVYSAAILEYLTAEVLELAGNASKDLKVKRITPRHLQLAIRGDEELDAL |
| Mc1970206 | AP02807 | Histone H4 | Anti-Gram− | 8.6 × 10−23 | ETRGVLKVFLENVIRDAVTYTEHARRKTVTAMDVLYARKRQGKTLYGFGGGWGSLEWGEVAVGSPRDQAETNPRMLVG |
| Mc2019202 | AP02808 | Histone H2B | Anti-Gram− | 1.7 × 10-12 | SREIQTAVRLILPGELAKHAVSEGTKAVKKYNSMAELYIIIIKIKQFFFFFFFFFFFSSFFFSIFLYSIKP |
| Mc1808465 | AP02809 | Histone H3 | Anti-Gram− | 3.3 × 10−36 | RKLPFQRLVREIAQDFKTDLRFQSTAVMALQEASEAYLVGLFEDTNLCAIHAKRVTIMPKDIQLARRIRGERATLQTKNGYFYS |
| Mc1970206 | AP02810 | Histone H4 | Anti-Gram− | 5.1 × 10−23 | ETRGVLKVFLENVIRDAVTYTEHARRKTVTAMDVLYARKRQGKTLYGFGG*GWGSLEWGEVAVGSPRDQAETNPRMLVG |
| Mc1777530 | AP02896 | TroTbeta4 | Anti-Gram+; anti-Gram− | 2.8 × 10−11 | RIIRSAFREVFSCFLFIHQSVVMGDKPDVSGVTTFDKSKLKKAETQEKNTLPTKETIEQEKSGDVKLVCTISTRPLLQFYSV |
| Mc1329197 | AP03038 | SPINK9-v1 | Anti-Gram−, enzyme inhibitor | 9.5 × 10−7 | CKFDKKTCKSSCVLLSKYKCNDKCLDIYKPVCGSDGRTYSNQCELDLASCKSNGKIKKVSDGECTNAVLHQILVNIVAFHTPRQNI |
| Species | Antibacterial Activity | Zone Of Inhibition (mm) | MIC a (µg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram(−) | Salmonella agona | − | NA | NA |
| Salmonella typhimurium | + | 20 ± 1 | 0.4 | |
| Salmonella enteritidis | + | 18 ± 0.5 | 0.04 | |
| Salmonella infantis | + | 22 ± 1 | 4 | |
| Salmonella typhi | + | 20 ± 1 | >4 | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | + | 12 ± 0.5 | 4 | |
| Pseudomonas perfectomarina | + | 20 ± 1.5 | 0.04 | |
| Escherichia coli | + | 22 ± 1 | 0.04 | |
| Gram(+) | Corynebacterium xerosis | + | 12 ± 0.5 | 0.04 |
| Kytococcus dedenturius | − | NA | NA | |
| Exiguobacterium amuntiacum | − | NA | NA | |
| Bacillus koreensis | + | 20 ± 0.5 | 4 | |
| Micrococcus luteus | − | NA | NA | |
| Microbacterium oleivorans | + | 17 ± 0.5 | 4 | |
| Staphylococcus cohnii | − | NA | NA | |
| Staphylococcus xylosus | − | NA | NA | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | − | NA | NA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Elizárraga, V.H.; Ocharán-Mercado, A.; Olguín-López, N.; Hernández-Matehuala, R.; Caballero-Pérez, J.; Ibarra-Alvarado, C.; Rojas-Molina, A. New Insights into the Toxin Diversity and Antimicrobial Activity of the “Fire Coral” Millepora complanata. Toxins 2022, 14, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14030206
Hernández-Elizárraga VH, Ocharán-Mercado A, Olguín-López N, Hernández-Matehuala R, Caballero-Pérez J, Ibarra-Alvarado C, Rojas-Molina A. New Insights into the Toxin Diversity and Antimicrobial Activity of the “Fire Coral” Millepora complanata. Toxins. 2022; 14(3):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14030206
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Elizárraga, Víctor Hugo, Andrea Ocharán-Mercado, Norma Olguín-López, Rosalina Hernández-Matehuala, Juan Caballero-Pérez, César Ibarra-Alvarado, and Alejandra Rojas-Molina. 2022. "New Insights into the Toxin Diversity and Antimicrobial Activity of the “Fire Coral” Millepora complanata" Toxins 14, no. 3: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14030206
APA StyleHernández-Elizárraga, V. H., Ocharán-Mercado, A., Olguín-López, N., Hernández-Matehuala, R., Caballero-Pérez, J., Ibarra-Alvarado, C., & Rojas-Molina, A. (2022). New Insights into the Toxin Diversity and Antimicrobial Activity of the “Fire Coral” Millepora complanata. Toxins, 14(3), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14030206







