Screening of Pig-Derived Zearalenone-Degrading Bacteria through the Zearalenone Challenge Model, and Their Degradation Characteristics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
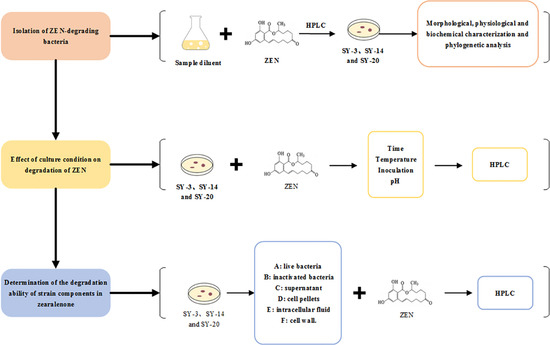
2.1. Isolation of ZEN-Degrading Bacteria
2.2. Morphological, Physiological and Biochemical Characterization, and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Growth Curves of ZEN-Degrading Strains
2.4. Effect of the Culture Conditions on the Degradation of ZEN
2.5. Determination of the Degradation Ability of Strain Components in ZEN
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Chemicals and Medium
5.2. ZEN-Challenged Pig Model
5.3. Isolation of the ZEN-Degrading Bacteria
5.4. Screening for ZEN-Degrading Bacteria
5.5. Morphological, Physiological, and Biochemical Characterization
5.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
5.7. Effect of the Culture Conditions on the Degradation of ZEN
5.8. Determination of the Degradation Ability of the Strain Components in ZEN
5.9. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Placinta, C.M.; D’Mello, J.P.F.; Macdonald, A.M.C. A review of worldwide contamination of cereal grains and animal feed with Fusarium mycotoxins. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1999, 78, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.W.; Klich, M. Mycotoxins. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stob, M.; Baldwin, R.S.; Tuite, J.; Andrews, F.N.; Gillette, K.G. Isolation of an anabolic, uterotrophic compound from corn infected with Gibberella zeae. Nature 1962, 196, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urry, W.H.; Wehrmeister, H.L.; Hodge, E.B.; Hidy, P.H. The structure of zearalenone. Tetrahedron Lett. 1966, 7, 3109–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z.J.; Liu, X.D.; Chen, L.Y.; Dai, J.F.; Karrow, N.A.; Sun, L.H. Occurrence of Aflatoxin B1, deoxynivalenol and zearalenone in feeds in China during 2018–2020. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obremski, K.; Gajecki, M.; Zwierzchowski, W.; Zielonka, L.; Otrocka-Domagala, I.; Rotkiewicz, T.; Mikolajczyk, A.; Gajecka, M.; Polak, M. Influence of zearalenone on reproductive system cell proliferation in gilts. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2003, 6, 239–245. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/8935641_Influence_of_zearalenone_on_reproductive_system_cell_proliferation_in_gilts (accessed on 28 February 2022).
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Jia, Z.Q.; Yin, S.T.; Shan, A.S.; Gao, R.; Qu, Z.; Liu, M.; Nie, S.P. Toxic effects of maternal zearalenone exposure on uterine capacity and fetal development in gestation rats. Reprod. Sci. 2014, 21, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denli, M.; Blandon, J.C.; Salado, S.; Guynot, M.E.; Pérez, J.F. Effect of dietary zearalenone on the performance, reproduction tract and serum biochemistry in young rats. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2017, 45, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girish, C.K.; Smith, T.K. Effects of feeding blends of grains naturally contaminated with Fusarium mycotoxins on small intestinal morphology of turkeys. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Meng, Q.W.; Li, J.N.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Bi, C.P.; Shan, A.S. Modified halloysite nanotubes reduce the toxic effects of zearalenone in gestating sows on growth and muscle development of their offsprings. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sebaei, A.S.; Sobhy, H.M.; Fouzy, A.S.M.; Hussain, O.A. Occurrence of zearalenone in grains and its reduction by gamma radiation. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenholm, H.L.; Charmley, L.L.; Prelusky, D.B.; Waener, R.M. Washing procedures using water or sodium carbonate solutions for the decontamination of three cereals contaminated with deoxynivalenol and zearalenone. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1992, 40, 2147–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.J.; Li, Y.L.; Luo, X.H.; Wang, R.; Zheng, R.H.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.F.; Yang, D.; Fang, W.M.; Chen, Z.X. Detoxification of zearalenone and ochratoxin A by ozone and quality evaluation of ozonised corn. Food Addit. Contam. Part A-Chem. 2016, 33, 1700–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandre, A.P.S.; Castanha, N.; Costa, N.S.; Santos, A.S.; Badiale-Furlong, E.; Augsto, P.E.D.; Calori-Domingues, M.A. Ozone technology to reduce zearalenone contamination in whole maize flour: Degradation kinetics and impact on quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 6814–6821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adb Alla, E.S.A.M. Zearalenone: Incidence, toxigenic fungi and chemical decontamination in Egyptian cereals. Food/Nahrung 1997, 41, 362–365. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/food.19970410610 (accessed on 28 February 2022). [CrossRef]
- Kriszt, R.; Krifaton, C.; Szoboszlay, S.; Cserhati, M.; Kriszt, B.; Kukolya, J.; Czeh, A.; Feher-Toth, S.; Torok, L.; Szoke, Z.; et al. A new zearalenone biodegradation strategy using non-pathogenic Rhodococcus pyridinivorans K408 strain. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.L.; He, X.X.; Xue, K.S.; Li, Y.; Xu, D.; Qian, H. Biological detoxification of zearalenone by Aspergillus niger strain FS10. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 72, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Jin, H.T.; Lan, J.; Zhang, R.Y.; Ren, H.B.; Zhang, X.B.; Yu, G.P. Detoxification of zearalenone by three strains of lactobacillus plantarum from fermented food in vitro. Food Control 2015, 54, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Hu, Y.C.; He, J.; Wu, L.; Liao, F.; Luo, B.; He, Y.J.; Zuo, Z.C.; Ren, Z.H.; Zhong, Z.J.; et al. Zearalenone degradation by two Pseudomonas strains from soil. Mycotoxin Res. 2014, 30, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinyiro, S.E.; Wokadala, C.; Xu, D.; Yao, W. Adsorption and degradation of zearalenone by bacillus strains. Folia Microbiol. 2011, 56, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, M.F.; Dieguez, S.N.; Riccio, B.; Aranguren, S.; Giordano, A.; Denzoin, L.; Soraci, A.L.; Tapia, M.O.; Ross, R.; Apas, A.; et al. Zearalenone adsorption capacity of lactic acid bacteria isolated from pigs. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2017, 48, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.P.; Zhao, L.H.; Ma, Q.G.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Gao, C.Q.; Ji, C. Degradation of zearalenone in swine feed and feed ingredients by Bacillus subtilis ANSB01G. World Mycotoxin J. 2014, 7, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.S.; Qiu, L.P.; Wu, H.; Tang, Y.Q.; Yu, Y.G.; Li, X.F.; Liu, D.M. Degradation of zearalenone by the extracellular extracts of Acinetobacter sp. SM04 liquid cultures. Biodegradation 2011, 22, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.H.; Wang, H.J.; Zhu, Z.W.; Ji, F.; Yin, X.C.; Hong, Q.; Shi, J.R. Isolation and characterization of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens ZDS-1: Exploring the degradation of Zearalenone by Bacillus spp. Food Control 2016, 68, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Cheng, K.C.; Liu, J.R. Isolation and characterization of a Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain with zearalenone removal ability and its probiotic potential. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.Q.; Yang, F.; Yang, P.L.; Liu, J.; Lv, Z.H. Microbial reduction of zearalenone by a new isolated Lysinibacillus sp. ZJ-2016-1. World Mycotoxin J. 2018, 11, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieplińska, K.; Gajęcka, M.; Dąbrowski, M.; Rykaczewska, A.; Lisieska-Żołnierczyk, S.; Bulińska, M.; Zielonka, L.; Gajęcki, M.T. Time-Dependent Changes in the Intestinal Microbiome of Gilts Exposed to Low Zearalenone Doses. Toxins 2019, 11, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.H.; Wang, J.J.; Shan, A.S.; Xu, L. Changes in intestinal barrier functions and gut microbiota in rats exposed to zearalenone. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 204, 111072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Liu, W.B.; Zhao, L.H.; Cao, L.R.; Shen, Z.Y. Low doses of individual and combined deoxynivalenol and zearalenone in naturally moldy diets impair intestinal functions via inducing inflammation and disrupting epithelial barrier in the intestine of piglets. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 333, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, P.J.; Pai, C.K.; Liu, J.R. Isolation and characterization of a Bacillus licheniformis strain capable of degrading zearalenone. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkai, P.; Szabó, I.; Cserháti, M.; Krifaton, C.; Risa, A.; Radó, J.; Balázs, A.; Berta, K.; Kriszt, B. Biodegradation of aflatoxin-B1 and zearalenone by Streptomyces sp. collection. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 108, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bisgaard, M. Arthritis in ducks. I. Aetiology and public health aspects. Avian Pathol. 1981, 10, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.M.; Long, T.; Hou, Y.Z.; Qin, C.L.; Wang, M.C.; Ding, J.C. Isolation and identification of the pathogen of Proteus mirabilis disease in chicken. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 1990, 7, 31–33. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Chai, J.Q. Research progress of Proteus mirabilis. Chin. J. Vet. Sci. 2017, 37, 196–200. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker, C.; Poore, C.A.; Li, X.; Mobley, H.L.T. Pathogenesis of Proteus mirabilis urinary tract infection. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zada, S.; Alam, S.; Ayoubi, S.A.; Shakeela, Q.; Nisa, S.; Niaz, Z.; Khan, I.; Ahmed, W.; Bibi, Y.; Ahmed, S.; et al. Biological Transformation of Zearalenone by Some Bacterial Isolates Associated with Ruminant and Food Samples. Toxins 2021, 13, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.J.; Kang, J.S.; Cho, W.T.; Lee, C.H.; Ha, J.K.; Song, K.B. In vitro degradation of zearalenone by Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 1921–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Tinyiro, S.E.; Yao, W.R.; Yu, H.; Guo, Y.H.; Qian, H.; Xie, Y.F. The ability of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus natto to degrade zearalenone and its application in food. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e14122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Wang, H.T.; Shih, W.Y.; Ciou, Y.A.; Chang, Y.Y.; Ananda, L.; Wang, S.Y.; Hsu, J.T. Application of Zearalenone (ZEN)-Detoxifying Bacillus in Animal Feed Decontamination through Fermentation. Toxins 2019, 11, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, S.; Wu, Z.S.; Wei, M.M.; Liu, X.C.; He, Y.H.; Ye, B.C. Bacillus subtilis SL-13 biochar formulation promotes pepper plant growth and soil improvement. Can. J. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, P.; Yin, Q.Q.; Liu, C.Q.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, F.; Gao, T.Z. Compound probiotics alleviating aflatoxin B1 and zearalenone toxic effects on broiler production performance and gut microbiota. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 194, 110420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.N.; Zheng, Y.D.; Tao, H.; Liu, J.; Zhao, P.; Yang, F.; Lv, Z.H.; Wang, J.Q. Effects of Bacillus subtilis ZJ-2019-1 on Zearalenone Toxicosis in Female Gilts. Toxins 2021, 13, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.Q.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, X.R.; Rong, X.P.; Zhao, L.H.; Ji, C.; Lei, Y.P.; Li, F.J.; Chen, J.; et al. Comparison of Ameliorative Effects between Probiotic and Biodegradable Bacillus subtilis on Zearalenone Toxicosis in Gilts. Toxins 2021, 13, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Zhang, Z.M.; Hu, Y.C.; Wu, L.; Liao, F.; He, J.; Luo, B.; He, Y.J.; Zuo, Z.C.; Ren, Z.H.; et al. Isolation and characterization of Pseudomonas otitidis TH-N1 capable of degrading Zearalenone. Food Control 2015, 47, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.P. Temperature and microorganism. Microbiology 1982, 6, 291–294. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Ding, K.; Yu, Z.H.; Li, W.; Li, Y.X.; He, W.L.; Cao, P.H.; Zhao, L.M.; Jia, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; et al. Screening and degradation characteristics of strains degrading zearalenone. Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 33, 5266–5276. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nezami, H.; Polychronaki, N.; Salminen, S.; Mykkanen, H. Binding rather than metabolism may explain the interaction of two food-Grade Lactobacillus strains with zearalenone and its derivative alpha-earalenol. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 3545–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, T.C.; Yi, P.J.; Lee, T.Y.; Liu, J.R. Probiotic characteristics and zearalenone-removal ability of a Bacillus licheniformis strain. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiannikouris, A.; Francois, J.; Poughon, L.; Dussap, C.G.; Bertin, G.; Jeminet, G.; Jouany, J.P. Alkali extraction of beta-D-glucans from Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell wall and study of their adsorptive properties toward zearalenone. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3666–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Wang, Q.H.; Zhou, Y.L.; Yin, L.F.; Zhang, G.M.; Ma, Y.H. High-level expression of a ZEN-detoxifying gene by codon optimization and biobrick in Pichia pastoris. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 193, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swamy, H.V.L.N.; Smith, T.K.; MacDonald, E.J.; Boermans, H.J.; Squires, E.J. Effects of feeding a blend of grains naturally contaminated with Fusarium mycotoxins on swine performance, brain regional neurochemistry, and serum chemistry and the efficacy of a polymeric glucomannan mycotoxin adsorbent. J. Anim. Sci. 2002, 80, 3257–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- National Research Council (NRC). Nutrient Requirements of Swine, 11th ed.; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.Z.; Cai, M.Y.; Wang, B.L. Common Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, 2nd ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2001; pp. 353–379. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]







| Characteristics | SY-3 | SY-14 | SY-20 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxidase test | − | + | + |
| Catalase test | + | + | + |
| Glucose | + | + | + |
| Fructose | + | + | + |
| Galactose | + | − | − |
| Cellobiose | − | + | + |
| Mannose | − | + | + |
| Inulin | + | + | + |
| Saccharose | − | + | + |
| Lactose | − | + | + |
| Maltose | − | + | + |
| Mannitol | − | + | + |
| Methyl red test | − | + | + |
| Voges-Proskauer | − | + | + |
| Amylase | − | + | + |
| Indole | + | − | − |
| Ingredients | Content (%) | Nutritional Level | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | 60.60 | Digestible energy (MJ/kg) | 14.71 |
| Full-fat expanded soybean | 10.00 | Crude protein (%) | 19.47 |
| Peeled soybean meal | 15.00 | Lysine (%) | 1.41 |
| Soybean protein concentrate | 3.00 | Calcium (%) | 0.71 |
| Fish meal | 4.00 | Total phosphorus (%) | 0.60 |
| Whole milk powder | 2.00 | Available phosphorus (%) | 0.36 |
| Soybean oil | 2.00 | ||
| Lysine (79.8%) | 0.24 | ||
| Methionine (98%) | 0.04 | ||
| Threonine (98%) | 0.08 | ||
| Calcium hydrogen phosphate | 0.65 | ||
| Limestone | 0.79 | ||
| Salt | 0.40 | ||
| Choline chloride (30%) | 0.20 | ||
| Premix 1 | 1.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Li, F.; Ning, H.; Zhang, W.; Niu, D.; Shi, Z.; Chai, S.; Shan, A. Screening of Pig-Derived Zearalenone-Degrading Bacteria through the Zearalenone Challenge Model, and Their Degradation Characteristics. Toxins 2022, 14, 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14030224
Yang X, Li F, Ning H, Zhang W, Niu D, Shi Z, Chai S, Shan A. Screening of Pig-Derived Zearalenone-Degrading Bacteria through the Zearalenone Challenge Model, and Their Degradation Characteristics. Toxins. 2022; 14(3):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14030224
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xue, Feng Li, Hangyi Ning, Wei Zhang, Dongyan Niu, Zhuo Shi, Sa Chai, and Anshan Shan. 2022. "Screening of Pig-Derived Zearalenone-Degrading Bacteria through the Zearalenone Challenge Model, and Their Degradation Characteristics" Toxins 14, no. 3: 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14030224
APA StyleYang, X., Li, F., Ning, H., Zhang, W., Niu, D., Shi, Z., Chai, S., & Shan, A. (2022). Screening of Pig-Derived Zearalenone-Degrading Bacteria through the Zearalenone Challenge Model, and Their Degradation Characteristics. Toxins, 14(3), 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14030224